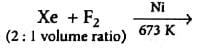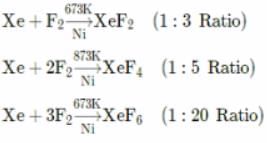All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August Week 3 for NEET Exam
Match column with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
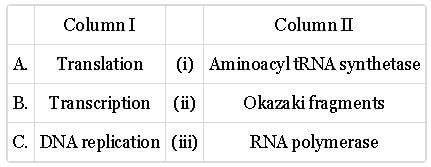
- a)A-(i), B-(i), C-(iii)
- b)A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii)
- c)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
- d)A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.


a)
A-(i), B-(i), C-(iii)
b)
A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii)
c)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
d)
A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i)

|
Lead Academy answered |
DNA Replication: DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It occurs during the cell cycle to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic instructions. DNA replication is a highly accurate process in which the DNA double helix is unwound, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary strand.
Transcription: Transcription is the process by which a segment of DNA is used as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule. It is the first step in the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes how genetic information is used to produce proteins. In transcription, an enzyme called RNA polymerase reads the DNA template and assembles a single-stranded RNA molecule, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), by matching RNA nucleotides to the DNA template.
Translation: Translation is the process in which the information contained in an mRNA molecule is used to synthesize a protein. This process occurs at ribosomes, cellular structures that serve as the protein-manufacturing factories. During translation, the mRNA is read in sets of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, the building blocks of proteins.
The force between two current carrying conductors is due to which of the following- a)Magnetic effect of electric current
- b)Electrostatic interaction
- c)Electromagnetic induction
- d)Polarisation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The force between two current carrying conductors is due to which of the following
a)
Magnetic effect of electric current
b)
Electrostatic interaction
c)
Electromagnetic induction
d)
Polarisation

|
Virat answered |
Current carring wire produce magnetic field
Which of the following laws give the direction of induced e.m.f- a)Faraday’s Law
- b)Ampere’s Theorem
- c)Biot Savart Law
- d)Lenz’s Law
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following laws give the direction of induced e.m.f
a)
Faraday’s Law
b)
Ampere’s Theorem
c)
Biot Savart Law
d)
Lenz’s Law

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Lenz’s law is used for determining the direction of induced current.
Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction states that the direction of induced current in a given magnetic field is such that it opposes the induced change by changing the magnetic field.
Following is the formula of Lenz’s law:
ϵ=−N (∂ϕB/∂t)
Where,
- ε is the induced emf
- ∂ΦB is the change in magnetic flux
- N is the number of turns in the coil
Lenz’s law finds application in electromagnetic braking and in electric generators
In a current carrying conductor varying electric field generates- a)Magnetic field
- b)Potential gradient
- c)Resistance
- d)Current
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a current carrying conductor varying electric field generates
a)
Magnetic field
b)
Potential gradient
c)
Resistance
d)
Current
|
|
Animesh Nhagal answered |
Moving electrons in conducter produce electromagnetic wave...
A solenoid coil of 300 turns /m is carrying a current of 5 A. Calculate the magnitude of magnetic intensity inside the solenoid.- a)1.9 T
- b)1.9 X 10-6 T
- c)1.9 X 10-3 T
- d)1.9 X 10-7 T
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A solenoid coil of 300 turns /m is carrying a current of 5 A. Calculate the magnitude of magnetic intensity inside the solenoid.
a)
1.9 T
b)
1.9 X 10-6 T
c)
1.9 X 10-3 T
d)
1.9 X 10-7 T
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
We know, Magnetic field of solenoid,
= μonI
=4πx10-7x300x5
=4πx15x10-5
=6πx10-9
=18.89x10-9
≈1.9x10-3T
= μonI
=4πx10-7x300x5
=4πx15x10-5
=6πx10-9
=18.89x10-9
≈1.9x10-3T
The magnetic field inside a toroid of radius R is B. If the current through it is doubled and the radius increased four times keeping the number of turns per unit length same, then the magnetic field produced by it will be- a)B
- b)2B
- c)4B
- d)B/2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic field inside a toroid of radius R is B. If the current through it is doubled and the radius increased four times keeping the number of turns per unit length same, then the magnetic field produced by it will be
a)
B
b)
2B
c)
4B
d)
B/2
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
In the 1st case,
B1= μ0Ni/2πr
In the 2nd case,
B2= μ0N2i/2π4r
Comparing both of them,
μ0Ni/2πr=μ0N2i/2π4r
B1=B2/2
B2=2B1
B1= μ0Ni/2πr
In the 2nd case,
B2= μ0N2i/2π4r
Comparing both of them,
μ0Ni/2πr=μ0N2i/2π4r
B1=B2/2
B2=2B1
Which of the following statements is not correct about XeF2?
- a)It can be obtained by direct reaction between F2 and Xe at high pressure
- b)XeF2 undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give O2 and Xe
- c)XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent
- d)XeF2 contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct about XeF2?
a)
It can be obtained by direct reaction between F2 and Xe at high pressure
b)
XeF2 undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give O2 and Xe
c)
XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent
d)
XeF2 contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
XeF2 is obtained by direct reaction of Xe and F2 at high pressure. It undergoes alkali hydrolysis to produce Xe and O2. XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent where Xe+2 can change to +6 state.
Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?- a)Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs
- b)Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments
- c)Radon is used in radiotherapy of cancer
- d)Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?
a)
Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs
b)
Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments
c)
Radon is used in radiotherapy of cancer
d)
Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
|
|
Arindam Chaudhary answered |
Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
Helium is not used for filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres. It is primarily used in other applications such as:
Argon:
- Widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs to prevent the filament from oxidizing.
- Used in welding and metal fabrication to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases.
Neon:
- Used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments due to its ability to produce a bright light when an electric current passes through it.
- Also commonly used in neon signs for advertising.
Radon:
- Used in radiotherapy of cancer as a radiation source to destroy cancer cells.
- It can also be used in some geological research applications to trace the movement of underground gases.
In contrast, helium is typically used in applications such as:
- Cryogenics to achieve low temperatures
- In filling balloons for various purposes
- In cooling nuclear reactors and MRI machines
Therefore, while noble gases have a variety of important uses, filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres with helium is not one of them.
Helium is not used for filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres. It is primarily used in other applications such as:
Argon:
- Widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs to prevent the filament from oxidizing.
- Used in welding and metal fabrication to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases.
Neon:
- Used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments due to its ability to produce a bright light when an electric current passes through it.
- Also commonly used in neon signs for advertising.
Radon:
- Used in radiotherapy of cancer as a radiation source to destroy cancer cells.
- It can also be used in some geological research applications to trace the movement of underground gases.
In contrast, helium is typically used in applications such as:
- Cryogenics to achieve low temperatures
- In filling balloons for various purposes
- In cooling nuclear reactors and MRI machines
Therefore, while noble gases have a variety of important uses, filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres with helium is not one of them.
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a)Helium has the lowest boiling point among the noble gases
- b)Argon is used in electric bulbs
- c)Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration
- d)Xe forms XeF6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
Helium has the lowest boiling point among the noble gases
b)
Argon is used in electric bulbs
c)
Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration
d)
Xe forms XeF6
|
|
Swati Bose answered |
Explanation:
The correct statement is option 'C': Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration.
Explanation:
- Statement a: Helium has the lowest boiling point among the noble gases.
- This statement is correct. Helium has the lowest boiling point (-268.93°C) among all the noble gases. It is a colorless and odorless gas that remains in a gaseous state at room temperature and pressure.
- Statement b: Argon is used in electric bulbs.
- This statement is correct. Argon is commonly used in electric bulbs to maintain an inert atmosphere and prevent oxidation of the filament. It is an abundant noble gas and is chemically inert.
- Statement c: Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration.
- This statement is incorrect. Krypton is not obtained during radioactive disintegration. Krypton (Kr) is a noble gas that is chemically unreactive and does not undergo radioactive disintegration. It is obtained through the fractional distillation of liquid air.
- Statement d: Xe forms XeF6.
- This statement is correct. Xenon (Xe) can form compounds, and one of them is xenon hexafluoride (XeF6). XeF6 is a strong oxidizing agent and is used in chemical reactions and synthesis.
Therefore, the correct statement is option 'C': Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration. Krypton is not obtained through radioactive disintegration, but rather through fractional distillation of liquid air.
The correct statement is option 'C': Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration.
Explanation:
- Statement a: Helium has the lowest boiling point among the noble gases.
- This statement is correct. Helium has the lowest boiling point (-268.93°C) among all the noble gases. It is a colorless and odorless gas that remains in a gaseous state at room temperature and pressure.
- Statement b: Argon is used in electric bulbs.
- This statement is correct. Argon is commonly used in electric bulbs to maintain an inert atmosphere and prevent oxidation of the filament. It is an abundant noble gas and is chemically inert.
- Statement c: Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration.
- This statement is incorrect. Krypton is not obtained during radioactive disintegration. Krypton (Kr) is a noble gas that is chemically unreactive and does not undergo radioactive disintegration. It is obtained through the fractional distillation of liquid air.
- Statement d: Xe forms XeF6.
- This statement is correct. Xenon (Xe) can form compounds, and one of them is xenon hexafluoride (XeF6). XeF6 is a strong oxidizing agent and is used in chemical reactions and synthesis.
Therefore, the correct statement is option 'C': Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration. Krypton is not obtained through radioactive disintegration, but rather through fractional distillation of liquid air.
Given below are the steps of protein synthesis. Arrange them in. correct sequence and select the correct option.
(i) Codon-anticodon reaction between mRNA and aminoacyl tRNA complex.
(ii) Attachment of mRNA and smaller sub-unit of ribosome.
(iii) Charging or aminoacylation of tRNA.
(iv) Attachment of larger sub unit of ribosome to the mRNA-tRNAMet complex.
(v) Linking of adjacent amino acids.
(vi) Formation of polypeptide chain.- a)(ii) → (i) → (iii) → (v) → (iv) → (vi)
- b)(v) → (ii) → (i) → (iii) → (iv) → (vi)
- c)(iii) → (ii) → (iv) → (i) → (v) → (vi)
- d)(iii) → (ii) → (i) → (iv) → (v) → (vi)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are the steps of protein synthesis. Arrange them in. correct sequence and select the correct option.
(i) Codon-anticodon reaction between mRNA and aminoacyl tRNA complex.
(ii) Attachment of mRNA and smaller sub-unit of ribosome.
(iii) Charging or aminoacylation of tRNA.
(iv) Attachment of larger sub unit of ribosome to the mRNA-tRNAMet complex.
(v) Linking of adjacent amino acids.
(vi) Formation of polypeptide chain.
(i) Codon-anticodon reaction between mRNA and aminoacyl tRNA complex.
(ii) Attachment of mRNA and smaller sub-unit of ribosome.
(iii) Charging or aminoacylation of tRNA.
(iv) Attachment of larger sub unit of ribosome to the mRNA-tRNAMet complex.
(v) Linking of adjacent amino acids.
(vi) Formation of polypeptide chain.
a)
(ii) → (i) → (iii) → (v) → (iv) → (vi)
b)
(v) → (ii) → (i) → (iii) → (iv) → (vi)
c)
(iii) → (ii) → (iv) → (i) → (v) → (vi)
d)
(iii) → (ii) → (i) → (iv) → (v) → (vi)
|
|
Anshu Kaur answered |
Overview of Protein Synthesis Steps
Protein synthesis is a vital biological process that involves several key steps. The correct sequence of events is crucial for accurate translation of mRNA into proteins.
Steps in the Correct Sequence
1. Charging or Aminoacylation of tRNA (iii)
- Before translation, tRNA molecules are charged with their respective amino acids by specific enzymes called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
2. Attachment of mRNA and Smaller Sub-unit of Ribosome (ii)
- The small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA, scanning for the start codon (AUG), which signals the beginning of translation.
3. Attachment of Larger Sub-unit of Ribosome to the mRNA-tRNAMet Complex (iv)
- Once the start codon is recognized, the large ribosomal subunit attaches to form a complete ribosome, ready for translation.
4. Codon-Anticodon Reaction Between mRNA and Aminoacyl tRNA Complex (i)
- The charged tRNA with its corresponding amino acid binds to the mRNA codon through complementary base pairing between the codon and the tRNA's anticodon.
5. Linking of Adjacent Amino Acids (v)
- The ribosome facilitates the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids brought by the tRNAs, elongating the polypeptide chain.
6. Formation of Polypeptide Chain (vi)
- As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, the polypeptide chain grows until a stop codon is reached, leading to the termination of translation.
Conclusion
The correct sequence (iii) → (ii) → (iv) → (i) → (v) → (vi) reflects the organized process of protein synthesis, ensuring that proteins are accurately synthesized based on the genetic code presented by mRNA. Thus, option 'D' is the correct answer.
Protein synthesis is a vital biological process that involves several key steps. The correct sequence of events is crucial for accurate translation of mRNA into proteins.
Steps in the Correct Sequence
1. Charging or Aminoacylation of tRNA (iii)
- Before translation, tRNA molecules are charged with their respective amino acids by specific enzymes called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
2. Attachment of mRNA and Smaller Sub-unit of Ribosome (ii)
- The small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA, scanning for the start codon (AUG), which signals the beginning of translation.
3. Attachment of Larger Sub-unit of Ribosome to the mRNA-tRNAMet Complex (iv)
- Once the start codon is recognized, the large ribosomal subunit attaches to form a complete ribosome, ready for translation.
4. Codon-Anticodon Reaction Between mRNA and Aminoacyl tRNA Complex (i)
- The charged tRNA with its corresponding amino acid binds to the mRNA codon through complementary base pairing between the codon and the tRNA's anticodon.
5. Linking of Adjacent Amino Acids (v)
- The ribosome facilitates the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids brought by the tRNAs, elongating the polypeptide chain.
6. Formation of Polypeptide Chain (vi)
- As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, the polypeptide chain grows until a stop codon is reached, leading to the termination of translation.
Conclusion
The correct sequence (iii) → (ii) → (iv) → (i) → (v) → (vi) reflects the organized process of protein synthesis, ensuring that proteins are accurately synthesized based on the genetic code presented by mRNA. Thus, option 'D' is the correct answer.
What is the process of activation of amino acids in the presence of ATP and its linkage to their cognate tRNA known as?- a)Aminoacetylation of ATP
- b)Charging of ATP
- c)Aminoacetylation of tRNA
- d)Charging of tRNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the process of activation of amino acids in the presence of ATP and its linkage to their cognate tRNA known as?
a)
Aminoacetylation of ATP
b)
Charging of ATP
c)
Aminoacetylation of tRNA
d)
Charging of tRNA

|
Lead Academy answered |
- In order to form a peptide bond, a certain quantity of energy is required.
- The first phase in this process is known as charging of tRNA.
- It is also known as Aminoacylation of tRNA.
- In this process, the amino acids are activated in the presence of ATP and are linked to their cognate tRNA.
What would happen, if in a gene encoding a polypeptide of 50 amino acids, 25th codon (UAU) is mutated to UAA?- a)A polypeptide of 49 amino acids will be formed
- b)A polypeptide of 25 amino acids will be formed
- c)A polypeptide of 24 amino acids will be formed
- d)Two polypeptides of 24 and 25 amino acids will be formed
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What would happen, if in a gene encoding a polypeptide of 50 amino acids, 25th codon (UAU) is mutated to UAA?
a)
A polypeptide of 49 amino acids will be formed
b)
A polypeptide of 25 amino acids will be formed
c)
A polypeptide of 24 amino acids will be formed
d)
Two polypeptides of 24 and 25 amino acids will be formed
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
UAA is a nonsense codon. It signals for polypeptide chain termination. Hence, only 24 amino acids chain will be formed.
The difference(s) between mRNA and tRNA is/are that:
(i) mRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive base - pairing
(ii) tRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive pairing
(iii) tRNA is usually smaller than mRNA
(iv) mRNA bears anticodon but tRNA has codons- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)All of these
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference(s) between mRNA and tRNA is/are that:
(i) mRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive base - pairing
(ii) tRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive pairing
(iii) tRNA is usually smaller than mRNA
(iv) mRNA bears anticodon but tRNA has codons
(i) mRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive base - pairing
(ii) tRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive pairing
(iii) tRNA is usually smaller than mRNA
(iv) mRNA bears anticodon but tRNA has codons
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
All of these
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
mRNA is the longest RNA with maximum molecular weight but it is least abundant. tRNA is the smallest and coiled like a clover leaf with elaborated 3-dimensional structure. mRNA consists of 75-6000 bases while tRNA has 73-93 bases.
In a mRNA molecule, untranslated regions (UTRs) are present at- a)5 - end (before start codon)
- b)3 - end (after stop codon)
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)3 - end only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a mRNA molecule, untranslated regions (UTRs) are present at
a)
5 - end (before start codon)
b)
3 - end (after stop codon)
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
3 - end only
|
|
Harshitha Kumar answered |
In a mRNA molecule, untranslated regions (UTRs) are present at both the 5' end (before the start codon) and the 3' end (after the stop codon). The correct answer is option 'C'.
Explanation:
mRNA (messenger RNA) is a single-stranded RNA molecule that carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It contains several regions, including the coding region and the untranslated regions (UTRs).
1. Untranslated Regions (UTRs):
- Untranslated regions (UTRs) are the regions at the ends of the mRNA molecule that are not translated into protein. They are located both at the 5' end (before the start codon) and the 3' end (after the stop codon) of the mRNA molecule.
- UTRs play important regulatory roles in gene expression by influencing the stability, localization, and translation efficiency of the mRNA molecule.
- The 5' UTR, also known as the leader sequence, is present at the beginning of the mRNA molecule. It contains regulatory elements such as the Kozak sequence, which is involved in the initiation of translation.
- The 3' UTR, also known as the trailer sequence, is present at the end of the mRNA molecule. It contains regulatory elements such as binding sites for microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins, which can control mRNA stability and translation.
2. Coding Region:
- The coding region of mRNA contains the nucleotide sequence that encodes the amino acid sequence of a protein. It is located between the start codon (usually AUG) and the stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA).
- During translation, the ribosomes read the codons in the mRNA molecule and assemble the corresponding amino acids to form a protein.
In conclusion, untranslated regions (UTRs) are present at both the 5' and 3' ends of an mRNA molecule. They play important regulatory roles in gene expression by influencing mRNA stability, localization, and translation efficiency.
Explanation:
mRNA (messenger RNA) is a single-stranded RNA molecule that carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It contains several regions, including the coding region and the untranslated regions (UTRs).
1. Untranslated Regions (UTRs):
- Untranslated regions (UTRs) are the regions at the ends of the mRNA molecule that are not translated into protein. They are located both at the 5' end (before the start codon) and the 3' end (after the stop codon) of the mRNA molecule.
- UTRs play important regulatory roles in gene expression by influencing the stability, localization, and translation efficiency of the mRNA molecule.
- The 5' UTR, also known as the leader sequence, is present at the beginning of the mRNA molecule. It contains regulatory elements such as the Kozak sequence, which is involved in the initiation of translation.
- The 3' UTR, also known as the trailer sequence, is present at the end of the mRNA molecule. It contains regulatory elements such as binding sites for microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins, which can control mRNA stability and translation.
2. Coding Region:
- The coding region of mRNA contains the nucleotide sequence that encodes the amino acid sequence of a protein. It is located between the start codon (usually AUG) and the stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA).
- During translation, the ribosomes read the codons in the mRNA molecule and assemble the corresponding amino acids to form a protein.
In conclusion, untranslated regions (UTRs) are present at both the 5' and 3' ends of an mRNA molecule. They play important regulatory roles in gene expression by influencing mRNA stability, localization, and translation efficiency.
Complete the following reactions by filling the appropriate choice.
(A) 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + _(i)_ + _(ii)_
(B) XeF6 + 3H2O → _(iii)_ + 6HF- a)(i) F2, (ii) H2O, (iii) XeOF4
- b)(i) 24HF, (ii) 3O2, (iii) XeO3
- c)(i) 2HF, (ii) 2H2O, (iii) XeO
- d)(i) HF, (ii) H2O, (iii) Xe2O3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Complete the following reactions by filling the appropriate choice.
(A) 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + _(i)_ + _(ii)_
(B) XeF6 + 3H2O → _(iii)_ + 6HF
(A) 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + _(i)_ + _(ii)_
(B) XeF6 + 3H2O → _(iii)_ + 6HF
a)
(i) F2, (ii) H2O, (iii) XeOF4
b)
(i) 24HF, (ii) 3O2, (iii) XeO3
c)
(i) 2HF, (ii) 2H2O, (iii) XeO
d)
(i) HF, (ii) H2O, (iii) Xe2O3
|
|
Upasana Sharma answered |
The given reaction is incomplete. Please provide the missing reactant or product in order to complete the reaction.
UTRs are the untranslated regions present on- a)rRNA
- b)tRNA
- c)mRNA
- d)hnRNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
UTRs are the untranslated regions present on
a)
rRNA
b)
tRNA
c)
mRNA
d)
hnRNA
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
mRNA has some additional sequences that are not translated and are referred as untranslated regions (UTRs). The UTRs are present at both the 5'-end (before the start codon) and the 3'-end (after the stop codon). They are required for an efficient translation process.
Which RNA carries the amino acids from the amino acid pool to mRNA during protein synthesis?- a)rRNA
- b)mRNA
- c)tRNA
- d)hnRNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which RNA carries the amino acids from the amino acid pool to mRNA during protein synthesis?
a)
rRNA
b)
mRNA
c)
tRNA
d)
hnRNA
|
|
Anshu Kaur answered |
Role of tRNA in Protein Synthesis
During protein synthesis, the translation process requires the transportation of amino acids to the ribosome, where they are assembled into proteins. The molecule responsible for this critical function is transfer RNA (tRNA).
What is tRNA?
- tRNA is a type of RNA that serves as an adaptor molecule in protein synthesis.
- It has a unique structure with an anticodon region that pairs with the corresponding codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA).
- Each tRNA molecule is specific to one amino acid, which it carries to the ribosome.
Function of tRNA
- Amino Acid Transport: tRNA transports amino acids from the amino acid pool in the cytoplasm to the ribosome.
- Codon Recognition: The anticodon on tRNA matches with the codon on mRNA, ensuring the correct amino acid is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain.
- Peptide Bond Formation: Once the correct tRNA is in place at the ribosome, the amino acid it carries is added to the nascent protein via peptide bonds.
Importance in Translation
- tRNA is essential for translating the genetic code carried by mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids.
- Without tRNA, the ribosome would not be able to correctly interpret the mRNA sequence, resulting in nonfunctional or incorrectly formed proteins.
In summary, tRNA plays a vital role in translating the genetic information from mRNA into functional proteins by transporting the necessary amino acids during protein synthesis. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - tRNA.
During protein synthesis, the translation process requires the transportation of amino acids to the ribosome, where they are assembled into proteins. The molecule responsible for this critical function is transfer RNA (tRNA).
What is tRNA?
- tRNA is a type of RNA that serves as an adaptor molecule in protein synthesis.
- It has a unique structure with an anticodon region that pairs with the corresponding codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA).
- Each tRNA molecule is specific to one amino acid, which it carries to the ribosome.
Function of tRNA
- Amino Acid Transport: tRNA transports amino acids from the amino acid pool in the cytoplasm to the ribosome.
- Codon Recognition: The anticodon on tRNA matches with the codon on mRNA, ensuring the correct amino acid is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain.
- Peptide Bond Formation: Once the correct tRNA is in place at the ribosome, the amino acid it carries is added to the nascent protein via peptide bonds.
Importance in Translation
- tRNA is essential for translating the genetic code carried by mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids.
- Without tRNA, the ribosome would not be able to correctly interpret the mRNA sequence, resulting in nonfunctional or incorrectly formed proteins.
