UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) > Computer Memory
Computer Memory | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Memory Hierarchy |

|
| Parameters of Memory |

|
| Types of Memory |

|
| Secondary Memory Devices: Storage Method and Capacity |

|
| Basic Units of Memory Measurements |

|
| Cloud Computing |

|
Introduction
- Computer memory is a vital component within a computer system, serving to store both data and instructions crucial for processing and generating output.
- It accommodates storage needs ranging from immediate, short-term requirements to those necessary for extended durations.
- Memory encompasses various devices tasked with storing data, whether temporarily or permanently.
- Its function is indispensable in facilitating smooth data processing and retrieval, contributing significantly to overall system performance and functionality.
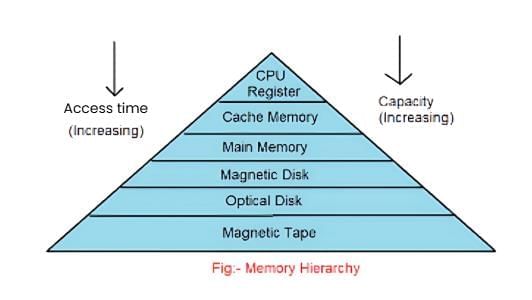
Memory Hierarchy
- The memory hierarchy is a structured arrangement of storage within contemporary computer architectures.
- It employs a hierarchical model designed to optimise both the speed and capacity of memory resources.
- This hierarchy facilitates the utilisation of memory components with the fastest access speeds and highest storage capacities.
- The organisation of the memory hierarchy aims to strike a balance between speed and capacity requirements, ensuring efficient data processing and storage management.
- The hierarchy enables computers to access data swiftly while accommodating a range of storage needs.
Parameters of Memory
- Storage Capacity: This parameter reflects the size of memory, typically measured in words or bytes. It encompasses both internal and main memory capacities.
- Access Modes: Memories consist of multiple locations, and information within these locations can be accessed in various ways, including randomly, sequentially, or directly.
- Access Time: Access time refers to the duration between initiating a read or write operation and the availability of data at the desired location.
- Physical Characteristics: Memory devices can be classified into electronic, magnetic, mechanical, and optical categories based on their physical properties.
- Permanence of Storage: Some materials, particularly magnetic ones, offer high permanence of storage, ensuring data retention for future use.
Types of Memory
Memory is typically divided into two main categories:
- Primary memory is also known as main memory.
- Secondary memory is also referred to as auxiliary memory.
Primary Memory
- Main memory, also known as internal memory, directly interacts with the CPU, enabling the storage of data for immediate processing and tracking of ongoing operations.
- As it is volatile, primary memory loses its contents when power is switched off, making it temporary in nature.
Primary memory can be categorised further into two types:
- Cache memory: High-speed memory that stores frequently accessed data for rapid retrieval by the CPU.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Provides temporary storage for data and instructions actively used by the CPU during program execution.
Random Access Memory
- Also known as read/write memory, RAM (Random Access Memory) allows the CPU to both read from and write data and instructions to it.
- RAM serves as temporary storage for input data, output data, and interim results during program execution

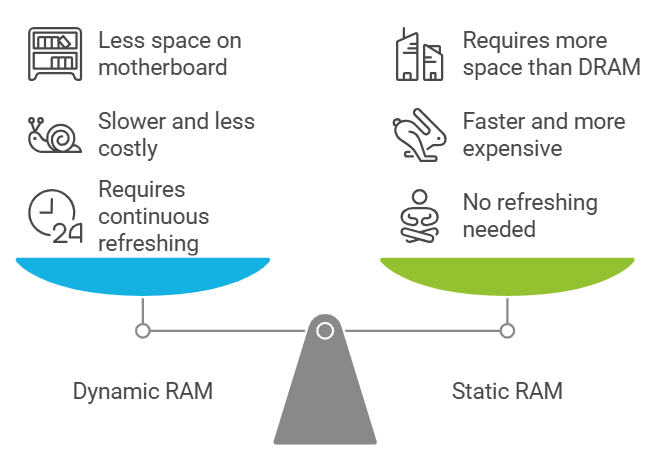
RAM is classified into two categories:
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM): Comprising memory cells with one capacitor and one transistor each, DRAM requires continuous refreshing to maintain stored information. It is slower, less costly, and occupies less space on the motherboard.
- Static RAM (SRAM): Retains data as long as power is supplied to the memory chip, eliminating the need for periodic refreshing. SRAM employs multiple transistors per memory cell and does not use capacitors. Due to its high speed, SRAM is commonly utilized as cache memory, albeit at a higher cost compared to DRAM.
Cache Memory
- Cache memory acts as a storage buffer, holding frequently accessed data temporarily and facilitating rapid access for the CPU.
- Positioned between RAM and the CPU, cache memory operates at very high speeds, enhancing processing efficiency.
- Its primary function is to accelerate data retrieval, thereby boosting overall system performance.
- Due to its high cost, cache memory is typically smaller in size compared to RAM.
- Computer cache memory is usually measured in kilobytes (KB) or megabytes (MB), with sizes ranging from 256 KB to several megabytes, depending on the design of the CPU.
Read Only Memory
- Also referred to as non-volatile memory or permanent storage, ROM (Read Only Memory) retains its content even when power is turned off.
- ROM possesses read-only capability, meaning data can be read from it but not written to it.
- Once programmed during manufacturing, ROM chips cannot be reprogrammed or rewritten.
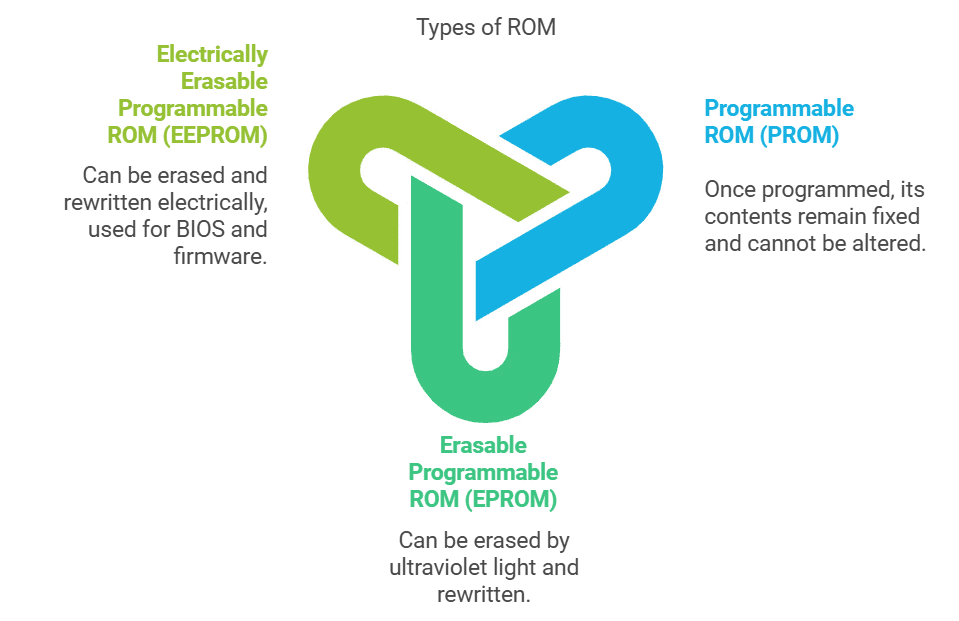
ROM is categorised into three types:
- Programmable ROM (PROM): Once programmed, its contents remain fixed and cannot be altered. PROMs are typically programmed during manufacturing.
- Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM): Similar to PROM, EPROM can be erased by exposure to strong ultraviolet light and then rewritten, hence also known as Ultraviolet Erasable Programmable ROM (UVEPROM).
- Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM): Similar to EPROM, EEPROM can be erased and rewritten electrically. It offers flexibility as the burning process is reversible through exposure to electric pulses. EEPROM is commonly used for holding BIOS and other firmware.
Tit -Bits
- Flash memory is a semiconductor-based non-volatile rewritable memory used in devices like digital cameras, mobile phones, and printers.
- Virtual memory is a technique enabling the execution of processes not entirely in main memory. A key benefit is accommodating programs larger than the available main memory.
- A buffer is a temporary physical storage utilised to hold data during the execution of processes from one location to another.
Question for Computer MemoryTry yourself: What type of memory loses its contents when power is turned off?View Solution
Secondary Memory
- Secondary memory stores large volumes of data and information for extended durations.
- Data in secondary memory cannot be directly processed by the CPU and must be copied into primary storage (RAM) first.
- It serves to store data and programs when they are not actively being processed, functioning as a non-volatile and permanent storage solution.
Secondary memory devices encompass various types:
Magnetic Storage:
- Hard Disk Drive
- Floppy Disk
- Magnetic Tape
Optical Storage:
- CD
- DVD
- Blu-ray Disk
Solid State Storage:
- Pen/Flash Drive
- Memory card
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
- A hard disk drive (HDD) is a non-volatile, random-access digital data storage device commonly used for storing and retrieving digital information.
- HDDs utilise rotating disks, known as platters, coated with magnetic material to store data.
- Programs installed on a computer are typically stored on the hard disk.
- The hard disk consists of a spindle that holds multiple platters, each requiring two read/write heads for accessing data.
- All read/write heads are connected to a single access arm to ensure synchronised movement.
- Information is organised into bands called tracks, with each platter having the same number of tracks. A track location cutting across all platters is termed a cylinder.
- Tracks are further divided into pie-shaped sections known as sectors.

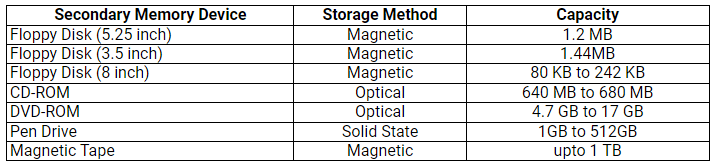
Floppy Disk (Diskette)
- Floppy disks are utilised for data storage, albeit with limited capacity and slower access speeds compared to hard disks.
- They are typically round in shape and consist of a thin plastic disk coated with iron oxide.
- Data is recorded or retrieved from the disk's surface through a slot on the envelope.
- Floppy disks are removable from the drive, allowing for easy transportation of data.
- They are available in three sizes: 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch.

Magnetic Tape
- Magnetic tapes are constructed from a plastic film material coated with magnetic substances, providing a permanent storage solution for data.
- Capable of both reading and recording data, magnetic tapes facilitate sequential data storage.
- Typically, magnetic tapes are 12.5 mm to 25 mm wide and range from 500 m to 1200 m in length.
- Data stored on magnetic tapes comprises tiny segments of magnetised and demagnetised areas on the material's surface.
- Magnetic tapes offer durability and the ability to be written, erased, and rewritten as needed.
- They boast high data storage capacity, with access to data typically occurring in a sequential manner.

Compact Disk
- CDs, or Compact Disks, represent the most prevalent and cost-effective form of optical disk storage.
- They serve as data storage devices and are commonly used for storing digital audio as well.
- Files on CDs are stored in contiguous sectors.

CDs are classified into three primary types:
1. CD-ROM (Read-Only Memory)
- CD-ROMs are designed for data that will not be changed or deleted.
- The information is written onto the disc during the manufacturing process, and users can only read the data.
- This type of CD is commonly used for software, games, and digital media that require a stable data set.
2. CD-R (Recordable)
- CD-Rs allow users to write data onto the disc once.
- After the data is written, it cannot be altered or erased.
- This type is useful for creating personal music compilations, backing up files, or sharing data that does not need to be modified.
3. CD-RW (Rewritable)
- CD-RWs offer the flexibility to write, delete, and rewrite data multiple times.
- This makes them ideal for tasks that require frequent updates, such as data backups or temporary file storage
Digital Video Disk
- DVD, also known as Super Density Disk (SDD) or Digital Versatile Disk, is an optical disk storage medium introduced by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995.
- Offering higher storage capacity than compact discs, DVDs maintain the same physical dimensions.
- Depending on the disk type, DVDs can store several gigabytes of data, ranging from 4.7 GB to 17.08 GB.
- DVDs are commonly used for storing music or movies and can be played back on televisions or computers.
- They are non-rewritable media, meaning once data is recorded, it cannot be erased or rewritten.

Tit-Bits
- Data transfer rate indicates the speed at which data is written to or read from a disk.
- The root directory serves as the primary folder on a disk, holding information about all other folders present on the disk.
Blu-ray Disk
- Blu-ray disks (BD) are optical disk storage media designed to store data, typically in DVD format.
- Each layer of a Blu-ray disk can hold approximately 25 GB (23.31 GB) of data.
- The name "Blu-ray" refers to the blue laser used to read the disk, enabling higher data density compared to the red laser used in DVDs.
- Blu-ray disks can store almost five times more data than single-layer DVDs.

Variations in Blu-ray formats include:
- BD-ROM (Read-only)
- BD-R (Recordable)
- BD-RW (Rewritable)
- BD-RE (Rewritable)
Pen/Thumb Drive
- A pen drive, also known as a flash drive, is a portable data storage device comprising flash memory with a USB interface.
- These drives are characterised by their small size, portability, and rewritable nature.
- USB flash drives are considerably smaller than floppy disks and are typically removable.
- They come in various storage capacities ranging from 256MB to 64GB and are commonly used for transferring and storing information between computers.
Question for Computer MemoryTry yourself: What type of memory is also known as main memory?View Solution
Memory Cards
- These clip-shaped data storage devices are commonly utilised in a variety of electronic devices such as digital cameras, mobile phones, and laptops.
- They are characterised by their small size, re-recordable capability, easy portability, and lightweight design.
Secondary Memory Devices: Storage Method and Capacity
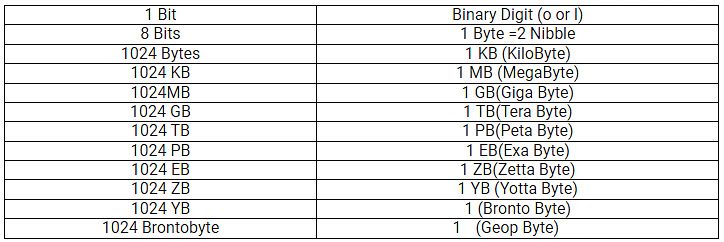
Basic Units of Memory Measurements
Cloud Computing
- Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services over the internet, including storage, processing, and management of data. This technology enables users to access and utilise resources remotely, without the need for physical infrastructure on-site.
- It encompasses a wide range of services such as data storage, software applications, and computing power, all accessible via the internet.

Types of Cloud Deployments
- Public Cloud: Managed by third parties, offering services to the public and reducing IT infrastructure costs.
- Private Cloud: Distributed systems providing dynamic resource provisioning on a private infrastructure.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, offering the benefits of both.
Cloud Computing Services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Virtualised infrastructure managed by external providers for businesses.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Software applications delivered over the internet on a subscription basis.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): On-demand environments for developing, testing, and managing software applications.
Next-Generation Memories
- FeFET/FeRAM: These technologies are currently under research and development.
- Nanotube RAM: Targeted to displace DRAM.
- Phase Change Memory (PCM): New versions ready for market.
- ReRAM: Positioned for AI applications.
- Spin-Orbit Torque-MRAM (SOT-MRAM): Targeted to replace SRAM.
Tit-Bits
- The rate at which data is written to disc or read from disc is called the data transfer rate.
- Root directory is the main folder of disk. It contains information about all folders on the disk.
The document Computer Memory | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) is a part of the UPSC Course Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
744 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Computer Memory - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What is the memory hierarchy and why is it important in computer architecture? |  |
Ans. The memory hierarchy is a structured arrangement of different types of memory in a computer system, organized by speed, cost, and size. It typically includes registers, cache, main memory (RAM), and secondary storage (like hard drives). This hierarchy is important because it optimizes performance and cost; faster, more expensive memory is used for immediate data access, while larger, slower memory is used for long-term storage. By efficiently organizing memory, computers can achieve better speed and responsiveness.
| 2. What are the main types of memory used in computers? |  |
Ans. The main types of memory used in computers include volatile memory (like RAM) and non-volatile memory (like ROM and flash memory). Volatile memory loses its data when power is off, while non-volatile memory retains data even when powered down. Additionally, cache memory is a high-speed type of volatile memory that stores frequently accessed data to speed up processing.
| 3. How do secondary memory devices differ from primary memory? |  |
Ans. Secondary memory devices, such as hard drives and SSDs, are used for long-term data storage, while primary memory, like RAM, is used for temporary storage of data that the CPU is currently processing. Primary memory is faster but more expensive per unit of storage, whereas secondary memory offers larger capacity at a lower cost but is slower to access.
| 4. What are basic units of memory measurements, and how are they defined? |  |
Ans. The basic units of memory measurements include bits, bytes, kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB). A bit is the smallest unit of data, representing a binary value (0 or 1). A byte consists of 8 bits. Kilobytes are approximately 1,024 bytes, megabytes are about 1,024 kilobytes, gigabytes are around 1,024 megabytes, and terabytes are approximately 1,024 gigabytes.
| 5. What are some interesting facts about computer memory that everyone should know? |  |
Ans. Some interesting facts about computer memory include: 1) The first computer memory was made of vacuum tubes, which were large and inefficient. 2) Modern RAM can transfer data at speeds exceeding 25 GB/s. 3) Flash memory, commonly used in USB drives and SSDs, can endure around 10,000 write cycles. 4) The concept of virtual memory allows computers to use disk space as an extension of RAM, improving multitasking capabilities. 5) The storage capacity of memory continues to grow rapidly, with SSDs available in capacities of several terabytes.
Related Searches
















