Test: Reproduction in Plants - UPSC MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reproduction in Plants
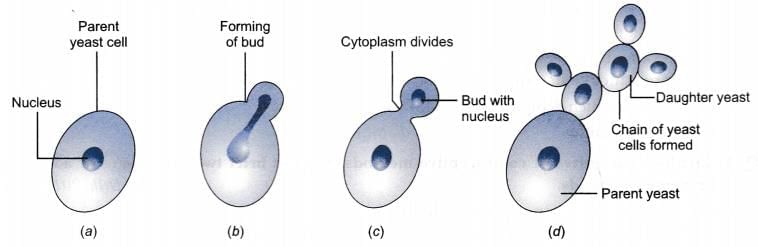
The small bulb-like projection coming out from yeast cell is called a ______.
What is the process called when pollen lands on the stigma of a flower of a different plant of the same kind?
State whether the following statement is True or False
Plants can reproduce only through sexual means.
In plants, which type of flowers possess both the male reproductive structure (androecium) and the female reproductive structure (gynoecium)?
In flowering plants, which structure serves as the enlarged basal portion of the pistil and contains ovules that develop into seeds upon fertilization?
What term is used to describe a flower that has either male or female reproductive parts, but not both?
Pollen grains can be carried by wind or water for pollination. Is this statement TRUE or FALSE?
The process of fusion of the female and male gamete is called ___________ .
How do new plants produced by vegetative propagation differ from those produced from seeds?
Within the reproductive structures of flowering plants, where is the site of pollen grain formation?
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as:
How do algae reproduce rapidly when water and nutrients are available?