UPSC CSE Prelims Paper 1 (GS) Mock Test - 14 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPSC CSE Prelims Paper 1 (GS) Mock Test - 14
Bioasphalt is an asphalt alternative made from non-petroleum based renewable resources.
Which of the following are the potential sources of the Bioasphalt?
1. sugar, molasses and rice
2. corn and potato starches
3. Natural tree and gum resins
4. Natural latex rubber and vegetable oils
5. Lignin, cellulose, palm oil waste
6. Coconut waste, peanut oil waste
Which of the following are the potential sources of the Bioasphalt?
1. sugar, molasses and rice
2. corn and potato starches
3. Natural tree and gum resins
4. Natural latex rubber and vegetable oils
5. Lignin, cellulose, palm oil waste
6. Coconut waste, peanut oil waste
Fossil fueled power stations are major emitters of CO2. Which of the following statements are correct about the fossil fuels?
1. Brown coal emits 3 times as much CO2 as natural gas.
2. Black coal emits twice as much CO2 per unit of electric energy.
1. Brown coal emits 3 times as much CO2 as natural gas.
2. Black coal emits twice as much CO2 per unit of electric energy.
A satellite in a geostationary orbit appears stationary, always at the same point in the sky, to ground observers. A perfect stable geostationary orbit is an ideal that can only be approximated. In practice, the satellite drifts out of this orbit because of perturbations such as the
1. Solar wind
2. Radiation pressure
3. Variations in the Earth's gravitational field
4. Gravitational effect of the Moon and Sun
1. Solar wind
2. Radiation pressure
3. Variations in the Earth's gravitational field
4. Gravitational effect of the Moon and Sun
Which one of the following dramas was written by Sriharsha?
Which of the following syndrome is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21)
Which of the following statements are correct about the exports by a country?
A microbial fuel cell (MFC) or biological fuel cell is a
The fiscal policy of a Government is best described as
There has been a steady decline in the total volume of ozone in Earth's stratosphere (the ozone layer) since 1970s to the tune of
Which of the following are the strategies to reduce the current account deficit?
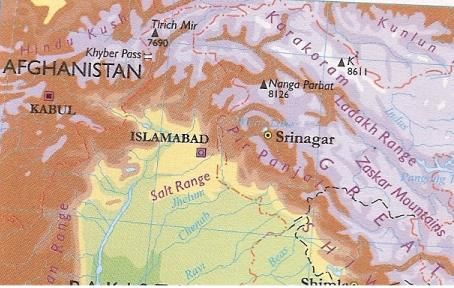
Consider the following map below and match the mountain peaks
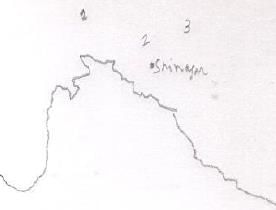
Which of the following statements are correct about the Chandipur-on-sea?
1. It is located Andhra Pradesh
2. It is unique in bio-diversity
3. It is described often as 'the land of hidden treasures'
4. It is the the location of the Indian Army's Integrated Test Range (ITR)
Which of the following is caused by decisions on the part of the central bank to increase the money supply much more than markets had previously expected?
Which of the following phenomena are associated with the demographic dividend?
1. A rising share of working age people in a population
2. Rise in fertility rate
3. Decline in youth dependency rate
Carbon credits were one of the outcomes of the
A closed economy is an economy in which no activity is conducted with outside economies. It is also known as
Bark is a tree's natural armor and protects from external threats. Which of the following functions are carried out by bark?
1. Ridding the tree of wastes by absorbing and locking them into its dead cells and resins
2. Transporting large quantities of nutrients throughout the tree
3. Preventing loss of water from the tree by evaporation
In which one of the following Smruti is found the statement: “the royal charters were written on cloth or copper plate"?
The Indian Rhinoceros is one of the 45 species of globally threatened mammals found in the
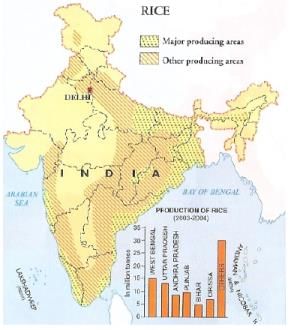
The following map shows the major producing area of
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water towards the ocean surface driven by
Which of the following statements are correct about the tropical rainforest
1. A tropical rainforest is a place roughly within 28° north or south of the equator
2. Minimum normal annual rainfall between 100 and 150 cm
3. Mean monthly temperatures exceed 10°C during all months of the year
The largest family of flowering plants with 750 species in the Himalaya hotspot is the
India is divided into how many biogeographic regions
In Karl Marx's ideology Membership in a class is defined by one's relationship to the
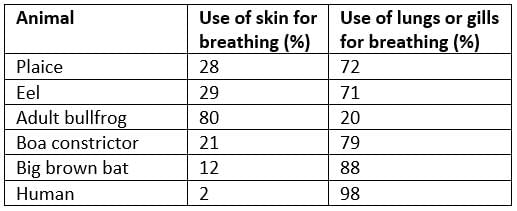
Which one of the following animals breathe through the skin?
Which of the following statements are correct about the FDI and FII?
1. Foreign direct investment is involved in direct production activities and is a short-term investment
2. Foreign institutional investment is a long term investment in the financial market
Bacillus Thuringiensis Brinjal, popularly known as Bt brinjal has been developed by
With reference to "Aam Admi Bima Yojana", consider the following statements:
1. Aam Admi Bima Yojana is a prestigious scheme of the Central and State / Union Territory Governments and administered by LIC
2. It is a scheme for the rural landless households, wherein the head of rural landless families or one earning member in each such family will be insured
3. In the event of death of a member prior to the terminal date, the Sum Assured of Rs.30,000/- will become payable to the nominee
4. In the event of death by accident or Total Permanent Disability due to accident, Rs.75,000/- is payable