All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of July Week 3 for NEET Exam
Which of the following is/are correct statement(s)?a)s + py→ two sp-hybrid orbitals lying in the yz planeb)s + px → two sp-hybrid orbitals lying in xz planec)(s + px + pz) → three sp2-hybrid orbitals lying in xz planed)(s + py) → two sp-hybrid orbitals lying along y-axisCorrect answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Incorrect (b)
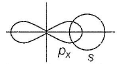
two sp-hybrid orbitals are along x-axis.
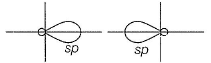
two sp-hybrid orbitals are along x-axis.
Expansion of octet can not take place in- a)N
- b)S
- c)Si
- d)P
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Expansion of octet can not take place in
a)
N
b)
S
c)
Si
d)
P

|
Harshad Nair answered |
N(7) = 1s22s22p3
Nitrogen does not have (2d) orbitals. Thus, (more than 8) electrons cannot be accomodated in second orbit.
Nitrogen does not have (2d) orbitals. Thus, (more than 8) electrons cannot be accomodated in second orbit.
Q. Which of the following species contain at least one atom that violates the octet rule?a)O— Cl—-Ob)F— Xe— Fc)PCI5d)SF6Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
(a) Octet of Cl expanded to (9).
(b) Octet Xe expanded to (10).
(c) Octet of P expanded to (10).
(b) Octet Xe expanded to (10).
(c) Octet of P expanded to (10).
In an elastic collision in one dimension if a body A collides against the body B of equal mass at rest, then the body A will- a)moves with the same velocity but in opposite direction
- b)move with twice its initial velocity
- c)moves with the same velocity in the same direction
- d)come to rest.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an elastic collision in one dimension if a body A collides against the body B of equal mass at rest, then the body A will
a)
moves with the same velocity but in opposite direction
b)
move with twice its initial velocity
c)
moves with the same velocity in the same direction
d)
come to rest.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Since collision is elastic and mass is same then after velocity exchange A body will stop and B will start moving with A's velocity in the same direction.
When a ball is allowed to fall from a height of 20 m, 40% of its energy is lost due to impact. After one impact the ball will go up to a height of- a)12 m
- b)15 m
- c)8 m
- d)10 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a ball is allowed to fall from a height of 20 m, 40% of its energy is lost due to impact. After one impact the ball will go up to a height of
a)
12 m
b)
15 m
c)
8 m
d)
10 m
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Before the impact the KE was ½ x m x (2g x 20) = 20mg
And let say v be the velocity after impact and for height h, v2= 2gh
Thus KE = ½ mv2 = ½m2gh = ⅗ x 20mg
Thus we get mgh = 12mg
thus h = 12 m
And let say v be the velocity after impact and for height h, v2= 2gh
Thus KE = ½ mv2 = ½m2gh = ⅗ x 20mg
Thus we get mgh = 12mg
thus h = 12 m
A bomb of mass 4 kg explodes in air into two pieces of masses 3 kg and 1 kg. The smaller mass goes at a speed of 90 m/s. The total energy imparted to two fragments is.- a)2.4 kj
- b)5.4 kj
- c)5.9 kJ
- d)3.8 kJ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bomb of mass 4 kg explodes in air into two pieces of masses 3 kg and 1 kg. The smaller mass goes at a speed of 90 m/s. The total energy imparted to two fragments is.
a)
2.4 kj
b)
5.4 kj
c)
5.9 kJ
d)
3.8 kJ
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
By conservation of momentum we get the speed of the bigger part let say, v = 1 x90 / 3
Hence we get v = 30
Thus the total KE of the system after collision is ½ (3 X 900 + 1 X 8100)
Thus KE = ½ (10800) = 5400
Now if we apply WET to the system, as no external force has acted upon it, we get
W = ΔKE
= 5400 - 0
= 5.4 kJ
Hence we get v = 30
Thus the total KE of the system after collision is ½ (3 X 900 + 1 X 8100)
Thus KE = ½ (10800) = 5400
Now if we apply WET to the system, as no external force has acted upon it, we get
W = ΔKE
= 5400 - 0
= 5.4 kJ
A bomb at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface explodes and breaks into three pieces that fly apart horizontally as shown below. Select all of the following statements that must be true after the bomb has exploded.1. The total kinetic energy of the bomb fragments is the same as that of the bomb before explosion.
