All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of May Week 1 for NEET Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of cylindrical vessel whose height is equal to its radius. The electric flux of electric field of charge q through the surface of the vessel is- A:0
- B:
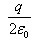
- C:
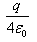
- D:
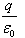
The answer is b.
A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of cylindrical vessel whose height is equal to its radius. The electric flux of electric field of charge q through the surface of the vessel is
A:
0
B:
C:
D:
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Given that, A charge q is placed at the centre of open end Q a cylindrical vessel,we have to find the flux through the surface of the vessel.
so, when charge Q is placed at the centre of open end of a cylindrical vessel then only half of the charge will contribute to the flux, because half will lie inside the surface and half will lie outside the surface.
so, flux through the surface of vessel is q/2ε0
so, when charge Q is placed at the centre of open end of a cylindrical vessel then only half of the charge will contribute to the flux, because half will lie inside the surface and half will lie outside the surface.
so, flux through the surface of vessel is q/2ε0
If the electric field is given by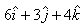 ; calculate the electric flux through as surface of area 10 units lying in y-z plane.
; calculate the electric flux through as surface of area 10 units lying in y-z plane.- a)50 units
- b)40 units
- c)60 units
- d)30 units
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the electric field is given by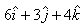 ; calculate the electric flux through as surface of area 10 units lying in y-z plane.
; calculate the electric flux through as surface of area 10 units lying in y-z plane.
a)
50 units
b)
40 units
c)
60 units
d)
30 units

|
EduRev JEE answered |
As surface of area lies in the Y-Z plane, thus its area vector points in X direction i.e. A=10i
Electric flux ϕ=E.A
∴ ϕ=(6i+3j+4k).(10i)
⟹ ϕ=6×10=60 unit
Electric flux ϕ=E.A
∴ ϕ=(6i+3j+4k).(10i)
⟹ ϕ=6×10=60 unit
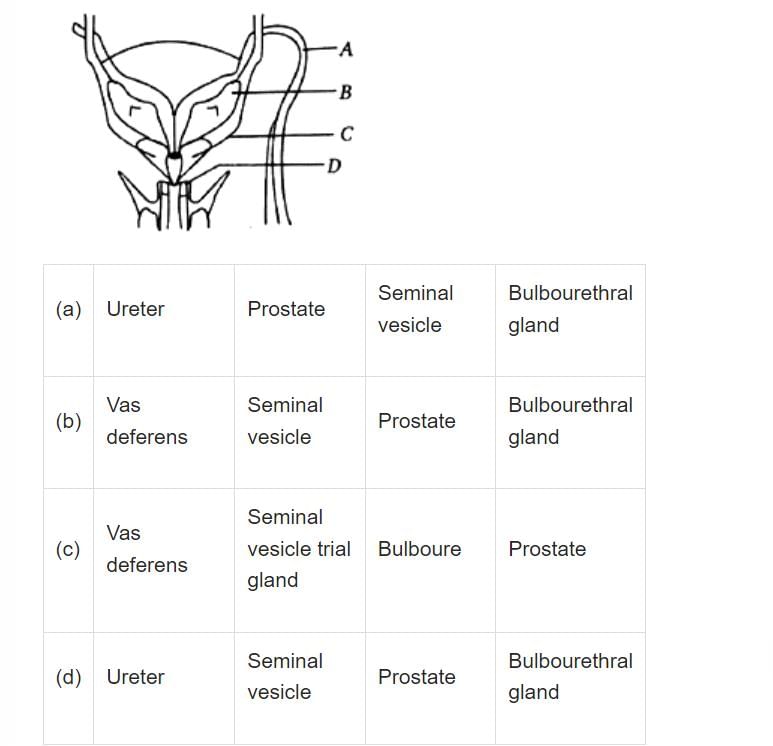
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland- a)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
a)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Kiran Singh answered |
Contributors to Seminal Plasma
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen that carries sperm. It is composed of a mixture of secretions from various male reproductive organs. The following are the contributors of seminal plasma:
(i) Seminal Vesicle - The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands that secrete a fluid that makes up 60-70% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains fructose, prostaglandins, and other substances that provide energy to the sperm and help them survive in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Prostate - The prostate gland is a single gland located below the bladder that produces a milky fluid that makes up about 15-30% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains enzymes, citric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation.
(iii) Urethra - The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and carries semen and urine out of the body. It contributes a small amount of fluid to the seminal plasma.
(iv) Bulbourethral Gland - The bulbourethral gland, also known as Cowper's gland, is a pair of small glands located at the base of the penis. They secrete a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidic urine remaining in the urethra.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seminal plasma is a mixture of secretions from different male reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, and bulbourethral gland. The various secretions work together to provide energy to the sperm, help them survive in the female reproductive tract, and ensure that the semen can be ejaculated and transported effectively.
