Energy Bands | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Band Theory of Solids |

|
| Three Types of Energy Bands in A Solid |

|
| More about Energy Bands |

|
| Classification on the basis of energy bands |

|
| Insulators |

|
| Semiconductors |

|
Band Theory of Solids
In a substance, as many atoms are close to each other, the energy levels of the atom form a continuous band, wherein the electrons move. This is called the band theory of solids.
- We know that in an atom, the protons and the neutrons constitute the central part called the nucleus.
- The electrons revolve around the nucleus in defined orbits.
- The orbits are named as 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 3d etc. each of which has a discrete energy level.
- All electrons in the same orbit have the same energy.
- The electrons in the innermost orbits which are completely filled constitute the valence electrons whereas the electrons in the outermost orbit which do not completely fill that shell are called conduction electrons.
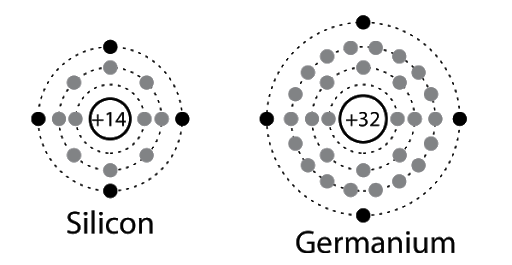
- As seen in the diagram below, both Si and Ge have 4 electrons in the outermost shell.

- When in the crystal, the atoms are close to each other and hence they may be the flow of electrons from one atom to another in the conduction band.
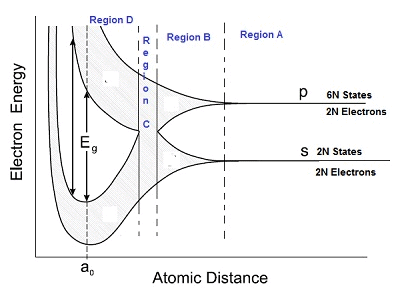
- Let us discuss in detail by considering interatomic distance in the X-axis and energy in the Y-axis:
- As seen in the diagram below, the graph is divided into 4 regions – Region A, B, C and D.

Region A
- In region A, the interatomic distance is large between atoms and in region D, the interatomic distance is small.
- Consider that the Si or Ge crystal contains N atoms. Electrons of each atom will have discrete energies in different orbits.
- If the atoms are isolated, that is, separated from each other by a large distance, the electron energy will be the same.
- However, in a crystal, the atoms are close to each other separated by a distance of 2-3 Ao. Hence, electrons interact with each other and also with the neighbouring atoms.
- The overlap or the interaction will be felt more by the electrons in the outermost orbit while the inner electron energies will remain unaffected.
- Hence, in the case of Si and Ge crystals, we need to consider the changes in energies of electron in the outermost orbit only.
- For Si, the outermost orbit is the third orbit (n = 3) while for Ge, the outermost orbit is the fourth orbit (n = 4).
- The number of electrons in both cases is 4 – namely 2s and 2p. Hence, the outer electrons in the crystal are 4.
- The maximum possible number of outer electrons in the orbit is 8 (2s + 6p electrons).
- This is the case of well-separated or isolated atoms as shown in region A.
Region B
- Suppose the atoms start coming nearer to each other to form a solid.
- The energies of the electrons in the outermost orbit may increase or decrease, due to the interaction between electrons of different atoms.
- The 6N states for l=1, which originally had identical energies in the isolated atoms, spread out and form an energy band as shown in the region B.
- Similarly, the 2N states for l = 0 splits into a second band separated from the first one.
Region C
- At still smaller spacing, however, there comes a region in which the bands merge with each other.
- The lowest energy state that is a split from the upper atomic level appears to drop below the upper state that has come from the lower atomic level.
- In this region, no energy gap exists where the upper and the lower energy states get mixed.
Region D
- If the distance between the atom further decreases, the energy bands again split apart and are separated by an energy gap Eg.
- The total number of available energy states 8N has been re-apportioned between the two bands (4N states each in the lower and upper energy bands).
- Here there are exactly as many states in the lower band (4N) as there are available valence electrons from the atoms (4N).
- This lower band called the valence band is completely filled while the upper band is completely empty. The upper band is called the conduction band.
Three Types of Energy Bands in A Solid
- Valence energy band
- Conduction energy band
- Forbidden energy gap.
Table: Difference between valence, forbidden and conduction energy bands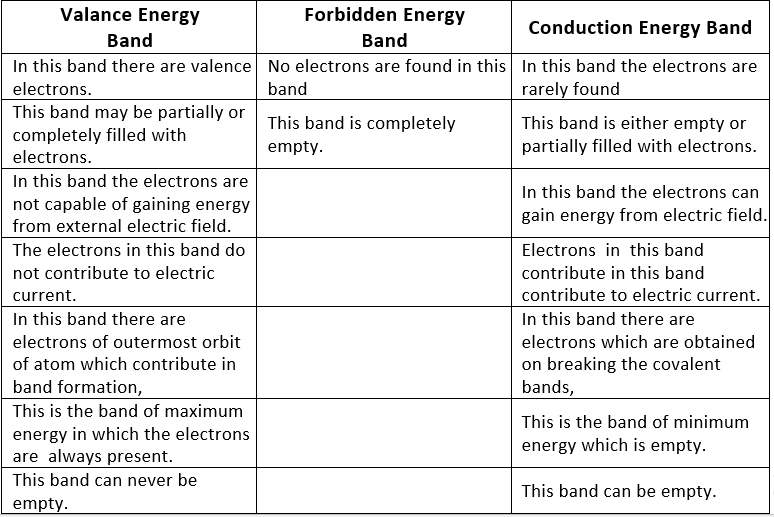
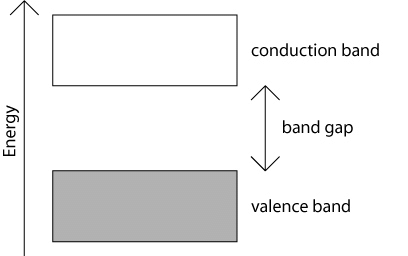
More about Energy Bands
- The conduction band is also known as the first permitted energy band or first band.
- As there are energy levels f electrons in an atom, similarly there are three specific energy bands for the electrons in the crystal formed by these atoms as shown in the figure.

