Chronology: Medieval History | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Chronology - Medieval India (1192-1761)
Medieval India was a period of profound transformation, characterized by the rise and fall of powerful dynasties, significant cultural and architectural achievements, and the advent of European colonialism. This era, stretching from the 12th to the 18th century, saw the establishment of Islamic rule in North India, the splendour of the Mughal Empire, and the shaping of the subcontinent's socio-political landscape. Key events include the formation of the Delhi Sultanate, the expansion and consolidation under the Mughals, and the early European interventions that set the stage for colonial rule.

Ghurid Dynasty and Early Islamic Conquests (1192-1206)

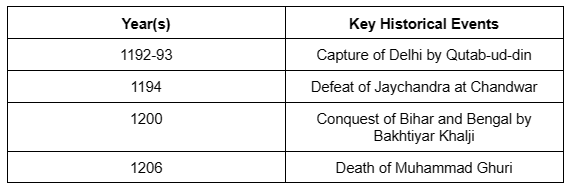
The Ghurid Dynasty marked the commencement of Muslim rule in North India, characterized by the conquest of Delhi by Qutab-ud-din Aibak. This period saw significant battles, including the defeat of Jaychandra at Chandwar and the conquests of Bihar and Bengal by Bakhtiyar Khalji, laying the foundation for Islamic rule in India.
Mamluk or Slave Dynasty (1206-1290)
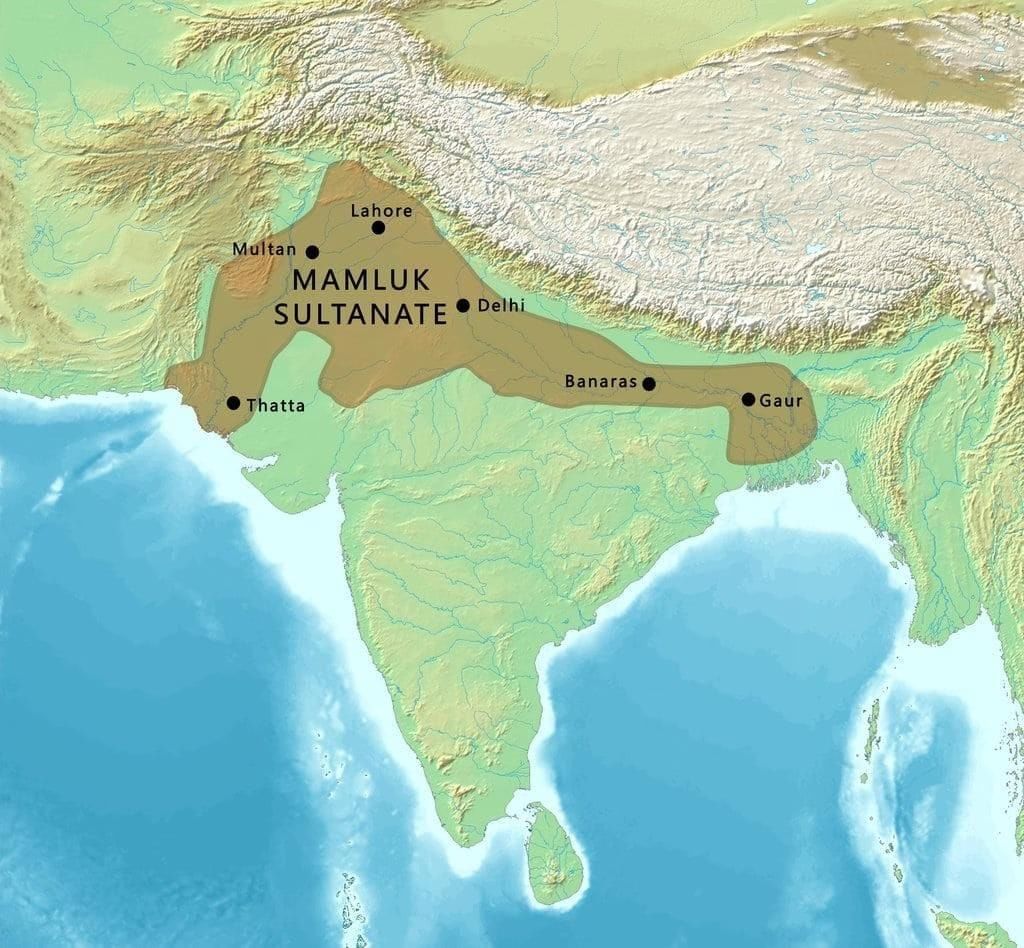
The Slave Dynasty, founded by Qutb-ud-din Aibak, is known for founding the Delhi Sultanate. Qutb-ud-din Aibak began building the famous Qutb Minar, but it was finished by his successor, Iltutmish. This time also included the rule of Raziya Sultan, one of the few female rulers in Islamic history.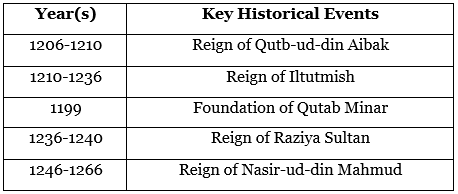
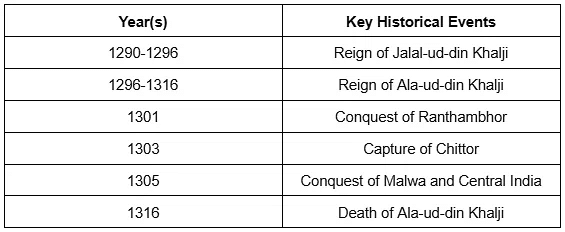
Khalji Dynasty (1290-1320)

