All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of September Week 1 for NEET Exam
What is the proper sequence in mitosis?- a)Anaphase, metaphase, telophase and prophase
- b)Telophase, anaphase, metaphase and prophase
- c)Metaphase, telophase, prophase and anaphase
- d)Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the proper sequence in mitosis?
a)
Anaphase, metaphase, telophase and prophase
b)
Telophase, anaphase, metaphase and prophase
c)
Metaphase, telophase, prophase and anaphase
d)
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. These phases occur in this strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
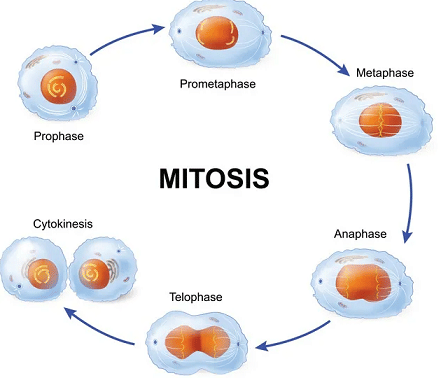
1. Prophase - During prophase, chromosomes get visible (chromatids), the centrioles migrate to the poles, nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear and spindle formation is seen. Prophase in mitosis is longer than any other phases of mitosis because the cell has to prepare for the actual division that takes place from early through late prophase.
2. Metaphase - During this, chromosomes lineup around the centre (Cells in metaphase have the chromosomes, which appear as long thin strands under the microscope).
3. Anaphase - here, chromatids separate and move to opposite poles by spindle fibers. This allows each daughter cell to have an identical copy of each of the original cell’s chromosomes.
4.Telophase - During this phase, chromosomes disappear (become chromatin), nuclear membrane reforms, nucleoli reappears, spindle disappears and centrioles duplicate.
The correct answer is option D.
How many mitotic divisions are needed for a single cell to make 128 cells?- a)7
- b)14
- c)28
- d)32
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many mitotic divisions are needed for a single cell to make 128 cells?
a)
7
b)
14
c)
28
d)
32
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells.
Hence the process of the division will be:
► 1 cell gives 2 daughter cells (1st mitosis)
► 2 cells give 4 daughter cells (2nd mitosis)
► 4 cells give 8 daughter cells (3rd mitosis)
► 8 cells give 16 daughter cells (4th mitosis)
► 16 cells give 32 daughter cells (5th mitosis)
► 32 cells give 64 daughter cells (6th mitosis)
► 64 cells give 128 daughter cells (7th mitosis)
Hence the process of the division will be:
► 1 cell gives 2 daughter cells (1st mitosis)
► 2 cells give 4 daughter cells (2nd mitosis)
► 4 cells give 8 daughter cells (3rd mitosis)
► 8 cells give 16 daughter cells (4th mitosis)
► 16 cells give 32 daughter cells (5th mitosis)
► 32 cells give 64 daughter cells (6th mitosis)
► 64 cells give 128 daughter cells (7th mitosis)
Hence 7 mitotic divisions cell needed for a single cell to make 128 cells.
Which stages of cell division do the figures A and B represent?
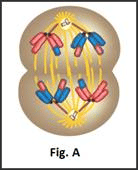
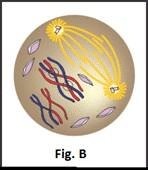
- a)A: Metaphase; B: Telophase
- b)A: Late anaphase; B: Prophase
- c)A: Telophase; B: Metaphase
- d)A: Prophase; B: Anaphase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which stages of cell division do the figures A and B represent?




a)
A: Metaphase; B: Telophase
b)
A: Late anaphase; B: Prophase
c)
A: Telophase; B: Metaphase
d)
A: Prophase; B: Anaphase

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- In Fig.A Chromatids are moving to opposite poles i.e Late anaphase.
- In Fig.B The duplicated DNA is compactly packed into chromosomes and spindle formation occurs i.e prophase.
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: Topic "Prophase” and “Anaphase” of chapter "Cell cycle and Cell division" of NCERT.
NCERT Reference: Topic "Prophase” and “Anaphase” of chapter "Cell cycle and Cell division" of NCERT.
A cell plate is laid during- a)Cytokinesis
- b)Karyokinesis
- c)Interphase
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell plate is laid during
a)
Cytokinesis
b)
Karyokinesis
c)
Interphase
d)
None of the above
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
- Cytokinesis is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells.
- Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and meiosis.
- During cytokinesis the spindle apparatus partitions and transports duplicated chromatids into the cytoplasm of the separating daughter cells. It thereby ensures that chromosome number and complement are maintained from one generation to the next and that, except in special cases, the daughter cells will be functional copies of the parent cell. After the completion of the telophase and cytokinesis, each daughter cell enters the interphase of the cell cycle.
Which of the phases of mitosis is the longest?- a)Telophase
- b)Prophase
- c)Anaphase
- d)Metaphase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the phases of mitosis is the longest?
a)
Telophase
b)
Prophase
c)
Anaphase
d)
Metaphase
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Prophase and telophase are stages involved in mitosis or meiosis. During G2 phase division of centrioles, mitochondria and chloroplasts occurs.
In mitosis, the number of chromosome sets in daughter cells will be- a)Half of parent cells
- b)Double of parent cells
- c)Different from parent cells
- d)Same as in parent cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In mitosis, the number of chromosome sets in daughter cells will be
a)
Half of parent cells
b)
Double of parent cells
c)
Different from parent cells
d)
Same as in parent cells