- Completely filled energy bands: The energy band, in which the maximum possible number of electrons are present according to capacity is known as completely filled bank.
- Partially filled energy bands: The energy band, in which a number of electrons present is less than the capacity of the band, is known as a partially filled energy band.
- Electric conduction is possible only in those solids which have an empty energy band or partially filled energy band.
- Energy gap or Band gap (Eg):
The minimum energy which is necessary for shifting electrons from valence band to conduction band is defined as band gap (Eg). - The forbidden energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band is known as band gap (Eg). i.e. Eg = Ec – Ev.
 |
Download the notes
Energy Bands
|
Download as PDF |
Classification on the basis of energy bands
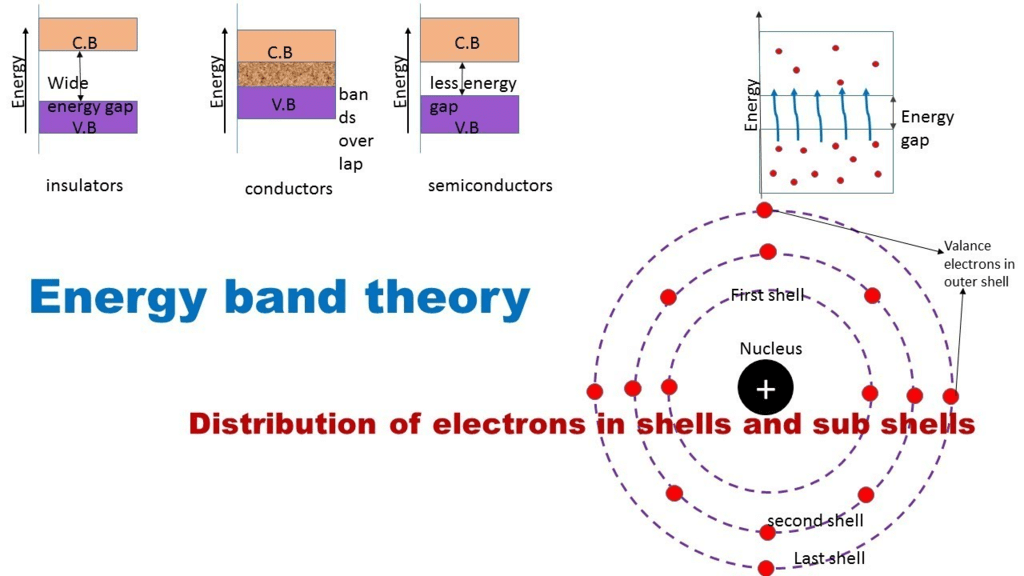
Depending upon the relative position of the valence band and the conduction band, the solids can be classified into conductors, insulators and semiconductors.
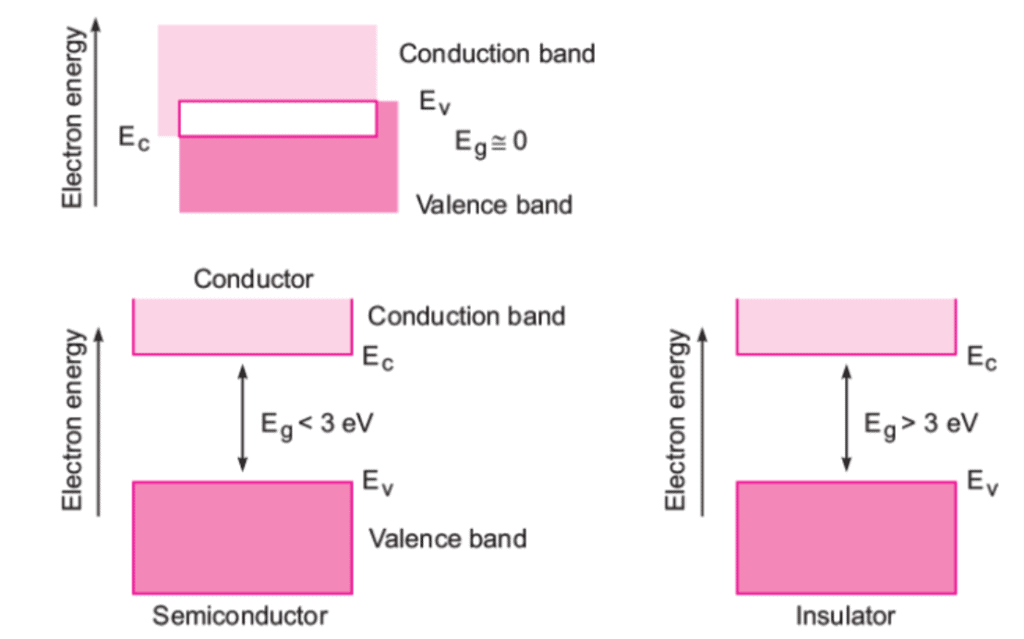
Conductors
- The conduction band and the valence band partly overlap each other and there is no forbidden energy band gap in between.
- The electrons from the valence band can easily move into the conduction band.
- Hence, a large number of electrons are available for conduction.
- The resistance of such materials is low and conductivity is high.
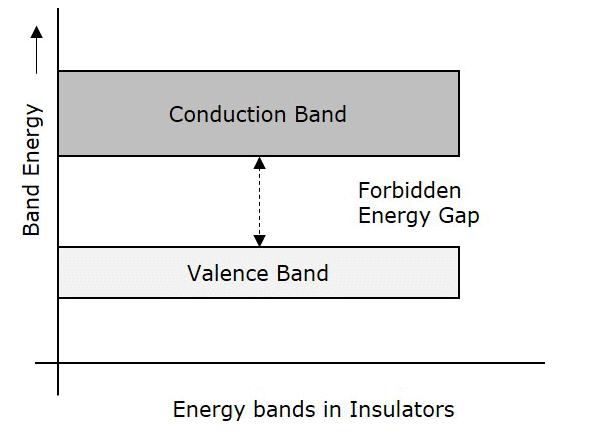
Insulators
- In case of insulators, a large energy gap exists between the valence band and the conduction band.
- The energy gap is so high that the electrons from the valence band cannot move to the conduction band by thermal excitation.
- As there are no electrons in the conduction band, electrical conduction is not possible.
Semiconductors
- A finite but a small energy gap exists between the valence band and the conduction band.
- At room temperature, some of the electrons from the valence band acquire energy and move into the conduction band.
- Hence, at high temperature, semiconductors have conductivity and resistance is also not as high as insulators.
- There are two types – Intrinsic semiconductor and Extrinsic semiconductor.
Table: Difference between Conductors, Semi-conductors and Insulators.
S.No. | Property | Conductors | Semi - conductors | Insulators | ||||||
