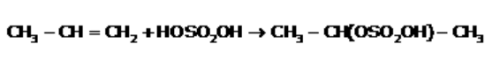All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of January Week 4 for NEET Exam
Find the amplitude of the S.H.M whose displacement y in cm is given by equation y= 3sin 157t +4cos157t where t is time in seconds.- a)20Hz
- b)25Hz
- c)50Hz
- d)40Hz
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the amplitude of the S.H.M whose displacement y in cm is given by equation y= 3sin 157t +4cos157t where t is time in seconds.
a)
20Hz
b)
25Hz
c)
50Hz
d)
40Hz

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
When the displacement of a SHM is:
y=a sin wt+ b cos wt
y=a sin wt+ b cos wt
- Amplitude of the SHM will be:
A=√a2+b2
Here, a = 3, b = 4
Amplitude, A= √(32+42) = 5 cm
Amplitude, A= √(32+42) = 5 cm
Hence option B is correct.
A second pendulum is mounted in a space shuttle. Its period of oscillations will decrease when rocket is- a)moving in geostationary orbit
- b)ascending up with uniform acceleration
- c)descending down with uniform acceleration
- d)moving up with uniform velocity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A second pendulum is mounted in a space shuttle. Its period of oscillations will decrease when rocket is
a)
moving in geostationary orbit
b)
ascending up with uniform acceleration
c)
descending down with uniform acceleration
d)
moving up with uniform velocity

|
Top Rankers answered |
- Time Period, T = 2π √(l/g')where,
l = Length of seconds pendulum
g’ = Apparent Gravity - For the period of oscillations of Seconds Pendulum to decrease, the Apparent gravity (g’) has to increase because:
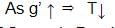
- Hence, Time Period of oscillations of Seconds Pendulum will decrease when the rocket is ascending up with uniform acceleration.
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-- a)Coordination of Cerebrum
- b)Involuntary activity of brain
- c)Coordination of Cerebellum
- d)Behaviour and emotional disturbances
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-
a)
Coordination of Cerebrum
b)
Involuntary activity of brain
c)
Coordination of Cerebellum
d)
Behaviour and emotional disturbances
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option A is correct becose, corpus callosam is trancverce connection between two cerebral hemisphears.. it helps in coordination between the two cerebral hemisphears..
If a simple pendulum oscillates with an amplitude 50 mm and time period 2s, then its maximum velocity isa)0.15 m/sb)0.1 m/sc)0.16 m/sd)0.8 m/sCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
We know that in a simple harmonic motion the maximum velocity,
Vmax = A⍵
Here A = 50 mm
Vmax = A⍵
Here A = 50 mm
And ⍵ = 2π / T
= 2π / 2
= π
= 2π / 2
= π
Hence Vmax = 50 x 10-3.π
= 0.15 m/s
= 0.15 m/s
Propene on ozonolysis forms:- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Formaldehyde
- c)Both acetaldehyde and formaldehyde
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Propene on ozonolysis forms:
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Formaldehyde
c)
Both acetaldehyde and formaldehyde
d)
Acetone
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
When propene on ozonolysis it yields a new structure called ozonide
and there cleavage takes place and it yields two products namely
1.acetaldehyde
2.formaldehyde
and there cleavage takes place and it yields two products namely
1.acetaldehyde
2.formaldehyde
What will be the phase difference between bigger pendulum (with time period 5T/4 )and smaller pendulum (with time period T) after one oscillation of bigger pendulum?- a)π/4
- b)π/2
- c)π/3
- d)π
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the phase difference between bigger pendulum (with time period 5T/4 )and smaller pendulum (with time period T) after one oscillation of bigger pendulum?
a)
π/4
b)
π/2
c)
π/3
d)
π
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
By the time bigger pendulum completes one vibration, the smaller pendulum would have completed 5/4 vibrations. That is smaller pendulum will be ahead by 1/4 vibration in phase. 1/4 vibration means λ/4 path or π/2 radians.
Ethylene reacts with HBr to give:- a)Acetylene
- b)Ethyl alcohol
- c)Acetaldehyde
- d)Ethyl bromide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethylene reacts with HBr to give:
a)
Acetylene
b)
Ethyl alcohol
c)
Acetaldehyde
d)
Ethyl bromide
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Ethylene reacts with HBr to form Ethyl bromide. The reaction propagates as follow:-
H2C=CH2 + HBr → H2C+-CH3 →H2BrC-CH3
Since π cloud is electron rich, so HBr dissociates into H+ and Br-. H+ attacks on alkene to give a carbocation and then Br- attacks to get ethyl bromide.