2. The total momentum of the bomb fragments is the same as that of the bomb before explosion.
3. The total momentum of all the bomb fragments together is zero.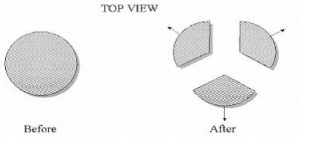
- a)1,2 and 3
- b)1 only
- c)3 only
- d)2 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A bomb at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface explodes and breaks into three pieces that fly apart horizontally as shown below. Select all of the following statements that must be true after the bomb has exploded.
1. The total kinetic energy of the bomb fragments is the same as that of the bomb before explosion.
2. The total momentum of the bomb fragments is the same as that of the bomb before explosion.
3. The total momentum of all the bomb fragments together is zero.
2. The total momentum of the bomb fragments is the same as that of the bomb before explosion.
3. The total momentum of all the bomb fragments together is zero.
a)
1,2 and 3
b)
1 only
c)
3 only
d)
2 only
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
So as no external force acts upon the system, we can say that momentum of the system remains conserved but as an internal force acts that explodes the bomb, the KE of the system is never conserved. But every fragment has some non zero momentum while the bomb initially has zero momentum.
Select the correct statement(s) about NO2.- a)It is paramagnetic in nature
- b)It forms dimer and paramagnetic is lost
- c)NO2 and dimer formed have sp2-hybridised N-atom
- d)Brown colour of NO2 fades and (N— N) bond length is greater than normal (N— N) bond length
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) about NO2.
a)
It is paramagnetic in nature
b)
It forms dimer and paramagnetic is lost
c)
NO2 and dimer formed have sp2-hybridised N-atom
d)
Brown colour of NO2 fades and (N— N) bond length is greater than normal (N— N) bond length
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Due to unpaired electron paramagnetic, N-atom in NO2 is electron deficie nt thus, to complete octet, dimer is formed.
In N2O4 formation, each N-atom gets
Thus, (a), (b), (c) and (d) are correct.
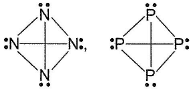
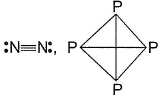
Mean bond enthalpy of different bonds are given
 Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
- a)
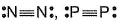
- b)
- c)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mean bond enthalpy of different bonds are given
Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
a)
b)
c)
d)
None of these

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Bond enthalpy of six (P— P) bond = 6 x 215 = 1290 k j mol-1
Bond enthalpy of six (N — N) bond = 6 x 160
= 960 kJ mol-1
Thus, P4 is more stable than N4.
Covalency of carbon in CO is three because- a)an unexcited carbon atom has two unpaired electrons
- b)the C-atom can be an acceptor of an electron pair
- c)the C-atom has four valence electrons
- d)the maximum covalency of carbon is three
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Covalency of carbon in CO is three because
a)
an unexcited carbon atom has two unpaired electrons
b)
the C-atom can be an acceptor of an electron pair
c)
the C-atom has four valence electrons
d)
the maximum covalency of carbon is three
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In structure I, octet of oxygen is complete but octet of carbon is incomplete. Hence, carbon is an acceptor of an electron pair from oxygen. Thus, covalency of carbon is three in CO.
Which physical quantity is conserved during both elastic and inelastic collision?- a)Kinetic energy
- b)Potential energy
- c)Linear momentum
- d)Velocity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which physical quantity is conserved during both elastic and inelastic collision?
a)
Kinetic energy
b)
Potential energy
c)
Linear momentum
d)
Velocity
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions, whereas kinetic energy is converted into other forms of energy during an inelastic collision. In both types of collisions, momentum is conserved.
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis, which out of the following will not form sigma bond.- a)1s and 1s
- b)1s and 2px
- c)2py and 2py
- d)1s and 2s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis, which out of the following will not form sigma bond.
a)
1s and 1s
b)
1s and 2px
c)
2py and 2py
d)
1s and 2s
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Sigma bond is always formed between two half-filled atomic orbitals along their internuclear axis.i.e the line joining the centres of the nuclei of two atoms(axial overlapping). 2py and 2py will not form a sigma bond because taking x-axis as the internuclear axis, there will be lateral (sideway) overlap between the two 2pv orbitals forming a straight pi bond.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
- a)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
a)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The term stele was coined by Van Tiegham and Dauliot (1886). It is the axial portion of plant axis. Anatomically, all the tissues on the innerside of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele. Eustele is the type of stele in which a ring of vascular bundles is present around the central pith and inner to the pericyde e.g., dicot stem. Stele containing irregularly scattered vascular bundles is called atactostele, e.g., monocot stem. Pteridophytes are the first plants possenssing stele.