1. | Electrical conductivity and its value | Very high 10-7 Ω/m | Between those of conductors and insulators i.e. 10-7 Ω/m to 10-13 Ω/m | Negligible 10-13 Ω/m | ||||||
2. | Resistivity and its value | Negligible Less than 10-5Ω-m | Between those of conductors and insulators i.e. 10-5Ω-m to 105Ω-m | Very high more than 105Ω-m | ||||||
| 3. | Band structure |  |  |  | ||||||
4. | Energy gap and its value | Zero or very small | More than that in conductors but less than that in insulators e.g. in Ge, ΔEg =0.72 eV is Si, ΔEg =1.1 eV in Ga As ΔEg =1.3 eV | Very large e.g. in diamond ΔEg = 7 eV | ||||||
5. | Current carriers and current flow | Due to free electrons and very high | Due to free electrons and holes more than that in insulators | Due to free electrons but negligible. | ||||||
6. | Number of current carriers (electrons or holes) at ordinary temperature | Very high | very low | negligible | ||||||
7, | Condition of valence band and conduction band at ordinary temperature | The valence and conduction bands are completely filled or conduction band is some what empty (e.g. in Na) | Valence band In somewhat empty and conduction band is somewhat filled | Valence band is completely filled and conduction band is completely empty. |
8. | Behaviour at 0 K | Behaves like a superconductor. | Behaves like an insulator | Behaves like an insulator |
9. | Temperature coefficient of resistance (α) | Positive | Negative | Negative |
10. | Effects of temperature on conductivity | Conductivity decreases | Conductivity increases | Conductivity increases |
11. | On increasing temperature the number of current carriers | Decreases | Increases | Increases |
12. | On mixing impurities their resistance | Increases | Decreases | Remains unchanged |
13. | Current flow in these takes place | Easily | Very slow | Does not take place |
14. | Examples | Cu. Ag, Au, Na, Pt, Hg etc. | Ge, Si, Ga, As etc. | Wood, plastic, mica, diamond, glass etc. |
|
291 videos|647 docs|183 tests
|
FAQs on Energy Bands - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the band theory of solids? |  |
| 2. What are the three types of energy bands in a solid? |  |
| 3. Can you provide more information about energy bands? |  |
| 4. How are materials classified based on energy bands? |  |
| 5. What are insulators and semiconductors? |  |