The Khalji Dynasty, under the leadership of rulers like Ala-ud-din Khalji, was known for military conquests and administrative reforms. Ala-ud-din's reign was significant for the expansion into Southern India, reforms in price control, and attempts to create a highly centralized empire.
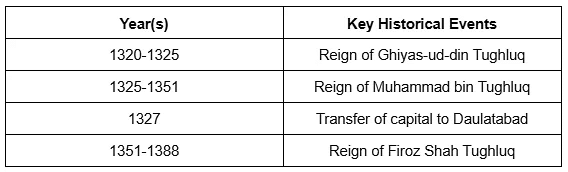
Tughluq Dynasty (1320-1414)

The Tughluq Dynasty is remembered for its ambitious projects, including the disastrous move of the capital to Daulatabad by Muhammad bin Tughluq, and Firoz Shah Tughluq's welfare measures. The dynasty witnessed the beginning of the decline of the Delhi Sultanate amidst revolts and economic distress.
Sayyid Dynasty (1414-1451)
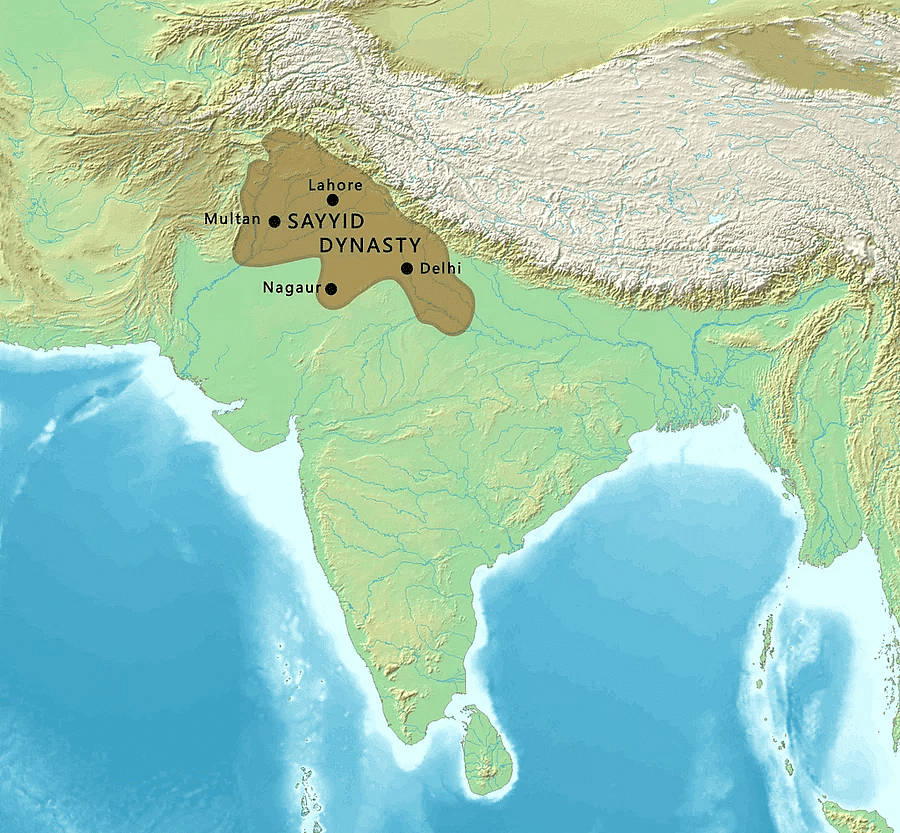
The Sayyid Dynasty was a time when the Delhi Sultanate was weakening. There were many internal conflicts, and the rulers had less control over their territory. They faced problems gaining support and struggled against stronger regional powers. This struggle eventually led to their fall.