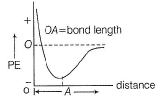
When a chemical bond is formed, there is decrease in- a)kinetic energy
- b)potential energy
- c)repulsive force
- d)attractive force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a chemical bond is formed, there is decrease in
a)
kinetic energy
b)
potential energy
c)
repulsive force
d)
attractive force

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
When two atoms approach to form a bond, there is decrease in potential energy (PE). After bond formation, at a minimum distance (called bond length). PE further increases.
There is a sphere of mass m moving with constant velocity v. It hits another sphere of same mass which is at rest. If e is the coefficient of restitution, then the ratio of the velocities of the two spheres after collision will be- a)
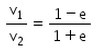
- b)
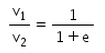
- c)
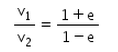
- d)
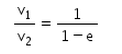
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a sphere of mass m moving with constant velocity v. It hits another sphere of same mass which is at rest. If e is the coefficient of restitution, then the ratio of the velocities of the two spheres after collision will be
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Here, a sphere of mass m moving with a constant velocity v hits another stationary sphere of the same mass. As per the given problem we can write
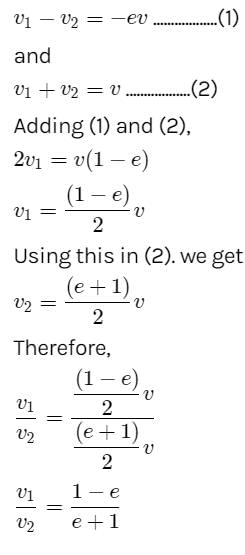
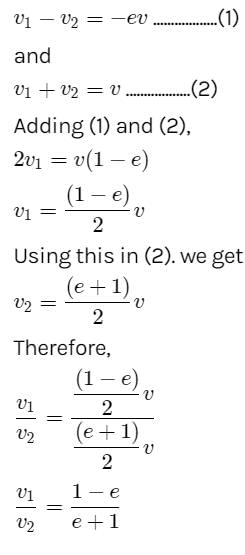
A particle of mass m moving with constant velocity v strikes another particle of same mass m but moving with the same velocity v in opposite direction stick together. The joint velocity after collision will be
- a)zero
- b)2v
- c)v
- d)v/2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass m moving with constant velocity v strikes another particle of same mass m but moving with the same velocity v in opposite direction stick together. The joint velocity after collision will be
a)
zero
b)
2v
c)
v
d)
v/2
|
|
Soumya Mukherjee answered |
Concept:
- Momentum: momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction.
- The unit of momentum (P) is kg m/s.
- Dimension: [MLT-1]
- Law of conservation of Momentum: A conservation law stating that the total linear momentum of a closed system remains constant through time, regardless of other possible changes within the system.
- P1 = P2
- m1 v1 = m2 v2
- Where, P1 = initial momentum of system, P2 = final momentum of system, m1 = mass of first object, v1 = velocity of first object, m2 = mass of second object and v2 = velocity of second object.
Calculation:
Given: m1 = m kg, m2 = m kg, u1 = v m/s, u2 = -v m/s
Given: m1 = m kg, m2 = m kg, u1 = v m/s, u2 = -v m/s
Let the common velocity of the combined body be V m/s
Mass of combined body M = m + m = 2m
Applying conservation of momentum:
m1 v1 + m2 v2 = M V
mv + (-mv) = 2mV
0 = 2mV
V = 0 m/s
Hence the correct answer will be zero (0) m/s.
Hence the correct answer will be zero (0) m/s.
Study the following statements regarding the anatomy of Isobllateral leal.
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)All are correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements regarding the anatomy of Isobllateral leal.
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
All are correct
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In an isobilateral (equifacial) leaf, vascular bundles are conjoint and collateral. Xylem lies towards the adaxial (upper) side and phloem lies towards abxialal (lower) side of leaf.
Maximum covalency is equal to the number- a)paired p-electrons
- b)unpaired s-electrons
- c)unpaired s and p-electrons
- d)s-and p-electrons in the valence shells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum covalency is equal to the number
a)
paired p-electrons
b)
unpaired s-electrons
c)
unpaired s and p-electrons
d)
s-and p-electrons in the valence shells

|
Kaavya Mukherjee answered |
s-and p-electrons have generally low energy than d-and f-electrons thus take part in chemical bonding.
