All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of July Week 2 for NEET Exam
Work done by gravitational force on a man, in lifting a bucket out of the well by rope tied to the bucket is- a)negative
- b)positive
- c)zero
- d)infinity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by gravitational force on a man, in lifting a bucket out of the well by rope tied to the bucket is
a)
negative
b)
positive
c)
zero
d)
infinity
|
|
Om Desai answered |
When the man pulls the bucket outside the well the gravitational potential of the man + bucket system increases and hence the work done by the gravitational force is negative.
Which of the following do not undergo anysecondary growth?
- a)Dicotyledonous stem
- b)Monocotyledonous root
- c)Monocotyledonous stem
- d)Both (B) and (C)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following do not undergo anysecondary growth?
a)
Dicotyledonous stem
b)
Monocotyledonous root
c)
Monocotyledonous stem
d)
Both (B) and (C)

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Monocotyledonous roots and stems generally do not undergo secondary growth:
-
Monocotyledonous rootsMonocot roots do not undergo secondary growth because they lack vascular cambium, which is found in the vascular bundle between the xylem and phloem.
-
Monocotyledonous stemsMonocot stems do not undergo secondary growth, but they can increase in girth. This is called anomalous thickening and does not result in the development of secondary xylem and phloem
Which of the following is not conserved in inelastic collision?- a)momentum
- b)kinetic energy
- c)both momentum and kinetic energy
- d)neither momentum nor kinetic energ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not conserved in inelastic collision?
a)
momentum
b)
kinetic energy
c)
both momentum and kinetic energy
d)
neither momentum nor kinetic energ
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
In an inelastic collision, the force of reformation is not equal to the force of deformation and thus some amount of energy is lost. But still as no external force acts upon the system momentum is still conserved.
Which of the following statement is not related to conservative force?- a)Work done in closed path is zero
- b)Work done is recoverable
- c)Path independent
- d)Path dependent
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is not related to conservative force?
a)
Work done in closed path is zero
b)
Work done is recoverable
c)
Path independent
d)
Path dependent
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
A force is said to be conservative if the work done by or against the force on a body is independent of path followed by the body and depends only on initial and final positions.
Work done by or against the conservative force in moving a particle along a closed path is zero.
Work done by or against the conservative force in moving a particle along a closed path is zero.
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
- a)
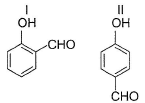
- b)
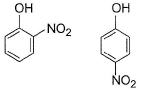
- c)

- d)
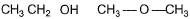
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
I. Intermolecular H-bonding makes boiling point higher than that of I. Thus, I is more volatile
II. Ortho nitrophenol is more volatile than para nitrophenol because O-Nitrophenol has intramolecular hydrogen bonding whereas para nitrophenol has inter molecular H bonding and so boils relatively at higher temperature
(c) BP of H2O > > H2S
(d) BP of CH3CH2OH (due to H-bonding) > > CH3— O — CH3
Frictional force is an example of- a)ectrostatic force
- b)Non conservative force
- c)conservative force
- d)nuclear force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Frictional force is an example of
a)
ectrostatic force
b)
Non conservative force
c)
conservative force
d)
nuclear force
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The friction is the phenomena that defines that there is a resistance which is present there between the two surfaces. This friction is applied tangentially to the surfaces in contact. Thus the main thing is that the forces on both of the surfaces act tangential to each other.
When conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body:- a)increases
- b)decreases
- c)remains unaltered
- d)there is no relationship between force and potential energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body:
a)
increases
b)
decreases
c)
remains unaltered
d)
there is no relationship between force and potential energy
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
We have a relation between potential energy and work done: 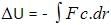
The negative sign just shows the inverse relation between potential energy and work done by conservative force.
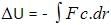
The negative sign just shows the inverse relation between potential energy and work done by conservative force.
The casparian thickening occurs in the cells of
- a)Pericycle of root
- b)Endodermis of stem
- c)Endodermis of root
- d)Pericycle of stem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The casparian thickening occurs in the cells of
a)
Pericycle of root
b)
Endodermis of stem
c)
Endodermis of root
d)
Pericycle of stem

