All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of May Week 3 for NEET Exam
Two equipotential surfaces have a potential of -10V and 90V respectively, what is the difference in potential between these surfaces?- a)90V
- b)80V
- c)0V
- d)100V
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two equipotential surfaces have a potential of -10V and 90V respectively, what is the difference in potential between these surfaces?
a)
90V
b)
80V
c)
0V
d)
100V
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Potential = high potential - low potential
so our high potential is 90V and low potential is 10V,
potential = 90-(-10)=100V
so our high potential is 90V and low potential is 10V,
potential = 90-(-10)=100V
When a positive charge is moved in an electrostatic field from a point at high potential to a low potential, its kinetic energy- a)Remains constant
- b)Decreases
- c)Increases
- d)Either increase or remain constant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a positive charge is moved in an electrostatic field from a point at high potential to a low potential, its kinetic energy
a)
Remains constant
b)
Decreases
c)
Increases
d)
Either increase or remain constant

|
Siddhi Bhardwaj answered |
You can generalise it by assuming a positive charge moving away from another positive charge. now both of them are repelling each other with some force. so that positive charge will accelerate which results in the increase in K.E.
The shape of equipotential surface for an infinite line charge is:- a)Coaxial cylindrical surfaces
- b)Parallel plane surfaces
- c)Parallel plane surfaces perpendicular to lines of force
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of equipotential surface for an infinite line charge is:
a)
Coaxial cylindrical surfaces
b)
Parallel plane surfaces
c)
Parallel plane surfaces perpendicular to lines of force
d)
None of above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The shape of equipotential surface for an infinite line charge is coaxial cylindrical because A curved surface on which potential is constant is equipotential curve . If we consider the line charge then the focus of the point should have the same potential hence it is a coaxial cylinder.
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential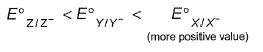 then,
then,- a)Y will oxidise X and not Z
- b)Y will oxidise Z and not X
- c)Y will oxidise both X and Z
- d)Z- will reduce both X and Y
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential
then,
a)
Y will oxidise X and not Z
b)
Y will oxidise Z and not X
c)
Y will oxidise both X and Z
d)
Z- will reduce both X and Y
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
In ECS, pair with more negative values of E°red reducing agent is above oxidising agent.
Thus, Z/Z- is the best reducing agent
Thus, Z- will reduce both X and Y and itself will be oxidised to Z .
Equipotential surfaces cannot- a)be parallel
- b)be spherical
- c)Intersect
- d)be irregularly shaped.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Equipotential surfaces cannot
a)
be parallel
b)
be spherical
c)
Intersect
d)
be irregularly shaped.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The electric field lines are perpendicular to the equipotential surface. The field lines can not intersect each other because the electric force can not have two directions at a point.
A metal sphere carries a charge of 5×10-8C and is at a potential of 200 V, relative to the potential far away. The potential at the centre of the sphere is:- a)-100V
- b)0
- c)200V
- d)2×10-6v
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal sphere carries a charge of 5×10-8C and is at a potential of 200 V, relative to the potential far away. The potential at the centre of the sphere is:
a)
-100V
b)
0
c)
200V
d)
2×10-6v
|
|
Keerthana Iyer answered |
Given data:
Charge on the sphere, q = 5.1 × 10⁻⁸ C
Potential difference, V = 200 V
We know that the formula for potential difference is:
V = kq/r
where k is Coulomb's constant, q is the charge on the sphere and r is the radius of the sphere.
Calculating the radius of the sphere:
r = kq/V
r = (9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2 × 5.1 × 10⁻⁸ C) / (200 V)
r = 2.295 × 10⁻⁴ m
The potential at the centre of the sphere is given by:
V' = kq/R
where R is the radius of the sphere.
As the point is at the centre of the sphere, R = r.
V' = kq/r
V' = (9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2 × 5.1 × 10⁻⁸ C) / (2.295 × 10⁻⁴ m)
V' = 2 × 10² V
Therefore, the potential at the centre of the sphere is 200 V (option C).
Charge on the sphere, q = 5.1 × 10⁻⁸ C
Potential difference, V = 200 V
We know that the formula for potential difference is:
V = kq/r
where k is Coulomb's constant, q is the charge on the sphere and r is the radius of the sphere.
Calculating the radius of the sphere:
r = kq/V
r = (9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2 × 5.1 × 10⁻⁸ C) / (200 V)
r = 2.295 × 10⁻⁴ m
The potential at the centre of the sphere is given by:
V' = kq/R
where R is the radius of the sphere.
As the point is at the centre of the sphere, R = r.
V' = kq/r
V' = (9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2 × 5.1 × 10⁻⁸ C) / (2.295 × 10⁻⁴ m)
V' = 2 × 10² V
Therefore, the potential at the centre of the sphere is 200 V (option C).
The value of electric field vector 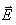 along the surface of constant potential of 100 V
along the surface of constant potential of 100 V- a)100 V/m
- b)-100 V/m
- c)10 V/m
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of electric field vector 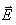 along the surface of constant potential of 100 V
along the surface of constant potential of 100 V
a)
100 V/m
b)
