Test: Federalism - 1 - UPSC MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Federalism - 1
Assertion (A): Federalism allows for the coexistence of multiple levels of government, each with its own powers and responsibilities.
Reason (R): Federal systems are designed to prevent conflict by having a single judiciary that resolves disputes between the central and state governments.
Reason (R): Federal systems are designed to prevent conflict by having a single judiciary that resolves disputes between the central and state governments.
Which of the following factors is NOT mentioned as a determinant of federation functionality?
Match the following timeline of events related to the reorganization and formation of new states in India based on linguistic and administrative needs:
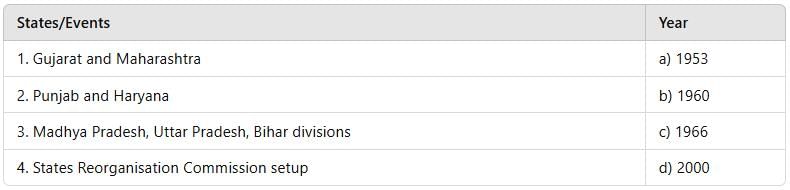

Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. The Union List comprises 100 subjects that are exclusively under the jurisdiction of the central government.
ii. The State List initially contained 66 subjects but currently has 61 subjects assigned to the state governments.
iii. Both the central and state governments can legislate on subjects in the Concurrent List, but if there is a conflict, the state law takes precedence.
iv. Residual subjects, which are not specified in any list, are assigned to the central government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. The Indian Constitution establishes a powerful central government to address national issues like poverty and illiteracy.
ii. The central government has no authority to alter the boundaries or names of states.
iii. During emergencies, the central government can legislate on subjects that fall under state jurisdiction.
iv. The Governor has the authority to dissolve the state assembly without the central government's consent.
Assertion (A): Jawaharlal Nehru's leadership was pivotal in establishing the framework of Indian federalism during the 1950s.
Reason (R): The dominance of the Congress party at both the central and state levels created a stable political environment conducive to federalism.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Demands for autonomy among States include calls for more significant powers to be assigned to them.
ii. Financial autonomy demands are focused solely on increasing state control over cultural issues.
iii. Administrative autonomy is characterized by resentment against central control over the administrative framework.
iv. Protests against the imposition of Hindi in the 1960s were primarily led by Hindi-speaking States advocating for their language.
Which of the following statements best captures the complexity of interstate disputes in India?
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The special provisions for certain states in India are primarily related to north-eastern states with significant indigenous tribal populations.
Statement II: Jammu and Kashmir's special status under Article 370 allows the Union government to impose financial emergencies in the state without the state's concurrence.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:



