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Casparian strips occur in the Endodermis. It is a cell wall material that is deposited in the radial and transverse walls of the endodermis of roots.
Select the odd one out- a)Viscous force
- b)Frictional force
- c)Electrostatic force
- d)Air-resistance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the odd one out
a)
Viscous force
b)
Frictional force
c)
Electrostatic force
d)
Air-resistance
|
|
Pranav Datta answered |
The odd one out among the given options is option 'C', which represents the Electrostatic force.
**Viscous Force:**
- Viscous force refers to the resistance that a fluid (liquid or gas) exerts on an object moving through it.
- It is a type of frictional force that opposes the relative motion of the object and the fluid.
- Viscous force is responsible for phenomena like drag experienced by objects moving through a fluid medium.
- Examples of viscous force include the resistance experienced by a car moving through air or a boat moving through water.
**Frictional Force:**
- Frictional force is the force that opposes the motion or attempted motion of an object past another object with which it is in contact.
- It arises due to the roughness or irregularities present on the surfaces in contact.
- Frictional force plays a crucial role in our daily lives, such as walking, driving a car, or holding objects.
- It can be both advantageous (e.g., walking) and disadvantageous (e.g., wearing out of machine parts).
**Electrostatic Force:**
- Electrostatic force is the force of attraction or repulsion between charged objects.
- It arises due to the electric charge carried by the objects.
- Objects with the same charges repel each other, while objects with opposite charges attract each other.
- Electrostatic force is responsible for various phenomena such as the attraction of clothes after being dried in a dryer or the repulsion of two magnets.
**Air-Resistance:**
- Air resistance, also known as drag, is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air.
- It is caused by the collision of air molecules with the object in motion.
- Air resistance depends on factors such as the shape and size of the object, the speed of motion, and the density of the air.
- It affects objects moving through the air, like a falling parachute or a moving car.
**Explanation:**
The odd one out is electrostatic force because it is the only option that does not involve the interaction between objects in motion or with a fluid medium. Electrostatic force is related to the interaction between charged objects, whereas the other three forces (viscous force, frictional force, and air resistance) are associated with the motion of objects through a medium (fluid or air).
**Viscous Force:**
- Viscous force refers to the resistance that a fluid (liquid or gas) exerts on an object moving through it.
- It is a type of frictional force that opposes the relative motion of the object and the fluid.
- Viscous force is responsible for phenomena like drag experienced by objects moving through a fluid medium.
- Examples of viscous force include the resistance experienced by a car moving through air or a boat moving through water.
**Frictional Force:**
- Frictional force is the force that opposes the motion or attempted motion of an object past another object with which it is in contact.
- It arises due to the roughness or irregularities present on the surfaces in contact.
- Frictional force plays a crucial role in our daily lives, such as walking, driving a car, or holding objects.
- It can be both advantageous (e.g., walking) and disadvantageous (e.g., wearing out of machine parts).
**Electrostatic Force:**
- Electrostatic force is the force of attraction or repulsion between charged objects.
- It arises due to the electric charge carried by the objects.
- Objects with the same charges repel each other, while objects with opposite charges attract each other.
- Electrostatic force is responsible for various phenomena such as the attraction of clothes after being dried in a dryer or the repulsion of two magnets.
**Air-Resistance:**
- Air resistance, also known as drag, is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air.
- It is caused by the collision of air molecules with the object in motion.
- Air resistance depends on factors such as the shape and size of the object, the speed of motion, and the density of the air.
- It affects objects moving through the air, like a falling parachute or a moving car.
**Explanation:**
The odd one out is electrostatic force because it is the only option that does not involve the interaction between objects in motion or with a fluid medium. Electrostatic force is related to the interaction between charged objects, whereas the other three forces (viscous force, frictional force, and air resistance) are associated with the motion of objects through a medium (fluid or air).
For a conservative force, F is equal to- a)
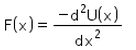
- b)
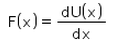
- c)
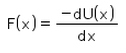
- d)
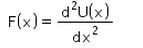
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a conservative force, F is equal to
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Potential energy at a point is defined in terms the amount of work done, which is defined in terms of force and thus we get potential as an integral of force applied over some position x. Hence F(x) = -dU(x) / dx which is the differentiation of potential energy wrt position.
The H-bond is shortest in
- a)S— H---S
- b)N— H ... O
- c)F— H ... F
- d)F— H ... O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The H-bond is shortest in
a)
S— H---S
b)
N— H ... O
c)
F— H ... F
d)
F— H ... O
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
A hydrogen bond is a weak type of force that forms a special type of dipole-dipole attraction which occurs when a hydrogen atom bonded to a strongly electronegative atom exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons.
F is the most electronegative atom. Hence hydrogen bond is shortest in F - H ........F.
F is the most electronegative atom. Hence hydrogen bond is shortest in F - H ........F.
A force which does not depend on the path taken to increase the potential energy is- a)Viscous force
- b)Frictional force
- c)Conservative force
- d)Non - Conservative force
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A force which does not depend on the path taken to increase the potential energy is
a)
Viscous force
b)
Frictional force
c)
Conservative force
d)
Non - Conservative force
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Gravitational and electrical forces are conservative. Friction is non-conservative because the amount of work done by friction depends on the path. One can associate a potential energy with a conservative force but not with a non-conservative force.
Aerating pores in the bark of plants is known as- a)Lenticels
- b)Stomata
- c)Air pore
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aerating pores in the bark of plants is known as
a)
Lenticels
b)
Stomata
c)
Air pore
d)
None of these

|
Kunal Rane answered |
In plants respiratory organs in stem is called lenticels. They are located as pores in the bark of plants.
Out of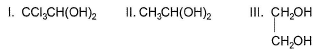 Q. unstable compound is/are
Q. unstable compound is/are - a)I and II
- b)Only I
- c)Only II
- d)Only III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of
Q. unstable compound is/are
a)
I and II
b)
Only I
c)
Only II
d)
Only III
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
I. CCI3CH (OH)2 with two — OH groups on same carbon atom is stable due to intramolecular H-bonding.
What is the dominant intermolecular force or bond that must be overcome in converting liquid CH3CH2OH to vapours?- a)H-bonding
- b)Dipole-dipole interactions
- c)Covalent bonds
- d)London dispersion force
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the dominant intermolecular force or bond that must be overcome in converting liquid CH3CH2OH to vapours?
a)
H-bonding
b)
Dipole-dipole interactions
c)
Covalent bonds
d)
London dispersion force

|
Swara Saha answered |
CH3CH2OH is in liquid state due to association as a result of intermolecular H-bonding.
Work done by or against a conservative force in a round trip is- a)zero
- b)minimum
- c)maximum
- d)may be maximum or zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done by or against a conservative force in a round trip is
a)
zero
b)
minimum
c)
maximum
d)
may be maximum or zero

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
A conservative force is a force with the property that the total work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the taken path. Equivalently, if a particle travels in a closed loop, the total work done (the sum of the force acting along the path multiplied by the displacement) by a conservative force is zero.
How many of the following constitute the stele?Vascular bundles, pericycle, endodermis, pith, cortex, epidermis- a)4
- b)3
- c)2
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many of the following constitute the stele?
Vascular bundles, pericycle, endodermis, pith, cortex, epidermis
a)
4
b)
3
c)
2
d)
5
|
|
Baishali Desai answered |
Understanding the Stele
The stele is a crucial part of the plant root and stem anatomy, involved primarily in the transport of water, nutrients, and food. It is essential to differentiate which structures constitute the stele.
Components of the Stele
The stele primarily includes:
- Vascular Bundles: These are responsible for the conduction of water (xylem) and nutrients (phloem).
- Pericycle: This is the layer of cells just inside the endodermis, from which lateral roots arise.
- Endodermis: This is the innermost layer of the cortex, forming a selective barrier to regulate the flow of water and nutrients into the vascular system.
Other Structures
The following do NOT constitute the stele:
- Pith: This is central tissue found in some stems, but is not part of the stele.
- Cortex: This is the layer of ground tissue between the epidermis and the vascular tissues, also not included in the stele.
- Epidermis: This is the outer protective layer of the plant, which does not form part of the stele.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B', as only three structures (vascular bundles, pericycle, and endodermis) comprise the stele. Recognizing these components is essential for understanding plant physiology, particularly in the context of nutrient and water transport.
The stele is a crucial part of the plant root and stem anatomy, involved primarily in the transport of water, nutrients, and food. It is essential to differentiate which structures constitute the stele.
Components of the Stele
The stele primarily includes:
- Vascular Bundles: These are responsible for the conduction of water (xylem) and nutrients (phloem).
- Pericycle: This is the layer of cells just inside the endodermis, from which lateral roots arise.
- Endodermis: This is the innermost layer of the cortex, forming a selective barrier to regulate the flow of water and nutrients into the vascular system.
Other Structures
The following do NOT constitute the stele:
- Pith: This is central tissue found in some stems, but is not part of the stele.
- Cortex: This is the layer of ground tissue between the epidermis and the vascular tissues, also not included in the stele.
- Epidermis: This is the outer protective layer of the plant, which does not form part of the stele.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'B', as only three structures (vascular bundles, pericycle, and endodermis) comprise the stele. Recognizing these components is essential for understanding plant physiology, particularly in the context of nutrient and water transport.
Conjoint type of vascular bundles are common in- a)Stems, roots and leaves
- b)Leaves and roots
- c)Stems and leaves
- d)Stems and roots
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Conjoint type of vascular bundles are common in
a)
Stems, roots and leaves
b)
Leaves and roots
c)
Stems and leaves
d)
Stems and roots

|
Rohan Unni answered |
In conjoint type of vascular bundles,the xylem and phloem are situated at the sameradius of vascular bundles. Such vascularbundles are common in stems and leaves. Theconjoint vascular bundles usually have thephloem located only on the outer side of xylem.
Guard cells of stomata are thicker- a)In middle
- b)Outer side
- c)Inner side
- d)Both side
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Guard cells of stomata are thicker
a)
In middle
b)
Outer side
c)
Inner side
d)
Both side

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
The cells surrounding the stomata are called guard cells. The guard cells of inner side are thicker and that of outer side is comparatively thinner.
Assertion (A): Plant tissues are classified into meristematic and permanent types, which contribute to their various functions.Reason (R):
The main functions of plant tissues include food assimilation, storage, and mechanical support.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Plant tissues are classified into meristematic and permanent types, which contribute to their various functions.
Reason (R):
The main functions of plant tissues include food assimilation, storage, and mechanical support.
The main functions of plant tissues include food assimilation, storage, and mechanical support.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Prasenjit Khanna answered |
Understanding Plant Tissues
Plant tissues are essential components of plants, classified into two main types: meristematic and permanent. Each type plays a vital role in the overall functioning of the plant.
Assertion (A) Explained
- Meristematic Tissues: These are undifferentiated cells that can divide and contribute to growth. They are found in regions of the plant that are actively growing, like tips of roots and stems.
- Permanent Tissues: These tissues are differentiated and have specific functions. They include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, each serving unique roles.
Reason (R) Explained
- Functions of Plant Tissues: The main functions of plant tissues encompass:
- Food Assimilation: Tissues like parenchyma are involved in photosynthesis and nutrient storage.
- Storage: Specialized tissues store starch, oils, and water.
- Mechanical Support: Sclerenchyma and collenchyma provide structural integrity and support to the plant.
Linking Assertion and Reason
- The reason elaborates on the functions of plant tissues, which directly relate to the types of tissues mentioned in the assertion.
- Meristematic tissues contribute to growth, while permanent tissues fulfill specific roles such as support and storage, thereby justifying the assertion.
Conclusion
Thus, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'. Understanding this relationship helps in grasping the fundamental concepts of plant biology, crucial for NEET preparation.
Plant tissues are essential components of plants, classified into two main types: meristematic and permanent. Each type plays a vital role in the overall functioning of the plant.
Assertion (A) Explained
- Meristematic Tissues: These are undifferentiated cells that can divide and contribute to growth. They are found in regions of the plant that are actively growing, like tips of roots and stems.
- Permanent Tissues: These tissues are differentiated and have specific functions. They include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, each serving unique roles.
Reason (R) Explained
- Functions of Plant Tissues: The main functions of plant tissues encompass:
- Food Assimilation: Tissues like parenchyma are involved in photosynthesis and nutrient storage.
- Storage: Specialized tissues store starch, oils, and water.
- Mechanical Support: Sclerenchyma and collenchyma provide structural integrity and support to the plant.
Linking Assertion and Reason
- The reason elaborates on the functions of plant tissues, which directly relate to the types of tissues mentioned in the assertion.
- Meristematic tissues contribute to growth, while permanent tissues fulfill specific roles such as support and storage, thereby justifying the assertion.
Conclusion
Thus, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'. Understanding this relationship helps in grasping the fundamental concepts of plant biology, crucial for NEET preparation.
Among the following sets, highest boiling points are of the species.
I. HF, HCI, HBr, HI
II. H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te
III. NH3,PH3, AsH3,SbH3
- a)HF, H2O, NH3
- b)HCI, H2S, PH3
- c)HBr, H2Te, AsH3
- d)HI, H2S, AsH3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following sets, highest boiling points are of the species.
I. HF, HCI, HBr, HI
II. H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te
III. NH3,PH3, AsH3,SbH3
II. H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te
III. NH3,PH3, AsH3,SbH3
a)
HF, H2O, NH3
b)
HCI, H2S, PH3
c)
HBr, H2Te, AsH3
d)
HI, H2S, AsH3