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen that carries sperm. It is composed of a mixture of secretions from various male reproductive organs. The following are the contributors of seminal plasma:
(i) Seminal Vesicle - The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands that secrete a fluid that makes up 60-70% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains fructose, prostaglandins, and other substances that provide energy to the sperm and help them survive in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Prostate - The prostate gland is a single gland located below the bladder that produces a milky fluid that makes up about 15-30% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains enzymes, citric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation.
(iii) Urethra - The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and carries semen and urine out of the body. It contributes a small amount of fluid to the seminal plasma.
(iv) Bulbourethral Gland - The bulbourethral gland, also known as Cowper's gland, is a pair of small glands located at the base of the penis. They secrete a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidic urine remaining in the urethra.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seminal plasma is a mixture of secretions from different male reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, and bulbourethral gland. The various secretions work together to provide energy to the sperm, help them survive in the female reproductive tract, and ensure that the semen can be ejaculated and transported effectively.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:At what point is the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell is maximum?
- A:
at the surface of spherical shell
- B:
outside the spherical shell
- C:
inside the spherical shell
- D:
at the centre of spherical shell
The answer is a.
At what point is the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell is maximum?
at the surface of spherical shell
outside the spherical shell
inside the spherical shell
at the centre of spherical shell

|
Bittu Raj Bittu answered |
This is because of when a charge given to a hollow sphere that is spherical shell then all charges will reside on its surface and as we know that electric field is directly proportional to given charge . so according to this concept we can say about this point.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The electric field intensity due to a sphere (solid or hollow) at an external point varies as-
- A:
1/r
- B:
does not depend upon r
- C:
1/r3
- D:
1/r2
The answer is d.
The electric field intensity due to a sphere (solid or hollow) at an external point varies as-
1/r
does not depend upon r
1/r3
1/r2
|
|
Agnal Jose answered |
It followw inverse square law as distance of observational point from source charge increases the electric field intensity decreases hence option d is correct
When common salt is dissolved in water:- a)Melting point of solution increases
- b)Boiling point of solution increases
- c)Boiling point of solution decreases
- d)both melting .point and boiling point decreases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When common salt is dissolved in water:
a)
Melting point of solution increases
b)
Boiling point of solution increases
c)
Boiling point of solution decreases
d)
both melting .point and boiling point decreases
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
So the boiling point of water will increase. When salt is added to water, then the intermolecular forces between water molecules gets altered due to dissociation of NaCl into sodium and chloride ions.
If an excess charge is placed on an isolated conductor, then, that amount of charge- a)gets neutralized.
- b)resides on the surface of conductor.
- c)either resides on the surface of conductor or gets neutralized.
- d)move inside the conductor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an excess charge is placed on an isolated conductor, then, that amount of charge
a)
gets neutralized.
b)
resides on the surface of conductor.
c)
either resides on the surface of conductor or gets neutralized.
d)
move inside the conductor
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
An isolated conductor is any metal object not connected to or not in contact with any other conductor . one of its common properties is that there is no charge of any nature within the surface of the conductor. All charge, if any, always resides on the outer surface only.thus , if we place any amount of charge, it would tend to reside on its surface.
Which of the two has lower freezing point, 2m NaCl or 5m NaCl aqueous solution?- a)2m NaCl solution
- b)Both have same freezing point
- c)5m NaCl solution
- d)The solutions cannot freeze
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the two has lower freezing point, 2m NaCl or 5m NaCl aqueous solution?
a)
2m NaCl solution
b)
Both have same freezing point
c)
5m NaCl solution
d)
The solutions cannot freeze
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The correct answer is option C
ΔTf= Kf x m Since ΔTf for 5m NaCl will be higher than for 2m, 5m NaCl solution freezes at a lower temperature.
ΔTf= Kf x m Since ΔTf for 5m NaCl will be higher than for 2m, 5m NaCl solution freezes at a lower temperature.
The molal elevation constant is the elevation in boiling point of- a)1M solution
- b)1m solution
- c)1N solution
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molal elevation constant is the elevation in boiling point of
a)
1M solution
b)
1m solution
c)
1N solution
d)
None of the above
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Molal elevation constant is a characteristic constant for a given solvent. It is the elevation of boiling point produced when one mole of solute is dissolved in 1 kg of solvent. The proportionality constant, Kb, is called the molal boiling point elevation constant. It is a constant that is equal to the change in the boiling point for a 1-molal solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute.
