Test: Historical Background - UPSC MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Historical Background
Which of the following are the features of the Regulating Act of 1773?
1) It is provided for the establishment of Supreme Court at Calcutta (1774).
2) It created executive council for Governor General of Bengal.
3) It made the governors of Bombay and Madras presidencies subordinate to the Governor General of Bengal.
4) It established Board of Control for managing Political Affairs.
1) It is provided for the establishment of Supreme Court at Calcutta (1774).
2) It created executive council for Governor General of Bengal.
3) It made the governors of Bombay and Madras presidencies subordinate to the Governor General of Bengal.
4) It established Board of Control for managing Political Affairs.
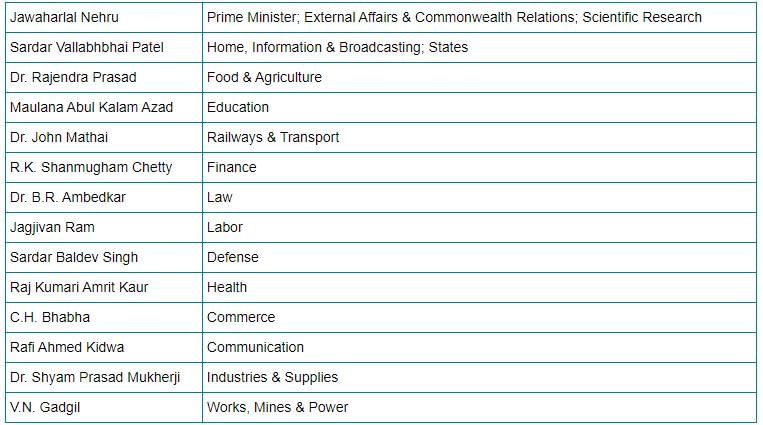
Which of the following leaders are correctly matched to their portfolios in the first cabinet of free India?
1) Sardar Baldev Singh - Defense
2) Dr. Rajendra Prasad - Food and Agriculture
3) Dr. John Mathai - Finance
1) Sardar Baldev Singh - Defense
2) Dr. Rajendra Prasad - Food and Agriculture
3) Dr. John Mathai - Finance
Which of the following is/are true?
1) Simon Commission which was appointed in 1927, submitted its report in 1930, which suggested abolition of dyarchy.
2) The Poona Pact was a reaction to the Simon Commission and its Report.
Which of the following statements regarding Cabinet Mission plan is/are CORRECT?
(i) Lord Wavell was not one of the members of the Cabinet Mission.
(ii) It provided for equal representation to Hindus and Muslims in the interim government.
(iii) Princely states could nominate members to Constituent Assembly.
In which year, the Indian National Congress officially demanded Constituent Assembly for framing Constitution of India?
Who among the following was the chairman of the subcommittee on fundamental rights in the Constituent Assembly of India?
In the context of Crips Mission, consider the following statements –
(i) It provided for complete independence to India.
(ii) It provided provinces the option to stay out of the Union of India.
(iii) It provided India with membership of Commonwealth Nations.
(iv) Muslim League accepted the proposals.
Which of the above statements is/are CORRECT ?
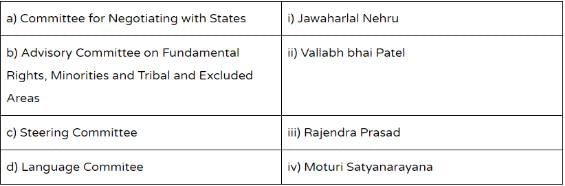
Match the following committees of the Constituent Assembly of India with their respective chairmans –
In the context of India’s Constitutional advance, which of the following statements regarding August Offer of 1940 is INCORRECT?