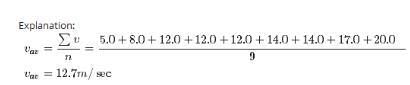All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of January Week 2 for NEET Exam
What is the major bromination product in the following reaction? 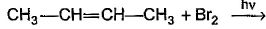
- a)
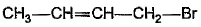
- b)
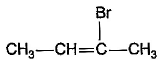
- c)
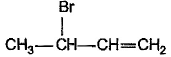
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
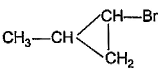
What is the major bromination product in the following reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The correct answer is option c
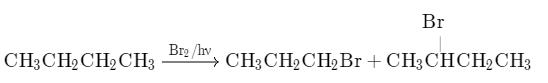
Thus, a racemic mixture is obtained. A racemic mixture is one that has an equal amount of left and right handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Thus, a racemic mixture is obtained. A racemic mixture is one that has an equal amount of left and right handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
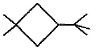
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).PassageA hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.Q. Which of the following satisfy the criteria of X ?- a)
- b)
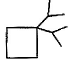
- c)
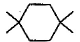
- d)
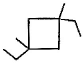
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).
Passage
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. Which of the following satisfy the criteria of X ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In option c, there are only two different position which can be chlorinated,
So, option c is correct.
So, option c is correct.
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 -15) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. In the following free radical bromination reaction, the im portant product(s) is/are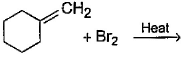
- a)
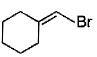
- b)
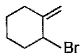
- c)
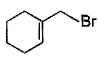
- d)
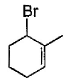
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 -15) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. In the following free radical bromination reaction, the im portant product(s) is/are
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
This is the case of allylic substitution. The radical will delocalise itself to two locations. And so, we will get two different positions for radical substitution.

There is also a possibility at C6, but it is not in our option.

There is also a possibility at C6, but it is not in our option.
Which of the following reactions can bring about chlorination of cyclohexane?- a)
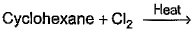
- b)
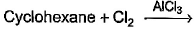
- c)
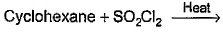
- d)
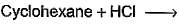
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions can bring about chlorination of cyclohexane?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
For SO2Cl2: The reactivity patterns of SO2Cl2 and SOCl2 are quite different. SOCl2 is a good electrophile, and can be thought of as a source of Cl− ions. These ions can go on to react in their typical nucleophilic fashion. SO2Cl2 however is often a Cl2 source, as it readily decomposes giving off sulfur dioxide. Usually, much easier/safer to use this than measuring out (and getting into solution) chlorine gas. The chlorination of simple alkanes by Cl2 gas (or something that makes it in solution) happens by a radical mechanism i.e. Cl⋅ not Cl
For Cl2 and heat/light:
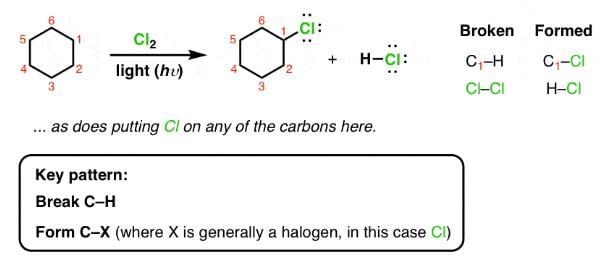
For Cl2 and heat/light:

For Cl with AlCl3: It is used for chlorination of compounds like benzene
For HCl: It is used for halogenations of a double bond.
For HCl: It is used for halogenations of a double bond.
Which of the following is not a possible termination step in the free radical chlorination of methane?- a)
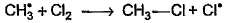
- b)

- c)
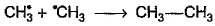
- d)
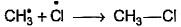
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a possible termination step in the free radical chlorination of methane?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Termination is the last step. So there shouldn't be any free radical atom remaining. In first option there is Cl• remaining it can't be termination step.The steps in free radical halogenation are as
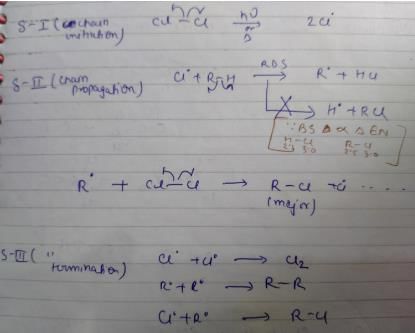
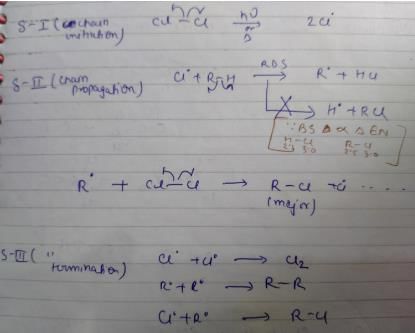
Direction (Q. Nos, 19 - 22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. How many different isomers of alkenes {including stereoisomers) exist that all upon catalytic hydrogenation adds one mole of H2 to give the same 2, 2, 3,5-tetramethyl hexane?
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos, 19 - 22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How many different isomers of alkenes {including stereoisomers) exist that all upon catalytic hydrogenation adds one mole of H2 to give the same 2, 2, 3,5-tetramethyl hexane?

|
Ashish Mishra answered |
7 is correct.
Skeletal muscle bundles [fascicles] are held together by a common connective tissue layer called:- a)Perimysium
- b)Endomysium
- c)Fascia
- d)Aponeurosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Skeletal muscle bundles [fascicles] are held together by a common connective tissue layer called:
a)
Perimysium
b)
Endomysium
c)
Fascia
d)
Aponeurosis
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons. A skeletal muscle refers to multiple bundles (fascicles) of cells joined together called muscle fibers. The fibers and muscles are surrounded by connective tissue layers called fasciae.
The number of degrees of freedom a diatomic molecule is- a)6
- b)5.0
- c)3
- d)5.3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of degrees of freedom a diatomic molecule is
a)
6
b)
5.0
c)
3
d)
5.3