Maximum covalency = (s + p) valence electrons,
covalency of C =4, valence electrons = 4 S = 6 valence electrons = 6
Maximum covalency = (s + p) valence electrons,
covalency of C =4, valence electrons = 4 S = 6 valence electrons = 6
Ratio of σ and π-bonds is equal to 1 in
- a)benzene
- b)tetracyanomethane
- c)allene(C3H4)
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ratio of σ and π-bonds is equal to 1 in
a)
benzene
b)
tetracyanomethane
c)
allene(C3H4)
d)
CO2
|
|
Jithin Saini answered |
Correct Answer : B
Explanation : Tetracyanomethane, where σ bond =8, ratio = 1, π bond = 8.
Carbon dioxide, O=C=O
σ = 2, π = 2
Ratio = 1.
Passage IIConsider the following structure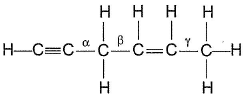
Q. Shortest (C— H) bond is- a)
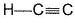
- b)
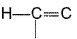
- c)
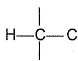
- d)all (C— H) bonds are of equal length.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
Consider the following structure
Q.
Shortest (C— H) bond is
a)
b)
c)
d)
all (C— H) bonds are of equal length.

|
Ruchi Basak answered |
Greater the electronegativity of carbon atom
(sp3 < sp2 < sp)
Greater the attraction for (C— H) bonding pair hence, shorter the (C— H)bond.
(sp3 < sp2 < sp)
Greater the attraction for (C— H) bonding pair hence, shorter the (C— H)bond.
Which of the following conditions of xylem is present in both monocot and dicot stems?- a)Endarch
- b)Polyarch
- c)Mesarch
- d)Exarch
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conditions of xylem is present in both monocot and dicot stems?
a)
Endarch
b)
Polyarch
c)
Mesarch
d)
Exarch
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Based on position of protoxylem in relation to metaxylem, the xylem may be exarch/centripetal, endarch/centrifugal, mesarch and centerarch. In endarch condition, protoxylem lies on the inner side of metaxylem e.g., dicot and monocot stems.
Well develped pith is found in- a)monocot root and monocot stem
- b)monocot stem and dicot root
- c)monocot root and dicot stem
- d)dicot root and dicot stem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Well develped pith is found in
a)
monocot root and monocot stem
b)
monocot stem and dicot root
c)
monocot root and dicot stem
d)
dicot root and dicot stem
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
In a dicot stem, a well developed pith (made of parenchymatous or occasionally sclerenchymatous cells) is present whereas in a monocot stem, pith is absent. In a dicot root, pith is poorly developed whereas in a monocot root, a well developed pith is present.
Casparian strips are the bands of thickenings present on _____ walls of endodermis.- a)radial
- b)tangential
- c)central
- d)both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Casparian strips are the bands of thickenings present on _____ walls of endodermis.
a)
radial
b)
tangential
c)
central
d)
both (a) and (b)
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Endodermis is the innermost layer of cortex that consistws of tightly packed barrel shaped cells. It is called starch sheath in case of dicot stems. Radial and and tangential walls of endodermal cells possess thickenings of lignin, suberin and cutin in the form of strips or bands, which are known as casparian bands or casparian strips.
A moving white hockey puck collides elastically with a stationary red hockey puck on a frictionless horizontal surface. No net external force acts on the two-puck system. Select all of the following statements that must be true for this elastic collision.1. The kinetic energy of the white puck is conserved (same before and after the collision)
2. The linear momentum of the white puck is conserved.
3. The linear momentum of the two puck system is conserved.- a)1 and 3 only
- b)1 and 2 only
- c)3 only
- d)1 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A moving white hockey puck collides elastically with a stationary red hockey puck on a frictionless horizontal surface. No net external force acts on the two-puck system. Select all of the following statements that must be true for this elastic collision.
