Test: Types of Oscillator - 2 - UPSC MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Types of Oscillator - 2
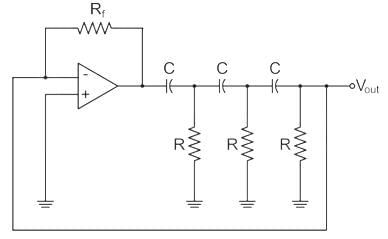
For an RC phase shift oscillator, the following statements are cited:
a) Amplifier gain is negative
b) Phase shift introduced by the feedback circuit is either 0 or 360°
c) Amplifier gain is positive
d) Phase shift introduced by the feedback circuit is 180°
Which of the following options is correct?
Which of the following applications about the oscillators is FALSE?
Among the following, which is a fixed frequency oscillator?
R-C phase shift oscillator and Wein bridge oscillator are the commonly used circuits for generating ________ waveform of a required frequency.
Which of these is incorrect for a Wien Bridge oscillator?
Which type of feedback is used by Colpitts oscillator?
Which of the following are not the characteristics of a crystal oscillator?
In the below circuit, the output frequency is 0.5 Mhz.
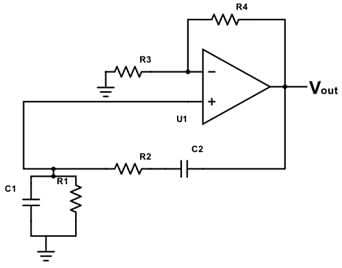
C1 = 5nF, R4 = 40kΩ, R3 = 20kΩ. Find the value of R.
RFC choke is placed in Colpitts oscillator instead of resistor is to provide _________
When frequency of oscillation of a crystal oscillator becomes parallel resonance frequency reactance of crystal oscillator becomes __________
When constructing variable frequency oscillator among clapp oscillator and colpitts oscillator which one is preferred?
Which of these is a disadvantage of the Wien Bridge oscillator?
Which of the following oscillator can be used, where high stability of frequency is required?