H2C=CH2 + HBr → H2C+-CH3 →H2BrC-CH3
Since π cloud is electron rich, so HBr dissociates into H+ and Br-. H+ attacks on alkene to give a carbocation and then Br- attacks to get ethyl bromide.
Ethene and ethyne can be distinguished by:- a)Bromine water
- b)KMnO4 solution
- c)Ammoniacal Cuprous chloride solution
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethene and ethyne can be distinguished by:
a)
Bromine water
b)
KMnO4 solution
c)
Ammoniacal Cuprous chloride solution
d)
Any of the above
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The two hydrocarbons can be easily distinguished by simple chemical tests, as ethyne molecule is supposed to have acidic hydrogen.
1. When ethyne is bubbled through ammoniacal silver nitrate solution , a yellow-white precipitate of silver acetylide would be formed.
C2H2 + 2AgNO3 = Ag2C2 + 2HNO3
2. Similarly, ethyne forms a red precipitate of copper acetylide (Cu2C2) when it is passed through ammoniacal cuprous chloride solution.
Ethene does not react with AgNO3 or Cu2Cl2 solution.
A frequency of 1Hz corresponds to:- a)2 vibrations per second
- b)1 vibration per second
- c)10 vibrations per second
- d)a time period of ½ second
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A frequency of 1Hz corresponds to:
a)
2 vibrations per second
b)
1 vibration per second
c)
10 vibrations per second
d)
a time period of ½ second
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Frequency used to be measured in cycles per second, but now we use the unit of frequency - the Hertz (abbreviated Hz). One Hertz (1Hz) is equal to one vibration per second. So the weight above is bouncing with a frequency of about 1Hz. The sound wave corresponding to Middle C on a piano is around 256Hz.
A particle executes linear simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 2 cm. When the particle is at 1 cm from the mean position, the magnitude of its velocity is equal to that of its acceleration. Then its time period in seconds is:- a)2π/√3
- b)2π√3
- c)√3/2π
- d)1/ 2π√3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle executes linear simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 2 cm. When the particle is at 1 cm from the mean position, the magnitude of its velocity is equal to that of its acceleration. Then its time period in seconds is:
a)
2π/√3
b)
2π√3
c)
√3/2π
d)
1/ 2π√3
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
velocity at distance x in shm is given as
v= w sqrt(A2-x2)
so A = 2 x =1
v = w sqrt(4-1) = wsqrt3
now acc at distance x is a= w2 x = w2
as mag a = mag v
w2 = wsqrt3
w= sqrt3
2pi/T= sqrt3
T = 2pi/sqrt3
Cis isomer have:- a)High boiling point than trans isomer
- b)Lower boiling point than trans isomer
- c)Same boiling point
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cis isomer have:
a)
High boiling point than trans isomer
b)
Lower boiling point than trans isomer
c)
Same boiling point
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The cis isomer in this case has a boiling point of 60.3 degC, while the trans isomer has a boiling point of 47.5 degC. In the cis isomer the two polar C-Cl bond dipole moments combine to give an overall molecular dipole, so that there are intermolecular dipole–dipole forces (or Keesom forces), which add to the London.
Addition of halogens to alkenes is an example of:- a)Nucleophilic addition reaction
- b)Electrophilic addition reaction
- c)Electrophilic substitution reaction
- d)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Addition of halogens to alkenes is an example of:
a)
Nucleophilic addition reaction
b)
Electrophilic addition reaction
c)
Electrophilic substitution reaction
d)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction

|
Avantika Chakraborty answered |
Halogens can act as electrophiles to attack a double bond in alkene. Double bond represents a region of electron density and therefore functions as a nucleophile.
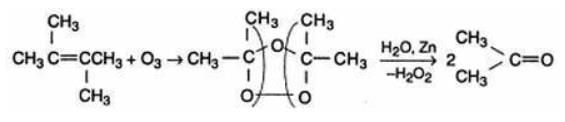
The alkene which on ozonolysis gives only acetone is:- a)(CH3)2C = CH2
- b)CH3CH = CHCH3
- c)CH3CH = C(CH3)2
- d)(CH3)2C = C(CH3)2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The alkene which on ozonolysis gives only acetone is:
a)
(CH3)2C = CH2
b)
CH3CH = CHCH3
c)
CH3CH = C(CH3)2
d)
(CH3)2C = C(CH3)2

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
The reductive ozaonalysis of 2,3 -Dimethyl-2-butene yields acetone.The reaction is as follows: 2,3 -Dimethyl-2-butene acetone
When H+ attacks CH3 – CH = CH2 , carbonation which is more stable is- a)CH3 – CH2 – CH2
- b)CH2+ – CH2 – CH3
- c)CH3 – CH+ – CH2
- d)CH3 – CH2 – CH2+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When H+ attacks CH3 – CH = CH2 , carbonation which is more stable is
a)
CH3 – CH2 – CH2
b)
CH2+ – CH2 – CH3
c)
CH3 – CH+ – CH2
d)
CH3 – CH2 – CH2+
|
|
Nitin Khanna answered |
CH3 – CH = CH2 → CH3 – CH+ – CH2
The reason for this is only that carbocation is formed which has maximum stability. In this case, we have 6 α-H while for option a, b and d; we have 0, 2 and 2 α-H respectively. So only carbocation in option c forms.
The reason for this is only that carbocation is formed which has maximum stability. In this case, we have 6 α-H while for option a, b and d; we have 0, 2 and 2 α-H respectively. So only carbocation in option c forms.
Photochemical chlorination of alkane is initiated by process called:- a)Homolysis
- b)Pyrolysis
- c)Substitution
- d)Peroxidation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Photochemical chlorination of alkane is initiated by process called:
a)
Homolysis
b)
Pyrolysis
c)
Substitution
d)
Peroxidation
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Photochemical chlorination of alkane take place by free radical mechanism which are possible by Homolysis of C - C bond
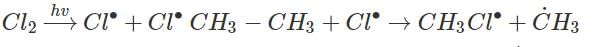
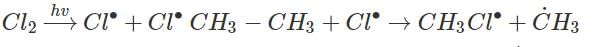
The membrane which cover the brain and the spinal cord is :-
- a)White matter
- b)Grey matter
- c)Peritonium
- d)Meninges
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The membrane which cover the brain and the spinal cord is :-
a)
White matter
b)
Grey matter
c)
Peritonium
d)
Meninges

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Meninges are the membranes that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord. There are three layers of meanings: dura mater (closest to the bone), arachnoid (loosely around the brain), pia mater (closely attached to the brain and spinal cord surface).
Which of the following is a richly vascular layer with lots of blood capillaries :-- a)Duramater
- b)Piamater
- c)Epidermis of skin
- d)Both (1) & (2)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a richly vascular layer with lots of blood capillaries :-
a)
Duramater
b)
Piamater
c)
Epidermis of skin
d)
Both (1) & (2)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The pia mater of the brain is the innermost of the three membranes, that cover it. It is the vascular membrane of the brain. It carries the minute branches of the two internal carotids and the two vertebral arteries. It also returns the blood to the heart. The dura mater is the most external membrane of the brain. It forms the internal periosteum of the skull. The dura mater is a dense, tough, inelastic fibrous membrane. The epidermis contains no blood vessels, and cells in the deepest layers are nourished by diffusion from blood capillaries extending to the upper layers of the dermis. So, the correct answer is option B.
Corpus callosum connects :-- a)Two cerebral hemisphere
- b)Two optic lobes
- c)Two olfactory lobes
- d)Optic chiasma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Corpus callosum connects :-
a)
Two cerebral hemisphere
b)
Two optic lobes
c)
Two olfactory lobes
d)
Optic chiasma
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The part of the brain that connects the two hemispheres of the brain is called the corpus callosum. It contains a bundle of neuronal fibers found in humans and other higher order mammals that allow the two hemispheres to talk to one another.
The velocity of a particle moving with simple harmonic motion is . . . . at the mean position.- a)Zero
- b)Minimum
- c)Maximum
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The velocity of a particle moving with simple harmonic motion is . . . . at the mean position.
a)
Zero
b)
Minimum
c)
Maximum
d)
None of the above
|
|
Niharika Nair answered |
V = ω√(A2 – x2)
So the velocity is maximum at mean position
So the velocity is maximum at mean position
Where is the midbrain located?- a)Between hypothalamus and pons
- b)Between cerebrum and hypothalamus
- c)Between cerebellum and medulla
- d)Between pons and medulla
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where is the midbrain located?
a)
Between hypothalamus and pons
b)
Between cerebrum and hypothalamus
c)
Between cerebellum and medulla
d)
Between pons and medulla

|
Top Rankers answered |
The midbrain is located between the hypothalamus of the forebrain and the pons of the hindbrain. The midbrain is also known as the mesencephalon and controls several motor movements.
