Introduction to Computer - Computer Fundamentals, Computer Awareness | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Computer
Computer is a general purpose machine which can be programmed to perform Arithmetic and Logical operations. The physical parts of the Computer are known as Hardware, and Programs or Instructions given to the Computer to carry out different tasks are known as Software.

How does a Computer work?
A computer accepts inputs or directions from a user and carries out certain instructions based on the programs already written in it and performs a task.
Hardware parts of the Computer
Micro Processor
- It is an Integrated Circuit (IC) used to perform different operations (arithmetic or logical) inside the computer.
- Examples include Intel Pentium, Intel i3, i5, i7, etc.
- Simply put, the microprocessor executes the tasks inside a computer.
- The speed of a computer largely depends on the speed of its microprocessor.
- The speed of the microprocessor is usually expressed in gigahertz (GHz).
- This indicates how many instructions it can execute in one second.
(A) Non-Volatile Memory – Hard Disk: It is a permanent storage device. When we save data such as songs, Word or Excel files, it is stored in permanent memory. Other types of permanent memory devices include Flash Memory, ROM, EPROM, EEPROM, etc.
(B) Volatile Memory – RAM: It is a temporary storage device. When the computer's power is turned off, the data stored in RAM is lost. RAM can be considered as the computer’s real-time working memory.
Memory
Why do we need both Hard Disk and RAM in a Computer?
Consider a library: where do we store books? In shelves or racks, similar to a hard disk or permanent memory. Do we read books on the shelves? No. We take them to a table to read and then return them. The table is analogous to RAM. Real-time operations in a computer are carried out inside RAM. If you want to work with more books at once, you need a bigger table. Similarly, for faster performance and running multiple applications, a computer requires more RAM. Thus, the size of RAM is one of the parameters determining a computer's speed.
Interfacing Circuits
These are Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) with ICs and other components used to communicate with devices inside and outside the computer. Example: Network Interface.
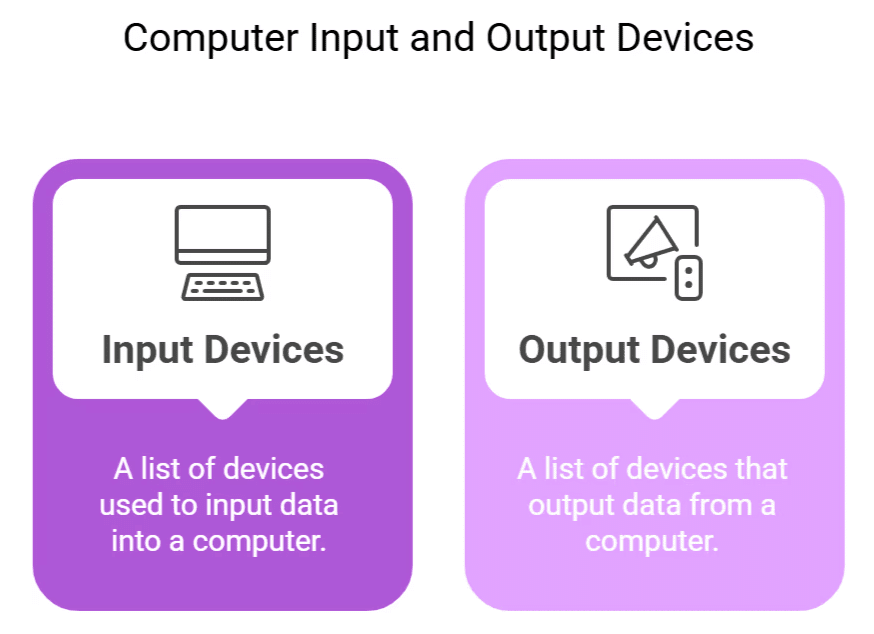
Peripheral Devices (I/O Devices)
Just as a person needs hands, mouth, and ears to interact, a computer requires peripheral devices to communicate with users. Peripheral devices include input and output devices.
The monitor you are reading on is an output device, while the mouse and keyboard are input devices.
Software Parts of the Computer
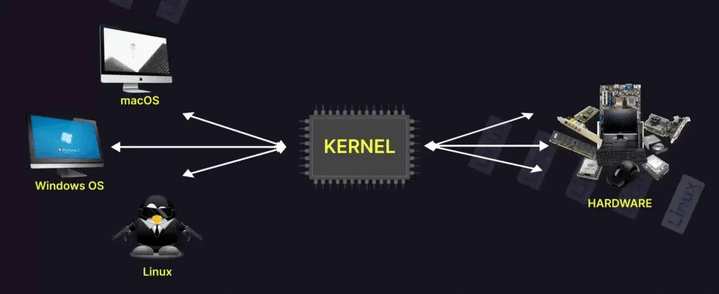
Kernel
The kernel is the basic set of programs written for the microprocessor. It is mainly written in machine language, which is the most fundamental programming language consisting of instructions for performing logical and arithmetic operations on data. Machine language code is converted into hexadecimal values, then into binary numbers (1s and 0s). These binary values are stored in the microprocessor's program memory, and the microprocessor executes tasks based on these instructions. Inside the microprocessor chip are millions of transistors arranged to perform arithmetic and logical operations on binary numbers.
Operating System
The operating system is software written over the kernel that manages both hardware and software resources in a computer. It is a general-purpose software providing services to applications. The operating system acts as an intermediary between the hardware and the applications. The hardware itself cannot understand user inputs; the operating system converts user commands into hardware language to perform tasks. Examples of operating systems include Microsoft Windows, Linux, and Android.
Applications
These are programs or Software written to carry out specific tasks. Examples are Microsoft Office (for data processing), Firefox (for web browsing), VLC Media Player (for playing videos) etc.
Some Input Devices in Computer
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Scanner
- Joystick
- Web Camera
- Bar code reader
- Biometric Scanners
- Microphones
- Touch pad
Some Output Devices in Computer
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speakers
- Head phones
- Projector
Different Memory Types in a Computer
RAM- Random Access Memory
- SRAM- Static RAM
- DRAM- Dynamic RAM
ROM- Read Only Memory
- PROM- Programmable ROM
- EPROM- Electrically Programmable ROM
- EEPROM- Electrically Erasable PROM
- Hard Disc- Magnetic Memory
- Compact Disc(CD)- Optical Memory- External Memory
- Digital Video Disc (DVD)- Optical Memory- External Memory
- Blu-Ray Disc (BD)- Optical Memory- External Memory
- Floppy Disc- Magnetic Memory- External Device
- Flash Memory (Pen Drive) – EEPROM Technology
- Micro SD Card (Memory Card) – EEPROM Technology
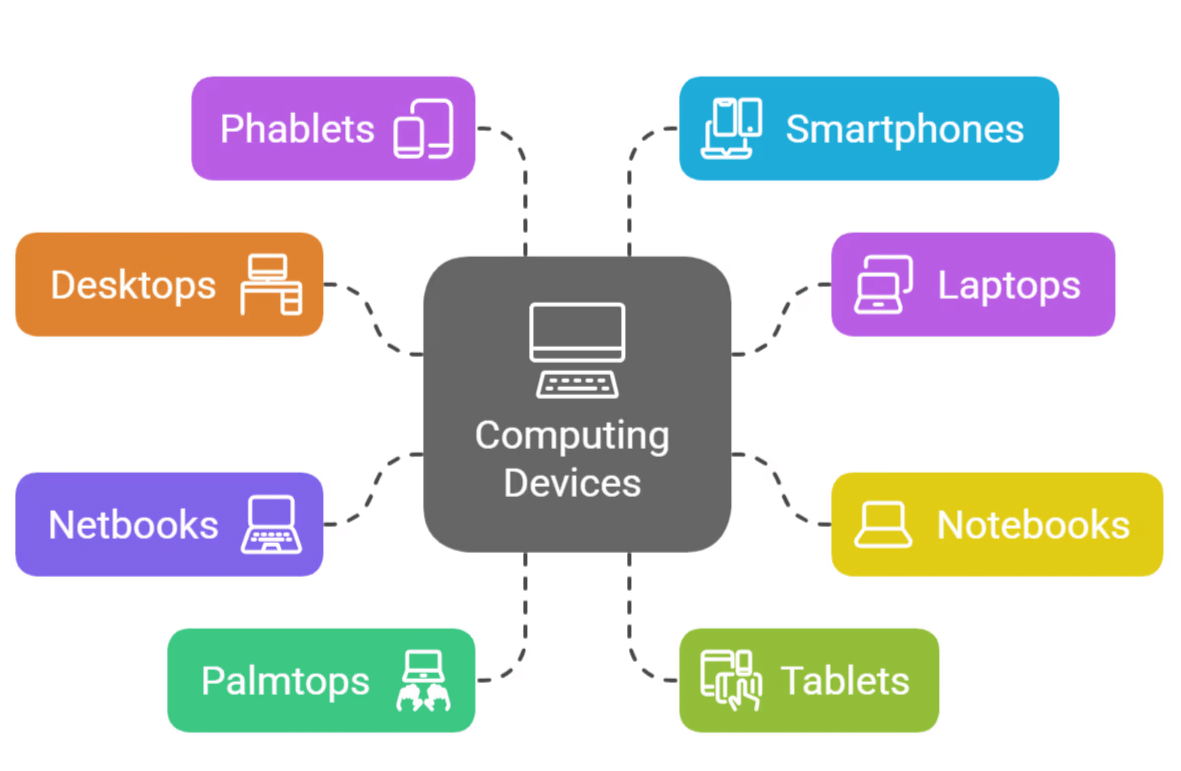
Different Types of Computing Devices
- Desktop
- Laptop
- Notebook
- Netbook (A Notebook with SIM card slot)
- Palmtop
- Tablet
- Fablet (An intermediate device between Tablet and Smart Phone)
- Smart Phones
Types of Software
1. Application Software: Computer programs designed to perform user tasks. Examples include VLC Media Player, MS Office, etc.
2. System Software: Programs that start and run computer systems and networks.
Examples include device drivers and operating systems.
3. Development Software: Programs used by software developers to create, debug, and maintain other computer programs.
Examples include compilers, interpreters, and debuggers.
