KVS PRT Mock Test - 3 - KVS PGT/TGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KVS PRT Mock Test - 3
A French woman
P: committed suicide
Q: where she had put up
R: who had come to Calcutta
S: by jumping from the first floor balcony of the hotel
The Proper sequence should be:
Q: where she had put up
R: who had come to Calcutta
S: by jumping from the first floor balcony of the hotel
Which of the following shortcuts can be used to insert a new line in the same cell?
A ______ is a software that manages the time of a microprocessor to ensure that all time critical events are processed as efficiently as possible. This software allows the system activities to be divided into multiple independent elements called tasks.
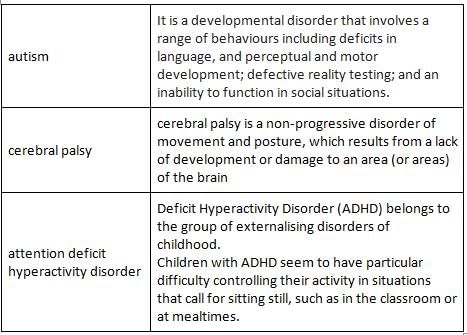
Following are the examples of developmental disorder, except
Which of the following are the key postulates of constructivism?
I: Individual learners actively build knowledge and skills
II: Information exists within the constructs of our minds
III: Behaviour of the learner must be reinforced to ensure learning
IV: Learning is a socially mediated process
Choose the correct statement.
Statement I: The main function of mental hygiene is the prevention of mental illness.
Statement II: Curative function of mental hygiene emphasises on the treatment techniques.
Which of the following can be a way of involving the community in the education process?
I Parent meetings in school.
II. Participation through contribution of money, material and labour
Direction: Identify the type of adverb in the underlined segment of the given sentence.
I usually put butter and syrup on my pancakes.
In the given sentence, identify the segment which contains a grammatical error.
There was hardly few food left by the time we got there.
A, B and C walk around a circle of circumference 600 metres at 150, 120 and 100 metres/minute respectively. All three start simultaneously from the same point and walk in the same direction. When will the three be together again for the first time?
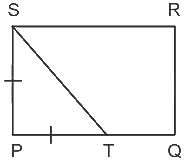
PQRS is a rectangle, in which T is a point on PQ in such a way that SP = PT. Again QT = 2PT. If the value of A(Δ SPT) = 16 cm2. Find the value of the area of the rectangle PQRS.
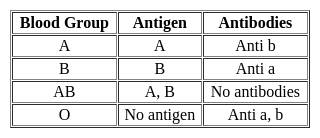
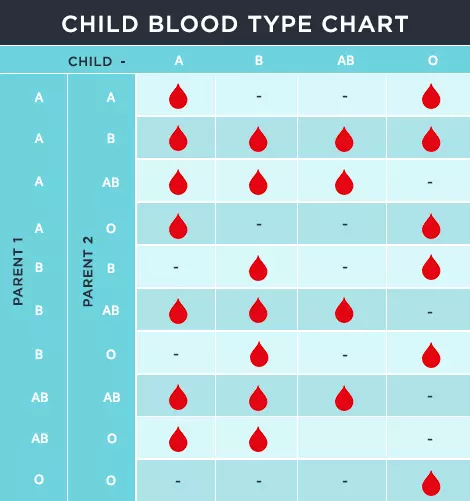
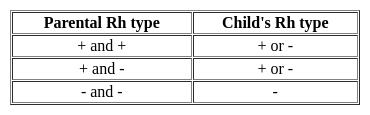
A man with blood group ‘O’ marries a woman with blood group ‘A’. The chance of their first child having blood group ‘O’ is