Which part of the neuron is present in a high concentration in the grey matter?- a)Cell body
- b)Axon
- c)Dendrites
- d)Synaptic knobs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the neuron is present in a high concentration in the grey matter?
a)
Cell body
b)
Axon
c)
Dendrites
d)
Synaptic knobs
|
|
Gayatri Desai answered |
Grey Matter and Neurons
Grey matter is a type of neural tissue found in the brain and spinal cord. It consists of cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses, and appears grey due to the presence of unmyelinated axons and glial cells. Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system and they transmit information through electrical impulses.
Concentration of Cell Bodies in Grey Matter
The grey matter contains a high concentration of cell bodies compared to other parts of the neuron. The cell body, also known as the soma or perikaryon, is the main part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and various organelles necessary for cellular functions. It is responsible for maintaining the metabolic and structural integrity of the neuron.
Functions of Cell Bodies
The cell body plays several important roles in the neuron:
1. Protein synthesis: The cell body contains ribosomes and other organelles involved in protein synthesis. It produces proteins that are essential for the survival and functioning of the neuron.
2. Metabolism: The cell body generates energy and metabolizes various substances required for neuronal processes. It produces ATP through cellular respiration to fuel the neuron's activities.
3. Integration of information: The cell body receives signals from dendrites and processes them. It integrates these signals and determines whether to transmit or inhibit the electrical impulse.
4. Structural support: The cell body provides structural support to the neuron by giving it its shape and stability. It also connects to other neurons through synapses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell body is present in a high concentration in the grey matter. It is responsible for various vital functions such as protein synthesis, metabolism, integration of information, and structural support. Understanding the distribution and functions of different parts of the neuron, including the cell body, is essential in comprehending the complexity of the nervous system and its role in various physiological processes.
Grey matter is a type of neural tissue found in the brain and spinal cord. It consists of cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses, and appears grey due to the presence of unmyelinated axons and glial cells. Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system and they transmit information through electrical impulses.
Concentration of Cell Bodies in Grey Matter
The grey matter contains a high concentration of cell bodies compared to other parts of the neuron. The cell body, also known as the soma or perikaryon, is the main part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and various organelles necessary for cellular functions. It is responsible for maintaining the metabolic and structural integrity of the neuron.
Functions of Cell Bodies
The cell body plays several important roles in the neuron:
1. Protein synthesis: The cell body contains ribosomes and other organelles involved in protein synthesis. It produces proteins that are essential for the survival and functioning of the neuron.
2. Metabolism: The cell body generates energy and metabolizes various substances required for neuronal processes. It produces ATP through cellular respiration to fuel the neuron's activities.
3. Integration of information: The cell body receives signals from dendrites and processes them. It integrates these signals and determines whether to transmit or inhibit the electrical impulse.
4. Structural support: The cell body provides structural support to the neuron by giving it its shape and stability. It also connects to other neurons through synapses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell body is present in a high concentration in the grey matter. It is responsible for various vital functions such as protein synthesis, metabolism, integration of information, and structural support. Understanding the distribution and functions of different parts of the neuron, including the cell body, is essential in comprehending the complexity of the nervous system and its role in various physiological processes.
The box like bony structure which encloses the brain is called :-- a)Cranium
- b)Pericardium
- c)Peritoneum
- d)Periosteum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The box like bony structure which encloses the brain is called :-
a)
Cranium
b)
Pericardium
c)
Peritoneum
d)
Periosteum

|
Ramesh Chand answered |
The box enclosing and protecting the brain is called as the cranium . The cranium is the part of the skull, that encloses the brain. Therefore option A is the correct answer.
Cerebellum is concerned with :-- a)Co-ordination of muscular movement
- b)Memory
- c)Vision
- d)Reflex action
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cerebellum is concerned with :-
a)
Co-ordination of muscular movement
b)
Memory
c)
Vision
d)
Reflex action
|
|
Sanjana Singh answered |
Cerebellum is a part of the brain and is responsible for motor control which includes muscle movement , equilibrium and balance as it relates to movement .
So 'a' is correct.
So 'a' is correct.
The periodic time (tp) is given by- a)ω / 2 π
- b)2 π / ω
- c)2 π × ω
- d)π/ω
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The periodic time (tp) is given by
a)
ω / 2 π
b)
2 π / ω
c)
2 π × ω
d)
π/ω
|
|
Divyansh Saha answered |
Periodic time is the time taken for one complete revolution of the particle.
∴ Periodic time, tp = 2 π/ω seconds.
∴ Periodic time, tp = 2 π/ω seconds.
Vicinal and geminal dihalides are not distinguished by:- a)KCN/hydrolysis
- b)Alcoholic KOH
- c)Aq.KOH/Tollen's reagent
- d)Both A and B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vicinal and geminal dihalides are not distinguished by:
a)
KCN/hydrolysis
b)
Alcoholic KOH
c)
Aq.KOH/Tollen's reagent
d)
Both A and B
|
|
Parth Jain answered |
Introduction:
Vicinal and geminal dihalides are types of organic compounds that contain two halogen atoms (such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine) attached to adjacent or same carbon atoms, respectively. These compounds can be distinguished by various chemical reactions. However, in this case, we need to determine which of the given reactions does not differentiate between vicinal and geminal dihalides.
Explanation:
KCN/hydrolysis:
- Vicinal dihalides, which have halogen atoms attached to adjacent carbon atoms, can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with KCN (potassium cyanide) followed by hydrolysis.
- This reaction leads to the formation of a nitrile (RCN) when the halogen atoms are attached to different carbon atoms.
- On the other hand, geminal dihalides, which have halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom, do not undergo this reaction as there is no adjacent carbon atom to react with KCN.
- Therefore, this reaction can be used to distinguish vicinal and geminal dihalides.
Alcoholic KOH:
- Alcoholic KOH (potassium hydroxide) is used to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides.
- It promotes the elimination reaction known as the E2 mechanism.
- In the case of vicinal dihalides, both halogen atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atoms, and the reaction with alcoholic KOH can lead to the formation of an alkene.
- However, geminal dihalides, which have halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom, do not undergo this reaction as there is no adjacent carbon atom to eliminate a halide from.
- Therefore, this reaction can also be used to distinguish vicinal and geminal dihalides.
Aq. KOH/Tollens reagent:
- Aq. KOH (aqueous potassium hydroxide) and Tollens reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate) are used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
- Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids by Tollens reagent, whereas ketones do not react.
- Neither vicinal nor geminal dihalides are aldehydes or ketones, so this reaction is not relevant to distinguishing between them.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reaction with alcoholic KOH (option B) does not distinguish between vicinal and geminal dihalides. Both vicinal and geminal dihalides do not undergo elimination reactions with alcoholic KOH, as geminal dihalides lack adjacent carbon atoms. The other reactions mentioned (KCN/hydrolysis and aq. KOH/Tollens reagent) can be used to differentiate between vicinal and geminal dihalides based on their reactivity.
Vicinal and geminal dihalides are types of organic compounds that contain two halogen atoms (such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine) attached to adjacent or same carbon atoms, respectively. These compounds can be distinguished by various chemical reactions. However, in this case, we need to determine which of the given reactions does not differentiate between vicinal and geminal dihalides.
Explanation:
KCN/hydrolysis:
- Vicinal dihalides, which have halogen atoms attached to adjacent carbon atoms, can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with KCN (potassium cyanide) followed by hydrolysis.
- This reaction leads to the formation of a nitrile (RCN) when the halogen atoms are attached to different carbon atoms.
- On the other hand, geminal dihalides, which have halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom, do not undergo this reaction as there is no adjacent carbon atom to react with KCN.
- Therefore, this reaction can be used to distinguish vicinal and geminal dihalides.
Alcoholic KOH:
- Alcoholic KOH (potassium hydroxide) is used to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides.
- It promotes the elimination reaction known as the E2 mechanism.
- In the case of vicinal dihalides, both halogen atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atoms, and the reaction with alcoholic KOH can lead to the formation of an alkene.
- However, geminal dihalides, which have halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom, do not undergo this reaction as there is no adjacent carbon atom to eliminate a halide from.
- Therefore, this reaction can also be used to distinguish vicinal and geminal dihalides.
Aq. KOH/Tollens reagent:
- Aq. KOH (aqueous potassium hydroxide) and Tollens reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate) are used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
- Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids by Tollens reagent, whereas ketones do not react.
- Neither vicinal nor geminal dihalides are aldehydes or ketones, so this reaction is not relevant to distinguishing between them.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reaction with alcoholic KOH (option B) does not distinguish between vicinal and geminal dihalides. Both vicinal and geminal dihalides do not undergo elimination reactions with alcoholic KOH, as geminal dihalides lack adjacent carbon atoms. The other reactions mentioned (KCN/hydrolysis and aq. KOH/Tollens reagent) can be used to differentiate between vicinal and geminal dihalides based on their reactivity.
Chapter doubts & questions for January Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of January Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily