Nitin Singhania Test: Buddhism And Jainism - 1 - UPSC MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Nitin Singhania Test: Buddhism And Jainism - 1
Consider the following pairs:
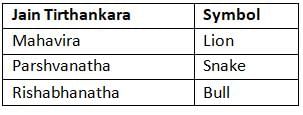
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
Vajrayana Buddhism combines Veda-based rituals with Buddhist philosophies.
Statement-II:
Navayana Buddhism rejects monk & monasticism, karma, rebirth in the afterlife, samsara, meditation, enlightenment, & Four Noble Truths.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Vajrayana Buddhism combines Veda-based rituals with Buddhist philosophies.
Statement-II:
Navayana Buddhism rejects monk & monasticism, karma, rebirth in the afterlife, samsara, meditation, enlightenment, & Four Noble Truths.
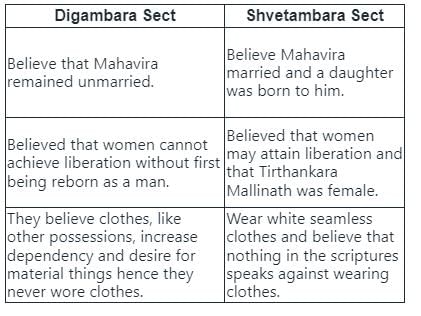
What is a key belief that distinguishes the Digambara School from the Svetambara School in Jainism?
Consider the following pairs:
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
What is a key difference between Hinayana and Mahayana Buddhism in terms of their ultimate goals?
Consider the following statements:
- The Buddha gave his first sermon, the Dharma-chakra-pravartana, at Deer Park in Sarnath.
- Buddhism recognizes the existence of the soul (atman) similar to Jainism.
- The Three Jewels of Buddhism include Buddha, Dhamma, and Sangha.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
Monks of the Digambara School opposes complete nudity.
Statement-II:
Monks of the Svetambara School wear simple white clothing.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following statements:
- Hinayana Buddhism does not believe in idol or image worship of Buddha.
- Mahayana Buddhism’s ultimate goal is spiritual upliftment for all beings.
- Vajrayana Buddhism incorporates Vedic rituals into its practice.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Hinayana Buddhism emphasizes individual salvation through self-discipline and meditation, and its scholars predominantly used the Pali language.
Statement-II: Mahayana Buddhism, on the other hand, believes in the heavenliness of Buddha and Bodhisattvas, and its scholars predominantly used the Sanskrit language.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following statements about the Buddhist concept of the Middle Path:
- The Middle Path refers to a way of life that avoids the extremes of asceticism and sensual indulgence.
- The Middle Path is only applicable to monastic members of the Buddhist Sangha.
- Following the Middle Path leads to the realization of Nirvana, the ultimate goal of Buddhism.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
What is the main deity in Vajrayana Buddhism (Tantric Buddhism)?
Consider the following statements regarding Mahayana Buddhism:
- Mahayana Buddhism introduces the concept of the Bodhisattva, beings who seek enlightenment not only for themselves but for all sentient beings.
- The Lotus Sutra is a key text in Theravada Buddhism that outlines the path to becoming a Bodhisattva.
- Mahayana Buddhism practices include the six perfections, aimed at developing qualities such as generosity, patience, and wisdom.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Sallekhana: Practice of voluntary fasting to death
2. Murtipujaka: Worship saints rather than idols
3. Digambara: Monks wear simple white clothing
4. Pratikraman: Practice of repentance in Jainism
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements regarding the teachings and practices of Jainism:
- Jainism teaches the concept of anekantavada, which suggests that truth and reality have multiple aspects and no single viewpoint is the complete truth.
- Sallekhana, the practice of fasting to death, is considered an act of suicide in Jain philosophy.
- The Digambara sect of Jainism believes that women cannot achieve liberation (moksha) in their current birth.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Buddha attained enlightenment (Nirvana) at the age of 35 under a pipal tree.
Statement-II: After attaining Nirvana in Bodh Gaya, Buddha's first sermon to his five companions was at Deer Park in Sarnath near Varanasi.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
What is the significance of the Three Jewels (Triratna) embraced under Buddhism?
Consider the following statements about the Noble Eightfold Path in Buddhism:
- Right Livelihood involves engaging in occupations that harm other beings.
- Right Effort is about cultivating positive states of mind and abandoning negative ones.
- Right Mindfulness involves a correct understanding of the nature of reality.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Tara - Main deity of Vajrayana Buddhism
2. Nagasena - Answered questions by Menander I
3. Bodhidharma - Transmitter of Buddhism to Japan
4. Mahavira - First Tirthankara of Jainism
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
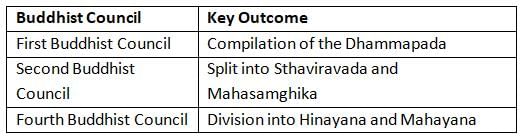
Consider the following statements about the Buddhist councils:
- The Fourth Buddhist Council was held under the patronage of King Kanishka, where Buddhism split into Hinayana and Mahayana sects.
- The First Buddhist Council compiled the Buddha's teachings into the Sutta Pitaka and Vinaya Pitaka.
- The Third Buddhist Council was convened by Emperor Ashoka to purify the Buddhist movement from schismatic tendencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about Navayana Buddhism:
- Navayana Buddhism was propounded by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar as a means to address social inequalities and castism in Hindu society.
- Navayana rejects traditional Buddhist practices such as meditation and enlightenment.
- Navayana Buddhism incorporates the worship of Hindu gods and goddesses.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?