Test: Class 7 General Science NCERT Based - 3 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Class 7 General Science NCERT Based - 3
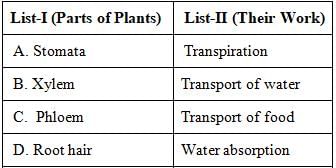
Match the List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below :
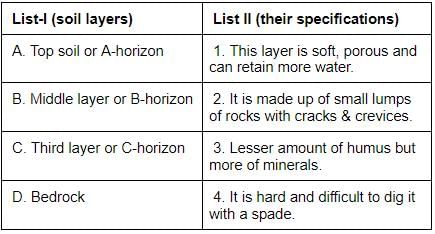


Consider the following assertions:
1. The best topsoil for growing plants is loamy.
2. Loamy soil is a mixture of sand,clay and slit.
3. The size of the silt particles is between those of sand and clay.
4. Sandy soil is suitable for growing wheat, gram and paddy.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of?
What is the percentage of oxygen in inhaled and exhaled air, respectively?
In the context of respiration in various animals, consider the following assertions —
1. The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration.
2. In the cell, the food (glucose) is broken down into carbon dioxide and water using oxygen.
3. Food can also be broken down, without using oxygen. This is called aerobic respiration.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
Which of the following terms is/are transported in the body, through blood? :
1. Digested food
2. Oxygen
3. Waste material
What is the function of white blood cells or granules?
Consider the following:
1. Blood
2. Blood vessels
3. Heart
4. Renal (kidney)
Which of the above organs is/are not the part of the human circulatory system?
Consider the following:
1. Fish
2. Hydra
3. Sponge
In which of the above organisms, no circulatory system is found?
Match List I to List II and select the correct answer with the code given below:
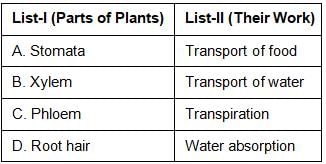
Code:
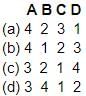
Consider the following assertions, in the context of Vegetative Propagation:
1. Plants produced by vegetative propagation take less time to grow.
2. Plants produced by seeds bear flowers earlier than those produced from vegetative propagation.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
Consider the following assertions in terms of fertility in various organisms:
1. Reproduction in yeast takes place through budding.
2. Reproduction process in algae takes place through fragmentation.
3. Plants such as moss and fern also reproduce by means of spores.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
In the context of pollination in plants, consider the following assertions :
1. Pollination of pollen grains is done on the stigma of flowers from the pollinators.
2. If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant, it is called cross-pollination. When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of a flower of a different plant of the same kind, it is called self-pollination.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
Which equipment measures the distance covered by a vehicle?
In the context of magnetic and heating effects of the electric current, consider the following assertions :
1. The wire gets hot when an electric current passes through it.
2. When electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
What is the SI unit of electric charge?
What is the work done in moving a unit positive charge from infinity to that point in the electric field called?
The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to:
How many electrons taken together make one coulomb?
In the context of plane mirror, consider the following assertions —
1. An image formed by a plane mirror is erect and of the same size as the object.
2. In the image formed by a plane mirror, the ‘right’ appears ‘left’ and the ‘left’ appears ‘right’.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
In the context of the different uses of the concave mirror, consider the following assertions —
1. It is used by doctors to examine eyes, ears, nose and throat.
2. It is used as side mirrors in automobiles.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
In the context of lenses, consider the following assertions —
1. The image formed by a convex lens is real, inverted and larger in size than the object.
2. The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect, and smaller in size than the object.
Which of the above assertions is/are correct?
Consider the following:
1. Refraction
2. Reflection
3. Diffraction
Which of the above is/are necessary for an image formation in a mirror?
What happens when light energy bends as it passes from one type of substance to another type?
What might explain why light travels in a straight line?
What is the power of a concave lens?
What type of a mirror is used in anti-shop-lifting-devices?
Due to which phenomenon the stick if immersed in water appears to be bent?