|
Akshara Chopra answered |
Explanation:Degrees of freedom of a system refers to the possible independent motions a system can have.the total degrees of freedom describing the motion of a diatomic molecule is 5.3 for translation and 2 for rotation
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.Q. How many different alkenes on hydrogenation, can gives X ?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. How many different alkenes on hydrogenation, can gives X ?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
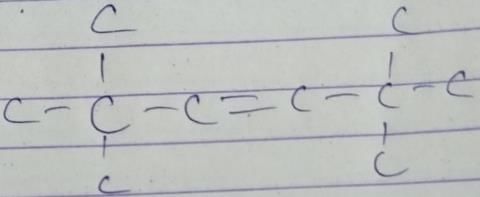
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. When light is shined on a mixture of chlorine and ethane, chloroethane is formed besides dichloroethane, trichloroethane and several other products. What reaction condition can optimise the yield of chloroethane?- a)Higher reaction temperature
- b)High concentration of chlorine gas
- c)Excess of ethane reactan
- d)Low reaction temperature
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. When light is shined on a mixture of chlorine and ethane, chloroethane is formed besides dichloroethane, trichloroethane and several other products. What reaction condition can optimise the yield of chloroethane?
a)
Higher reaction temperature
b)
High concentration of chlorine gas
c)
Excess of ethane reactan
d)
Low reaction temperature
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
When chlorine and Ethane are taken with chlorine in excess only then we have more than one product like chloroethane, dichloroethane, trichloroethane etc. To avoid this we should take Ethane in excess because when we will take it then in excess then we will have only single time chlorination and we will get monochloroethane.
Kinetic theory explains the behavior- a)of liquids based on the idea that the liquids consist of rapidly moving atoms or molecules
- b)of gases based on the idea that the gas consists of rapidly moving atoms or molecules
- c)of solids based on the idea that the solid consists of rapidly vibrating atoms or molecules
- d)of solids and liquids based on the idea that they gas consist of rapidly vibrating atoms or molecules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinetic theory explains the behavior
a)
of liquids based on the idea that the liquids consist of rapidly moving atoms or molecules
b)
of gases based on the idea that the gas consists of rapidly moving atoms or molecules
c)
of solids based on the idea that the solid consists of rapidly vibrating atoms or molecules
d)
of solids and liquids based on the idea that they gas consist of rapidly vibrating atoms or molecules
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Kinetic theory explains the behaviour of gases based on the idea that the gas consists of rapidly moving atoms or molecules. This is possible as the inter-atomic forces, which are short range forces that are important for solids and liquids, can be neglected for gases.
During free radical bromination of isobutane, an alkene is produced as by product via disproportionation of the intermediate alkyl free radical. What is this alkene?- a)1-butene
- b)2-butene
- c)2-methyl propene
- d)Both ‘b’ and ‘c’
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During free radical bromination of isobutane, an alkene is produced as by product via disproportionation of the intermediate alkyl free radical. What is this alkene?
a)
1-butene
b)
2-butene
c)
2-methyl propene
d)
Both ‘b’ and ‘c’
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
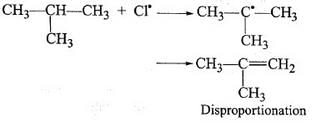
As shown in the above mechanism 1-butene and 2-butene cannot be formed by this free radical. release of 1 hydrogen radical gives 2-methyl propene as disproportionated product.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Which of the following statem ents regarding free radical halogenation o f alkane is not true?- a)Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in the propagation step is exothermic in both chlorination and bromination
- b)Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in propagation step is exothermic in chlorination but endothermic in bromination
- c)A single halogen radical may bring about halogenation of thousands of alkane molecules
- d)Continuous source of energy is required to continue the free radical halogenation reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statem ents regarding free radical halogenation o f alkane is not true?
a)
Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in the propagation step is exothermic in both chlorination and bromination
b)
Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in propagation step is exothermic in chlorination but endothermic in bromination
c)
A single halogen radical may bring about halogenation of thousands of alkane molecules
d)
Continuous source of energy is required to continue the free radical halogenation reaction
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Hydrogen abstraction by halogen radical in the propagation step is exothermic in chlorination but endothermic in bromination. Hence, the option (A) is an incorrect statement.
Mean free path is the- a)maximum distance between collisions
- b)minimum distance between collisions
- c)average distance between collisions
- d)(maximum distance + minimum distance )/ 2 between collisions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mean free path is the
a)
maximum distance between collisions
b)
minimum distance between collisions
c)
average distance between collisions
d)
(maximum distance + minimum distance )/ 2 between collisions

|
Kaavya Mukherjee answered |
Explanation:the mean free path is the average distance traveled by a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, a photon) between successive impacts (collisions), which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.
Axial skeleton consists of- a)22 bones
- b)65 bones
- c)80 bones
- d)70 bones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Axial skeleton consists of
a)
22 bones
b)
65 bones
c)
80 bones
d)
70 bones

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
The axial skeleton comprises 80 bones distributed along the main axis of the body.
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points.
I. 3 -methyl pentane
II. 3-chloropentane
III. 3-bromopentane
IV. 3,3-dichloropentane
- a)IV < III < II < I
- b)I < II < IV < III
- c)I < II < III < IV
- d)II < I < IV < III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points.
I. 3 -methyl pentane
II. 3-chloropentane
III. 3-bromopentane
IV. 3,3-dichloropentane
II. 3-chloropentane
III. 3-bromopentane
IV. 3,3-dichloropentane
a)
IV < III < II < I
b)
I < II < IV < III
c)
I < II < III < IV
d)
II < I < IV < III
|
|
Om Desai answered |
For boiling point, we have to consider both branching and Molecular mass. In 4 bromopentane molecular mass is nearly the same as compared to 3 chloro pentane but we have 3,3-dichloropentane extended into 2 directions so the boiling point of 3,3-dichloropentane will be more and the other order will be followed by option C.
The correctorganisation of skeletal muscle is :- a)muscle bundles →→ myofibrils →→ muscle cells →→ sarcomere
- b)fascicles →→ muscle fibres →→ myofilaments →→ sarcomere
- c)muscle bundles →→ muscle cells →→ muscle fibres →→ sarcomere
- d)fascia →→ muscle cells →→ myofibrils →→ sarcomere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correctorganisation of skeletal muscle is :
a)
muscle bundles →→ myofibrils →→ muscle cells →→ sarcomere
b)
fascicles →→ muscle fibres →→ myofilaments →→ sarcomere
c)
muscle bundles →→ muscle cells →→ muscle fibres →→ sarcomere
d)
fascia →→ muscle cells →→ myofibrils →→ sarcomere

