Test: Indian Drainage System - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Indian Drainage System
Which of the following rivers flows through a ‘rift’ valley?
Which of the following is/are West flowing river(s) of India?
1. Mahanadi
2. Krishna
3. Narmada
4. Kavery
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
Which of the following best explain why the lower course of a river is sometimes choked with sediments?
1. The valley of a river is widest in its lower course.
2. The velocity of a river in its lower course is low.
3. The delta sometimes develops in a river’s lower course.
4. Much of the river water is drawn for irrigation in the lower course.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
Which of the following rivers flows from south to north?
Which one of the following rivers in India has been declared as the National River?
Which of the following rivers is not the tributary of Yamuna?
Which one of the following rivers of India does not make a delta?
Which of the major rivers of India does not form a delta?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the
codes given below:
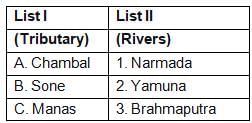
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
Which one among the following is the correct sequence of the rivers from north to south?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the
codes given below:
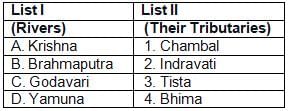
The reservoir GB Pant Sagar is located on which river?
Which one of the following rivers flows into the Arabian Sea?
Deltas are common in India for the East-flowing river systems, whereas they are nearly absent on the West coast because West-flowing rivers
Which of the following three rivers of the peninsula India have the Amarkantak region as their source?
Arrange the following tributaries of river Indus from North to South :
1. Chenab
2. Jhelum
3. Ravi
4. Sutlej
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
Which one of the following pairs of a river and its tributary is not correctly matched?
The Amarkantak Hills is the source of which of the following rivers?
1. Narmada
2. Mahanadi
3. Tapti
4. Son
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following rivers has the largest catchment area?
Which one of the following waterfalls in India has the most height?
Which of these west-flowing rivers flow between two mountain ranges?
Gandak river is associated with one of the following river systems—
Which one of the following is not a tributary of river Alaknanda?
Which of the following pairs of waterfalls — the river is not properly matched?
Rajarappa is situated on the confluence of which rivers?
Consider the following tributaries of river Brahmaputra :
1. Lohit
2. Tista
3. Subansiri
4. Sankosh
Arrange the above rivers from west to east:
Which one of the following does not belong to Himalayan rivers?



















