Flow Control Link Layer | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
FlowControl
It refers to a set of procedures used to restrict the amount of data flow between sending and receiving stations. It tells the sender how much data it can transmit before it must wait for an acknowledgement from the receiver.
There are two methods that are used. They are.
1. Stop and wait
2. Sliding window
Stop and Wait:
In this method the sender waits for acknowledgement after every frame it sends. Only after an acknowledgement has been received, then the sender sends the next frame.
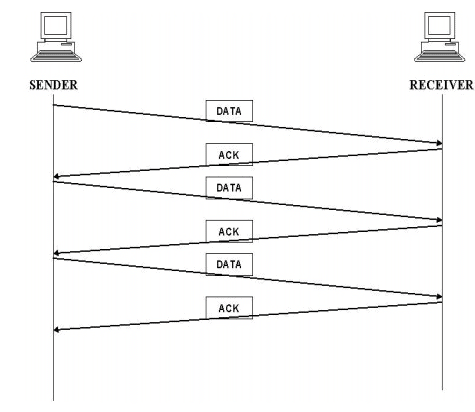
The advantage is simplicity. The disadvantage is inefficiency.
Sliding Window:
In this method, the sender can transmit several frames before needing an acknowledgement. The receiver acknowledges only some of the frames, using a single ACK to confirm the receipt of multiple data frames.The sliding window refers to imaginary boxes at both the sender and receiver. This window provides the upper limit on the number of frames that can be transmitted before requiring an acknowledgement. To identify each frame, the sliding window scheme introduces the sequence number. The frames are numbered as 0 to n-1. And the size of the window is n-1. Here the size of the window is 7, and the frames are numbered as 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
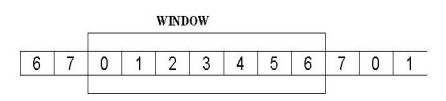
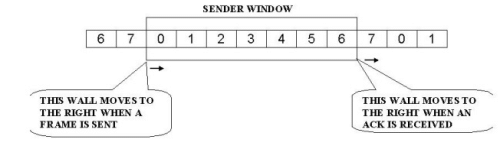
At the beginning the sender's window contains n-1 frames. As frames are sent out, the left boundary of the window moves inward, shrinking the size of the window. Once an ACK is received, the window expands at the right side boundary to allow in a number of new frames equal to the number of frames acknowledged by that ACK.
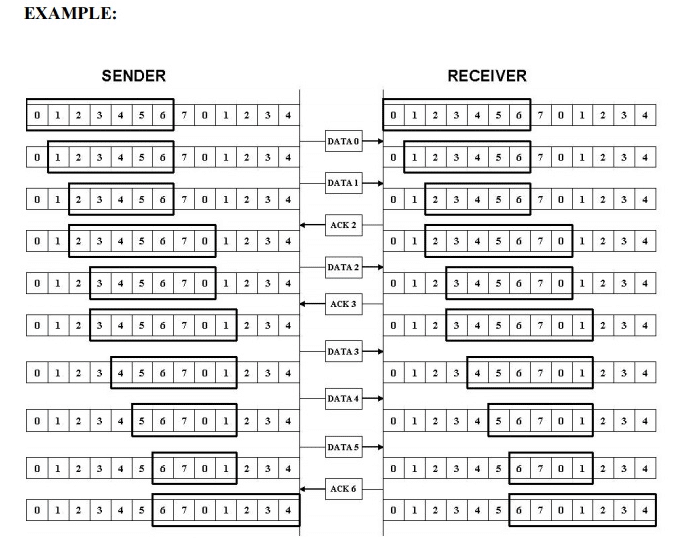
Error Control
Error control is implemented in such a way that every time an error is detected, a negative acknowledgement is returned and the specified frame is retransmitted. This process is called automatic repeat request (ARQ).
The error control is implemented with the flow control mechanism. So there are two types in error control. They are,
1. Stop and wait ARQ
2. Sliding window ARQ
Stop And Wait ARQ:
It is a form of stop-and-wait flow control, extended to include retransmission of data in case of lost or damaged frames.
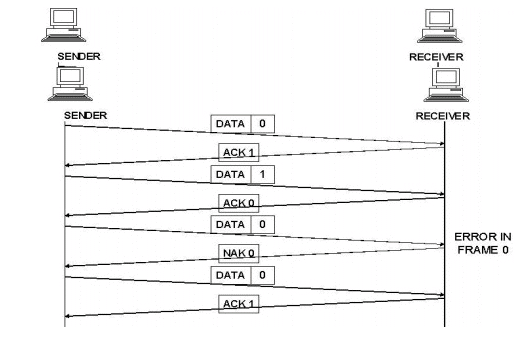
Damaged Frame:
When a frame is discovered by the receiver to contain an error, it returns a NAK frame and the sender retransmits the last frame.
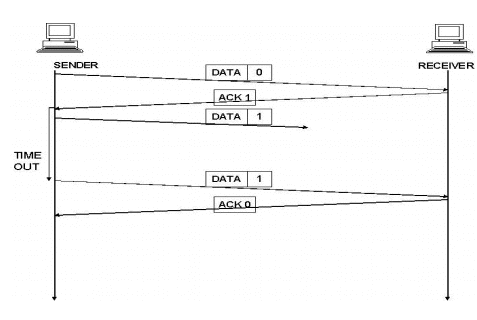
Lost Data Frame:
The sender is equipped with a timer that starts every time a data frame is transmitted. If the frame lost in transmission the receiver can never acknowledge it. The sending device waits for an ACK or NAK frame until its timer goes off, then it tries again. It retransmits the last data frame
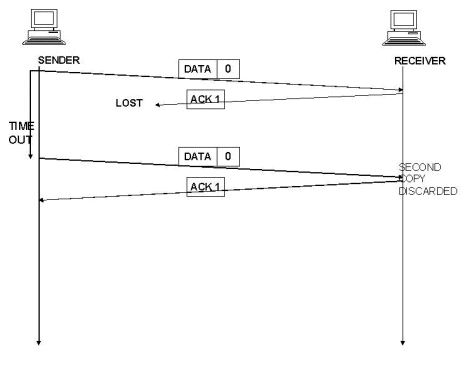
Lost Acknowledgement
The data frame was received by the receiver but the acknowledgement was lost in transmission. The sender waits until the timer goes off, then it retransmits the data frame. The receiver gets a duplicated copy of the data frame. So it knows the acknowledgement was lost so it discards the second copy.
Sliding Window ARQ
It is used to send multiple frames per time. The number of frames is according to the window size. The sliding window is an imaginary box which resides on both the sender and receiver sides.
It has two types. They are.
1. Go-back-n ARQ
2. Selective reject ARQ
Go-Back-N ARQ:
In this method, if one frame is lost or damaged, all frames sent since the last frame were acknowledged or retransmitted.
Damaged Frame:
SELECTIVE REPEAT ARQ
Selective repeat ARQ retransmits only the damaged or lost frames instead of sending multiple frames. The selective transmission increases the efficiency of transmission and is more suitable for noisy links. The receiver should have a sorting mechanism.
DAMAGED FRAME:
|
23 videos|171 docs|81 tests
|
FAQs on Flow Control Link Layer - Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is flow control in the link layer? |  |
| 2. How does flow control work in the link layer? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of flow control in the link layer? |  |
| 4. What are the different flow control techniques used in the link layer? |  |
| 5. How does flow control relate to error detection and correction in the link layer? |  |
















