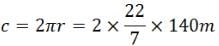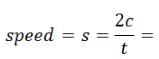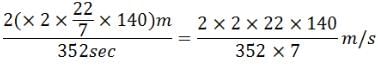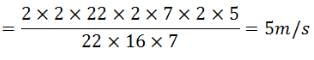Test: Motion: 1 - Class 9 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Motion: 1
What is the speed of an artificial satellite moving in a circular orbit of radius 42250 km if it takes 24 hours to revolve around the earth?
Find the average speed of a bicycle if it completes two round of a circular track of radius 140m in 5min 52 sec.
Assertion (A): The distance-time graph for an object in uniform motion is a straight line.
Reason (R): Uniform motion implies constant speed.
A train 120m long moving on a straight and level track with uniform speed passes a pole in 6 seconds. Find the time it will take to cross a 50m long bridge.
A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 m/s², with what velocity will it strike the ground?
A runner completes 2 full laps on a circular track of radius 7 m. What is the total distance traveled, and what is the displacement?
A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s² (downward), what is the maximum height reached by the ball?
Which of the following statements about motion are correct?
(i) The simplest type of motion is motion along a straight line.
(ii) The magnitude of displacement can be equal to the distance travelled by an object.
(iii) The motion of a freely falling body is an example of non-uniformly accelerated motion.
(iv) The distance-time graph for uniform motion is a straight line.
A particle moves in a circular path of radius 5 m, completing one full revolution in 4 seconds. What is the speed of the particle, and is the motion accelerated?
Which of the following can determine the acceleration of a moving object?