Laxmikanth Test: Amendment of the Constitution - UPSC MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Laxmikanth Test: Amendment of the Constitution
What is the primary body responsible for initiating a Constitution amendment in India?
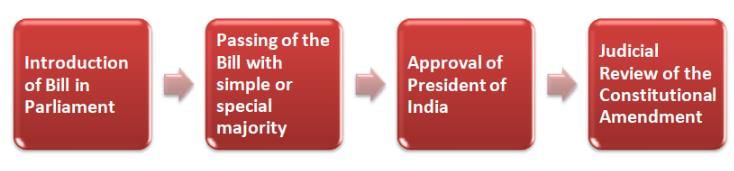
Article 368 provides for the procedure for amendment of the Constitution. About amendment, consider the following:
1. All amendments to the Constitution are initiated only in the Parliament.
2. The Constitution Commission is required to amend the Constitution.
3. After the passage of the amendment bill in the Parliament and, in some cases, in State legislatures, the referendum is required for ratification of the amendment.
4. Sovereignty of elected representatives is the basis of the amendment procedure.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about the position of states concerning constitutional amendments:
1. The states can initiate a constitutional amendment bill in the USA, unlike in India.
2. The constitution does not provide a time limit for getting the required amendment cleared by the states in India.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. The Constitution can be amended by a simple majority for changes related to the quorum in Parliament and the salaries of its members.
2. Amendments affecting the distribution of legislative powers between the Union and the states require ratification by state legislatures.
3. The abolition or creation of legislative councils in states requires only simple majority in Parliament.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The amendment process is similar to the process of passing regular bills in Parliament, except for the requirement of a special majority.
Statement-II: The amendment process strikes a balance between flexibility and rigidity. It is not so flexible that it can be easily changed by the ruling parties, nor is it so rigid that it cannot adapt to changing needs.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
No Time Frame for State Consent: The Constitution doesn't set a time limit for state legislatures to approve or reject an amendment. It also doesn't clarify if states can change their approval.
Statement-II:
Facile Procedure for Amendments: The Constitution provides a relatively easy process for amending itself, allowing changes to meet evolving needs. This approach is different from some other countries like Canada, the USA, or Australia.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following pairs regarding provisions that require a special majority in Parliament and consent of states for constitutional amendments:
1. Distribution of legislative powers between the Union and the States.-Consent required from at least half of the state legislatures
2. Seventh Schedule Lists - Consent required from at least half of the state legislatures
3. Representation of States in Parliament - Consent required from half of the state legislatures
4. Fundamental Rights - Consent required from all state legislatures
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements:
1. Article 368 of the Indian Constitution deals with the procedure for amending the Constitution.
2. Amendments related to the federal structure require a special majority in Parliament and ratification by at least half of the state legislatures.
3. All amendments to the Constitution require the involvement of the state legislatures.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following provisions in the Constitution that can be amended by a simple majority of the two Houses of Parliament, outside the scope of Article 368 :
1. Citizenship clauses
2. Abolition or creation of legislative councils in states
3. Election of the President and its manner
Q. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about the Constitutional amendment in India.
1. A private member of the Parliament cannot introduce a constitutional amendment bill
2. The prior permission of the President is required for the introduction of every constitutional amendment bill
3. Special days are reserved for introducing constitutional amendment bills
Q. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about the procedure to amend the Indian constitution:
1. A constitutional amendment bill requires the prior permission of the President.
2. It can only be introduced in the' Lok Sabha first as it is the house of the people from which the constitution derives its authority.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
1. The President cannot send back a constitutional amendment bill for reconsideration to the Parliament.
2. Elected representatives alone have the power to amend the Constitution.
3. The judiciary cannot initiate the process of Constitutional Amendment but can effectively change the Constitution by interpreting it differently.
4. The Parliament can amend any section of the Constitution.
Q. Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following pairs regarding provisions that require a special majority in Parliament and consent of states for constitutional amendments:
1. Election of the President - Consent required from all states
2. Executive Power - Consent required from half of the state legislatures
3. Supreme Court and High Courts - Consent required from half of the state legislatures
4. Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council - Consent required from all states
Identify the correct pair
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:The procedure for constitutional amendment is somewhat vague in certain areas, which may lead to different interpretations and judicial scrutiny.
Statement-II:The Indian Constitution strikes a balance between rigidity and flexibility, allowing essential changes to be made without undermining constitutional stability.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following pairs regarding provisions that require a special majority in Parliament and consent of states for constitutional amendments:
1. Directive Principles of State Policy - Special Majority in Parliament only
2. Election of the President - Consent required from half of the state legislatures
3. Creation or Abolition of Legislative Councils - Consent required from half of the state legislatures
4. Parliament's Power to Amend the Constitution - Special Majority in Parliament and Consent of States
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?