Automated Teller Machine - Computer Abbreviations, Computer Awareness | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Automated Teller Machine
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) are considered as the most influential technological innovation of the 21st century. An Automated Teller Machine is a Telecommunication Device installed in the public so that people have access to their money without going to the Bank.

- The customer is identified by entering a Plastic Card with a Magnetic Strip or Chip in the ATM. All the information regarding the customer is available in the card. The customer needs to enter some PIN (Personal Identification Number) to perform the Transactions.
- ATM is a data terminal which connects to the Bank Computer Network to retrieve the information through the Host Computer. The ATMs are connected to the Bank Computer Network using Internet or Telephone Lines.
- There are provisions to count the notes and measure the thickness of the bundle of notes to ensure the correctness of the number of notes dispensed to the Customer.
ATM in Banking: History & Significance
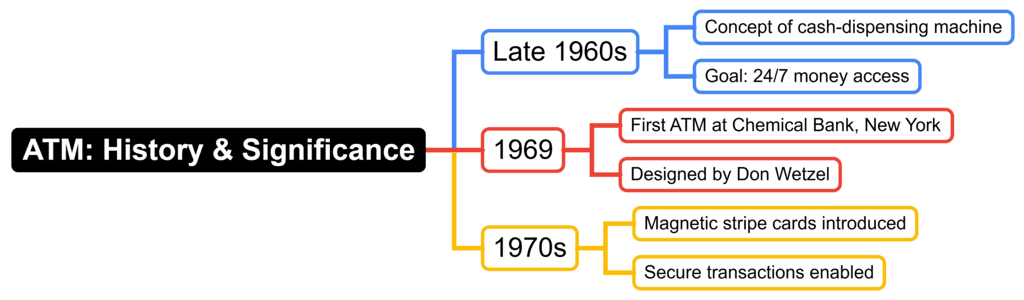
Conceptualization (Late 1960s)
- The concept of a machine that could dispense cash and handle basic banking tasks started in the late 1960s.
- The goal was to create a device that gave people access to their money at any time, reducing their need to rely on bank hours.
First ATM Installation (1969)
- The first working ATM was installed on September 2, 1969, at Chemical Bank in Rockville Centre, New York.
- This machine, designed by Don Wetzel, allowed customers to take out cash, make deposits, and check their account balances.
Magnetic Stripe Technology (1970s)
- In the 1970s, ATMs became more advanced with the addition of magnetic stripe technology.
- This technology made it possible to store information on cards, allowing users to carry out various transactions safely.
Types of Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)
ATMs, or Automated Teller Machines, come in various types to serve different banking and transaction needs. Here are some common types of ATMs:
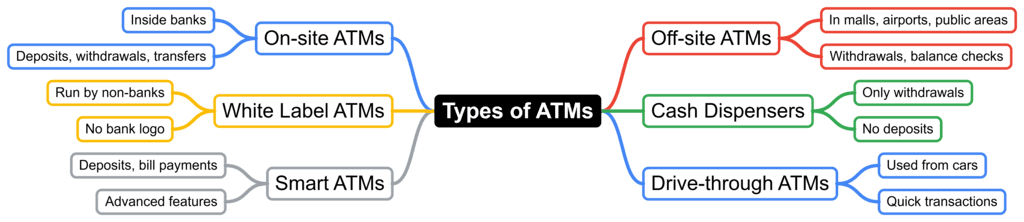
- On-site ATMs: These machines are found inside bank buildings. They are mainly used for various banking tasks like making deposits, taking out cash, and moving money between accounts.
- Off-site ATMs: These are located outside of bank branches, such as in shopping malls, airports, and other public areas. Their primary function is to allow users to withdraw cash and check their account balances.
- White Label ATMs: These ATMs are managed by companies that are not banks but still provide banking services. They are called "white label" because they do not display the operator's logo on the machines.
- Cash Dispensers: These are basic ATMs that only allow users to take out cash. They do not have the ability to accept deposits or perform other banking functions.
- Smart ATMs: These are advanced machines that offer more than just cash withdrawals. They can accept deposits, allow for bill payments, and help with more complicated account management tasks.
- Drive-through ATMs: These ATMs provide a convenient option for users who want to complete quick transactions without having to leave their cars.
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) based on Labels
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) have evolved to offer various types to cater to diverse user needs and technological advancements. Here are several types of ATMs: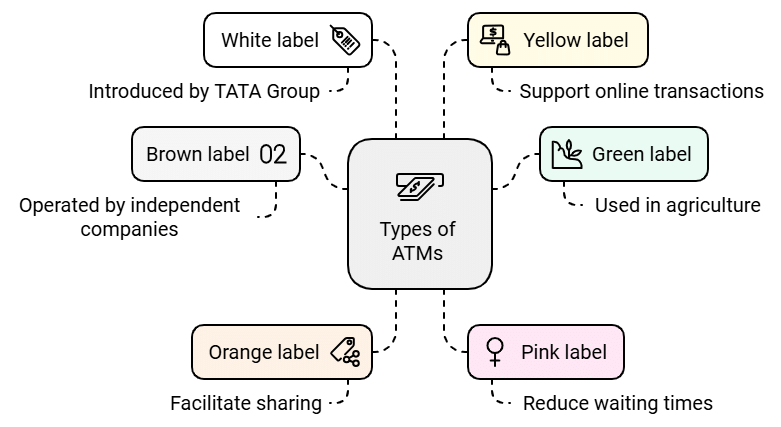
- Brown label: ATMs operated by independent companies instead of banks or credit unions.
- Green label: These ATMs, commonly known as Automated Teller Machines, are run by organizations that are not banks. They are also used in agriculture.
- Orange label: ATMs used for transactions that involve sharing.
- Pink label: ATMs designed specifically for women, aiming to reduce long lines and waiting times.
- White label: These ATMs, introduced by the TATA Group, are owned by particular companies rather than banks.
- Yellow label: ATMs that facilitate online shopping.
- Transaction Process: To carry out a transaction, customers need to use a plastic card, such as a bank debit card or a credit card. The transaction is completed after the customer successfully enters their PIN for authentication.
How does an ATM Work?
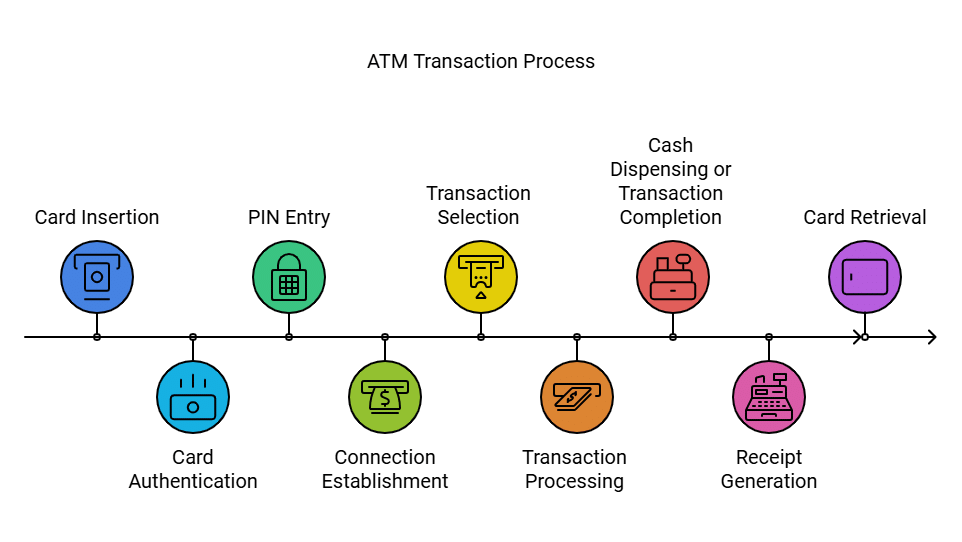
- Card Insertion: The user puts their bank card (either debit or credit) into the ATM's card reader.
- Card Authentication: The ATM reads the card's magnetic stripe or chip to check the user’s identity by verifying the data stored on the card.
- PIN Entry: The user types in their Personal Identification Number (PIN) on the ATM’s keypad. This PIN is an important security step to ensure that only the right person can access their account.
- Connection Establishment: The ATM creates a secure link with the bank’s main computer or a payment network. This connection can be made through dedicated phone lines, internet connections, or other secure networks.
- Transaction Selection: The user chooses the type of transaction they want from the menu displayed on the screen. Options can include cash withdrawal, balance check, funds transfer, and more banking services.
- Transaction Processing: The ATM sends the transaction request along with the user's authentication information to the bank's main computer or payment network. The main computer checks the request, looks at the user’s account balance, and confirms if the transaction is allowed.
- Cash Dispensing or Transaction Completion: If the transaction is approved, the ATM gives out the requested cash. For transactions that do not involve cash, like balance checks or fund transfers, the ATM shows the completed transaction on the screen.
- Receipt Generation: The ATM prints a receipt that details the transaction, showing the amount taken out, the balance left, or other important details. Users can decide whether to get a printed receipt or not.
- Card Retrieval: The user takes their card from the ATM, completing the transaction. It is important for users to remember to take their card to prevent security issues.
- Connection Termination: Once the transaction is complete, the secure connection between the ATM and the bank's main computer is closed.
- Cash Reconciliation: Regularly, the ATM checks to make sure that the amount of cash inside matches the transactions recorded.
- Maintenance and Security: ATMs are routinely serviced to ensure they work properly. Security measures, like surveillance cameras, are used to help prevent fraud.
Note: The way ATMs operate can differ based on the model and type of machine, as well as the banking system used. More advanced ATMs, such as Interactive Teller Machines (ITMs) or those with biometric features, might include extra steps in the transaction process.
Benefits of ATM – Automated Teller Machine
- Cash Withdrawals: ATMs allow users to take out cash from their bank accounts easily. Customers can choose from preset amounts or enter a specific amount they wish to withdraw.
- Deposits (cash or check): Many ATMs let users deposit cash and checks. Older models require envelopes for deposits, but newer ones allow people to insert cash or checks directly, automatically counting the cash or scanning the checks.
- Account Inquiries: ATMs provide options for checking account balances and viewing recent transactions. This feature helps customers keep track of their money without needing to visit a bank.
- Fund Transfers: Customers can transfer money between their accounts or send it to others at the same or different banks, as long as the ATM network supports this service.
- Bill Payments: Some ATMs allow users to pay bills for utilities, credit cards, and more directly from their bank accounts, making it convenient to manage payments without needing online banking.
- Account Statements: Customers can request account statements that show their recent banking activities. These statements can be printed right at the ATM or sent to the customer's email address.
Technological Enhancements of ATM
- Over the years, ATMs have added new security features like biometric authentication and one-time password (OTP) systems to keep transactions safe.
- Today’s ATMs come with touch screens, voice guidance, and the option to choose different languages, making them easier for more people to use.
- ATMs are very important in modern banking because they provide convenience to customers and allow banking services to be available outside of regular branch hours.
- They have changed a lot from being simple machines that only give out cash to becoming multifunctional devices that can handle various banking tasks.
Importance of ATM Machine
- Convenience: ATMs make it easy for people to access banking services, such as withdrawing and depositing cash, at any time of the day. They are located in many places, allowing individuals to manage their money without worrying about bank hours or specific locations.
- Increased Financial Inclusion: ATMs play a vital role in bringing banking services to areas where people may not have easy access to banks, especially in rural or remote regions. This helps more people participate in the financial system.
- Reduced Load on Bank Branches: By taking care of everyday transactions, ATMs lessen the number of customers visiting bank branches. This allows bank staff to focus on more complicated issues and improve overall customer service.
- Economic Efficiency: ATMs help money move more smoothly in the economy by giving people quick access to their cash. This can encourage more spending and stimulate economic growth.
- Enhances Safety: With the ability to withdraw cash as needed, individuals can carry less money, which can make them feel safer. Additionally, ATMs offer a secure way to deposit cash directly into accounts, lowering the risk of theft.
- Empowerment Through Self-Service: ATMs give users the power to handle basic financial transactions on their own. This self-service option helps people learn more about managing their money and promotes financial independence.
ATMs are very safe and secure machines. They are helpful for bank transactions. Nowadays they are available in every region. ATMs are upgraded with time. Many new functions have been implemented in the machines.
|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Automated Teller Machine - Computer Abbreviations, Computer Awareness - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What is the history and significance of Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) in banking? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)? |  |
| 3. How do Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) work? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of using Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)? |  |
| 5. What technological enhancements have been made to ATMs in recent years? |  |

