1. The kinetic energy of the white puck is conserved (same before and after the collision)
2. The linear momentum of the white puck is conserved.
3. The linear momentum of the two puck system is conserved.
2. The linear momentum of the white puck is conserved.
3. The linear momentum of the two puck system is conserved.
a)
1 and 3 only
b)
1 and 2 only
c)
3 only
d)
1 only

|
Infinity Academy answered |
- In an elastic collision, both kinetic energy and linear momentum are conserved
- The white puck is moving and collides with the stationary red puck. Therefore, the kinetic energy of the white puck before the collision is not necessarily conserved individually, but the total kinetic energy of the system (both pucks) is conserved
- The linear momentum of the white puck alone is not conserved because it is involved in the collision. However, the total linear momentum of the two-puck system is conserved since there are no external forces acting on it
- Based on the analysis:
- Statement (1) is false because the kinetic energy of the white puck alone is not conserved
- Statement (2) is false because the linear momentum of the white puck alone is not conserved
- Statement (3) is true because the linear momentum of the two-puck system is conserved
Thus, the only statement that must be true is statement (3)
Select the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.- a)Phloem parenchyma is absent.
- b)Vascular bundles are scattered, conjoint, collateral and closed.
- c)Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath.
- d)Ground tissue is differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericyde and pith
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
a)
Phloem parenchyma is absent.
b)
Vascular bundles are scattered, conjoint, collateral and closed.
c)
Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath.
d)
Ground tissue is differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericyde and pith
|
|
Meghana Datta answered |
Incorrect Statement Explanation
The anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem has distinct characteristics that differentiate it from dicotyledonous stems. The statement in option 'D' is incorrect because of the following reasons:
Ground Tissue Composition
- In monocots, the ground tissue does not differentiate into distinct regions like cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith.
- Instead, the ground tissue is generally homogeneous and lacks the specialized structures found in dicots.
Vascular Bundle Arrangement
- Monocots have scattered vascular bundles throughout the stem, which is a key feature.
- Each vascular bundle is composed of xylem and phloem, arranged in a conjoint, collateral, and closed manner.
Bundle Sheath Presence
- Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath, which is a layer of cells that can help in the transport and support of the vascular tissue.
Absence of Phloem Parenchyma
- In monocots, phloem parenchyma is typically absent, which is another distinguishing feature when compared to dicots.
In summary, the ground tissue in monocot stems lacks the differentiation into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith, making option 'D' the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
The anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem has distinct characteristics that differentiate it from dicotyledonous stems. The statement in option 'D' is incorrect because of the following reasons:
Ground Tissue Composition
- In monocots, the ground tissue does not differentiate into distinct regions like cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith.
- Instead, the ground tissue is generally homogeneous and lacks the specialized structures found in dicots.
Vascular Bundle Arrangement
- Monocots have scattered vascular bundles throughout the stem, which is a key feature.
- Each vascular bundle is composed of xylem and phloem, arranged in a conjoint, collateral, and closed manner.
Bundle Sheath Presence
- Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath, which is a layer of cells that can help in the transport and support of the vascular tissue.
Absence of Phloem Parenchyma
- In monocots, phloem parenchyma is typically absent, which is another distinguishing feature when compared to dicots.
In summary, the ground tissue in monocot stems lacks the differentiation into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith, making option 'D' the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-25) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)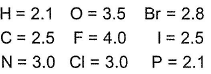
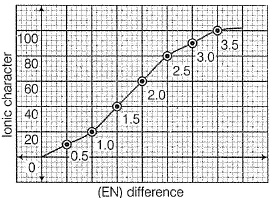
Graph shows variation of percentage ionic character with (EN) difference of two elements.
Q. Which of the following bonds is most polar?- a)H— Br
- b)N— H
- c)N— O
- d)P— H
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-25) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)
Passage I
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)
Graph shows variation of percentage ionic character with (EN) difference of two elements.
Q. Which of the following bonds is most polar?
a)
H— Br
b)
N— H
c)
N— O
d)
P— H
|
|
Simran Chauhan answered |
Which plant part possesses polyarch condition of vascular bundles with a well developed pith?- a)Dicot root
- b)Monocot root
- c)Dicot stem
- d)Monocot stem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant part possesses polyarch condition of vascular bundles with a well developed pith?
a)
Dicot root
b)
Monocot root
c)
Dicot stem
d)
Monocot stem
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
vascular bundles in monocot roots are radial, polyarch and exarch. Large number (more than 6) of xylem and phloem groups alternate with each other. A well devloped pith is present in monocot root.
Hypodermis is _______ in sunflower stem and _______in maize stem.- a)parenchymatous, collenchymatous
- b)collenchymatous, sderenchymatous
- c)sderenchymatous, collenchymatous
- d)sderenchymatous, sderenchymatous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hypodermis is _______ in sunflower stem and _______in maize stem.
a)
parenchymatous, collenchymatous
b)
collenchymatous, sderenchymatous
c)
sderenchymatous, collenchymatous
d)
sderenchymatous, sderenchymatous
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In a dicot stem (e.g., In sunflower), hypodermis is made up of collenchyma, which may be green. In monocot stem (e.g., maize), hypodermis is formed of non green sderenchyma tissue.