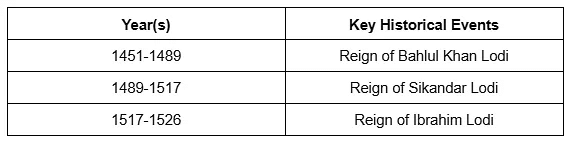
Lodi Dynasty (1451-1526)

The Lodi Dynasty was the last dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, known for its Afghan origins. Under Sikandar Lodi, the empire saw a period of relative stability and expansion. However, the dynasty's end came with the defeat of Ibrahim Lodi at the hands of Babur in the First Battle of Panipat, leading to the rise of the Mughal Empire.
Mughal Empire (1526-1857)
The Mughal Empire, established by Babur after the First Battle of Panipat, is renowned for its cultural and architectural achievements. Akbar's reign, in particular, was noted for religious tolerance and administrative innovations. The empire reached its greatest territorial extent under Aurangzeb, but his policies contributed to its eventual decline. This decline opened the door for later colonial influence.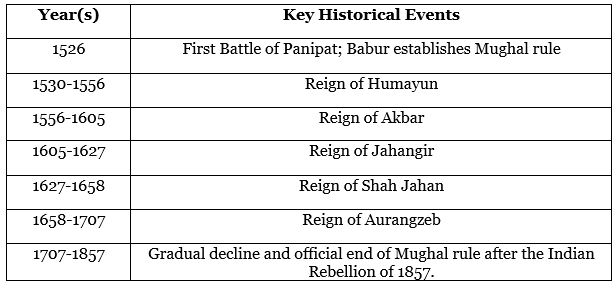
Regional Kingdoms and Sultanates (Throughout Mughal Era)
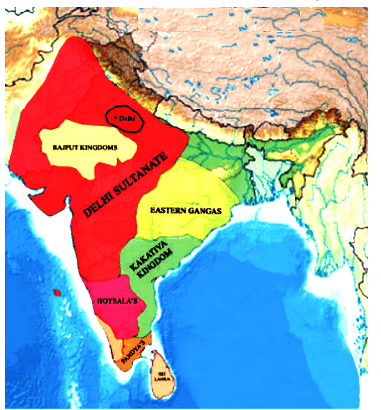
Parallel to the Mughal Empire, several regional kingdoms and sultanates flourished, including the Vijayanagar Empire, known for its prosperity and cultural achievements. The period saw significant events like Timur's invasion, the birth of Guru Nanak, founder of Sikhism, and the rise and fall of Maratha leader Shivaji.

Early Colonial Period (1498-1761)

The early colonial period began with Vasco da Gama's voyage to India, which initiated European involvement in Indian affairs. The British East India Company's victory at the Battle of Plassey marked the beginning of British dominance in India. The Third Battle of Panipat in 1761 was another pivotal event, weakening the Marathas and creating a power vacuum that eventually contributed to the rise of British influence in India.

The chronology of Medieval India (1192-1761) reflects a transformative era of dynamic dynastic rule, cultural and architectural innovations, and the advent of European influence. This period, pivotal in shaping India's history, saw the rise of Islamic rule, the grandeur of the Mughal Empire, and the early colonial incursions, laying the foundation for modern India.
|
210 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Chronology: Medieval History - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the key achievements of the Ghurid Dynasty in medieval India? |  |
| 2. What were the main features of the Mamluk or Slave Dynasty? |  |
| 3. How did the Khalji Dynasty influence the socio-economic landscape of India? |  |
| 4. What was the impact of the Mughal Empire on Indian culture and society? |  |
| 5. How did regional kingdoms and sultanates function during the Mughal era? |  |

















