Test: Mountains Peaks & Ranges - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mountains Peaks & Ranges
Considering the locations of mountains in India, which one among the following is in the right sequence from south to north?
Arrange the following mountain ranges from north to south order
and select the correct answer from the codes:
1. Dhauladhar
2. Ladakh
3. PirPanjal
4. Zaskar
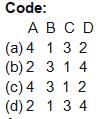
Codes:
Which one of the following statements is not correct regarding the Himalayas?
Which one of the following mountain ranges is spread over only one state in India?
Which one of the following is the oldest mountain range in India?
What is the name given to the foothills zone of Himalayas?
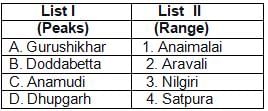
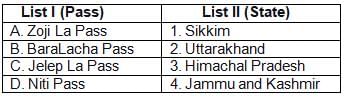
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the
codes given below:
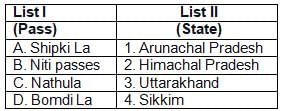

Which of the following passes is in Arunachal Pradesh?
Among the following which mountain range is the oldest in India?
Which of the following landforms occupy the North-Western parts of Bihar State?
Which of the following statements about Nathu La Pass are correct?
1. It links Sikkim with Tibet
2. It was the main artery of the ancient Silk Route
3. It was reopened in the year 2006
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Consider the following statements—
1. Zojila Pass in PirPanjal range connects Jammu and Srinagar
2. Banihal Pass connects Srinagar to Drass and Kargil.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
What is the other name of the highest range in the Western Ghats?
The hill range that separates the State of Manipur from the State of Nagaland is known As