Molal elevation constant is a characteristic constant for a given solvent. It is the elevation of boiling point produced when one mole of solute is dissolved in 1 kg of solvent. The proportionality constant, Kb, is called the molal boiling point elevation constant. It is a constant that is equal to the change in the boiling point for a 1-molal solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute.
If the vapour pressure of pure solvent A is 17.5 mm and lowering of vapour pressure of solution formed by adding a non-volatile electrolyte is 0.0175 mm then what is the relative lowering of vapour pressure?- a)0.1
- b)1.01
- c)0.001
- d)0.01
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the vapour pressure of pure solvent A is 17.5 mm and lowering of vapour pressure of solution formed by adding a non-volatile electrolyte is 0.0175 mm then what is the relative lowering of vapour pressure?
a)
0.1
b)
1.01
c)
0.001
d)
0.01
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is option C
Relative lowering of vapour pressure:
= lowering of vapour pressure of solution/ vapour pressure of pure solvent
=0.0175/17.5=0.001
Relative lowering of vapour pressure:
= lowering of vapour pressure of solution/ vapour pressure of pure solvent
=0.0175/17.5=0.001
The Gaussian surface for a point charge will be- a)Cube
- b)Cylinder
- c)Sphere
- d)Cuboid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Gaussian surface for a point charge will be
a)
Cube
b)
Cylinder
c)
Sphere
d)
Cuboid
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The electric field of a sphere of uniform charge density and total charge charge Q can be obtained by applying Gauss' law. Considering a Gaussian surface in the form of a sphere at radius r > R, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the surface and is directed outward.
The Gaussian surface for a line charge will be- a)Sphere
- b)Cylinder
- c)Cube
- d)Cuboid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Gaussian surface for a line charge will be
a)
Sphere
b)
Cylinder
c)
Cube
d)
Cuboid
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Electric Field of Line Charge. The electric field of an infinite line charge with a uniform linear charge density can be obtained by a using Gauss' law. Considering a Gaussian surface in the form of a cylinder at radius r, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the cylinder and is directed outward.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The flux associated with a spherical surface is 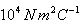 . What will be the flux, if the radius of the spherical shell is doubled?
. What will be the flux, if the radius of the spherical shell is doubled?
- A:
it will remains unchanged.
- B:
It will be the half of the previous one.
- C:
It will become zero.
- D:
It will also get doubled.
The answer is a.
The flux associated with a spherical surface is . What will be the flux, if the radius of the spherical shell is doubled?
it will remains unchanged.
It will be the half of the previous one.
It will become zero.
It will also get doubled.
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Electric flux is directly proportional to the number of electric field lines passing through a surface. The number of field lines passing through a surface become 1/4th when radius of the Gaussian surface is doubled, but at the same time, the surface area has increased 4 fold, so the electric flux remains unchanged
Which of the following is a colligative property?- a)Molality
- b)Viscosity
- c)Relative lowering of vapour pressure
- d)Surface tension
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a colligative property?
a)
Molality
b)
Viscosity
c)
Relative lowering of vapour pressure
d)
Surface tension
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Colligative properties- The properties that depend upon the ratio of the number of solute molecules and total molecules not upon the nature of solute molecules named as colligative properties.
Example- Osmotic pressure, elevation of boiling point, depression in freezing point and relative lowering of vapour pressure.
Which of the following unit of concertration is independent of temperature?- a)Molarity
- b)Molality
- c)Mole fraction
- d)all
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following unit of concertration is independent of temperature?
a)
Molarity
b)
Molality
c)
Mole fraction
d)
all

|
Kritika Singh answered |
Those concentration terms which involve volume are temperature dependent while those which not involve volume are temperature independent....
A solution was made by dissolving 2 g of a solute in 100 g of acetone. The solution boiled at 56.95° C. The boiling point of pure acetone is 55.95° C, and the Kb =1.71°C/m. What is the molecular weight of the solute?- a)22 g
- b)34.2 g
- c)42.3 g
- d)30 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution was made by dissolving 2 g of a solute in 100 g of acetone. The solution boiled at 56.95° C. The boiling point of pure acetone is 55.95° C, and the Kb =1.71°C/m. What is the molecular weight of the solute?
a)
22 g
b)
34.2 g
c)
42.3 g
d)
30 g
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
∆Tb =(Kb × 1000 × W2) / M2 × W1
⇒ M2 = (Kb × 1000 × W2) / ∆Tb × W1
= (1.71 × 1000 × 2) / 1 × 100
= 34.2g
∆Tb =(Kb × 1000 × W2) / M2 × W1
⇒ M2 = (Kb × 1000 × W2) / ∆Tb × W1
= (1.71 × 1000 × 2) / 1 × 100
= 34.2g
The colligative properties of a solution are- a)Proportional to the number of solute particles present
- b)Proportional to percentage of solute
- c)Proportional to normality of solution
- d)Proportional to volume of solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The colligative properties of a solution are
a)
Proportional to the number of solute particles present
b)
Proportional to percentage of solute
c)
Proportional to normality of solution
d)
Proportional to volume of solution

|
Swara Mukherjee answered |
It is also a colligative property and depends on the number of solute molecules and not their identity. For dilute solutions, osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the molarity (C) of the solution at a given temperature (T).