Bundle sheath extensions in a dicot leaf and in a monocot leaf are ________ and ________ respectively.- a)parenchymatous, collenchymatous
- b)parenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
- c)sclerechymatous, parenchymatous
- d)collenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bundle sheath extensions in a dicot leaf and in a monocot leaf are ________ and ________ respectively.
a)
parenchymatous, collenchymatous
b)
parenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
c)
sclerechymatous, parenchymatous
d)
collenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
|
|
Nitya Kaur answered |
Understanding Bundle Sheath Extensions
Bundle sheath extensions are specialized structures in plant leaves that play a crucial role in the transportation of nutrients and water. Their composition varies between dicots and monocots.
Dicot Leaves: Parenchymatous Extensions
- In dicot leaves, the bundle sheath extensions are primarily composed of parenchyma cells.
- Parenchyma is a fundamental tissue, which is soft, flexible, and involved in storage, photosynthesis, and tissue repair.
- The parenchymatous nature allows for efficient gas exchange and storage of photosynthetic products.
Monocot Leaves: Sclerenchymatous Extensions
- In contrast, monocot leaves have sclerenchyma cells in their bundle sheath extensions.
- Sclerenchyma provides strength and rigidity to the plant due to its thick cell walls, often made of lignin.
- This structural support is crucial in monocots, which often have elongated leaves and require additional strength to withstand environmental stresses.
Conclusion
- The correct answer to the question is option B: parenchymatous in dicots and sclerenchymatous in monocots.
- Understanding the differences in bundle sheath extensions helps in comprehending the adaptive strategies of various plant types in their environments.
This differentiation is essential for students preparing for competitive exams like NEET, as it highlights the functional diversity of plant tissues.
Bundle sheath extensions are specialized structures in plant leaves that play a crucial role in the transportation of nutrients and water. Their composition varies between dicots and monocots.
Dicot Leaves: Parenchymatous Extensions
- In dicot leaves, the bundle sheath extensions are primarily composed of parenchyma cells.
- Parenchyma is a fundamental tissue, which is soft, flexible, and involved in storage, photosynthesis, and tissue repair.
- The parenchymatous nature allows for efficient gas exchange and storage of photosynthetic products.
Monocot Leaves: Sclerenchymatous Extensions
- In contrast, monocot leaves have sclerenchyma cells in their bundle sheath extensions.
- Sclerenchyma provides strength and rigidity to the plant due to its thick cell walls, often made of lignin.
- This structural support is crucial in monocots, which often have elongated leaves and require additional strength to withstand environmental stresses.
Conclusion
- The correct answer to the question is option B: parenchymatous in dicots and sclerenchymatous in monocots.
- Understanding the differences in bundle sheath extensions helps in comprehending the adaptive strategies of various plant types in their environments.
This differentiation is essential for students preparing for competitive exams like NEET, as it highlights the functional diversity of plant tissues.
Read the following statements.
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eusteleAbove given features describe which of the following plant parts?- a)Monocot stem
- b)Monocot
- c)Dicot stem
- d)Dicot root
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements.
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eustele
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eustele
Above given features describe which of the following plant parts?
a)
Monocot stem
b)
Monocot
c)
Dicot stem
d)
Dicot root
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The epidermis of dicot stem bears several unbranched multicellular hair or trichomes. The hypodermis is made of 3−4 layered sub-epidermal collenchyma tissue. Vascular strand is in the form of eustele or a ring of vascular bundles present around the central pith and inner to the pericycle.
Select the correct pair out of the follwing.- a)Hypostomatic leaf - Dicots
- b)Epistomatic leaf - Monocots
- c)Amphistomatic leaf - Free-floating hydrophytes
- d)Presence of sunken stomata in leaf - Submerged hydrophytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct pair out of the follwing.
a)
Hypostomatic leaf - Dicots
b)
Epistomatic leaf - Monocots
c)
Amphistomatic leaf - Free-floating hydrophytes
d)
Presence of sunken stomata in leaf - Submerged hydrophytes
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In dicot leaves, stomata are generally present on lower epiderm is (hypostomatic), whereas in monocot leaves, they are present on both the surfaces (amphistomatic). In free -floating hydrophytes, stomata are restricted to upper epidermis (epistomatic) whereas in submerged hydrophytes, stomata are either non-functional or ab sent. In algae and fungi, stomata are totally absent. Stomata are sunken (deepseated) in case of xerophytes.