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Each organised skeletal muscle in our body is made of a number of muscle bundles or fascicles held together by a common collagenous connective tissue layer called fascia. Each muscle bundle contains a number of muscle fibres. A characteristic feature of the muscle fibre is the presence of a large number of parallelly arranged filaments in the sarcoplasm called myofilaments or myofibrils. The portion of the myofibril between two successive ‘Z’ lines is considered as the functional unit of contraction and is called a sarcomere.
hat is relative reactivity of secondary versus primary hydrogens in free radical bromination of n-butane if the ratio of 1-bromo to 2-bromobutane formed is 7 : 39?- a)200 :1
- b)20 :1
- c)5 :1
- d)1 : 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
hat is relative reactivity of secondary versus primary hydrogens in free radical bromination of n-butane if the ratio of 1-bromo to 2-bromobutane formed is 7 : 39?
a)
200 :1
b)
20 :1
c)
5 :1
d)
1 : 20
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Correct Answer :- b
Explanation : The 2o hydrogens are 20 times more reactive than the 1o ones.
How many different monochlorination products would be obtained on free radical chlorination of methyl cyclobutane?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
How many different monochlorination products would be obtained on free radical chlorination of methyl cyclobutane?
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
After free radical halogenation of methyl cyclobutane, we have its 8different isomers. They are as follow:-
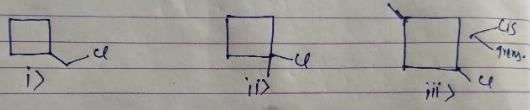

From i) and ii), we get only positional isomers. From iii) we will have 2 isomers, cis and Trans. They won't show a chiral centre.
In iv) we have 2 chiral centres which will give us 4 isomers.So, in total there would be 4+2+1+1 = 8 isomers.


From i) and ii), we get only positional isomers. From iii) we will have 2 isomers, cis and Trans. They won't show a chiral centre.
In iv) we have 2 chiral centres which will give us 4 isomers.So, in total there would be 4+2+1+1 = 8 isomers.
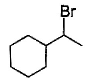
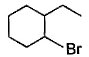
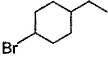
The major monobromination product which results when ethyl cyclohexane is subjected to free radical bromination, is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
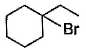
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The major monobromination product which results when ethyl cyclohexane is subjected to free radical bromination, is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Free radical bromination reaction is highly selective, occurs mainly at the carbon where most stable free radical is formed.
We know that the stability of free radical is in the order,
Tertiary radical > Secondary radical > Primary radical
In (a), (b) and (c), the bromination occurs at secondary carbon whereas in (d) the bromination occurs at tertiary carbon. Since, tertiary radicals are more stable than secondary radical the major product of monobromination of ethyl cyclohexane is (d).
The stability of tertiary radical is due to the higher number of α−Hygrogens which give more hyperconjugation effect than secondary.
The following X-ray shows :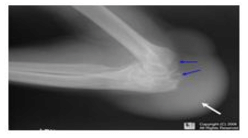
- a)a person with osteoporosis in his knee
- b)a person with gout in his knee
- c)a person with muscular dystrophy
- d)a person with bone cancer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following X-ray shows :
a)
a person with osteoporosis in his knee
b)
a person with gout in his knee
c)
a person with muscular dystrophy
d)
a person with bone cancer

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
The X-ray of knee shows gout in the knee. Gout is a kind of arthritis. It can cause an attack of sudden burning pain, stiffness and swelling in joint.
One mole of hydrogen gas is heated at constant pressure from 300 K to 420 K. Calculate the increase in its internal energy.- a)2.49 kJ
- b)2.65 kJ
- c)2.15 kJ
- d)2.85 kJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of hydrogen gas is heated at constant pressure from 300 K to 420 K. Calculate the increase in its internal energy.
a)
2.49 kJ
b)
2.65 kJ
c)
2.15 kJ
d)
2.85 kJ

|
Madhurima Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
Hydrogen is a diatomic gas. (CV = 2.5R)
Change in internal energy
ΔU = nCVΔT = 1 x 2.5 x 8.31 x 120 = 2493J = 2.49KJ
Calculate the change in internal energy of 3.00 mol of helium gas when its temperature is increased by 2.00 K.- a)85.0 J
- b)95.0 J
- c)65.0 J
- d)75.0 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the change in internal energy of 3.00 mol of helium gas when its temperature is increased by 2.00 K.
a)
85.0 J
b)
95.0 J
c)
65.0 J
d)
75.0 J
|
|
Athira Chavan answered |
Understanding Internal Energy Change
The internal energy change (ΔU) of an ideal gas can be calculated using the formula:
ΔU = n * C_v * ΔT
Where:
- n = number of moles
- C_v = molar specific heat at constant volume
- ΔT = change in temperature
Parameters for Helium Gas
- Helium is a monoatomic ideal gas.
- For monoatomic gases, C_v is approximately 3/2 R, where R is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K).
Calculation Steps
1. Identify Variables:
- n = 3.00 mol (given)
- C_v = (3/2) * R = (3/2) * 8.314 J/mol·K = 12.471 J/mol·K
- ΔT = 2.00 K (given)
2. Plug in Values:
ΔU = n * C_v * ΔT
ΔU = 3.00 mol * 12.471 J/mol·K * 2.00 K
3. Perform the Calculation:
- ΔU = 3.00 * 12.471 * 2.00
- ΔU = 3.00 * 24.942
- ΔU = 74.826 J (approximately 75.0 J)
Conclusion
The calculated change in internal energy for 3.00 mol of helium gas when the temperature is increased by 2.00 K is approximately 75.0 J. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', which aligns with the calculated value.
The internal energy change (ΔU) of an ideal gas can be calculated using the formula:
ΔU = n * C_v * ΔT
Where:
- n = number of moles
- C_v = molar specific heat at constant volume
- ΔT = change in temperature
Parameters for Helium Gas
- Helium is a monoatomic ideal gas.
- For monoatomic gases, C_v is approximately 3/2 R, where R is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K).
Calculation Steps
1. Identify Variables:
- n = 3.00 mol (given)
- C_v = (3/2) * R = (3/2) * 8.314 J/mol·K = 12.471 J/mol·K
- ΔT = 2.00 K (given)
2. Plug in Values:
ΔU = n * C_v * ΔT
ΔU = 3.00 mol * 12.471 J/mol·K * 2.00 K
3. Perform the Calculation:
- ΔU = 3.00 * 12.471 * 2.00
- ΔU = 3.00 * 24.942
- ΔU = 74.826 J (approximately 75.0 J)
Conclusion
The calculated change in internal energy for 3.00 mol of helium gas when the temperature is increased by 2.00 K is approximately 75.0 J. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', which aligns with the calculated value.
One mole of hydrogen gas is heated at constant pressure from 300 K to 420 K. Calculate the energy transferred by heat to the gas- a)3.86 kJ
- b)3.49 kJ
- c)3.66 kJ
- d)3.26 kJ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of hydrogen gas is heated at constant pressure from 300 K to 420 K. Calculate the energy transferred by heat to the gas
a)
3.86 kJ
b)
3.49 kJ
c)
3.66 kJ
d)
3.26 kJ