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
Same mitosis is also called equavational division becz. before and after mitosis ploidy is same..
At which stage of mitosis do chromatids separate and pass to different poles?- a)Anaphase
- b)Telophase
- c)Prophase
- d)Metaphase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At which stage of mitosis do chromatids separate and pass to different poles?
a)
Anaphase
b)
Telophase
c)
Prophase
d)
Metaphase
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Anaphase -The shortest stage of mitosis. The centromeres divide, and the sister chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart - or 'disjoin' - and move to the opposite ends of the cell, pulled by spindle fibres attached to the kinetochore regions.
Which is untrue about orbital velocity?
- a)increases with the increase in height of satellite
- b)depends on mass and radius of planet around which it revolves
- c)it is independent of mass of satellite
- d)decreases with an increase in radius of orbit
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is untrue about orbital velocity?
a)
increases with the increase in height of satellite
b)
depends on mass and radius of planet around which it revolves
c)
it is independent of mass of satellite
d)
decreases with an increase in radius of orbit
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The untrue statement about orbital velocity is:
1. increases with the increase in height of satellite
Explanation: Orbital velocity is the speed at which an object revolves around a planet or other celestial body in a stable orbit. According to the equation for orbital velocity, v = √(GM/r+h), where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the planet, and r is the radius of the orbit.
As the height of the satellite increases (meaning it gets far to the planet), its h increase , so reasulting in decrease in velocity .
The other statements are true:
2. depends on mass and radius of planet around which it revolves: As mentioned in the equation, orbital velocity depends on both the mass (M) of the planet and the radius (r) of the orbit.
3. it is independent of mass of satellite: The mass of the satellite does not appear in the equation for orbital velocity, so it does not affect the speed at which the satellite orbits the planet.
4. decreases with an increase in radius of orbit: From the equation, we can see that as the radius of the orbit (r) increases, the orbital velocity (v) decreases.
1. increases with the increase in height of satellite
Explanation: Orbital velocity is the speed at which an object revolves around a planet or other celestial body in a stable orbit. According to the equation for orbital velocity, v = √(GM/r+h), where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the planet, and r is the radius of the orbit.
As the height of the satellite increases (meaning it gets far to the planet), its h increase , so reasulting in decrease in velocity .
The other statements are true:
2. depends on mass and radius of planet around which it revolves: As mentioned in the equation, orbital velocity depends on both the mass (M) of the planet and the radius (r) of the orbit.
3. it is independent of mass of satellite: The mass of the satellite does not appear in the equation for orbital velocity, so it does not affect the speed at which the satellite orbits the planet.
4. decreases with an increase in radius of orbit: From the equation, we can see that as the radius of the orbit (r) increases, the orbital velocity (v) decreases.
In an endothermic reaction, the value of ΔH is always- a)Constant
- b)> 0
- c)< 0
- d)= 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an endothermic reaction, the value of ΔH is always
a)
Constant
b)
> 0
c)
< 0
d)
= 0
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
According to me, for an endothermic reaction ,the value of ∆H is always >0 .
India’s first artificial satellite was:- a)Sputnik
- b)Rohini
- c)Insat
- d)Aryabhatta
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
India’s first artificial satellite was:
a)
Sputnik
b)
Rohini
c)
Insat
d)
Aryabhatta
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
India's first artificial satellite was Aryabhata. Launched by soviet union on 19 April 1975
Centromere is required for- a)Transcription
- b)Cytoplasmic cleavage
- c)Movement of chromosomes towards poles
- d)Crossing over
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Centromere is required for
a)
Transcription
b)
Cytoplasmic cleavage
c)
Movement of chromosomes towards poles
d)
Crossing over

|
Aravind Saha answered |
The arms of chromosome are known as chromatids. These arms are held together at a point called the centromere (or primary constriction). Centromere occurs any where along the length of chromosome. During ceIl division spindle fibres are attached to centromere and help in the movement of chromosomes towards the poles.
Cell division is initiated in plants by- a)Cytokinin
- b)Abscisic acid
- c)Gibberellin
- d)Auxin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell division is initiated in plants by
a)
Cytokinin
b)
Abscisic acid
c)
Gibberellin
d)
Auxin
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Mitosis is the mechanism by which the chromosome content of a somatic cell (haploid or diploid) is kept constant through successive cell divisions. The division of the cell is initiated by division of the nucleus i.e. Karyokinesis followed by division of cytoplasm i.e. Cytokinesis.
A satellite which appears to be at a fixed position at a definite height to an observer is called:- a)Geostationary satellite and geosynchronous satellite
- b)Polar satellite
- c)Geostationary satellite
- d)Geosynchronous satellite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A satellite which appears to be at a fixed position at a definite height to an observer is called:
a)
Geostationary satellite and geosynchronous satellite
b)
Polar satellite
c)
Geostationary satellite
d)
Geosynchronous satellite
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
As the relative velocity of the satellite with respect to the earth is zero, it appears stationary from the Earth surface and therefore it is called is geostationary satellite or geosynchronous satellite.
In a cell cycle, during which phase are chromosomes arranged on the equatorial plate?- a)Metaphase
- b)Prophase
- c)Anaphase
- d)Telophase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a cell cycle, during which phase are chromosomes arranged on the equatorial plate?
a)
Metaphase
b)
Prophase
c)
Anaphase
d)
Telophase
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
During metaphase, the chromosomes get arranged in the form of a plate called the equatorial plate or metaphase plate at the equator of the spindle. This plate is at right angles to the axis of the spindle and is formed of the kinetochores, the arms of chromatids trailing away. The centromeres are drawn to the equator by the equal pull of two chromosomal fibres which connect the sister kinetochores to the opposite poles. The process of drawing the chromosomes onto the equator of the spindle is known as congression.
The difference between Cp and Cv is equal to- a)8.314 ergs K-1 mol-1
- b)2 kcal mol-1
- c)8.314 JK-1mol-1
- d)1.99 cal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between Cp and Cv is equal to
a)
8.314 ergs K-1 mol-1
b)
2 kcal mol-1
c)
8.314 JK-1mol-1
d)
1.99 cal
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Cp-Cv = R
R is gas constant whose value is 8.314 J/K/mol
R is gas constant whose value is 8.314 J/K/mol
What is the value of γ for a monoatomic gas?- a)1.40
- b)1.30
- c)1.67
- d)1.20
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the value of γ for a monoatomic gas?
a)
1.40
b)
1.30
c)
1.67
d)
1.20
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
For monatomic species, γ = 1.67
Weightlessness is:- a)a situation in which the effective weight of the body becomes zero
- b)a situation in which the effective weight of the body becomes 10N
- c)a situation in which the effective weight of the body becomes 9.8N.
- d)a situation in which the effective mass of the body becomes zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Weightlessness is:
a)
a situation in which the effective weight of the body becomes zero
b)
a situation in which the effective weight of the body becomes 10N
c)
a situation in which the effective weight of the body becomes 9.8N.
d)
a situation in which the effective mass of the body becomes zero

|
Akshay Shah answered |
Weight becomes zero in a freefall or when the total force on your body is zero.For example in a freely falling lift the contact force on your body is zero,so the wieghting machine would show zero reading.so you are wieghtless.
On which of the following factors the enthalpy change of a reaction is NOT dependent?- a)Nature of reactants and products
- b)Various intermediate reactions
- c)State of reactants and products
- d)Enthalpy of reactants and products
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On which of the following factors the enthalpy change of a reaction is NOT dependent?
a)
Nature of reactants and products
b)
Various intermediate reactions
c)
State of reactants and products
d)
Enthalpy of reactants and products
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The enthalpy change for a reaction does not depend upon the. use of different reactants for the same product. difference in initial or final temperatures of involved substances.
The condition in which q will be equal to ΔH of a system is- a)constant P and T
- b)constant P and V
- c)constant P, T and V
- d)constant T and V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The condition in which q will be equal to ΔH of a system is
a)
constant P and T
b)
constant P and V
c)
constant P, T and V
d)
constant T and V
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Under the condition, the heat q of the reaction is equal to the enthalpy change ΔH of the system. Under constant pressure and temperature, the free energy in a reaction is known as Gibbs free energy G.
G = H - TS
G = H - TS
Kepler’s second law states that the straight line joining the planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time. The statement is equivalent to saying that:- a)longitudnal acceleration is zero
- b)total acceleration is zero
- c)transverse acceleration is zero
- d)radial acceleration is zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Kepler’s second law states that the straight line joining the planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time. The statement is equivalent to saying that:
a)
longitudnal acceleration is zero
b)
total acceleration is zero
c)
transverse acceleration is zero
d)
radial acceleration is zero
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
According to the second law the orbital radius and angular velocity of the planet in the elliptical orbit will vary. The planet travels faster when closer to the Sun, then slower when farther from the Sun. Hence we can say that the transverse acceleration is zero while radial and longitudinal accelerations are not zero.
The chemical reaction:
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) ; Δh= -890.4kJ is- a)endothermic
- b)exothermic
- c)unpredictable
- d)depend on the reaction conditions
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical reaction:
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) ; Δh= -890.4kJ is
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) ; Δh= -890.4kJ is
a)
endothermic
b)
exothermic
c)
unpredictable
d)
depend on the reaction conditions
|
|
Preethi Chakraborty answered |
Since heat is released as shown in the reaction with a negative sign, the above reaction is exothermic.
The squares of the periods of revolution of the planets are proportional to the ___________of their semimajor axis of its orbit.- a)sqaures
- b)sqaures root
- c)cube
- d)cube roots
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The squares of the periods of revolution of the planets are proportional to the ___________of their semimajor axis of its orbit.
a)
sqaures
b)
sqaures root
c)
cube
d)
cube roots
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The Law of Periods: The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of its orbit.
Different planets have different escape velocities because:- a)different planets have different atmosphere
- b)they have different distances from sun
- c)escape velocity depends on the body that has to escape the atmosphere of the planet
- d)they have different masses and sizes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Different planets have different escape velocities because:
a)
different planets have different atmosphere
b)
they have different distances from sun
c)
escape velocity depends on the body that has to escape the atmosphere of the planet
d)
they have different masses and sizes

|
Nitin Nair answered |
The formula for calculating the escape velocity from the surface of a celestial body (e.g. a planet) is:

where G is the universal gravitation constant, M is the planet’s mass and R is its radius.Different planets have different mass and radius - and therefore different escape velocity.
A satellite moves in a circular orbit around earth. The radius of this orbit is one half that of moon’s orbit. The satellite completes one revolution in:
- a)(2) 3/2 lunar month
- b)(2) 3 lunar month
- c)(2) -3/2 lunar month
- d)(2)1/2 lunar month
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A satellite moves in a circular orbit around earth. The radius of this orbit is one half that of moon’s orbit. The satellite completes one revolution in:
a)
(2) 3/2 lunar month
b)
(2) 3 lunar month
c)
(2) -3/2 lunar month
d)
(2)1/2 lunar month
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
We know that the time period of revolution for any object in orbit of radius r is 3
T = 2π (r3 / Gm) 1/2
Where m is the mass of earth.
As the ratio of radius of orbit of satellite to that of moon is 1:2
Hence there time period has a ratio of 1: 23/2
T = 2π (r3 / Gm) 1/2
Where m is the mass of earth.
As the ratio of radius of orbit of satellite to that of moon is 1:2
Hence there time period has a ratio of 1: 23/2
Which of the following reactions is an endothermic process?- a)C + O2 → CO2 ; ΔH = -x kj
- b)2H2 + O2 → 2H2O ; ΔH = -y kj
- c)CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O ; ΔH = -q kj
- d)N2 + O2 → 2NO ; ΔH = z kj
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions is an endothermic process?
a)
C + O2 → CO2 ; ΔH = -x kj
b)
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O ; ΔH = -y kj
c)
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O ; ΔH = -q kj
d)
N2 + O2 → 2NO ; ΔH = z kj
|
|
Megha Desai answered |
For endothermic reactions, enthalpy is with no-ve sign in the end of reaction.
The values of ΔH for endothermic and exothermic reactions are- a)positive for both
- b)negative for both
- c)positive and negative
- d)negative and positive
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The values of ΔH for endothermic and exothermic reactions are
a)
positive for both
b)
negative for both
c)
positive and negative
d)
negative and positive
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
For endothermic reaction, ∆H = positive value since heat is absorbed during the course of reaction. For exothermic, ∆H = negative value as heat is released during the course of reaction.
What is the relation between ΔH and ΔU ?- a)ΔH = ΔU
- b)ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT
- c)ΔH = ΔU – RT
- d)ΔH = ΔU + RT
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relation between ΔH and ΔU ?
a)
ΔH = ΔU
b)
ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT
c)
ΔH = ΔU – RT
d)
ΔH = ΔU + RT
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Enthalpy is a state function, and the change in enthalpy of a system is equal to the sum of the change in the internal energy of the system ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT and the PV work done. Enthalpy is a state function whose change indicates the amount of heat transferred from a system to its surroundings or vice versa, at constant pressure.
Chapter doubts & questions for September Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of September Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