In a dorsiventral leaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem is respectively on the______ surfaces.- a)adaxial and abaxial
- b)adaxial and adaxial
- c)abaxial and adaxial
- d)abaxial and abaxial
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a dorsiventral leaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem is respectively on the______ surfaces.
a)
adaxial and abaxial
b)
adaxial and adaxial
c)
abaxial and adaxial
d)
abaxial and abaxial
|
|
Roshni Basak answered |
Explanation:
Dorsiventral Leaf:
A dorsiventral leaf is a type of leaf that exhibits two distinct surfaces - adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) surfaces. This type of leaf is commonly found in dicotyledonous plants.
Location of Palisade Tissue:
- The palisade tissue is typically located on the adaxial surface of the leaf.
- Palisade tissue is responsible for photosynthesis and is composed of elongated cells arranged parallel to the leaf surface to maximize light absorption.
Location of Phloem:
- The phloem, which is involved in the transport of organic compounds such as sugars, is usually located on the abaxial surface of the leaf.
- The phloem is part of the vascular tissue system in plants, along with the xylem.
Therefore, in a dorsiventral leaf, the palisade tissue is located on the adaxial surface (upper surface), while the phloem is located on the abaxial surface (lower surface). This arrangement allows for efficient photosynthesis and transport of nutrients throughout the leaf.
Dorsiventral Leaf:
A dorsiventral leaf is a type of leaf that exhibits two distinct surfaces - adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) surfaces. This type of leaf is commonly found in dicotyledonous plants.
Location of Palisade Tissue:
- The palisade tissue is typically located on the adaxial surface of the leaf.
- Palisade tissue is responsible for photosynthesis and is composed of elongated cells arranged parallel to the leaf surface to maximize light absorption.
Location of Phloem:
- The phloem, which is involved in the transport of organic compounds such as sugars, is usually located on the abaxial surface of the leaf.
- The phloem is part of the vascular tissue system in plants, along with the xylem.
Therefore, in a dorsiventral leaf, the palisade tissue is located on the adaxial surface (upper surface), while the phloem is located on the abaxial surface (lower surface). This arrangement allows for efficient photosynthesis and transport of nutrients throughout the leaf.
Direction (Q. Nos. 27 and 28) This section contains 2 question. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. In acidic medium,H2O2 changes Cr2O72- to CrO5 which has two (-O-O-) bonds. Oxidation state of Cr in CrO3 is
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 27 and 28) This section contains 2 question. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. In acidic medium,H2O2 changes Cr2O72- to CrO5 which has two (-O-O-) bonds. Oxidation state of Cr in CrO3 is
|
|
Sparsh Datta answered |
When H2O2 is added to an acidified solution of a dichromate, Cr2O72-, aO deep blue coloured complex, chromic peroxide, CrO5 [ or CrO(O2)2] is formed.
Cr2O72- +2H++4H2O2 ---> 2CrO(O2)2 +5H2O
This deep blue coloured complex.
Oxidation state of Cr is +6 due to the presence of two peroxide linkages which can be calculated as Cr peroxide normal
x+(-1)4+(-2) =0
x-6 =0
x=+6
Cr2O72- +2H++4H2O2 ---> 2CrO(O2)2 +5H2O
This deep blue coloured complex.
Oxidation state of Cr is +6 due to the presence of two peroxide linkages which can be calculated as Cr peroxide normal
x+(-1)4+(-2) =0
x-6 =0
x=+6
Bond order of (B— H) x and y bonds in diborane are respectively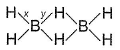
- a)1, 1
- b)0, 0.5
- c)0.5, 0.5
- d)1, 0.5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond order of (B— H) x and y bonds in diborane are respectively
a)
1, 1
b)
0, 0.5
c)
0.5, 0.5
d)
1, 0.5

|
Sankar Bose answered |
Vascular bundle is enclosed with in a well developed sderenchymatous sheath in- a)monocot stem
- b)dicot stem
- c)monocot root
- d)dicot root
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vascular bundle is enclosed with in a well developed sderenchymatous sheath in
a)
monocot stem
b)
dicot stem
c)
monocot root
d)
dicot root
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In most monocot stems, a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath is generally present on the outside of each vascular bundle.
Select the mismatched pair- a)Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles
- b)Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem
- c)Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns
- d)Radial vascular bundles - Maize root
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the mismatched pair
a)
Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles
b)
Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem
c)
Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns
d)
Radial vascular bundles - Maize root
|
|
Aditya Yadav answered |
Explanation:
Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem:
In maize stem, the vascular bundles are arranged in a bicollateral manner, meaning there are two separate vascular cambia present in the stem that produce xylem and phloem inwards and outwards. This arrangement is unique to maize stems and helps in the efficient transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles:
Sunflower stem bundles have collateral and open vascular bundles, where the xylem and phloem are located adjacent to each other in the same vascular bundle. The structure of these bundles allows for easy exchange of substances between xylem and phloem, aiding in the growth and development of the plant.
Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns:
Ferns have concentric vascular bundles, where xylem is surrounded by phloem in a circular arrangement. This type of vascular bundle arrangement is characteristic of ferns and helps in the efficient transport of water, minerals, and organic compounds throughout the plant.
Radial vascular bundles - Maize root:
In maize roots, the vascular bundles are arranged in a radial manner, with xylem and phloem alternating around the central core. This radial arrangement allows for efficient nutrient and water uptake from the soil and transport throughout the root system.
Therefore, the mismatched pair in the given options is "Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem" as maize stems indeed have bicollateral vascular bundles.
Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem:
In maize stem, the vascular bundles are arranged in a bicollateral manner, meaning there are two separate vascular cambia present in the stem that produce xylem and phloem inwards and outwards. This arrangement is unique to maize stems and helps in the efficient transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles:
Sunflower stem bundles have collateral and open vascular bundles, where the xylem and phloem are located adjacent to each other in the same vascular bundle. The structure of these bundles allows for easy exchange of substances between xylem and phloem, aiding in the growth and development of the plant.
Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns:
Ferns have concentric vascular bundles, where xylem is surrounded by phloem in a circular arrangement. This type of vascular bundle arrangement is characteristic of ferns and helps in the efficient transport of water, minerals, and organic compounds throughout the plant.
Radial vascular bundles - Maize root:
In maize roots, the vascular bundles are arranged in a radial manner, with xylem and phloem alternating around the central core. This radial arrangement allows for efficient nutrient and water uptake from the soil and transport throughout the root system.
Therefore, the mismatched pair in the given options is "Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem" as maize stems indeed have bicollateral vascular bundles.
Where is the phloem usually located in conjoint vascular bundles found in stems and leaves?- a)Along different radii
- b)Within cambium
- c)Inner side of xylem
- d)Outer side of xylem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Where is the phloem usually located in conjoint vascular bundles found in stems and leaves?
a)
Along different radii
b)
Within cambium
c)
Inner side of xylem
d)
Outer side of xylem

|
Ambition Institute answered |
In conjoint vascular bundles, which are common in stems and leaves, the phloem is typically located on the outer side of the xylem. This arrangement ensures efficient transport of food (sugars produced in the leaves) through the phloem, which is situated closer to the outer part of the stem or leaf where sugars are needed for growth or storage.
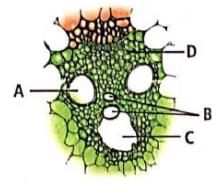
Refer the given figure which represents a section of vascular bundle as seen in T.S. of a monocot stem and select the option that correctly labels A, B, C and D.
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer the given figure which represents a section of vascular bundle as seen in T.S. of a monocot stem and select the option that correctly labels A, B, C and D.



a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
A monocot stem lacks secondary growth. The vascular bundles are oval or rounded in outline. They contain both phloem and xylem. Phloem lies towards the outside and the xylem on the inner side. Cambium is absent as the whole procambium is consumed in the formation of vascular tissues. Xylem is in the form of letter Y. It is endarch, i.e., protoxylem lies towards the centre of the stem. Xylem is made up of vessels, tracheids, xylem parenchyma and a few xylem fibres. Metandem generally consists of two large oval or rounded vessels lying at the upper two angles of xylem. Protoxylem cavity is present at the end of protoxylem vessels.
Stele includes- a)pericycle
- b)vascular bundles
- c)pith
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stele includes
a)
pericycle
b)
vascular bundles
c)
pith
d)
all of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Word 'stele' is taken from Greek language, which means 'pillar'. Stele consists of pericycle, vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) and pith (if present).
Chapter doubts & questions for July Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of July Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup