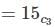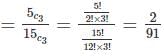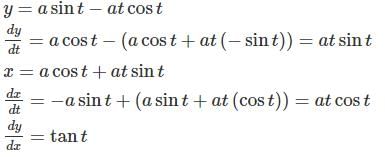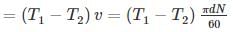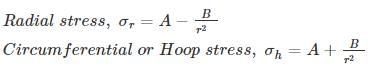Full Test 4 - EKT Mechanical - AFCAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Full Test 4 - EKT Mechanical
A bag contains 4 white, 5 red and 6 blue balls. Three balls are drawn at random form the bag. The probability that all of them are red is:
If x = a(cos t + t sin t), y = a(sin t – t cos t). The value of dy/dx is
If ω is a cube root of unity then the value of (1 − ω8)(1 − ω4)(1 − ω2)(1 − ω) is ___
The property by virtue of which liquid opposes relative motion between its different layers is called
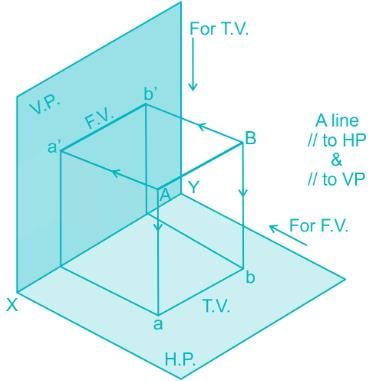
A line AB is parallel to both HP and VP. Its side view will be ______
The horse power transmitted by a belt is dependent upon
The velocity in m/s of a particle moving in a straight line is given by v = t3 – t2, its acceleration after three seconds is
The quantity, which is equal to rate to change of momentum is known as:
Which Newton's law of motion gives the measure of force?
The diameter of core of a circular section is given as:
For the analysis of thick cylinders, the theory applicable is