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. This is necessary as:- a)The scrotum can contain lengthy ducts for the transfer of sperms
- b)Scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes necessary for spermatogenesis
- c)Scrotum reduces the pressure around testes necessary for spermatogenesis
- d)Scrotum can store huge amounts of sperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. This is necessary as:
a)
The scrotum can contain lengthy ducts for the transfer of sperms
b)
Scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes necessary for spermatogenesis
c)
Scrotum reduces the pressure around testes necessary for spermatogenesis
d)
Scrotum can store huge amounts of sperms
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. The scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes (2-2.5°C lower than the normal internal body temperature) necessary for spermatogenesis.
Hence, the Correct Answer is B
NCERT Reference: page no. 43 topic “3.1 THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ” of chapter 3 of NCERT
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland- a)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
a)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)

|
Sravya Datta answered |
The male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate and paired bulb urethral glands. Secretions of these glands constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes. The secretions of bulbourethral glands also helps in the lubrication of the penis. Urethra is the duct that extends through the penis in male reproductive system and serve a common passage for both sperm and urine. In female, urethra has no reproductive function.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following quantity is a scalar?
- A:
Torque
- B:
Dipole moment
- C:
Electric Flux
- D:
Electric Field Intensity
The answer is c.
Which of the following quantity is a scalar?
Torque
Dipole moment
Electric Flux
Electric Field Intensity

|
Shivani answered |
Yeah scalar is electric flux...as it is the dot product of Electric field "E"✗ section areaA....FLUX=E.A Torque=r×F(((cross product of perpendiculr dis &force.)))....vector... dipole moment &electric field r also vectors...
The charge enclosed by a spherical Gaussian surface is 8.85 X 10-8 C.What will be the electric flux through the Surface?- a)1012N m2C-1
- b)Zero
- c)108N m2C-1
- d)104N m2C-1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The charge enclosed by a spherical Gaussian surface is 8.85 X 10-8 C.What will be the electric flux through the Surface?
a)
1012N m2C-1
b)
Zero
c)
108N m2C-1
d)
104N m2C-1
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
we know that the flux linked with a Gaussian surface is given as
Φ = E.ds = q/ε0
here,
q = 8.85x10^-8 C
ε0 = 8.85x10^-12 F/m
so,
Φ = 8.85x10^-8 / 8.85x10^-12
thus, flux will be
Φ = 104 Nm^2/C
The information that is/are needed to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute is/are- a)The amount of solute used in the experiment
- b)The molal boiling or freezing constant value of the solvent
- c)The amount of solvent used in the experiment
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The information that is/are needed to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute is/are
a)
The amount of solute used in the experiment
b)
The molal boiling or freezing constant value of the solvent
c)
The amount of solvent used in the experiment
d)
All the above

|
Sidharth Gupta answered |
Ya d is right answer as in formula of elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point these all terms required
Beckmann thermometers are used to measure- a)boiling point of solution
- b)elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point
- c)any temperature
- d)freezing point of solution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Beckmann thermometers are used to measure
a)
boiling point of solution
b)
elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point
c)
any temperature
d)
freezing point of solution
|
|
Srishti Chavan answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that Beckmann thermometers are used to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point.
Here's a detailed explanation of why this is the correct answer:
Beckmann Thermometer:
A Beckmann thermometer is a type of liquid-in-glass thermometer that is specifically designed to measure small temperature differences accurately. It is named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann who invented it in the late 19th century.
Measurement of Elevation in Boiling Point or Depression in Freezing Point:
The Beckmann thermometer is primarily used to measure the elevation in boiling point or the depression in freezing point of a solution. This is achieved by comparing the boiling or freezing point of the solution with that of a pure solvent.
Elevation in Boiling Point:
When a solute is added to a solvent, the boiling point of the resulting solution increases. This is known as the elevation in boiling point. The degree of elevation depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this elevation in boiling point.
Depression in Freezing Point:
Similarly, when a solute is added to a solvent, the freezing point of the resulting solution decreases. This is known as the depression in freezing point. Again, the degree of depression depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this depression in freezing point.
Working Principle of a Beckmann Thermometer:
The Beckmann thermometer consists of a long capillary tube filled with a special liquid, usually mercury. The liquid expands or contracts with temperature changes, and the expansion or contraction is measured by a scale attached to the thermometer.
Calibration:
To use a Beckmann thermometer, it needs to be calibrated. This is done by measuring the temperature difference between the thermometer bulb and the end of the mercury column. This calibration is essential to ensure accurate measurements.
Applications:
The Beckmann thermometer finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmaceuticals. It is commonly used to determine the molecular weight of substances, as well as to measure the concentration of solutes in solutions.
In conclusion, Beckmann thermometers are specifically designed to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point of solutions. This makes them a valuable tool in various scientific disciplines.
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that Beckmann thermometers are used to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point.
Here's a detailed explanation of why this is the correct answer:
Beckmann Thermometer:
A Beckmann thermometer is a type of liquid-in-glass thermometer that is specifically designed to measure small temperature differences accurately. It is named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann who invented it in the late 19th century.
Measurement of Elevation in Boiling Point or Depression in Freezing Point:
The Beckmann thermometer is primarily used to measure the elevation in boiling point or the depression in freezing point of a solution. This is achieved by comparing the boiling or freezing point of the solution with that of a pure solvent.
Elevation in Boiling Point:
When a solute is added to a solvent, the boiling point of the resulting solution increases. This is known as the elevation in boiling point. The degree of elevation depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this elevation in boiling point.
Depression in Freezing Point:
Similarly, when a solute is added to a solvent, the freezing point of the resulting solution decreases. This is known as the depression in freezing point. Again, the degree of depression depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this depression in freezing point.
Working Principle of a Beckmann Thermometer:
The Beckmann thermometer consists of a long capillary tube filled with a special liquid, usually mercury. The liquid expands or contracts with temperature changes, and the expansion or contraction is measured by a scale attached to the thermometer.
Calibration:
To use a Beckmann thermometer, it needs to be calibrated. This is done by measuring the temperature difference between the thermometer bulb and the end of the mercury column. This calibration is essential to ensure accurate measurements.
Applications:
The Beckmann thermometer finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmaceuticals. It is commonly used to determine the molecular weight of substances, as well as to measure the concentration of solutes in solutions.
In conclusion, Beckmann thermometers are specifically designed to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point of solutions. This makes them a valuable tool in various scientific disciplines.
The secondary sexual characters develop in females because of:- a)estrogen
- b)androgens
- c)absence of androgens
- d)absence of estrogens
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The secondary sexual characters develop in females because of:
a)
estrogen
b)
androgens
c)
absence of androgens
d)
absence of estrogens
|
|
Bhaskar Yadav answered |
The Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics in Females
Introduction
Secondary sexual characteristics are physical traits that develop during puberty and distinguish males from females. In females, these characteristics include the growth and development of breasts, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, and the onset of menstruation. The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen.
Explanation
Estrogen is a primary female sex hormone that plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of female reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. It is produced primarily by the ovaries, although small amounts are also produced by the adrenal glands and fat cells.
Role of Estrogen in the Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Estrogen is responsible for the development of several secondary sexual characteristics in females, including:
1. Breast Development: Estrogen stimulates the growth and development of breast tissue. It promotes the accumulation of fat in the breasts and increases the size and number of mammary glands.
2. Widening of Hips: Estrogen influences the deposition of fat in the hip and thigh regions, leading to an increase in hip width. This contributes to the characteristic feminine body shape.
3. Changes in Body Fat Distribution: Estrogen influences the distribution of body fat, causing it to be stored more in the breasts, hips, and thighs rather than the abdominal region. This leads to a more curvaceous and feminine body shape.
4. Onset of Menstruation: Estrogen plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of the reproductive system, including the uterus and ovaries. It triggers the release of hormones that initiate the menstrual cycle.
5. Softening of Skin: Estrogen contributes to the softness and smoothness of female skin. It promotes the production of collagen, which helps maintain the elasticity and hydration of the skin.
6. Development of Female Reproductive Organs: Estrogen is involved in the growth and development of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina. It helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
Conclusion
The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen. Estrogen is responsible for breast development, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, the onset of menstruation, softening of skin, and the development of female reproductive organs. Without estrogen, these characteristics would not develop fully, and the individual would not exhibit the typical traits associated with femininity.
Note: Estrogen levels can vary among individuals, and some individuals may have conditions or disorders that affect estrogen production or response, resulting in variations in the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Introduction
Secondary sexual characteristics are physical traits that develop during puberty and distinguish males from females. In females, these characteristics include the growth and development of breasts, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, and the onset of menstruation. The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen.
Explanation
Estrogen is a primary female sex hormone that plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of female reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. It is produced primarily by the ovaries, although small amounts are also produced by the adrenal glands and fat cells.
Role of Estrogen in the Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Estrogen is responsible for the development of several secondary sexual characteristics in females, including:
1. Breast Development: Estrogen stimulates the growth and development of breast tissue. It promotes the accumulation of fat in the breasts and increases the size and number of mammary glands.
2. Widening of Hips: Estrogen influences the deposition of fat in the hip and thigh regions, leading to an increase in hip width. This contributes to the characteristic feminine body shape.
3. Changes in Body Fat Distribution: Estrogen influences the distribution of body fat, causing it to be stored more in the breasts, hips, and thighs rather than the abdominal region. This leads to a more curvaceous and feminine body shape.
4. Onset of Menstruation: Estrogen plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of the reproductive system, including the uterus and ovaries. It triggers the release of hormones that initiate the menstrual cycle.
5. Softening of Skin: Estrogen contributes to the softness and smoothness of female skin. It promotes the production of collagen, which helps maintain the elasticity and hydration of the skin.
6. Development of Female Reproductive Organs: Estrogen is involved in the growth and development of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina. It helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
Conclusion
The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen. Estrogen is responsible for breast development, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, the onset of menstruation, softening of skin, and the development of female reproductive organs. Without estrogen, these characteristics would not develop fully, and the individual would not exhibit the typical traits associated with femininity.
Note: Estrogen levels can vary among individuals, and some individuals may have conditions or disorders that affect estrogen production or response, resulting in variations in the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Leydig cells:- a)Are present in seminiferous tubules and secrete androgens
- b)Are present in seminiferous tubules and help in maturation of sperms
- c)Are present in interstitial space and secrete androgens
- d)Are present in interstitial space and help in maturation of sperms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Leydig cells:
a)
Are present in seminiferous tubules and secrete androgens
b)
Are present in seminiferous tubules and help in maturation of sperms
c)
Are present in interstitial space and secrete androgens
d)
Are present in interstitial space and help in maturation of sperms
|
|
Moumita Datta answered |
**Leydig Cells:**
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of Leydig, are specialized cells found in the interstitial space of the testes. These cells play a crucial role in the production and secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
**Location and Function:**
Leydig cells are located in the connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules, which are responsible for sperm production. They are not present within the seminiferous tubules themselves. Therefore, option C, which states that Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space, is the correct answer.
**Androgen Secretion:**
Leydig cells are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. These androgens are crucial for the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. Testosterone plays a vital role in the development of the male reproductive organs, such as the testes and prostate gland, as well as the growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and muscle development.
**Regulation of Androgen Secretion:**
The secretion of androgens by Leydig cells is regulated by the luteinizing hormone (LH) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. LH stimulates the production and release of testosterone from Leydig cells. In turn, testosterone negatively regulates the secretion of LH through a negative feedback loop. This mechanism helps maintain optimal levels of testosterone in the body.
**Role in Sperm Maturation:**
While Leydig cells do not directly participate in the maturation of sperm, the androgens they secrete, such as testosterone, play a crucial role in the process. Testosterone is required for the initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis, the process by which sperms are produced. It supports the maturation of spermatogonia, promotes the division and differentiation of germ cells, and influences the development of spermatozoa.
In conclusion, Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space of the testes and are responsible for the secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. They play a vital role in the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics, as well as in supporting the process of spermatogenesis.
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of Leydig, are specialized cells found in the interstitial space of the testes. These cells play a crucial role in the production and secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
**Location and Function:**
Leydig cells are located in the connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules, which are responsible for sperm production. They are not present within the seminiferous tubules themselves. Therefore, option C, which states that Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space, is the correct answer.
**Androgen Secretion:**
Leydig cells are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. These androgens are crucial for the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. Testosterone plays a vital role in the development of the male reproductive organs, such as the testes and prostate gland, as well as the growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and muscle development.
**Regulation of Androgen Secretion:**
The secretion of androgens by Leydig cells is regulated by the luteinizing hormone (LH) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. LH stimulates the production and release of testosterone from Leydig cells. In turn, testosterone negatively regulates the secretion of LH through a negative feedback loop. This mechanism helps maintain optimal levels of testosterone in the body.
**Role in Sperm Maturation:**
While Leydig cells do not directly participate in the maturation of sperm, the androgens they secrete, such as testosterone, play a crucial role in the process. Testosterone is required for the initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis, the process by which sperms are produced. It supports the maturation of spermatogonia, promotes the division and differentiation of germ cells, and influences the development of spermatozoa.