4. Malicious Software or Malware: Programs designed to harm computers and networks.
Examples include viruses, worms, and Trojan horses.
Types of Computer Mouse
- Mechanical Type (Ball-based)
- Optical Type (Laser-based)

Types of Computer Keyboard Layouts
- QWERTY
- DVORAK
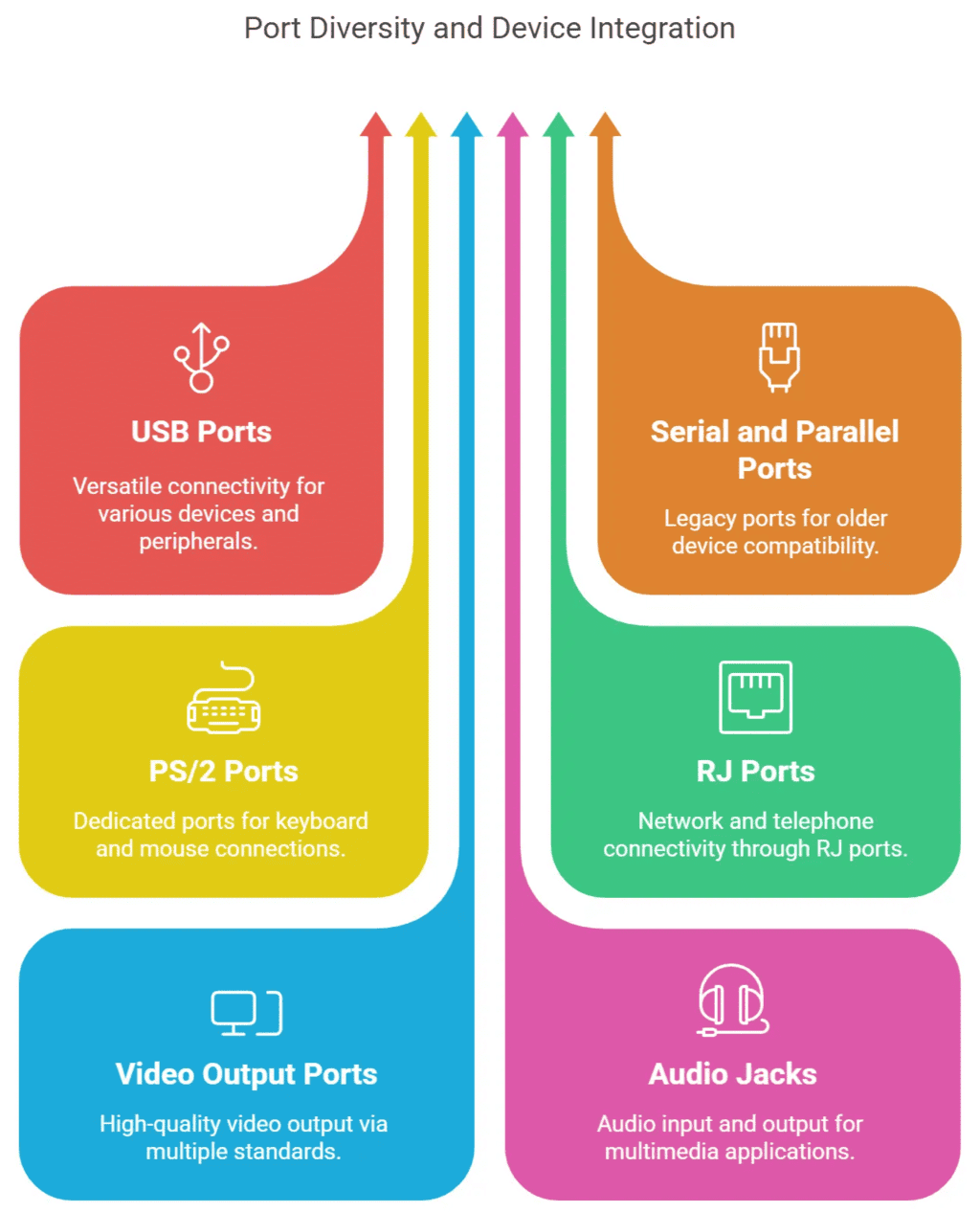
Ports available in a Computer/Laptop
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- RS232 (Serial Port)
- Parallel Port
- PS/2 Port (Keyboard or Mouse)
- RJ 45 (LAN Connection)
- RJ 14 (Telephone Line)
- S-Video (Video Output)
- HDMI (Video Output)
- DVI (Video Output)
- Micro/Min SD Card port (For Memory Cards)
- Microphone
- Headphone
Types of Printers
- Daisy Wheel
- Dot Matrix
- Inkjet
- Laser (Maximum Resolution)

|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Computer - Computer Fundamentals, Computer Awareness - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the basic components of a computer system? |  |
| 2. What is the role of the CPU in a computer system? |  |
| 3. How does memory differ from storage in a computer system? |  |
| 4. What are input and output devices in a computer system? |  |
| 5. What is the role of an operating system in a computer system? |  |






