|
Maheshwar Chawla answered |
F, O and N are electronegative elements. Thus, HF molecules are associated by intermolecules H-bonding giving it a liquid state and thus highest boiling point out of HF, HCl.HBr and HI.
Similarly, H2O has highest boiling point, and NH3 has highest boiling point.
Similarly, H2O has highest boiling point, and NH3 has highest boiling point.
The vascular bundles are closed when they- a)Lack pericycle
- b)Have cambium
- c)Lack cambium
- d)Have pericycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The vascular bundles are closed when they
a)
Lack pericycle
b)
Have cambium
c)
Lack cambium
d)
Have pericycle

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
In the monocotyledons, the vascular bundles have no cambium present in them. Hence, since they do not form secondary tissues they are referred to as closed.
Number of water molecules directly attached to one water molecule is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of water molecules directly attached to one water molecule is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Gaurav Saini answered |
One water molecule is directly attached to four water molecules. Thus, coordination number of water is 4.
Which of the following has maximum boiling point?- a)
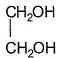
- b)CH3CH2CH2OH
- c)H2O
- d)CH3CH2CH2CH3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has maximum boiling point?
a)
b)
CH3CH2CH2OH
c)
H2O
d)
CH3CH2CH2CH3

|
Janhavi Banerjee answered |
Due to intermolecular H-bonding at two terminals boiling point of glycol is maximu
The shape of guard cells in grasses is- a)Round
- b)Elliptical
- c)Kidney
- d)Dumb-bell
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of guard cells in grasses is
a)
Round
b)
Elliptical
c)
Kidney
d)
Dumb-bell

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
In grasses, the guard cells are dumb-bell shaped
Ground tissue consists of- a)All tissues external to endodermis
- b)All tissues except epidermis and vascular tissue
- c)All tissues internal to endodermis
- d)Epidermis and cortex
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ground tissue consists of
a)
All tissues external to endodermis
b)
All tissues except epidermis and vascular tissue
c)
All tissues internal to endodermis
d)
Epidermis and cortex

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
Ground tissue consists of all tissues except epidermis and vascular bundle of stem and root. It forms the main parts of plant made up of
In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing cells are called- a)Parenchyma
- b)Sclerenchyma
- c)Chlorenchyma
- d)Mesophyll
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing cells are called
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Sclerenchyma
c)
Chlorenchyma
d)
Mesophyll

|
Krish Khanna answered |
In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containingcells are called mesophyll cells.
Separate xylem and phloem bundles are known as- a)Amphivessal
- b)Radial
- c)Bicollateral
- d)Collateral
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Separate xylem and phloem bundles are known as
a)
Amphivessal
b)
Radial
c)
Bicollateral
d)
Collateral

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Separate xylem and phloem bundles are found in dicotyledonous roots. This kind of vascular bundle is called radial vascular bundle.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Which of the following compounds are soluble in H2O ? - a)CH3CHO
- b)CH3COCH3
- c)CH3CH2OH
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which of the following compounds are soluble in H2O ?
a)
CH3CHO
b)
CH3COCH3
c)
CH3CH2OH
d)
All of these
|
|
Sinjini Shah answered |
All these are soluble in water due to intermolecular H-bonding.
Consider the following compoundsI. HCI
II. HF
III. CH3COOH
IV. CH4
V. CH3OH
VI. CH3COO-Q.
H-bonding is not present in- a)I, III and IV
- b)I, IV and VI
- c)II, III and V
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following compounds
I. HCI
II. HF
III. CH3COOH
IV. CH4
V. CH3OH
VI. CH3COO-
II. HF
III. CH3COOH
IV. CH4
V. CH3OH
VI. CH3COO-
Q.
H-bonding is not present in
H-bonding is not present in
a)
I, III and IV
b)
I, IV and VI
c)
II, III and V
d)
None

|
Abhiram Choudhary answered |
HCI: EN of Cl is smaller, hence less polar than HF.
CH4 :non-polar
CH3COO- : H attached to C-atom is non-polar hence
HCI, CH4, CH3COO- — lack H-bonding.
CH4 :non-polar
CH3COO- : H attached to C-atom is non-polar hence
HCI, CH4, CH3COO- — lack H-bonding.
Work done in motion of the body over a closed loop for conservative forces is- a)infintesimal
- b)non-zero
- c)zero
- d)infinity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Work done in motion of the body over a closed loop for conservative forces is
a)
infintesimal
b)
non-zero
c)
zero
d)
infinity
|
|
Jyoti Dey answered |
**Conservative Forces and Work Done over a Closed Loop**
In physics, a conservative force is a type of force that depends only on the initial and final positions of an object, and not on the path taken by the object. This means that the work done by a conservative force over any closed loop is zero.
**Explanation:**
To understand why the work done over a closed loop by a conservative force is zero, let's consider the definition of work done. Work is defined as the product of the force applied to an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force.
If a force is conservative, it can be expressed as the negative gradient of a scalar potential function. This means that the force can be written as the negative derivative of a potential energy function with respect to position.
Now, let's consider a closed loop. Since the starting and ending positions are the same, the change in potential energy over the loop is zero, as the potential energy depends only on the position. This implies that the change in potential energy is equal to the negative of the work done by the conservative force over the loop.
Since the change in potential energy is zero, the work done by the conservative force over the closed loop must also be zero. This means that the net work done by the conservative force in completing a closed loop is zero, regardless of the path taken.
**Example:**
For example, consider a ball moving in a gravitational field. The gravitational force is conservative, as it depends only on the position of the ball. If the ball is lifted to a certain height and then allowed to fall back to the starting position, the work done by the gravitational force over the closed loop is zero. This is because the potential energy at the starting and ending positions is the same, regardless of the path taken by the ball.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, for conservative forces, the work done over a closed loop is zero. This is because conservative forces can be expressed as the negative gradient of a potential energy function, and the potential energy depends only on the position of the object. Therefore, the change in potential energy over a closed loop is zero, resulting in zero work done by the conservative force.
In physics, a conservative force is a type of force that depends only on the initial and final positions of an object, and not on the path taken by the object. This means that the work done by a conservative force over any closed loop is zero.
**Explanation:**
To understand why the work done over a closed loop by a conservative force is zero, let's consider the definition of work done. Work is defined as the product of the force applied to an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force.
If a force is conservative, it can be expressed as the negative gradient of a scalar potential function. This means that the force can be written as the negative derivative of a potential energy function with respect to position.
Now, let's consider a closed loop. Since the starting and ending positions are the same, the change in potential energy over the loop is zero, as the potential energy depends only on the position. This implies that the change in potential energy is equal to the negative of the work done by the conservative force over the loop.
Since the change in potential energy is zero, the work done by the conservative force over the closed loop must also be zero. This means that the net work done by the conservative force in completing a closed loop is zero, regardless of the path taken.
**Example:**
For example, consider a ball moving in a gravitational field. The gravitational force is conservative, as it depends only on the position of the ball. If the ball is lifted to a certain height and then allowed to fall back to the starting position, the work done by the gravitational force over the closed loop is zero. This is because the potential energy at the starting and ending positions is the same, regardless of the path taken by the ball.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, for conservative forces, the work done over a closed loop is zero. This is because conservative forces can be expressed as the negative gradient of a potential energy function, and the potential energy depends only on the position of the object. Therefore, the change in potential energy over a closed loop is zero, resulting in zero work done by the conservative force.
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomenon[JEE Advanced 2014]- a)ice floats in water
- b)higher Lewis basicity of primary amines than tertiary amines in aqueous solution
- c)formic acid is more acidic than acetic acid
- d)dimerisation of acetic acid (in benzene
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomenon
[JEE Advanced 2014]
a)
ice floats in water
b)
higher Lewis basicity of primary amines than tertiary amines in aqueous solution
c)
formic acid is more acidic than acetic acid
d)
dimerisation of acetic acid (in benzene
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Hydrogen bonding is responsible for the open-cage structure of ice which explains why the density of ice is less than water.
Primary amines can stabilize themselves by forming hydrogen bonds. Although tertiary amines can also participate in H-bonding the extent is much lesser.
The + I effect of the CH3 is responsible for the weakening in acidic strength.
Dimerisation here is indeed because of H-bonding:
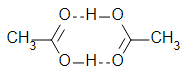
Which of the following correctly represents H-bonding?- a)
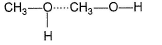
- b)
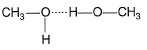
- c)
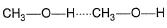
- d)
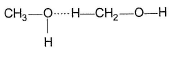
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly represents H-bonding?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Nilesh Chawla answered |
H-bonding is between polar 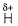 and electronegative 0, N and F C-atom or H attached to C is not polar. Thus, (a), (c), (d) are incorrect.
and electronegative 0, N and F C-atom or H attached to C is not polar. Thus, (a), (c), (d) are incorrect.
In which of the following boiling point of Column I is not higher than that of Column II?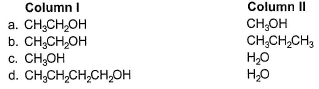
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following boiling point of Column I is not higher than that of Column II?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Bibek Desai answered |
(a) Intermolecular H-bonding, boiling point increases with molecular weight for compounds within the same family.
(b) H-bonding is absent is CH3CH2CH3.
(c) Methanol is the larger molecule but H2O has more H-bonding because of two O—H bonds.
Thus, boiling point of H2O(ll) > CH3OH(l).
(d) Molecular weight of butanol is much higher and overcomes attractive forces of butanol.
(b) H-bonding is absent is CH3CH2CH3.
(c) Methanol is the larger molecule but H2O has more H-bonding because of two O—H bonds.
Thus, boiling point of H2O(ll) > CH3OH(l).
(d) Molecular weight of butanol is much higher and overcomes attractive forces of butanol.
In the following alcohol, which — OH group is involved to the maximum extent in H-bonding?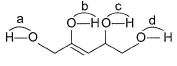
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following alcohol, which — OH group is involved to the maximum extent in H-bonding?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Raghav Chakraborty answered |
O — H group is attached to (ene) is m ost a cidic and thus, has maximum intermolecular H-bonding.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.Q. Match the species in Column I with rank order of their boiling point in Column II. (Species with lowest boifing points is at SN1).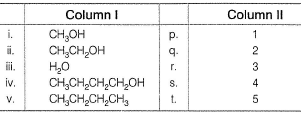

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the species in Column I with rank order of their boiling point in Column II. (Species with lowest boifing points is at SN1).
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Jatin Sharma answered |
n-butane lacks H-bonding. Hence, its boiling point is least.
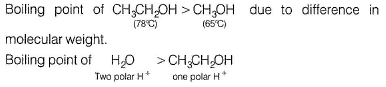
due to difference in polar H+ for H-bonding.
Boiling point of CH3CH2CH2CH2OH > H2O due to much larger size of alcohol.
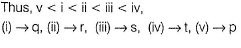
due to difference in polar H+ for H-bonding.
Boiling point of CH3CH2CH2CH2OH > H2O due to much larger size of alcohol.
In the following compounds, select the points of interm olecular H-bonding (linear),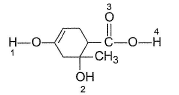
- a)1, 2, 3
- b)1, 3, 4
- c)1,2,4
- d)1,4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following compounds, select the points of interm olecular H-bonding (linear),
a)
1, 2, 3
b)
1, 3, 4
c)
1,2,4
d)
1,4

|
Arindam Unni answered |
1. Enoiic H, acidic and polar takes part in H-bonding.
2. 3° alcohol least acidic maximum basic.
3. Carbonyl oxygen is not involved.
4. Acidic and polar H, takes part in H-bonding.
Chapter doubts & questions for July Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of July Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