|
Krithika Kulkarni answered |
Explanation:
Hydrogen is a diatomic gas. (CP = 3.5R)
energy transferred by heat to the gas
Q=nCPΔT=1×3.5×8.31×120=3490J=3.49KJ
Which of these join the skull bones to each other to form the cranium?- a)Specialized connective tissue
- b)Loose fibrous connective tissues
- c)Dense fibrous connective tissues
- d)Dense irregular connective tissue
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these join the skull bones to each other to form the cranium?
a)
Specialized connective tissue
b)
Loose fibrous connective tissues
c)
Dense fibrous connective tissues
d)
Dense irregular connective tissue
|
|
Juhi Reddy answered |
The correct answer is option 'c' - dense fibrous connective tissues.
Explanation:
The cranium, also known as the skull, is the protective bony structure that surrounds and encloses the brain. It consists of several bones that join together to form a strong and rigid structure. These bones are connected to each other by dense fibrous connective tissues, which help to provide strength and stability to the cranium.
Here is a detailed explanation of why dense fibrous connective tissues are responsible for joining the skull bones together to form the cranium:
1. Function of connective tissues:
Connective tissues are a type of tissue that provide support and connect different structures in the body. They consist of cells and an extracellular matrix that contains fibers and ground substance. Connective tissues have various functions, including providing structural support, protecting organs, and connecting tissues and organs together.
2. Types of connective tissues:
There are several types of connective tissues in the body, including loose fibrous connective tissues, dense fibrous connective tissues, specialized connective tissues, and dense irregular connective tissues. Each type of connective tissue has different properties and functions.
3. Dense fibrous connective tissues:
Dense fibrous connective tissues are characterized by a high density of collagen fibers arranged in a parallel fashion. These fibers provide strength and resistance to tension forces. Dense fibrous connective tissues are found in structures that require strength and stability, such as tendons, ligaments, and the outer layer of bones.
4. Role in the cranium:
In the cranium, the dense fibrous connective tissues join the skull bones together at specialized joints called sutures. Sutures are fibrous joints that allow slight movement between the bones during growth and development but become fused and immovable in adulthood. The dense fibrous connective tissues in the sutures help to hold the skull bones firmly together, providing stability and protection to the brain.
5. Importance of strong connections:
The dense fibrous connective tissues in the cranium are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the skull and protecting the brain from injury. Without these strong connections, the skull bones would be more prone to dislocation or fracture, which could lead to severe damage to the brain.
In conclusion, dense fibrous connective tissues join the skull bones together to form the cranium. These tissues provide strength, stability, and protection to the brain by forming strong connections between the bones at the sutures.
Explanation:
The cranium, also known as the skull, is the protective bony structure that surrounds and encloses the brain. It consists of several bones that join together to form a strong and rigid structure. These bones are connected to each other by dense fibrous connective tissues, which help to provide strength and stability to the cranium.
Here is a detailed explanation of why dense fibrous connective tissues are responsible for joining the skull bones together to form the cranium:
1. Function of connective tissues:
Connective tissues are a type of tissue that provide support and connect different structures in the body. They consist of cells and an extracellular matrix that contains fibers and ground substance. Connective tissues have various functions, including providing structural support, protecting organs, and connecting tissues and organs together.
2. Types of connective tissues:
There are several types of connective tissues in the body, including loose fibrous connective tissues, dense fibrous connective tissues, specialized connective tissues, and dense irregular connective tissues. Each type of connective tissue has different properties and functions.
3. Dense fibrous connective tissues:
Dense fibrous connective tissues are characterized by a high density of collagen fibers arranged in a parallel fashion. These fibers provide strength and resistance to tension forces. Dense fibrous connective tissues are found in structures that require strength and stability, such as tendons, ligaments, and the outer layer of bones.
4. Role in the cranium:
In the cranium, the dense fibrous connective tissues join the skull bones together at specialized joints called sutures. Sutures are fibrous joints that allow slight movement between the bones during growth and development but become fused and immovable in adulthood. The dense fibrous connective tissues in the sutures help to hold the skull bones firmly together, providing stability and protection to the brain.
5. Importance of strong connections:
The dense fibrous connective tissues in the cranium are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the skull and protecting the brain from injury. Without these strong connections, the skull bones would be more prone to dislocation or fracture, which could lead to severe damage to the brain.
In conclusion, dense fibrous connective tissues join the skull bones together to form the cranium. These tissues provide strength, stability, and protection to the brain by forming strong connections between the bones at the sutures.
Consider the following bromination reaction.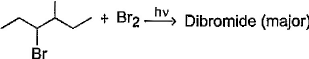 If a pure enantiomer of reactant is taken in the above reaction, the correct statement concerning product dibromide is/are
If a pure enantiomer of reactant is taken in the above reaction, the correct statement concerning product dibromide is/are - a)A racemic mixture is formed
- b)Two optically active isomers are formed
- c)A pair of diastereomers in equal amount is formed
- d)A pair of enantiomers but in unequal amounts is formed
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following bromination reaction.
If a pure enantiomer of reactant is taken in the above reaction, the correct statement concerning product dibromide is/are
a)
A racemic mixture is formed
b)
Two optically active isomers are formed
c)
A pair of diastereomers in equal amount is formed
d)
A pair of enantiomers but in unequal amounts is formed

|
Ashish Mishra answered |
B and C is correct
In which case are the atoms relatively rigidly fixed?- a)gases
- b)liquids and gases
- c)solids
- d)liquids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which case are the atoms relatively rigidly fixed?
a)
gases
b)
liquids and gases
c)
solids
d)
liquids

|
Pranav Saha answered |
Explanation:
Atoms in a gas are well separated with no regular arrangement. Atoms vibrate and move freely at high speeds
Atoms in a liquid are close together with no regular arrangement. Atoms vibrate, move about, and slide past each other.
Atoms in a solid are tightly packed, usually in a regular pattern. Atoms vibrate (jiggle) but generally do not move from place to place.
Kinetic theory relates measurable properties.- a)of liquids such as viscosity, conduction and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
- b)of super cooled liquids such as viscosity, creep and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
- c)of solids such as expansion, conduction and elongation with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
- d)of gases such as viscosity, conduction and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinetic theory relates measurable properties.
a)
of liquids such as viscosity, conduction and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
b)
of super cooled liquids such as viscosity, creep and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
c)
of solids such as expansion, conduction and elongation with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses
d)
of gases such as viscosity, conduction and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses

|
Moumita Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:Kinetic theory explains the behaviour of gases based on the idea that the gas consists of rapidly moving atoms or molecules. It also relates measurable properties of gases such as viscosity, conduction and diffusion with molecular parameters, yielding estimates of molecular sizes and masses.
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is at an initial temperature of 300 K. The gas undergoes an isovolumetric process, acquiring 500 J of energy by heat. It then undergoes an isobaric process, losing this same amount of energy by heat. Determine the work done on the gas.- a)123 J
- b)231 J
- c)333 J
- d)200 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is at an initial temperature of 300 K. The gas undergoes an isovolumetric process, acquiring 500 J of energy by heat. It then undergoes an isobaric process, losing this same amount of energy by heat. Determine the work done on the gas.
a)
123 J
b)
231 J
c)
333 J
d)
200 J

|
Aniket Basu answered |
Explanation:
At const volume,
Q = 500 J
Q=nCPΔT
500=1×2.5×8.31ΔT
ΔT=24.06
W=nRΔT=1×8.31×24.06=200J
Four liters of a diatomic ideal gas ( λ =1.4) confined to a cylinder is subject to a closed cycle. Initially, the gas is at 1.00 atm and at 300 K. First, its pressure is tripled under constant volume. Then, it expands adiabatically to its original pressure. Finally, the gas is compressed isobarically to its original volume. Find the temperature at the end of the cycle- a)276 K
- b)285 K
- c)300 K
- d)332 K
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Four liters of a diatomic ideal gas ( λ
=1.4
) confined to a cylinder is subject to a closed cycle. Initially, the gas is at 1.00 atm and at 300 K. First, its pressure is tripled under constant volume. Then, it expands adiabatically to its original pressure. Finally, the gas is compressed isobarically to its original volume. Find the temperature at the end of the cyclea)
276 K
b)
285 K
c)
300 K
d)
332 K

|
Anshu Joshi answered |
According to Atomic Hypothesis: little particles of atom- a)attract each other when they are at small distance apart, but repel upon being squeezed into one another
- b)repel each other when they are at small distance apart, but attract upon being squeezed into one another
- c)repel each other when they are at small distance apart, but repel upon being squeezed into one another
- d)repel each other when they are at large distance apart, but attract upon being separated from one another
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Atomic Hypothesis: little particles of atom
a)
attract each other when they are at small distance apart, but repel upon being squeezed into one another
b)
repel each other when they are at small distance apart, but attract upon being squeezed into one another
c)
repel each other when they are at small distance apart, but repel upon being squeezed into one another
d)
repel each other when they are at large distance apart, but attract upon being separated from one another

|
Saikat Sharma answered |
Explanation:At room temperature (=300K) the noble gases are all in the gas phase, they are banging around and colliding into one another like little pool balls. At this temperature, when the atoms collide they appear to elastically bounce off of one another, but this bounce is actually a result of atomic repulsion. The atoms are traveling so fast and they approach each other so quickly that their momentum 'squeezes' them together until the atomic repulsion pushes them back apart.
From following list, how many of them upon catalytic hydrogenation would produce more heat than that produced in catalytic hydrogenation of frans-2-butene?
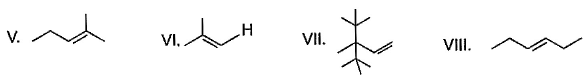
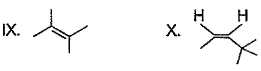
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
From following list, how many of them upon catalytic hydrogenation would produce more heat than that produced in catalytic hydrogenation of frans-2-butene?
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Correct answer is 4 because heat of hydrogenation is directly proportional to number of carbon atoms present in it
Which one of the following membranes secretes a watery fluid that lubricates and cushions the joint?- a)Tendons
- b)Synovial membrane
- c)Ligaments
- d)Cartilage
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following membranes secretes a watery fluid that lubricates and cushions the joint?
a)
Tendons
b)
Synovial membrane
c)
Ligaments
d)
Cartilage
|
|
Rishika Kaur answered |
Answer:
The correct answer is option 'B', the synovial membrane.
The synovial membrane is a specialized connective tissue membrane that lines the inner surface of joint cavities. It is responsible for secreting synovial fluid, a watery fluid that lubricates and cushions the joint.
Function of the synovial membrane:
The synovial membrane has several important functions in the joint:
1. Synovial fluid production: The synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid, which is a viscous, lubricating fluid. This fluid helps to reduce friction between the articular surfaces of the joint during movement.
2. Lubrication: The synovial fluid acts as a lubricant, allowing for smooth movement of the joint. It reduces friction and wear between the articulating surfaces of the bones.
3. Cushioning: The synovial fluid also acts as a shock absorber, providing cushioning and protecting the joint from excessive forces and impact during movement.
4. Nutrient supply: The synovial fluid carries nutrients to the articular cartilage, which does not have a direct blood supply. This helps to maintain the health and function of the cartilage.
5. Waste removal: The synovial fluid also helps to remove metabolic waste products from the joint, contributing to the overall health and function of the joint.
Composition of synovial fluid:
Synovial fluid is a clear, viscous fluid composed of several components, including:
1. Water: Water makes up the majority of synovial fluid, providing the fluidity and lubrication required for joint movement.
2. Hydrated hyaluronic acid: Hyaluronic acid is a high-molecular-weight glycosaminoglycan that helps to maintain the viscosity and lubricating properties of the synovial fluid.
3. Proteins: Synovial fluid contains various proteins, including albumin and globulins, which help to maintain the osmotic balance and provide nourishment to the articular cartilage.
4. Cells: The synovial fluid may contain a small number of white blood cells, which are responsible for the immune response and inflammation regulation within the joint.
In conclusion, the synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid, which plays a crucial role in lubricating and cushioning the joint. This fluid helps to reduce friction, protect the joint from excessive forces, provide nutrients to the cartilage, and remove waste products. The synovial membrane and synovial fluid are essential for maintaining the health and proper function of the joint.
The correct answer is option 'B', the synovial membrane.
The synovial membrane is a specialized connective tissue membrane that lines the inner surface of joint cavities. It is responsible for secreting synovial fluid, a watery fluid that lubricates and cushions the joint.
Function of the synovial membrane:
The synovial membrane has several important functions in the joint:
1. Synovial fluid production: The synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid, which is a viscous, lubricating fluid. This fluid helps to reduce friction between the articular surfaces of the joint during movement.
2. Lubrication: The synovial fluid acts as a lubricant, allowing for smooth movement of the joint. It reduces friction and wear between the articulating surfaces of the bones.
3. Cushioning: The synovial fluid also acts as a shock absorber, providing cushioning and protecting the joint from excessive forces and impact during movement.
4. Nutrient supply: The synovial fluid carries nutrients to the articular cartilage, which does not have a direct blood supply. This helps to maintain the health and function of the cartilage.
5. Waste removal: The synovial fluid also helps to remove metabolic waste products from the joint, contributing to the overall health and function of the joint.
Composition of synovial fluid:
Synovial fluid is a clear, viscous fluid composed of several components, including:
1. Water: Water makes up the majority of synovial fluid, providing the fluidity and lubrication required for joint movement.
2. Hydrated hyaluronic acid: Hyaluronic acid is a high-molecular-weight glycosaminoglycan that helps to maintain the viscosity and lubricating properties of the synovial fluid.
3. Proteins: Synovial fluid contains various proteins, including albumin and globulins, which help to maintain the osmotic balance and provide nourishment to the articular cartilage.
4. Cells: The synovial fluid may contain a small number of white blood cells, which are responsible for the immune response and inflammation regulation within the joint.
In conclusion, the synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid, which plays a crucial role in lubricating and cushioning the joint. This fluid helps to reduce friction, protect the joint from excessive forces, provide nutrients to the cartilage, and remove waste products. The synovial membrane and synovial fluid are essential for maintaining the health and proper function of the joint.
A meromyosin molecule doesn’t contain :- a)arm
- b)trunk
- c)tail
- d)head
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A meromyosin molecule doesn’t contain :
a)
arm
b)
trunk
c)
tail
d)
head
|
|
Rajesh Sengupta answered |
Understanding Meromyosin Structure
Meromyosin is a fragment of myosin, a crucial protein involved in muscle contraction. To comprehend what a meromyosin molecule contains or lacks, we must examine its structure closely.
Components of Myosin
- Myosin is typically composed of three main parts:
- Head: This portion binds to actin and has ATPase activity, facilitating muscle contractions.
- Tail: The tail region helps in dimerization and interacts with other myosin molecules, providing structural integrity to thick filaments.
- Arm: The arm connects the head to the tail, allowing flexibility and movement during contraction.
Defining Meromyosin
- Meromyosin is derived from myosin through limited proteolysis. It is generally divided into two parts:
- Heavy meromyosin (HMM): Contains the head and part of the tail.
- Light meromyosin (LMM): Comprises the remaining tail region.
Why Option B is Correct
- When examining the components of meromyosin, the term "trunk" is not a recognized structure within myosin or meromyosin.
- Therefore, in the context of the options provided:
- Arm: Present in meromyosin as it connects the head to the tail.
- Tail: Present in the form of heavy meromyosin.
- Head: Present as part of heavy meromyosin.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' (trunk), as meromyosin does not contain any structure referred to as a "trunk." Understanding these components is essential for grasping the mechanics of muscle contraction in the NEET syllabus.
Meromyosin is a fragment of myosin, a crucial protein involved in muscle contraction. To comprehend what a meromyosin molecule contains or lacks, we must examine its structure closely.
Components of Myosin
- Myosin is typically composed of three main parts:
- Head: This portion binds to actin and has ATPase activity, facilitating muscle contractions.
- Tail: The tail region helps in dimerization and interacts with other myosin molecules, providing structural integrity to thick filaments.
- Arm: The arm connects the head to the tail, allowing flexibility and movement during contraction.
Defining Meromyosin
- Meromyosin is derived from myosin through limited proteolysis. It is generally divided into two parts:
- Heavy meromyosin (HMM): Contains the head and part of the tail.
- Light meromyosin (LMM): Comprises the remaining tail region.
Why Option B is Correct
- When examining the components of meromyosin, the term "trunk" is not a recognized structure within myosin or meromyosin.
- Therefore, in the context of the options provided:
- Arm: Present in meromyosin as it connects the head to the tail.
- Tail: Present in the form of heavy meromyosin.
- Head: Present as part of heavy meromyosin.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' (trunk), as meromyosin does not contain any structure referred to as a "trunk." Understanding these components is essential for grasping the mechanics of muscle contraction in the NEET syllabus.
1 mole of a monoatomic gas is mixed with 3 moles of a diatomic gas. What is the molecular specific heat of the mixture at constant volume?- a)12.5 J / mol K
- b)18.7 J / mol K
- c)15.2 J / mol K
- d)22.6 J / mol K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
1 mole of a monoatomic gas is mixed with 3 moles of a diatomic gas. What is the molecular specific heat of the mixture at constant volume?
a)
12.5 J / mol K
b)
18.7 J / mol K
c)
15.2 J / mol K
d)
22.6 J / mol K

|
Aravind Saha answered |
Explanation:
for monoatomic gas
from conservation of energy
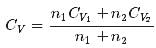
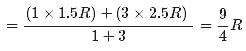
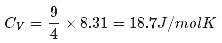
Actin filaments are found in all eukaryotic cells but reportedly absent in :- a)fish sperms
- b)both A & C
- c)nematode sperms
- d)human sperms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Actin filaments are found in all eukaryotic cells but reportedly absent in :
a)
fish sperms
b)
both A & C
c)
nematode sperms
d)
human sperms

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
Actin filament help in contraction and relaxation of muscles. Actin filament are found in all eukaryotic cells but it is absent in nematode sperms.
Read the following :
i. The synovial joints ischaracterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones.
ii. Saddle is a type of synovial joint- a)both are wrong
- b)Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.
- c)both are correct
- d)Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following :
i. The synovial joints ischaracterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones.
ii. Saddle is a type of synovial joint
i. The synovial joints ischaracterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones.
ii. Saddle is a type of synovial joint
a)
both are wrong
b)
Statement i) is correct and ii) is wrong.
c)
both are correct
d)
Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
|
|
Manasa Nair answered |
Explanation:
Statement i:
- The synovial joint is characterized by the presence of a fluid-filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones. This fluid helps to reduce friction between the bones during movement and provides nourishment to the joint structures.
Statement ii:
- Saddle is a type of synovial joint. A saddle joint is a type of synovial joint that allows movement in two planes, similar to the movement of a rider on a saddle. This type of joint is found in the thumb, specifically at the carpometacarpal joint.
Therefore, both statements are correct. The first statement describes a key feature of synovial joints, while the second statement correctly identifies the saddle joint as a type of synovial joint.
Statement i:
- The synovial joint is characterized by the presence of a fluid-filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones. This fluid helps to reduce friction between the bones during movement and provides nourishment to the joint structures.
Statement ii:
- Saddle is a type of synovial joint. A saddle joint is a type of synovial joint that allows movement in two planes, similar to the movement of a rider on a saddle. This type of joint is found in the thumb, specifically at the carpometacarpal joint.
Therefore, both statements are correct. The first statement describes a key feature of synovial joints, while the second statement correctly identifies the saddle joint as a type of synovial joint.
The vertebral formula of human is :- a)C7T11L5S(7)C(4)
- b)C8T12L4S(5)C(6)
- c)C6T12L6S(5)C(4)
- d)C7T12L5S(5)C(4)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The vertebral formula of human is :
a)
C7T11L5S(7)C(4)
b)
C8T12L4S(5)C(6)
c)
C6T12L6S(5)C(4)
d)
C7T12L5S(5)C(4)
|
|
Baishali Joshi answered |
Vertebral Formula of Humans
The vertebral formula refers to the number and type of vertebrae present in the human spine. It provides a standardized way of describing the arrangement of vertebrae in different regions of the spine. The correct vertebral formula for humans is option 'D': C7T12L5S(5)C(4).
Here is a breakdown of the vertebral formula and an explanation of each component:
1. C7: This indicates that there are 7 cervical vertebrae in the human spine. The cervical vertebrae are located in the neck region and are numbered from C1 to C7.
2. T12: This indicates that there are 12 thoracic vertebrae in the human spine. The thoracic vertebrae are located in the upper back region and are numbered from T1 to T12. These vertebrae are associated with the ribs.
3. L5: This indicates that there are 5 lumbar vertebrae in the human spine. The lumbar vertebrae are located in the lower back region and are numbered from L1 to L5. These vertebrae are the largest and support the weight of the upper body.
4. S(5): This indicates that there are 5 sacral vertebrae in the human spine. The sacral vertebrae are fused together to form the sacrum, which is a triangular bone located between the hip bones. The sacrum provides stability to the pelvis.
5. C(4): This indicates that there are 4 coccygeal vertebrae in the human spine. The coccygeal vertebrae are also fused together to form the coccyx, commonly known as the tailbone. The coccyx is a vestigial structure with no specific function in humans.
Therefore, the vertebral formula 'C7T12L5S(5)C(4)' accurately represents the arrangement of vertebrae in the human spine.
Conclusion:
The correct vertebral formula for humans is 'C7T12L5S(5)C(4)'. This formula indicates that humans have 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal vertebrae. Understanding the vertebral formula helps in accurately describing the anatomical structure and function of the human spine.
The vertebral formula refers to the number and type of vertebrae present in the human spine. It provides a standardized way of describing the arrangement of vertebrae in different regions of the spine. The correct vertebral formula for humans is option 'D': C7T12L5S(5)C(4).
Here is a breakdown of the vertebral formula and an explanation of each component:
1. C7: This indicates that there are 7 cervical vertebrae in the human spine. The cervical vertebrae are located in the neck region and are numbered from C1 to C7.
2. T12: This indicates that there are 12 thoracic vertebrae in the human spine. The thoracic vertebrae are located in the upper back region and are numbered from T1 to T12. These vertebrae are associated with the ribs.
3. L5: This indicates that there are 5 lumbar vertebrae in the human spine. The lumbar vertebrae are located in the lower back region and are numbered from L1 to L5. These vertebrae are the largest and support the weight of the upper body.
4. S(5): This indicates that there are 5 sacral vertebrae in the human spine. The sacral vertebrae are fused together to form the sacrum, which is a triangular bone located between the hip bones. The sacrum provides stability to the pelvis.
5. C(4): This indicates that there are 4 coccygeal vertebrae in the human spine. The coccygeal vertebrae are also fused together to form the coccyx, commonly known as the tailbone. The coccyx is a vestigial structure with no specific function in humans.
Therefore, the vertebral formula 'C7T12L5S(5)C(4)' accurately represents the arrangement of vertebrae in the human spine.
Conclusion:
The correct vertebral formula for humans is 'C7T12L5S(5)C(4)'. This formula indicates that humans have 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal vertebrae. Understanding the vertebral formula helps in accurately describing the anatomical structure and function of the human spine.
Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed. Ravi was diagnosed with myoglobin in his bloodstream. This had occurred due to :- a)myasthenia gravis
- b)muscle injury
- c)conversion of Hb into Mb
- d)Arthritis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed. Ravi was diagnosed with myoglobin in his bloodstream. This had occurred due to :
a)
myasthenia gravis
b)
muscle injury
c)
conversion of Hb into Mb
d)
Arthritis

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
Myoglobin is an iron and oxygen binding protein found in the muscle tissue of mammals. Presence of myoglobin in blood stream may be due to muscle injury of Ravi due to accident or sudden jerk.
The average kinetic energy of a molecule- a)is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
- b)is inversely proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
- c)is inversely proportional to the molecular mass of the gas
- d)is not dependent on absolute temperature of the gas
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The average kinetic energy of a molecule
a)
is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
b)
is inversely proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
c)
is inversely proportional to the molecular mass of the gas
d)
is not dependent on absolute temperature of the gas

|
Sanika Shaikh answered |
We know formula ,
E/N=(3/2)kbT
the average of kinectic energy per molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of gas.
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic). The number of molecules- a)is the same in all three vessels
- b)is the greatest in the vessel with neon
- c)is the greatest in the vessel with chlorine
- d)is the greatest in the vessel with uranium hexafluoride
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic). The number of molecules
a)
is the same in all three vessels
b)
is the greatest in the vessel with neon
c)
is the greatest in the vessel with chlorine
d)
is the greatest in the vessel with uranium hexafluoride

|
Sarthak Verma answered |
Explanation:Avogadro's law states that, "equal volumes of all gases, at the same temperature and pressure, have the same number of molecules".
In a 30.0-s interval, 500 hailstones strike a glass window with an area of 0.600 m2 at an angle of 45.0° to the window surface. Each hailstone has a mass of 5.00 g and a speed of 8.00 m/s. If the collisions are elastic, what is the pressure on the window?- a)1.97 Pa
- b)1.57 Pa
- c)1.13 Pa
- d)1.32 Pa
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a 30.0-s interval, 500 hailstones strike a glass window with an area of 0.600 m2 at an angle of 45.0° to the window surface. Each hailstone has a mass of 5.00 g and a speed of 8.00 m/s. If the collisions are elastic, what is the pressure on the window?
a)
1.97 Pa
b)
1.57 Pa
c)
1.13 Pa
d)
1.32 Pa

|
Kaavya Mukherjee answered |
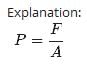
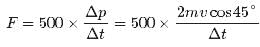
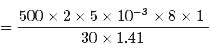
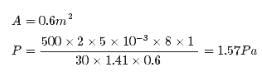
What is/are true regarding free radical iodination of an alkane?- a)It occurs very rapidly due to very small value of bond enthalpy of l2
- b)Direct iodination of alkane with l2 in the presence of light is impractical
- c)Iodination of an alkane can be achieved successfully using an oxidising agent catalyst
- d)Presence of some HCI activate the free radical iodination of alkane
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is/are true regarding free radical iodination of an alkane?
a)
It occurs very rapidly due to very small value of bond enthalpy of l2
b)
Direct iodination of alkane with l2 in the presence of light is impractical
c)
Iodination of an alkane can be achieved successfully using an oxidising agent catalyst
d)
Presence of some HCI activate the free radical iodination of alkane
|
|
Anirban Shah answered |
The statements (B) and (C) are true regarding free radical iodination of the alkane.
(B) Direct iodination of alkane with iodine in presence of light is impractical.
During this reaction, Hl, a strong reducing agent is obtained as byproduct, which catalyzes the reverse reaction thereby preventing direct iodination of alkane.
(C) Iodination of alkane can be achieved successfully using an oxidizing agent catalyst.
Presence of an oxidizing agent oxidizes unwanted byproduct Hl and enables iodination of alkane to proceed.
The number of degrees of freedom a monatomic molecule is- a)2
- b)1
- c)3.0
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of degrees of freedom a monatomic molecule is
a)
2
b)
1
c)
3.0
d)
4
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Explanation:Degrees of freedom of a system refers to the possible independent motions a system can have.Monoatomic gas molecule can have 3 independent motion and hence have 3 degrees of freedom (all are translational).
Kinetic theory- a)correctly explains specific heat capacities of many gases
- b)correctly explains specific heat capacities of super cooled liquids
- c)correctly explains specific heat capacities of many solids
- d)correctly explains specific heat capacities of many liquids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinetic theory
a)
correctly explains specific heat capacities of many gases
b)
correctly explains specific heat capacities of super cooled liquids
c)
correctly explains specific heat capacities of many solids
d)
correctly explains specific heat capacities of many liquids
|
|
Ishan Ghosh answered |
Explanation:
Kinetic Theory of Gases and Specific Heat Capacities:
The kinetic theory of gases is a model that describes the behavior of gases based on the motion of their particles. When it comes to specific heat capacities, the kinetic theory of gases correctly explains the specific heat capacities of many gases.
Specific Heat Capacities of Gases:
- According to the kinetic theory of gases, the specific heat capacity of a gas is related to the degrees of freedom of its molecules.
- The specific heat capacity of a gas depends on the translational, rotational, and vibrational motions of its molecules.
- The kinetic theory predicts that for monatomic gases, which have only translational motion, the specific heat capacity at constant volume is 3/2 R, where R is the gas constant.
- For diatomic gases, which can also rotate, the specific heat capacity at constant volume is 5/2 R.
Experimental Evidence:
- Experimental measurements of specific heat capacities of gases have been found to be in good agreement with the predictions of the kinetic theory.
- This provides strong evidence that the kinetic theory of gases correctly explains the specific heat capacities of many gases.
Therefore, option A is correct as the kinetic theory of gases correctly explains the specific heat capacities of many gases based on the motion of their particles.
The molecule of a monatomic gas has only three translational degrees of freedom. Thus, the average energy of a molecule at temperature 'T' is __________.- a)3kBT
- b)(1/3)kBT
- c)(3/2)kBT
- d)(3/4)kBT
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecule of a monatomic gas has only three translational degrees of freedom. Thus, the average energy of a molecule at temperature 'T' is __________.
a)
3kBT
b)
(1/3)kBT
c)
(3/2)kBT
d)
(3/4)kBT
|
|
Maulik Chakraborty answered |
Understanding Degrees of Freedom
In thermodynamics, the degrees of freedom of a molecule refer to the number of independent ways in which it can move. For a monatomic gas, the gas molecules can move in three-dimensional space, resulting in three translational degrees of freedom.
Energy and Temperature Relationship
The average energy of a molecule in a gas is related to its temperature through the equipartition theorem. This theorem states that each degree of freedom contributes an average energy of (1/2)kBT, where kB is the Boltzmann constant and T is the absolute temperature.
Calculation of Average Energy
Since a monatomic gas has three translational degrees of freedom, we can calculate the average energy as follows:
- Each degree of freedom contributes (1/2)kBT.
- Therefore, for three degrees of freedom:
- Total average energy = 3 * (1/2)kBT = (3/2)kBT.
Conclusion
Thus, the average energy of a molecule in a monatomic gas at temperature T is:
- (3/2)kBT.
This is why option 'C' is correct. The average energy reflects the kinetic energy associated with the translational motion of the gas molecules. Understanding these principles is crucial for grasping the behavior of gases in thermodynamics.
In thermodynamics, the degrees of freedom of a molecule refer to the number of independent ways in which it can move. For a monatomic gas, the gas molecules can move in three-dimensional space, resulting in three translational degrees of freedom.
Energy and Temperature Relationship
The average energy of a molecule in a gas is related to its temperature through the equipartition theorem. This theorem states that each degree of freedom contributes an average energy of (1/2)kBT, where kB is the Boltzmann constant and T is the absolute temperature.
Calculation of Average Energy
Since a monatomic gas has three translational degrees of freedom, we can calculate the average energy as follows:
- Each degree of freedom contributes (1/2)kBT.
- Therefore, for three degrees of freedom:
- Total average energy = 3 * (1/2)kBT = (3/2)kBT.
Conclusion
Thus, the average energy of a molecule in a monatomic gas at temperature T is:
- (3/2)kBT.
This is why option 'C' is correct. The average energy reflects the kinetic energy associated with the translational motion of the gas molecules. Understanding these principles is crucial for grasping the behavior of gases in thermodynamics.
Estimate the total number of air molecules (inclusive of oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor and other constituents) in a room of capacity 25.0 m3 at a temperature of 270C and 1 atm pressure.- a)6.50 x 1026
- b)6.60 x 1026
- c)6.10 x 1026
- d)6.30 x 1026
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Estimate the total number of air molecules (inclusive of oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor and other constituents) in a room of capacity 25.0 m3 at a temperature of 270C and 1 atm pressure.
a)
6.50 x
1026
b)
6.60 x
1026
c)
6.10 x
1026
d)
6.30 x
1026

|
Aniket Basu answered |
Two moles of an ideal gas (γ=1.4) expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What is the final pressure of the gas?- a)1.59 atm
- b)1.09 atm
- c)1.19 atm
- d)1.39 atm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two moles of an ideal gas (γ=1.4) expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What is the final pressure of the gas?
a)
1.59 atm
b)
1.09 atm
c)
1.19 atm
d)
1.39 atm

|
Anshu Joshi answered |
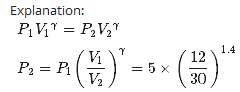
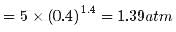
Chapter doubts & questions for January Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of January Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup