NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science - Challenges of Nation Building
Q1: Which among the following statements about the partition is incorrect?
(a) Partition of India was the outcome of the “two-nation theory”.
(b) Punjab and Bengal were the two provinces divided on the basis of religion.
(c) East Pakistan and West Pakistan were not contiguous.
(d) The scheme of Partition included a plan for transfer of population across the border.
Ans: (d)
Q2: Match the principles with instances:Ans: (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
Q3: Take a current political map of India (showing outlines of states) and mark the location of the following Princely States.
(a) Junagadh
(b) Manipur
(c) Mysore
(d) Gwalior
Ans: 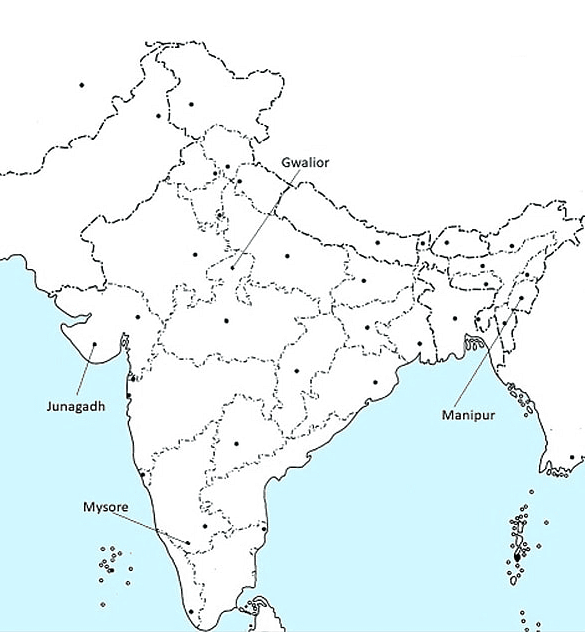
Q4: Here are two opinions:
Bismay: “The merger with the Indian State was an extension of democracy to the people of the Princely States.” Inderpreet: “I am not so sure, there was force being used. Democracy comes by creating consensus. ”
What is your opinion in the light of accession of Princely States and the responses of the people in these parts?
Ans: Accession of Princely States and merger with Indian union was to expand democracy all over the country because princely states never enjoyed their political rights. Indian government central government used force to extend democracy to some extent as this was mandatory to have a uniform base in the country.
Q5: Read the following very different statements made in August 1947:
“Today you have worn on your heads a crown of thorns. The seat of power is a nasty thing. You have to remain ever wakeful on that seat… you have to he more humble and forbearing… now there will be no end to your being tested. ”
-M.K, Gandhi “India will awake to a life of freedom…. we step out from, the old to the new…. we end, today a period of ill fortune and India discovers herself again. The achievement we celebrate today is but a step, an opening of opportunity …”, -Jawaharlal Nehru
Spell out the agenda of nation building that flows from these two statements. Which one appeals more to you and why?
Ans: These two statements focus on the agenda of secularism, democracy, sovereignty and freedom. It focuses on the path which will lead to the real development and prosperity of our country. The first statement appeals to me more than the second one because it invokes the countrymen to remain awake, alert and conscious as it is not the end of our struggle. The time to build the nation initiates now.
Q6: What are the reasons being used by Nehru for keeping India secular? Do you think these reasons were only ethical and sentimental? Or were there some prudential reasons as well?
Ans: Reasons for keeping India secular:
- All the Muslims did not leave India during partition, some muslims stayed in India as a minority and Jawaharlal Nehru wanted to deal with them in a very civilised and dignified manner.
- He advocated security and democratic rights of Muslims as a citizen of India.
No, these reasons were not only ethical and sentimental, but there were some prudential reasons also as:
- India’s secular nature cherished its long term goals and principles like socialism, equality, liberty and fraternity.
- Secularism stops any single faith to become superior and inferior to those who practicised another religion. Hence it considers all citizens equal irrespective of religious affiliation.
Q7: Bring out two major differences between the challenge of nation building for eastern and western regions of the country at the time of Independence.
Ans: The two major differences between eastern (Bengal) and Western (Punjab) regions can be summed up as follows:
- These regions were the muslim majority provinces to be joined. Hence, it was decided that new country Pakistan will comprise two territories i.e. West and East Pakistan.
- Secondly, there was a problem of minorities on both sides of border (East and West). Lakhs of Hindus and Sikhs in areas of Pakistan and Muslims on the Indian side of Punjab and Bengal found themselves trapped with no option except to leave their homes.
Q8: What was the task of the States Reorganisation Commission? What was its most salient recommendation?
Ans: The State Reorganisation Commission was set up in 1953 by central government to look into the matter of redrawing of boundaries of state:
- The commission evolved that states’ boundaries should reflect the boundaries of different languages to accommodate linguistic diversity.
- The State Reorganisation Act was passed in 1956 which resulted the creation of 14 states and 6 union territories.
- Its most salient recommendation was the formation of linguistic states i.e. to reorganise states on the basis of accommodation of their languages to prepare a uniform base for the nation.
Q9: It is said that the nation is to large extent an “imagined community” held together by common beliefs, history, political aspirations and imaginations. Identify the features that make India a nation.
Ans: India proved herself through all stages of three challenges at the time of nation building like:
- India is a secular country where people speak different languages and follow different cultures and religions to be recognised as a nation of unity in diversity with common faith and beliefs.
- Political aspiration ensures demo¬cratic setup based on parliamentary form of government creating political competition in a democratic framework.
- India’s imaginations established a welfare state on the principle of equality and special protection to socially disadvantaged groups and religions as well as cultural communities.
Q10: Read the following passage and answer the questions below:
“In the history of nation-building only the Soviet experiment bears comparison with the Indian. There too, a sense of unity had to be forged between many diverse ethnic groups, religious, linguistic communities and social classes. The scale-geographic as well as demographic was comparably massive. The raw material the state had to work with was equally unpropitious: a people divided by faith and driven by debt and disease.” —Ramachandra Guha
(a) List the commonalities that the author mentions between India and Soviet Union and give one example for each of these from India.
(b) The author does not talk about dissimilarities between the two experiments. Can you mention two dissimilarities?
(c) In retrospect which of these two experiments worked better and why?
Ans:
(a) Commonalities between India and Soviet Union:
- Both the nations shaped the nation on linguistic basis.
- To promote welfare motives, the economic and technological developments took place in India also.
- States were divided on the grounds of geographical boundary and strength of populations also in both the nations.
(b) Dissimilarities:
- Soviet Union was divided into 15 independent republics/countries to be disintegrated.
- India maintained its unity and integrity even among diversified nature of states and peoples without any more division.
(c) The Indian experiment worked better to promote linguistic and cultural plurality without affecting unity and integrity of the nation though India adopted some diplomatic measures to make country united.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science - Challenges of Nation Building
| 1. What are the challenges faced in nation building? |  |
| 2. How does political stability contribute to nation building? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of economic development in nation building? |  |
| 4. How can social integration be achieved in the process of nation building? |  |
| 5. How does strengthening institutions contribute to effective nation building? |  |






