In summary, tRNA plays a vital role in translating the genetic information from mRNA into functional proteins by transporting the necessary amino acids during protein synthesis. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - tRNA.
Magnetic Field inside a solenoid is ________.- a)increases from one end to another
- b)uniform
- c)varies from point to point
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Magnetic Field inside a solenoid is ________.
a)
increases from one end to another
b)
uniform
c)
varies from point to point
d)
None of the above

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Solenoid: A cylindrical coil of many tightly wound turns of insulated wire with a general diameter of the coil smaller than its length is called a solenoid.
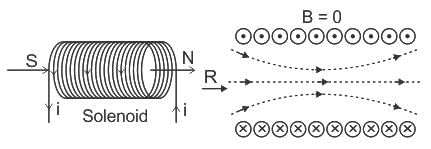
- A magnetic field is produced around and within the solenoid.
- The magnetic field within the solenoid is uniform and parallel to the axis of the solenoid.
The strength of the magnetic field in a solenoid is given by:-
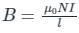
Where, N = number of turns,
l = length of the solenoid,
l = current in the solenoid and
μo = absolute permeability of air or vacuum.
The magnetic field inside a solenoid is uniform. So option 2 is correct.
l = length of the solenoid,
l = current in the solenoid and
μo = absolute permeability of air or vacuum.
The magnetic field inside a solenoid is uniform. So option 2 is correct.
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given :
Direction : Read the sequence of nucleotides in the given segment of mRNA and the respective amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain.
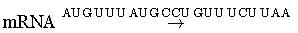
Polypeptide Met-Phe-Met-Pro-Val-Ser
Which codons respectively code for proline and valine amino acids in the given polypeptide chain, respectively?
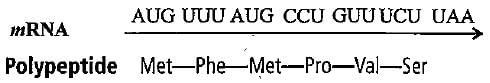
- a)CCU and GUU
- b)GUU and UCU
- c)UCU and UAA
- d)GUU and CCU
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given :
Direction : Read the sequence of nucleotides in the given segment of mRNA and the respective amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain.
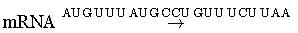
Polypeptide Met-Phe-Met-Pro-Val-Ser
Which codons respectively code for proline and valine amino acids in the given polypeptide chain, respectively?
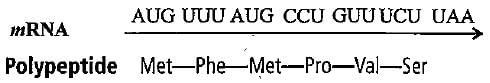
Direction : Read the sequence of nucleotides in the given segment of mRNA and the respective amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain.
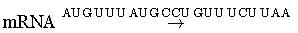
Polypeptide Met-Phe-Met-Pro-Val-Ser
Which codons respectively code for proline and valine amino acids in the given polypeptide chain, respectively?
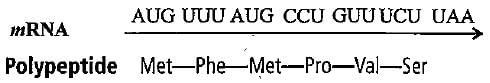
a)
CCU and GUU
b)
GUU and UCU
c)
UCU and UAA
d)
GUU and CCU
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on an mRNA strand that encodes a specific amino acid.
Sixty-four different three nucleotide combinations (codons) can be made using the four nucleotides in mRNA (43 = 64 combinations).
Following are the codons that represent Valine and proline respectively.
Valine: GUA, GUC, GUG, GUU
proline: CCT, CCC, CCA, CCG
Sixty-four different three nucleotide combinations (codons) can be made using the four nucleotides in mRNA (43 = 64 combinations).
Following are the codons that represent Valine and proline respectively.
Valine: GUA, GUC, GUG, GUU
proline: CCT, CCC, CCA, CCG
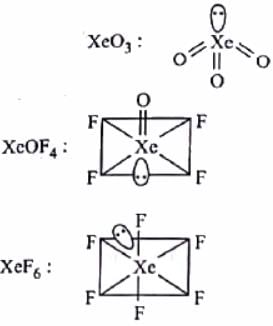
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
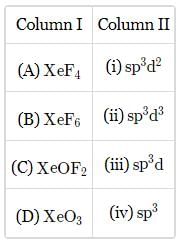
- a)(A) → (i); (B) → (ii); (C) → (iii); (D) → (iv)
- b)(A) → (iv); (B) → (iii); (C) → (ii); (D) → (i)
- c)(A) → (iii); (B) → (iv); (C) → (i); (D) → (ii)
- d)(A) → (ii); (B) → (iii); (C) → (iv); (D) → (i)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
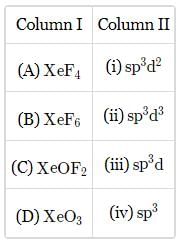
a)
(A) → (i); (B) → (ii); (C) → (iii); (D) → (iv)
b)
(A) → (iv); (B) → (iii); (C) → (ii); (D) → (i)
c)
(A) → (iii); (B) → (iv); (C) → (i); (D) → (ii)
d)
(A) → (ii); (B) → (iii); (C) → (iv); (D) → (i)
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Hybridization of an atom is identified by caliculating the sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs.
If sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 2. sp hybridization
If sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 3. sp2 hybridization
If sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 4. sp3 hybridization.XeO3 has 3 sigma bonds and 1 lone pair.So the sum is 4.So it is sp3
If sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 5. sp3d hybridization.XeOF2 has 3 sigma bonds and two lone pairs ,the sum is 5.So it is SP3d.
If sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 6 .sp3d2 hybridization.XeF4 has 4 sigma bonds and 2 lone pair.So the sum is 6.So it is sp3d2
If sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 7. sp3d2 hybridization.XeF6 has 6 sigma bonds and 1 lone pair. So the sum is 7.So it is sp3d3
So the option A is correct match.
During translation, activated amino acids get linked to (RNA). This process is commonly called as- a)charging of tRNA
- b)discharging of tRNA
- c)aminoacylation of tRNA
- d)both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During translation, activated amino acids get linked to (RNA). This process is commonly called as
a)
charging of tRNA
b)
discharging of tRNA
c)
aminoacylation of tRNA
d)
both (a) and (c)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
During translation, a (RNA) is specifically linked to an amino acid, this process takes place under the direction of an enzyme, aminoacyl tRNA synthetase that is extremely specific, i.e., recognises only one amino acid. (RNA) complexed with amino acid is called as charged tRNA. The process is referred to a charging or aminoacylation of tRNA.
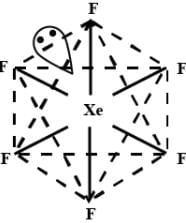
Which of the following is not correct about xenon hexafluoride?
- a)It has oxidation state of +6
- b)The hybridisation involved in XeF6 is sp3d3
- c)The shape of XeF6 is distorted octahedral and can be represented as
- d)On hydrolysis it gives Xe, HF and O2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about xenon hexafluoride?


a)
It has oxidation state of +6
b)
The hybridisation involved in XeF6 is sp3d3
c)
The shape of XeF6 is distorted octahedral and can be represented as
d)
On hydrolysis it gives Xe, HF and O2
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
On hydrolysis the products formed are XeO3 and HF.
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
In XeF2, XeF4, and XeF6, the number of lone pairs on Xe, is respectively.- a)2,3,1
- b)1,2,3
- c)4,1,2
- d)3,2,1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In XeF2, XeF4, and XeF6, the number of lone pairs on Xe, is respectively.
a)
2,3,1
b)
1,2,3
c)
4,1,2
d)
3,2,1
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
XeF2 has a linear shape. Its hybridization is sp3d which means it should have a trigonal bipyramidal shape. Since it has 3 lone pairs, they occupy the equatorial triangle.
XeF4 has sp3d2 hybridization. It has a square planar shape and 2 lone pair of electrons.
XeF6 has one lone pair of electrons. The 6 out of 8 electrons of Xenon are shared by 6 atoms of fluorine.
XeF4 has sp3d2 hybridization. It has a square planar shape and 2 lone pair of electrons.
XeF6 has one lone pair of electrons. The 6 out of 8 electrons of Xenon are shared by 6 atoms of fluorine.
Chapter doubts & questions for August Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily