Test: Law Of Tort - 7 - CLAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Law Of Tort - 7
Assertion A. Contributory negligence in an accident is a defense to a charge in criminal law.
Reason R. The fact that the deceased was also negligent and contributed to the accident does not afford a defense to the driver.
Reason R. The fact that the deceased was also negligent and contributed to the accident does not afford a defense to the driver.
X, the owner of a car, asked his friend Y to drive the car to his office. As the car was near his (X’s) office, it hit a pedestrian P on account of Y’s negligent driving and injured him seriously. P sued X for damages. Which one of the following is correct regarding the above?
The standard of care generally used in cases of negligence is the
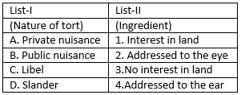
Match List-I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
For an action of nuisance, the following have been put up as defenses
1. The place is suitable for the purpose.
2. It is for the benefit of the locality.
3. It is done under statutory authority?
Which of the defenses given above is/are correct?
Which one of the following elements is not necessary to have a private right of action in respect of a public nuisance?
Which of the following remedies are available in an action in the tort of nuisance?
1. Abatement
2. Injunction
3. Specific restitution
4. Action for damages
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
In which of the following cases, ‘P’ did not owe duty of care to ‘Q’.
A is running a polyclinic well-equipped with operation theaters and supporting staff. S is a surgeon who makes use of this polyclinic to operate his patients. While operating a patient P, due to the negligence of nurse N (Who was a support staff of polyclinic), the surgical knife was left inside the abdomen of P. As a result, P developed several complications. Advise P as to against whom, i.e., A or S, he should file the suit for damages.
Legal Principle:
1. Whoever is under a duty of care to another shall be liable for any injury to the latter directly resulting from the breach of that duty.
2. Harm suffered voluntarily does not constitute legal injury.
Factual Situation: Gupta Confectioners sent certain items in a horse carriage to a customer's house, which happened to be by the side of a main road and near a school zone. The driver of the carriage delivered the items to the customers and went inside the house to collect the receipt, leaving the carriage unattended on tile road. Some naughty children nearby threw stones at the horses. The horses ran over confusion and were about to run over an old woman. A traffic police, at great risk to his life, somehow seized the horses and stopped the carriage. He suffered serious personal injuries in the process. The policemen seeks compensation from Gupta Confectioners.
Legal Principles:
1. Negligence is the omission to do some-thing, which a reasonable man would do, breach of which, if it causes damage, makes one liable to the person who suffered loss.
2. One owes a duty of care to another, if a responsible man can foresee that he will be affected by the breach of duty.
3. One is not liable if the injured party volunteers to take the risk.
Factual Situation: A cricket match is being held in a stadium. Akshit, being unable to afford the ticket price, is viewing the cricket match sitting atop a branch of a nearby tree. When a batsman hits a ball over the boundary, the ball in turn hits Akshit and sustains injury on his spinal cord due to fall from the tree.
Principle: A citizen is expected to take reasonable duty of care while driving on the road and not to cause injuries to any person.
Facts: X, the owner of a car, asked his friend Y to drive the car to his office. As the car was near his (X’s) office, it hit a pedestrian P on account of Y’s negligent driving and injured him seriously. P sued X for damages. Which one of the following is correct?
Principle: Contributory negligence in an accident is a defence for a charge in criminal law. Facts: X, the deceased was negligently crossing the busy road at Connaught Place in Delhi while Y’s car hit him resulting in the death of X. What is the liability of Y?
Principal : Negligence is a breach of duty or a failure of one party to exercise the standard of care required by law, resulting in damage to the party to whom the duty was owed. A plaintiff can take civil action against the respondent, if the respondent’s negligence causes the plaintiff injury or loss of property.
Facts : ‘D’ went to a café and ordered and paid for a tin/can of soft drink. The tin was opaque and thereof, the contents could not be seen from outside. She (‘D’) consumed some of the contents and then lifted the tin to pour the remainder of the content into a tumbler. The remains of a snail in decomposed state dropped out of the tin into the tumbler. ‘D’ later complained of a stomach pain and her as having gastroenteritis and being in a state of sever shock. She used the manufacturer of the drink for negligence.
Applying the afore-stated principle, which of the following derivations is correct as regards liability of the manufacturer in the given situation?
Principle : Whoever, unlawfully or negligently does any act which is, and which he knows or has reason to believe to he, likely to spread the infection of any disease dangerous to life, shall be guilty of a negligent act likely to spread infection into disease dangerous to life.
Facts : ‘K’, a person, knowing that he is suffering from Cholera, travels by a train without information the railway officers of his condition.
Legal Principle: A careless person becomes liable for his negligence when he owed a duty of care to others
Facts: As the bus was leaving the platform, Basappa rushed and boarded the bus keeping the door open. Beerappa who was standing at the edge of the platform, was hit by the door of the moving bus and injured. Beerappa takes Basappa to court demanding monetary compensation.
Principle : Trespass to land means direct interference with the possession of land without lawful justification. Trespass could be committed either by a person himself entering the land of another person or doing the same through some tangible object (s).
Facts : ‘A’ throws some stones upon his neighbor’s (B’s) premises
Principle: Nuisance is an unlawful interference with a person’s use or enjoyment with it, if the interference is connection wrong is trespass; whereas, if the interference is ‘consequential’, it amounts to nuisance.
Facts : ‘A’ plants a tree on his land. However, he allows its branches to project over the land of ‘B’.
Principle : Interference with another’s goods in such a way as to deny the latter’s title to the goods amounts to conversion, and thus it is a civil wrong. It is an act intentionally done inconsistent with the owner’s right, though the doer may not know of, or intend to challenge, the property or possession of the true owner.
Facts : ‘R’ went to a cycle-stand to park his bicycle. Seeing the stand fully occupied, he removed a few bicycles in order to rearrange a portion of the stand and make some space for his bicycle. He parked his bicycle properly, and put back all the bicycles except the one belonging to ‘S’, In fact, ‘R’ was in a hurry and therefore, he could not put back S’s bicycle somebody come on the way and took away S’s bicycle. The watchmen of the stand did not take care of it assuming that the bicycle was to parked inside the stand. ‘S’ filed a suit against ‘R’ for conversion.
Assertion (A): In the event of violation of any legal right (tort) the aggrieved party is entitled to recover unliquidated damages.
Reason (R): The object of awarding damages to the aggrieved party is to put him in the same position in which he would have been if the wrong would not have been committed. Damages are, therefore, assessed on that basis.
Assertion (A): The Constitution of India provides for the appointment of a Governor for a period of five years.
Reason (R): The Governor holds office during the pleasure of the President.
Which of the following acts invite tortuous liability and is not saved by the doctrine "volenti non fit injuria"?
Principle: A master shall be responsible for the wrongful acts of his servants in the course of his employment.
Facts: The Syndicate Bank was running a small savings scheme under which its authorized agents would go round and collect small savings from several people on a daily basis. These agents would get commission, on the deposits so collected. Ananth was one such agent, collecting deposits from factory workers engaged on daily wages. Though he regularly carried on his business for some time, slowly he started appropriating deposits for his personal use and one day he just disappeared. One Fatima, who had been handing over her savings to him found that nearly for a month before his disappearance, he was not depositing her savings at all. The bank, when approached, took the stand that Ananth was not its regular and paid employee and, therefore, it was not responsible for his misconduct. She filed a suit against the bank.
Principle: A person is liable for all the injuries caused on account of consequences of his careless act.
Facts: Ram, a snake charmer, was exhibiting his talents to a group of people. One of the snakes escaped and bit a child who had to be hospitalized for two days for treatment.