-100 V/m
c)
10 V/m
d)
Zero
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
As we know that electric field is in reverse sense of the directional gradient of electric potential, so if V is constant, E should be zero. So, for E to be zero, either V has to be zero, or constant, or the 3 directional derivative components of V must cancel out each other in space. So we cant claim that V always has to be zero, if E is zero in a region, since E is a vector & V is a scalar quantity. But if V is zero, then surely E has to be zero; the reverse case is not true always.
hope it was helpful...
Below is given the unorganised list of some important events in the human female reproductive cycle. Identify the correct sequence of these events and select the correct option.
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
- a)(i)→(iv)→(iii)→(v)→(ii)
- b)(ii)→(i)→(iii)→(iv)→(v)
- c)(iii)→(i)→(iv)→(ii)→(v)
- d)(i)→(iii)→(v)→(iv)→(ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Below is given the unorganised list of some important events in the human female reproductive cycle. Identify the correct sequence of these events and select the correct option.
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
a)
(i)→(iv)→(iii)→(v)→(ii)
b)
(ii)→(i)→(iii)→(iv)→(v)
c)
(iii)→(i)→(iv)→(ii)→(v)
d)
(i)→(iii)→(v)→(iv)→(ii)
|
|
Akash Menon answered |
(iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii)
Explanation:
The sequence of events in the human female reproductive cycle is as follows:
1. Secretion of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland
2. Growth of the follicle in the ovary
3. Ovulation, where the mature egg is released from the ovary
4. Growth of the corpus luteum, which is the remains of the follicle after ovulation
5. Sudden increase in the levels of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) which triggers ovulation
Therefore, the correct sequence of events is (iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii).
Explanation:
The sequence of events in the human female reproductive cycle is as follows:
1. Secretion of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland
2. Growth of the follicle in the ovary
3. Ovulation, where the mature egg is released from the ovary
4. Growth of the corpus luteum, which is the remains of the follicle after ovulation
5. Sudden increase in the levels of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) which triggers ovulation
Therefore, the correct sequence of events is (iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii).
Shape of equipotential surfaces for a uniform electric field along x-axis are- a)Planes along x-z direction
- b)Planes along x-y direction
- c)Planes normal to field
- d)Concentric spherical shells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Shape of equipotential surfaces for a uniform electric field along x-axis are
a)
Planes along x-z direction
b)
Planes along x-y direction
c)
Planes normal to field
d)
Concentric spherical shells
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
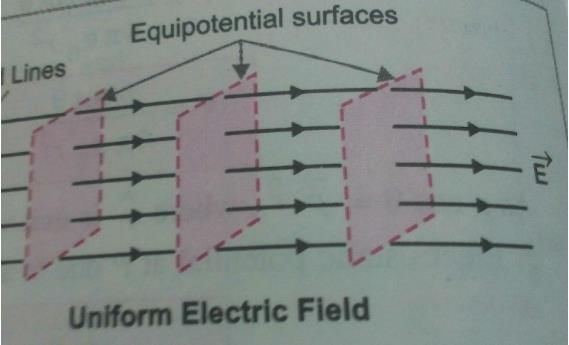
Shape of equipotential surfaces for a uniform electric field along x-axis are Planes normal to the field.
Optical analogue of an equipotential surface is- a)Wavefront of light
- b)Wave motion of light
- c)Reflection of light
- d)Interference of light
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Optical analogue of an equipotential surface is
a)
Wavefront of light
b)
Wave motion of light
c)
Reflection of light
d)
Interference of light
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Optical analogue of anequipotential surface is. Wavefronts are surfaces of constant phase. Similarly,equipotential surface due to point charge is spherical in shape and has same potential at each point on selected surface.
Read the following statements about menstrual cycle and select two correct statements.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about menstrual cycle and select two correct statements.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iv)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy. During pregnancy, the levels of estrogen and progesterone are high in the blood, which are required for the maintenance of uterus and thus, menstruation does not occur. On 14th day of the menstrual cycle, there is rapid increase in LH (called LH surge), that induces ovulation. The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones and pituitary hormones. If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates by 16th week of pregnancy.
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?- a)Progesterone
- b)Estrogen
- c)FSH
- d)FSH-RH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?
a)
Progesterone
b)
Estrogen
c)
FSH
d)
FSH-RH
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Progesterone is required for the maintenance of the endometrial lining of the uterus. As soon as the production of progesterone is reduced due to reduction in the production of LH from anterior lobe of the pituitary, the endometrium of the uterus breaks down and menstruation begins.
Study the graph carefully and correlate the hormone levels on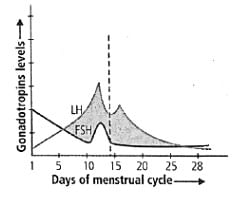 (i) 1-5 days
(i) 1-5 days
(ii) 12-14 days
(iii) 25-28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised).- a)(i) LH decreases and FSH increases
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level maintained and FSH level increases - b)(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH decreases and FSH increases
(iii) LH level increases and FSH level maintained - c)(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained - d)(i) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the graph carefully and correlate the hormone levels on

(i) 1-5 days
(ii) 12-14 days
(iii) 25-28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised).
(ii) 12-14 days
(iii) 25-28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised).
a)
(i) LH decreases and FSH increases
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level maintained and FSH level increases
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level maintained and FSH level increases
b)
(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH decreases and FSH increases
(iii) LH level increases and FSH level maintained
(ii) LH decreases and FSH increases
(iii) LH level increases and FSH level maintained
c)
(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
(ii) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
d)
(i) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The menstrual cycle is a series of cyclic physiological changes that take place in the female primates. It is regulated by the various hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen, progesterone. The follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates the development of follicles which secretes estrogen. The rise in the level of estrogen stimulates the thickening of the endometrium in the uterus. LH is secreted by the pituitary gland which causes ovulation. The rise in LH level is followed by the rise in the progesterone which is responsible for developing the follicles into corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone which is necessary for the maintenance of the uterus lining for implantation. The rise in progesterone and estrogen results in the decrease of FSH and LH. If there is no pregnancy, then the level of progesterone and estrogen decreases which results in the breaking of the endometrium i.e., menstrual flow. After the start of menstruation, the level of FSH and LH rises to start the new cycle.
Only One Option Correct TypeThis section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q.Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr, and CHCI3 is added. There is a colour in CHCI3 (lower) layer. It is due to - a)formation of l2 (violet)
- b)formation of Br2 (orange)
- c)formation of l2 and Br2 both
- d)formation of F2 (colourless)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr, and CHCI3 is added. There is a colour in CHCI3 (lower) layer. It is due to
a)
formation of l2 (violet)
b)
formation of Br2 (orange)
c)
formation of l2 and Br2 both
d)
formation of F2 (colourless)
|
|
Mihir Joshi answered |
Based on electro chemical series, oxidising power of
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2

On passing Cl2 in to a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr,
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCI + Br2 (orange)
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCI + l2 (violet)
2KI + Br2 → 2KBr + l2 (violet)
Br2 formed also oxidises Kl to l2 (violet)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
On passing Cl2 in to a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr,
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCI + Br2 (orange)
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCI + l2 (violet)
2KI + Br2 → 2KBr + l2 (violet)
Br2 formed also oxidises Kl to l2 (violet)
The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y, Z are 0.52, -3.03 and -1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is- a)Y > Z > X
- b)X > Y > Z
- c)Z > Y > X
- d)Z > X > Y
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y, Z are 0.52, -3.03 and -1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is
a)
Y > Z > X
b)
X > Y > Z
c)
Z > Y > X
d)
Z > X > Y

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
E°x = - 0.52 V
E°y = -3.03 V
E°z = - 1.18 V
E°y = -3.03 V
E°z = - 1.18 V
Their placements in ECS is in order Y > Z > X.
Thus, reducing nature is also in same order y > Z > X
Thus, reducing nature is also in same order y > Z > X
For human female which of the following is incorrect?- a)Menstrual cycle takes 28 days on an average
- b)Menopause occurs at 45−55 years of age
- c)The eggs released during pregnancy die
- d)Menstruation takes 4 days on an average
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For human female which of the following is incorrect?
a)
Menstrual cycle takes 28 days on an average
b)
Menopause occurs at 45−55 years of age
c)
The eggs released during pregnancy die
d)
Menstruation takes 4 days on an average
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
During pregnancy, high levels of progesterone inhibits FSH and LH secretion. In absence of these hormones, there is no chance of ovulation and thus no pregnancy.
The correct sequence of the various phases of a typical menstrual cycle is:
- a)Menstrual → Follicular → Secretory → Ovulatory
- b)Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory
- c)Ovulatory → Follicular → Secretory → Menstrual
- d)Menstrual → Secretory → Follicular → Ovulatory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of the various phases of a typical menstrual cycle is:
a)
Menstrual → Follicular → Secretory → Ovulatory
b)
Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory
c)
Ovulatory → Follicular → Secretory → Menstrual
d)
Menstrual → Secretory → Follicular → Ovulatory

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The correct sequence of the various phases of a typical menstrual cycle is:
- Menstrual
- Follicular
- Ovulatory
- Secretory
Explanation:
- Menstrual phase: Shedding of the uterine lining
- Follicular phase: Maturation of follicles in the ovary
- Ovulatory phase: Release of an egg from the ovary
- Secretory phase: Preparation of the uterus for possible pregnancy by thickening the lining
Therefore, the correct sequence is Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory, which corresponds to option B.
- Menstrual
- Follicular
- Ovulatory
- Secretory
Explanation:
- Menstrual phase: Shedding of the uterine lining
- Follicular phase: Maturation of follicles in the ovary
- Ovulatory phase: Release of an egg from the ovary
- Secretory phase: Preparation of the uterus for possible pregnancy by thickening the lining
Therefore, the correct sequence is Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory, which corresponds to option B.
Statement I : When AgNO3 solution is stirred with a spoon made of copper,solution turns blue.Statement II : In electrochemical series ,copper is above silver- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I : When AgNO3 solution is stirred with a spoon made of copper,solution turns blue.
Statement II : In electrochemical series ,copper is above silver
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Ameya Tiwari answered |
In electrochemical series, copper is above silver thus is a better reducing agent. When AgNO3 solution is stirred with copper spoon, Ag is displaced and copper is oxidised to Cu2+ (blue).
Thus, statement I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized, which one of the following is unlikely?- a)Corpus luteum will degenrate
- b) Progesterone secretion rapidly declines
- c)Estrogen secretion further decreases
- d)Primary follicle starts developing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized, which one of the following is unlikely?
a)
Corpus luteum will degenrate
b)
Progesterone secretion rapidly declines
c)
Estrogen secretion further decreases
d)
Primary follicle starts developing

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized the estrogen secretion does not decrease further while corpus luteum will disintegrate. Primary follicle starts developing and progesterone secretion rapidly declines.
Topic in NCERT: MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Line in NCERT: "In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates."

The roots that originate from the base of the stem are:- a)Fibrous roots
- b)Primary roots
- c)Prop roots
- d)Lateral roots
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The roots that originate from the base of the stem are:
a)
Fibrous roots
b)
Primary roots
c)
Prop roots
d)
Lateral roots
|
|
Mahi Nair answered |
Fibrous Roots:
Fibrous roots are the roots that originate from the base of the stem. These are also known as adventitious roots. They are formed from the stem or leaves of the plant. Fibrous roots are found in monocots, whereas dicots have a taproot system.
Characteristics of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots are thin and hair-like.
- They grow in a cluster or group.
- They do not penetrate deep into the soil.
- They are responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- They provide anchorage to the plant.
Examples of Plants with Fibrous Roots:
- Grass
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- Sugarcane
Importance of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots help in preventing soil erosion.
- They increase the surface area of the root system, which enhances the absorption of water and nutrients.
- They provide support to the plant, preventing it from falling.
- Fibrous roots help in stabilizing the soil and preventing landslides.
Conclusion:
Fibrous roots are important for the growth and development of plants. They play a vital role in providing support, preventing soil erosion, and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
Fibrous roots are the roots that originate from the base of the stem. These are also known as adventitious roots. They are formed from the stem or leaves of the plant. Fibrous roots are found in monocots, whereas dicots have a taproot system.
Characteristics of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots are thin and hair-like.
- They grow in a cluster or group.
- They do not penetrate deep into the soil.
- They are responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- They provide anchorage to the plant.
Examples of Plants with Fibrous Roots:
- Grass
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- Sugarcane
Importance of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots help in preventing soil erosion.
- They increase the surface area of the root system, which enhances the absorption of water and nutrients.
- They provide support to the plant, preventing it from falling.
- Fibrous roots help in stabilizing the soil and preventing landslides.
Conclusion:
Fibrous roots are important for the growth and development of plants. They play a vital role in providing support, preventing soil erosion, and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
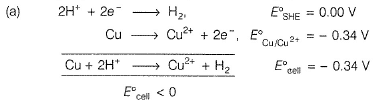
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu,(E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.34 V) indicates that- a)this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than H+/H2 couple
- b)this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2 couple
- c)Cu can displace H2 from acid
- d)Cu can not displace H2 from acid
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu,
(E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.34 V) indicates that
a)
this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than H+/H2 couple
b)
this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2 couple
c)
Cu can displace H2 from acid
d)
Cu can not displace H2 from acid

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
E°cell > 0 thus spontaneous
Cu2+/Cu couple is thus a stronger oxidising agent. Reverse reaction is non-spontaneous.
Cu + 2H+ → Cu2+ + H2, E°cell = - 0.34 V
Thus, copper cannot displace H2 from acid.
During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, which of the following occurs?I: The primary follicle grows and becomes a fully mature Graafian follicle.II: The endometrium of the uterus regenerates through proliferation.- a)Only I
- b)Only II
- c)I and II
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, which of the following occurs?
I: The primary follicle grows and becomes a fully mature Graafian follicle.
II: The endometrium of the uterus regenerates through proliferation.
a)
Only I
b)
Only II
c)
I and II
d)
None

|
Lead Academy answered |
During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, the following occurs:
The primary follicle grows and becomes a fully mature Graafian follicle.
The endometrium of the uterus regenerates through proliferation.
Follicle Development:
- The primary follicle grows in response to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- It develops into a secondary follicle and eventually becomes a mature Graafian follicle, ready for ovulation.
2. Endometrial Regeneration:
- The endometrium (uterine lining) regenerates and thickens through proliferation, preparing for possible implantation of a fertilized egg.
Correct Answer: C: I and II
Thus, both statements I and II are correct.
Given the standard electrode potentials I. K+/K = -2.93V,
II. Ag+/Ag = 0.80V,
III. Hg2+/Hg = 0.79 V
IV. Mg2+/Mg = -2.37V,
V. Cr3+/Cr = - 0.74 VThese metals are arranged in increasing reducing power as- a)I < II < IV < III < V
- b)II < III < V < IV < I
- c)I < IV < V < III < II
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given the standard electrode potentials
I. K+/K = -2.93V,
II. Ag+/Ag = 0.80V,
III. Hg2+/Hg = 0.79 V
IV. Mg2+/Mg = -2.37V,
V. Cr3+/Cr = - 0.74 V
II. Ag+/Ag = 0.80V,
III. Hg2+/Hg = 0.79 V
IV. Mg2+/Mg = -2.37V,
V. Cr3+/Cr = - 0.74 V
These metals are arranged in increasing reducing power as
a)
I < II < IV < III < V
b)
II < III < V < IV < I
c)
I < IV < V < III < II
d)
None of these

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Most negative E°red means the Mn+/M is at the top of ECS and is the best reducing agent.
Which of the following statement is correct?- a)Ecell and ΔrG of a cell reaction both are extensive properties
- b)Ecell and ΔrG of a cell reaction both are intensive properties
- c)Ecell is an intensive property while ΔrG of a cell reaction is an extensive property
- d)Ecell is an extensive property while ΔrG of a cell reaction is an intensive property
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is correct?
a)
Ecell and ΔrG of a cell reaction both are extensive properties
b)
Ecell and ΔrG of a cell reaction both are intensive properties
c)
Ecell is an intensive property while ΔrG of a cell reaction is an extensive property
d)
Ecell is an extensive property while ΔrG of a cell reaction is an intensive property
|
|
Divyansh Kulkarni answered |
Ecell and rG are both important thermodynamic properties used to describe the behavior of electrochemical cells. Ecell represents the cell potential or electromotive force (EMF), which is a measure of the driving force for the cell reaction. On the other hand, rG (Gibbs free energy change) represents the thermodynamic driving force for a chemical reaction, including electrochemical reactions.
Ecell is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present in the system. It is solely determined by the nature of the reactants and products involved in the cell reaction. Intensive properties are independent of the system's size or the amount of substance present. For example, the cell potential of a half-cell will remain the same regardless of whether it is combined with another half-cell to form a complete cell or if it is used in isolation.
On the other hand, rG is an extensive property because it depends on the amount of substance present in the system. The Gibbs free energy change is directly proportional to the quantity of reactants and products involved in the cell reaction. Extensive properties change with the size or amount of substance present. For example, if the number of moles of reactants and products in a cell reaction is doubled, the value of rG will also double.
Therefore, the correct statement is option C: Ecell is an intensive property while rG of a cell reaction is an extensive property. This means that the cell potential remains the same regardless of the scale of the reaction, while the Gibbs free energy change will vary depending on the amount of substance involved in the reaction.
In summary:
- Ecell (cell potential) is an intensive property, independent of the amount of substance.
- rG (Gibbs free energy change) is an extensive property, dependent on the amount of substance.
- Option C is correct because it correctly distinguishes between the intensive and extensive nature of Ecell and rG.
Ecell is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present in the system. It is solely determined by the nature of the reactants and products involved in the cell reaction. Intensive properties are independent of the system's size or the amount of substance present. For example, the cell potential of a half-cell will remain the same regardless of whether it is combined with another half-cell to form a complete cell or if it is used in isolation.
On the other hand, rG is an extensive property because it depends on the amount of substance present in the system. The Gibbs free energy change is directly proportional to the quantity of reactants and products involved in the cell reaction. Extensive properties change with the size or amount of substance present. For example, if the number of moles of reactants and products in a cell reaction is doubled, the value of rG will also double.
Therefore, the correct statement is option C: Ecell is an intensive property while rG of a cell reaction is an extensive property. This means that the cell potential remains the same regardless of the scale of the reaction, while the Gibbs free energy change will vary depending on the amount of substance involved in the reaction.
In summary:
- Ecell (cell potential) is an intensive property, independent of the amount of substance.
- rG (Gibbs free energy change) is an extensive property, dependent on the amount of substance.
- Option C is correct because it correctly distinguishes between the intensive and extensive nature of Ecell and rG.
The Eo M3+/M2+ values for Cr, Mn, Fe and Co are - 0.41 V, +1,57 V, + 0.77 V and m /m 1.97 V respectively. For which one of these metals the change in oxidation state from +2 to +3 is easiest?- a)Cr
- b)Mn
- c)Fe
- d)Co
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Eo M3+/M2+ values for Cr, Mn, Fe and Co are - 0.41 V, +1,57 V, + 0.77 V and m /m 1.97 V respectively. For which one of these metals the change in oxidation state from +2 to +3 is easiest?
a)
Cr
b)
Mn
c)
Fe
d)
Co

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
Mn3+ + e- → Mn2+ + 1.57 V
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ + 0.77 V
Co3+ + e- → Co2+ + 1.97
Cr3+/Cr2+ with most negative E°red is the best reducing agent.
Cr2+→ Cr3+ + e- , E° = 0.41 V
Thus, is oxidised from Cr2+ to Cr3+ most easily.
Cr2+→ Cr3+ + e- , E° = 0.41 V
Thus, is oxidised from Cr2+ to Cr3+ most easily.
Given, E° Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V
E° Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34V
E° Hg2+/Hg = 0.79VQ. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?- a)AgNO3 can be stored in a copper vessel
- b)Cu(NO3)2 can be stored in a magnesium vessel
- c)CuCl2 can be stored in a silver vessel
- d)HgCl2 can be stored in a copper vessel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given,
E° Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V
E° Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34V
E° Hg2+/Hg = 0.79V
E° Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34V
E° Hg2+/Hg = 0.79V
Q.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
a)
AgNO3 can be stored in a copper vessel
b)
Cu(NO3)2 can be stored in a magnesium vessel
c)
CuCl2 can be stored in a silver vessel
d)
HgCl2 can be stored in a copper vessel

|
Ashwini Chakraborty answered |
Based on electro chemical series, reactivity series is

(a) 2Ag+ + Cu → Cu2+ 2Ag
Cu is a better reducing agent than Ag hence Ag+ is reduced by Cu. Thus AgNO3 can not be stored in copper vessel.
(b) Cu2+ + Mg → Mg2+ + Cu
Mg will reduce Cu2+ to Cu thus can not be stored.
(c) Cu2+ + 2Ag → Cu + 2 Ag+
Cu is better reducing agent hence CuCI2 can be stored in silver vessel.
(d) Hg2+ + Cu → Cu2+ + Hg
Cu is better reducing agent. Hence, HgCI2 can not be stored in copper vessel.
(a) 2Ag+ + Cu → Cu2+ 2Ag
Cu is a better reducing agent than Ag hence Ag+ is reduced by Cu. Thus AgNO3 can not be stored in copper vessel.
(b) Cu2+ + Mg → Mg2+ + Cu
Mg will reduce Cu2+ to Cu thus can not be stored.
(c) Cu2+ + 2Ag → Cu + 2 Ag+
Cu is better reducing agent hence CuCI2 can be stored in silver vessel.
(d) Hg2+ + Cu → Cu2+ + Hg
Cu is better reducing agent. Hence, HgCI2 can not be stored in copper vessel.
One mole of Ag2CO3 is strongly heated in an open vessel. Residue wll be - a)1 mole of Ag2O
- b)2 moles of Ag
- c)1 mole of Ag2O and 1 mole of CO2
- d)2 moles of Ag , 0.5 mole of O2 and and 1 mole of CO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of Ag2CO3 is strongly heated in an open vessel. Residue wll be
a)
1 mole of Ag2O
b)
2 moles of Ag
c)
1 mole of Ag2O and 1 mole of CO2
d)
2 moles of Ag , 0.5 mole of O2 and and 1 mole of CO2

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
Oxides of the metals are decomposed to metals if in electro chemical series , Eored > 0 .7 9 V
For A g, E°Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V hence Ag2O is decomposed to metals. Products are Ag , CO2 and O2. Since reaction takes place in an open vessel, CO2 and O2 escape from mixture, residue being 2 moles of silver.
A regular cycling woman is not menstruating. Which one of the following is the most likely root cause of this?- a)Maintenance of the hypertrophical endometrial lining
- b)Maintenance of high concentration of sexhormones in the blood stream
- c)Retention of well-developed corpus luteum
- d)Fertilisation of the ovum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A regular cycling woman is not menstruating. Which one of the following is the most likely root cause of this?
a)
Maintenance of the hypertrophical endometrial lining
b)
Maintenance of high concentration of sexhormones in the blood stream
c)
Retention of well-developed corpus luteum
d)
Fertilisation of the ovum
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Menstruation does not take place if the ovum is fertilised.
The accompanying diagram shows the changes that take place in the endometrium during a normal menstrual cycle. Identify the changes and select the correct option.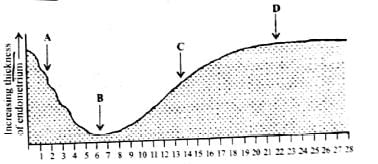

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The accompanying diagram shows the changes that take place in the endometrium during a normal menstrual cycle. Identify the changes and select the correct option.


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Menstruation occurs for 1−5 days and ovulation occurs on 14th day of a normal menstrual cycle.
Consider some facts about Standard Hydrogen Electrode(SHE).I. It is assigned a zero potential at all temperature corresponding to the reaction.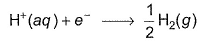
 II. Platinum electrode coated with platinum black is dipped in acidic solution and H2 gas is bubbled through it.
II. Platinum electrode coated with platinum black is dipped in acidic solution and H2 gas is bubbled through it.
III. Concentration of both are oxidised and reduced forms of hydrogen is maintained at unity. Select the correct facts- a)I , II ,III
- b)II ,III
- c)I ,II
- d)I ,III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider some facts about Standard Hydrogen Electrode(SHE).
I. It is assigned a zero potential at all temperature corresponding to the reaction.
II. Platinum electrode coated with platinum black is dipped in acidic solution and H2 gas is bubbled through it.
III. Concentration of both are oxidised and reduced forms of hydrogen is maintained at unity.
III. Concentration of both are oxidised and reduced forms of hydrogen is maintained at unity.
Select the correct facts
a)
I , II ,III
b)
II ,III
c)
I ,II
d)
I ,III

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
It is oxidation half-cell
H2 (reduced part) is at 1 bar. H+ (oxidised part) is at 1 M.
It is reduction half-cell
In this case also, oxidised and reduced parts are at unity.
Then (I), (II) and (III) are correct facts.
Consider the following half-reactions: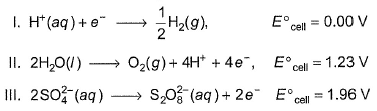 Select the correct statements on the basis of the above data
Select the correct statements on the basis of the above data- a)In dilute sulphuric acid,hydrogen ion will be reduced at cathode
- b)In concentrated sulphuric acid,water will be be oxidised at anode.
- c)In dilute sulphuric acid,water will be be oxidised at anode.
- d)In dilute sulphuric acid, sulphate ion is oxidised to
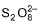
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following half-reactions:
Select the correct statements on the basis of the above data
a)
In dilute sulphuric acid,hydrogen ion will be reduced at cathode
b)
In concentrated sulphuric acid,water will be be oxidised at anode.
c)
In dilute sulphuric acid,water will be be oxidised at anode.
d)
In dilute sulphuric acid, sulphate ion is oxidised to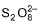

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
Thus, (c) is correct.
Concentrated H2SO4 ionises as H+ and HSO4- and then water is not oxidised in concentrated H2SO4 Thus, (b) is incorrect.
(d) In dilute sulphuric acid solution,
Statement TypeDirection : This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Statement I : CuSO4 can be stored in a vessel made of zinc.Statement II : 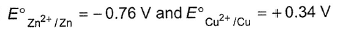 w.r.t SHE
w.r.t SHE - a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
Direction : This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Statement I : CuSO4 can be stored in a vessel made of zinc.
Statement II : 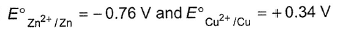 w.r.t SHE
w.r.t SHE
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
E°Zn2+/Zn = -0.76 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34 V
In electrochemical series, zinc is above copper and thus zinc is a better reducing agent than copper. When CuS04 is placed in zinc vessel, copper is displaced
Thus, CuSO4 cannot be stored in a vessel made of zinc.
Thus, statement I is incorrect and statement II is correct.
Thus, statement I is incorrect and statement II is correct.
Zinc ,silver and iron plates are dipped in CuSO4 solutions placed in different vessels as shown: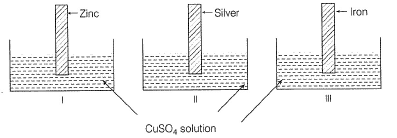 Blue colour of CuSO4 fades in
Blue colour of CuSO4 fades in - a)I , II ,III
- b)I, II
- c)II , III
- d)I , III
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Zinc ,silver and iron plates are dipped in CuSO4 solutions placed in different vessels as shown:
Blue colour of CuSO4 fades in
a)
I , II ,III
b)
I, II
c)
II , III
d)
I , III

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
Blue colour fades or changes to colourless if Cu2+ is reduced to Cu.
In electrochemical series (ECS), reactivity order is Zn, Fe, Cu, Ag
Thus, Zn and Fe reduce Cu2+ to Cu but Ag does not reduce Cu2+. Thus, in I and III, CuSO4 changes to colourless or fades by zinc and iron plates.
For the following half -cell reactions ,E° values are:Mn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)  MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23VMnO-4 (aq) + 4H+(aq) +3e-
MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23VMnO-4 (aq) + 4H+(aq) +3e-  MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V Thus
MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V Thus - a)Mn2+ reacts with MnO4- in acid solution to form MnO2
- b)Mn(MnO4)2 is stable in acid solution
- c)MnO2 disproportionates to Mn2+and MnO4- in acid solution
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following half -cell reactions ,E° values are:
Mn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)  MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23V
MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23V
 MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23V
MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23VMnO-4 (aq) + 4H+(aq) +3e-  MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V
MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V
 MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V
MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V Thus
a)
Mn2+ reacts with MnO4- in acid solution to form MnO2
b)
Mn(MnO4)2 is stable in acid solution
c)
MnO2 disproportionates to Mn2+and MnO4- in acid solution
d)
None of the above

|
Kavya Das answered |
3Mn2+(aq) + 2MnO4-(aq)+ 2H2O (/) → 5MnO2(s) + 4H+ E°cell = 0.47 V
Since E°cell > 0, hence spontaneous.
Thus, Mn2+ is oxidised to MnO2 by MnO4- in acidic medium.
Since E°cell > 0, hence spontaneous.
Thus, Mn2+ is oxidised to MnO2 by MnO4- in acidic medium.
A solution containing one mole per litre each of Cu(NO3)2 ,AgNO3 ,Hg2(NO3)2 and Mg(NO3)2 is being electrolysed using inert electrodes. The value of standard redution potentials are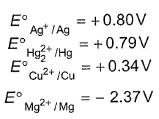 with increasing voltage , the sequence of deposition of metals on the cathode will be
with increasing voltage , the sequence of deposition of metals on the cathode will be- a)Ag ,Hg,Cu,Mg
- b)Mg,Cu,Hg,Ag
- c)Ag,Hg,Cu
- d)Cu,Hg,Ag
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution containing one mole per litre each of Cu(NO3)2 ,AgNO3 ,Hg2(NO3)2 and Mg(NO3)2 is being electrolysed using inert electrodes. The value of standard redution potentials are
with increasing voltage , the sequence of deposition of metals on the cathode will be
a)
Ag ,Hg,Cu,Mg
b)
Mg,Cu,Hg,Ag
c)
Ag,Hg,Cu
d)
Cu,Hg,Ag

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
These metals based on E°red values are placed in the following order:
Mg will reduce
Cu will reduce
Ag+ is reduced by all metals thus Ag first. Hg2+ is reduced by Cu, Mg thus Hg. Cu2+ is reduced by Mg only, thus Cu.
Thus, deposition :
The given figure shows female reproductive system. Which wall of the uterus (A, B or C) sloughs off during menstruation?- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure shows female reproductive system. Which wall of the uterus (A, B or C) sloughs off during menstruation?
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
All of these
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In the given figure, 'A' is endometrium that sloughs off during menstruation. B represents myometrium and C is perimetrium.
Select the correct statement(s) based on the following half-reaction: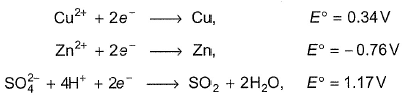
- a)Copper reacts with dil. H2SO4 forming H2 and SO2
- b)Copper reacts with conc. H2SO4 forming SO2
- c)Zinc reacts with conc. H2SO4 forming SO2
- d)Zinc reacts with dil. H2SO4 forming H2
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) based on the following half-reaction:
a)
Copper reacts with dil. H2SO4 forming H2 and SO2
b)
Copper reacts with conc. H2SO4 forming SO2
c)
Zinc reacts with conc. H2SO4 forming SO2
d)
Zinc reacts with dil. H2SO4 forming H2

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
If dil. H2SO4 is used, then H+ is the reacting species.
If cone. H2SO4 is used, then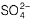 is the reacting species.
is the reacting species.
Thus, copper does not react with H+ (dil. H2SO4) forming H2.
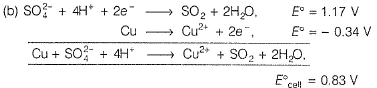
Since E°cell > 0, Thus copper reacts with cone. H2SO4 forming SO2.
(c) Zn +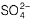 +4H+ → Zn2+ + SO2 + 2H2O
+4H+ → Zn2+ + SO2 + 2H2O
E°cell = 1.93 V, E°cell > 0, thus zinc also reacts with conc.
H2SO4 forming SO2.
(d) Zn + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2, E°cell = 0.76 V
E°cell > 0, thus zinc reacts with dil. H2SO4 forming H2.
If cone. H2SO4 is used, then
Thus, copper does not react with H+ (dil. H2SO4) forming H2.
Since E°cell > 0, Thus copper reacts with cone. H2SO4 forming SO2.
(c) Zn +
E°cell = 1.93 V, E°cell > 0, thus zinc also reacts with conc.
H2SO4 forming SO2.
(d) Zn + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2, E°cell = 0.76 V
E°cell > 0, thus zinc reacts with dil. H2SO4 forming H2.
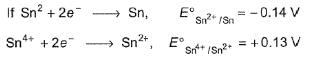
Then- a)Sn2+ is unstable and disproportionates to Sn4+ and Sn
- b)Sn2+ is stable and disproportionation reaction is not spontaneous
- c)Sn4+ is easily reduced to Sn
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
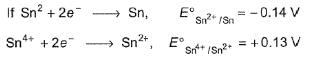
Then
a)
Sn2+ is unstable and disproportionates to Sn4+ and Sn
b)
Sn2+ is stable and disproportionation reaction is not spontaneous
c)
Sn4+ is easily reduced to Sn
d)
None of the above

|
Ameya Tiwari answered |
Since E° cell < 0, disproportionation of Sn2+ to Sn4+ (by oxidation) and Sn (by reduction) is not spontaneous.
The standard reduction potentials at 298K for the following half-cell are given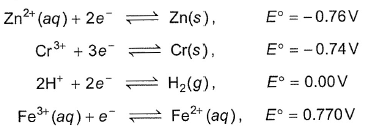 Which is the strongest reducing agent?
Which is the strongest reducing agent?- a)Zn(S)
- b)Cr(s)
- c)H2g
- d)Fe2+(aq)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard reduction potentials at 298K for the following half-cell are given
Which is the strongest reducing agent?
a)
Zn(S)
b)
Cr(s)
c)
H2g
d)
Fe2+(aq)

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
In electrochemical series (ECS), elements have been arranged in the increasing standard reduction potential starting from most negative to most positive value w.r.t. SHE (E°she= 0.00 V).
Most negative standard reduction potential means most easily oxidised and thus is the best reducing agent.
OR Reducing agent in (ECS) is always above oxidising agent. Thus, Zn(s) is the best reducing agent in given set.
Chapter doubts & questions for May Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of May Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