In conclusion, Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space of the testes and are responsible for the secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. They play a vital role in the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics, as well as in supporting the process of spermatogenesis.
Which one of the following is not a colligative property?- a)Osmotic pressure.
- b)Elevation of boiling point.
- c)Freezing point.
- d)Depression in freezing point.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a colligative property?
a)
Osmotic pressure.
b)
Elevation of boiling point.
c)
Freezing point.
d)
Depression in freezing point.
|
|
Shraddha Chavan answered |
Depression in freezing point is a colligative property but freezing point is not a colligative property.
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is directly proportional to- a)Density of solution
- b)Mole fraction of solute
- c)Mass of solvent
- d)Color of solution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is directly proportional to
a)
Density of solution
b)
Mole fraction of solute
c)
Mass of solvent
d)
Color of solution

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is directly proportional to mole fraction of solute. Hence it is a colligative property.
The cleavage divisions in humans is:- a)holoblastic, equal and indeterminate
- b)holoblastic, unequal and indeterminate
- c)holoblastic, equal and determinate
- d)holoblastic, unequal and determinate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cleavage divisions in humans is:
a)
holoblastic, equal and indeterminate
b)
holoblastic, unequal and indeterminate
c)
holoblastic, equal and determinate
d)
holoblastic, unequal and determinate
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The process of cleavage or cellulation happens through repeated mitotic divisions. These divisions result in cells called blastomeres. The mitotic process is very rapid. As the cleavage progresses the resultant daughter cells, namely the blastomeres get reduced in size. During cleavage, there is no growth in the blastomeres. The total size and volume of the embryo remain the same. The cleavages result in a compact mass of blastomeres called morula. It gets transformed into a blastula. While the wall of the blastula is called the blastoderm, the central cavity is called the blastocoel. Types of cleavages:
Equal holoblastic cleavage - In microlecithal and isolecithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of equal size. Eg: Amphioxus and placental mammals.
Unequal holoblastic cleavage - In mesolecithal and telolocithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of unequal size. Among the blastomeres, there are many small-sized micromeres and a few large-sized macromeres.
Equal holoblastic cleavage - In microlecithal and isolecithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of equal size. Eg: Amphioxus and placental mammals.
Unequal holoblastic cleavage - In mesolecithal and telolocithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of unequal size. Among the blastomeres, there are many small-sized micromeres and a few large-sized macromeres.
Camphor is used as solvent to determine the molecular mass of non-volatile solute by Rast method because for camphor- a)molal depression constant is high
- b)Melting point is high
- c)Being cheap
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Camphor is used as solvent to determine the molecular mass of non-volatile solute by Rast method because for camphor
a)
molal depression constant is high
b)
Melting point is high
c)
Being cheap
d)
All the above
|
|
Sahil Menon answered |
The correct answer is “molal depression constant is high”.
Camphor is used for the determination of molecular masses of solute by Rast method because its molal depression constant is very high 40Kmolality-1 .
Cervix is a part ______.- a)between uterus and vagina
- b)of epididymis
- c)of the kidney
- d)of fallopian tube
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cervix is a part ______.
a)
between uterus and vagina
b)
of epididymis
c)
of the kidney
d)
of fallopian tube
|
|
Rajat Jain answered |
**Cervix is a part between uterus and vagina**
The correct answer is option 'A': Cervix is a part between uterus and vagina. The cervix is a cylindrical-shaped structure that connects the uterus to the vagina. It is located at the lower end of the uterus, and its primary function is to allow the passage of menstrual blood from the uterus to the vagina, as well as to facilitate the entry of sperm into the uterus during sexual intercourse.
The cervix plays several important roles in the female reproductive system, including:
1. **Protective Barrier**: The cervix acts as a protective barrier between the uterus and the vagina, preventing the entry of harmful bacteria and pathogens into the upper reproductive organs.
2. **Mucus Production**: The cervix secretes mucus that changes in consistency throughout the menstrual cycle. This mucus helps in sperm transport, acting as a conduit for sperm to reach the uterus and fallopian tubes for fertilization.
3. **Cervical Os**: The cervix contains a small opening called the cervical os. This opening expands during childbirth to allow the passage of the baby from the uterus to the vagina.
4. **Cervical Length**: The length of the cervix can change during pregnancy. Monitoring cervical length is important in predicting the risk of preterm labor. A shortening cervix may indicate a higher risk of premature birth.
5. **Pap Smear**: The cervix is also the site where cervical cells are collected during a Pap smear. A Pap smear is a screening test used to detect abnormal cervical cells that may indicate the presence of cervical cancer or precancerous conditions.
In summary, the cervix is a crucial anatomical structure that connects the uterus and vagina in females. Its functions include providing a protective barrier, producing mucus, facilitating sperm transport, allowing for childbirth, and serving as the site for cervical cell collection for screening purposes.
The correct answer is option 'A': Cervix is a part between uterus and vagina. The cervix is a cylindrical-shaped structure that connects the uterus to the vagina. It is located at the lower end of the uterus, and its primary function is to allow the passage of menstrual blood from the uterus to the vagina, as well as to facilitate the entry of sperm into the uterus during sexual intercourse.
The cervix plays several important roles in the female reproductive system, including:
1. **Protective Barrier**: The cervix acts as a protective barrier between the uterus and the vagina, preventing the entry of harmful bacteria and pathogens into the upper reproductive organs.
2. **Mucus Production**: The cervix secretes mucus that changes in consistency throughout the menstrual cycle. This mucus helps in sperm transport, acting as a conduit for sperm to reach the uterus and fallopian tubes for fertilization.
3. **Cervical Os**: The cervix contains a small opening called the cervical os. This opening expands during childbirth to allow the passage of the baby from the uterus to the vagina.
4. **Cervical Length**: The length of the cervix can change during pregnancy. Monitoring cervical length is important in predicting the risk of preterm labor. A shortening cervix may indicate a higher risk of premature birth.
5. **Pap Smear**: The cervix is also the site where cervical cells are collected during a Pap smear. A Pap smear is a screening test used to detect abnormal cervical cells that may indicate the presence of cervical cancer or precancerous conditions.
In summary, the cervix is a crucial anatomical structure that connects the uterus and vagina in females. Its functions include providing a protective barrier, producing mucus, facilitating sperm transport, allowing for childbirth, and serving as the site for cervical cell collection for screening purposes.
The wider part of the fallopian tube is- a)Infundibulum
- b)Isthmus
- c)Ampulla
- d)Cervix
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The wider part of the fallopian tube is
a)
Infundibulum
b)
Isthmus
c)
Ampulla
d)
Cervix

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The infundibulum leads to a wider part of the oviduct called ampulla
Choose the incorrect match:- a)Testicular lobules in each testis → 250
- b)Number of primary follicles in each ovary at puberty → 6000 to 8000
- c)Sperm count in healthy male per ejaculate → 200 to 300 million
- d)Mammary lobes in each breast → 15 to 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Testicular lobules in each testis → 250
b)
Number of primary follicles in each ovary at puberty → 6000 to 8000
c)
Sperm count in healthy male per ejaculate → 200 to 300 million
d)
Mammary lobes in each breast → 15 to 20

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Option A is correct: Each testis contains about 250 testicular lobules.
Option B is incorrect: At puberty, each ovary contains approximately 60,000 to 80,000 primary follicles, not 6,000 to 8,000.
Option C is correct: A healthy male typically has a sperm count of 200 to 300 million per ejaculate.
Option D is correct: Each breast contains 15 to 20 mammary lobes.
Option B is incorrect: At puberty, each ovary contains approximately 60,000 to 80,000 primary follicles, not 6,000 to 8,000.
Option C is correct: A healthy male typically has a sperm count of 200 to 300 million per ejaculate.
Option D is correct: Each breast contains 15 to 20 mammary lobes.
Each seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside by:- a)Spermatogonia
- b)Primary spermatocytes
- c)Sertoli cells
- d)Both 1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Each seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside by:
a)
Spermatogonia
b)
Primary spermatocytes
c)
Sertoli cells
d)
Both 1 and 3
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
- Each testicular lobule contains one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules in which sperms are produced.
- Each seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside by two types of cells called male germ cells (spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells.
- The male germ cells undergo meiotic divisions finally leading to sperm formation, while Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells.
Hence, the Correct Answer is D
NCERT Reference: Page no. 43 topic “3.1 THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ” of chapter 3 of NCERT
What is the function of the finger-like projections called fimbriae in the female reproductive system?- a) Production of hormones
- b) Collection of the ovum after ovulation
- c) Maturation of the ova
- d) Secretion of lubricating fluid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the function of the finger-like projections called fimbriae in the female reproductive system?
a)
Production of hormones
b)
Collection of the ovum after ovulation
c)
Maturation of the ova
d)
Secretion of lubricating fluid

|
Lead Academy answered |
The finger-like projections called fimbriae play a crucial role in the female reproductive system by aiding in the collection of the ovum after ovulation. These fimbriae help to guide the released egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube, where fertilization typically occurs. This process is essential for the successful transport of the ovum towards the uterus for potential fertilization.
Chapter doubts & questions for May Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of May Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup