Refraction at Spherical Surface & Lenses | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Refraction at a Spherical Surface
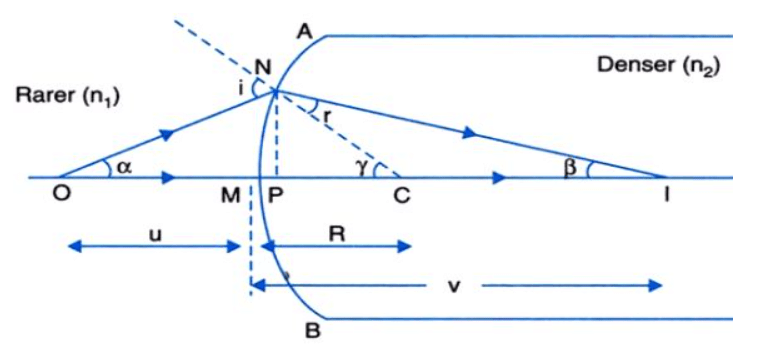
- Let us now see the refraction of light at the spherical surface. Now, the change in direction or bending of a light wave passing from one transparent medium to another caused by the change in wave’s speed is the Refraction.
- Suppose the above figure is a spherical surface. There is one medium with refractive index n1 and the second medium with refractive index n2.
- There is an object O and a ray of light from the object O is incident on the spherical mirror. Since it is moving from a rarer medium to a denser medium, the ray bends towards the normal.
- An image is formed and the radius of curvature of a spherical surface is R with the center C of the spherical surface.
Now as we know that:
- n1 is the refractive index of a medium from which rays are incident.
- n2 is the refractive index of another medium
We get:
► tanα = MN / OM
► tanγ = MN / MC
► tanβ = MN / MI
Now, for Δ NOC, i is the exterior angle.
i = ∠ NOM + ∠ NCM
i= MN / OM + MN / MC ...(1)
Similarly,
r = MN / MC – MN / MI ...(2)
Now by using Snell’s law we get:
n1 sin i = n2sin r
Substituting i and r from Eq. (1) and (2), we get
n1 / OM + n2 / MI = (n2 − n1) / MC
As, OM = -u, MI = +v, MC = +R
Hence, the equation becomes: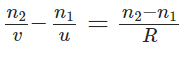
 |
Download the notes
Refraction at Spherical Surface & Lenses
|
Download as PDF |
Lens
A lens is a uniform transparent medium bounded between two spherical or one spherical and one plane surface.
Here are some terms related to Lens:
- Centre of Curvature: The centre of the actual glass sphere, of which your lens forms a part
- Principal Axis: When two spheres are part of your lens, it is the imaginary line joining the centres of curvatures of both spheres.
- Principal Focus: It is point on the principal axis, where light rays parallel to principal axis meet in case of a convex lens (or appear to meet after extrapolation in case of a concave lens).
- Optical Centre: It is a point within the lens where the diameter of the lens and the principal axis meet
- Focal Length: The distance between the focus and the optical centre
Types of Lens
- Convex Lens
A lens that is thinner at the edges and thicker at the middle is called a convex or converging lens. A convex lens is also referred to as a converging lens since it “converges” light rays that are incident on it. - Concave Lens
A lens which is thicker at edges and thinner at middle, is called a concave or diverging lens. A concave lens is also referred to as a diverging lens since it “diverges” light rays that are incident on it.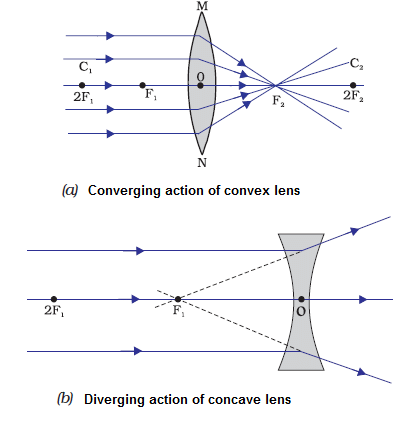 Convex and Concave Lens
Convex and Concave Lens
➢ Lens Formula
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
where, f = focal length of the lens, U = distance of object, U = distance of image.
Lens Maker’s formula
1/f=(μ – 1) (1/R1 – 1/R2)
where, μ = refractive index of the material of the lens and R1 and R2 are radii of curvature of the lens.
➢ Power of a Lens
The reciprocal of the focal length of a lens, when it is measured in metre, is called power of a lens.
Power of a lens, (P)= 1/f(metre)
Its unit is dioptre (D).
The power of a convex (converging) lens is positive and for a concave (diverging) lens it is negative.
➢ Focal Length of a Lens Combination
(i) When lenses are in contact 1/F – 1/f1 + 1/f2
Power of the combination P = P1 + P2
(ii) When lenses are separated by a distance d
1/F = 1/f1 + 1/f2 – d/f1f1
Power of the combination:
P = P1 + P2 – dP1P2
➢ Linear Magnification
m = I/O = v/u
For a small sized object placed linearly along the principal axis, its axial (longitudinal) magnification is given by
Axial magnification = – dv/du = (v/u)2
= (f / f+u)2 = (f - v/f)2
➢ Focal Length of a Convex Lens by Displacement Method
Focal length of the convex lens f = (a2 – d2) / 4a
where, a = distance between the image pin and object pin and
d = distance between two positions of lens.
The distance between the two pins should be greater than four times the focal length of the convex lens, i.e., a > 4f.
Height of the object O = √I1I2
➢ Cutting of a Lens
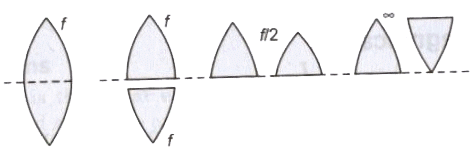
- If a symmetrical convex lens of focal length f is cut into two parts along its optic axis, then focal length of each part (a plane convex lens) is 2f. However, if the two parts are joined as shown in figure, the focal length of combination is again f.
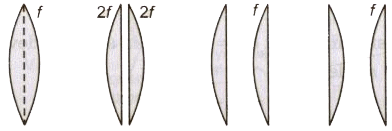
- If a symmetrical convex lens of focal length f is cut into two parts along the principal axis, then focal length of each part remains unchanged as f. If these two parts are joined with curved ends an one side, focal length of the combination is f/2. But on joining two 2 parts in opposite sense the net focal length becomes
|
291 videos|648 docs|183 tests
|
FAQs on Refraction at Spherical Surface & Lenses - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is refraction at a spherical surface? |  |
| 2. What are the types of lenses? |  |
| 3. How does refraction occur at a spherical lens? |  |
| 4. What are some applications of refraction in lenses? |  |
| 5. How can I calculate the refractive power of a lens? |  |



















