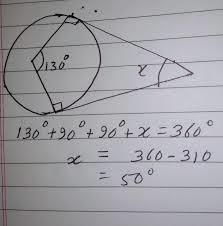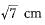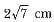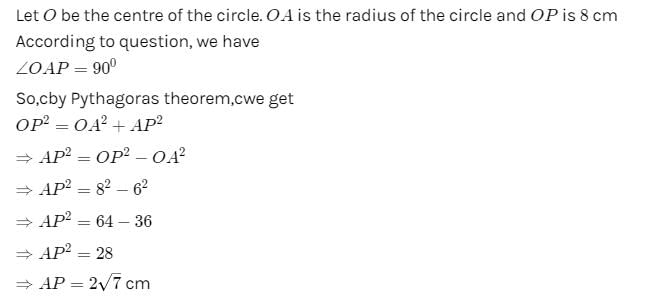All Exams >
Class 10 >
Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of November Week 2 for Class 10 Exam
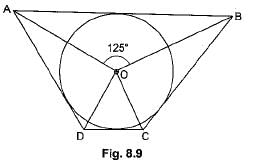
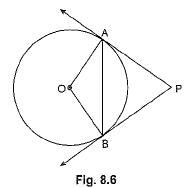
In Fig. 8.6, if PA and PB are tangents to the circle with centre O such that ∠APB = 50°, then ∠PAB is equal to
- a)35°
- b)65°
- c)40°
- d)70°
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Fig. 8.6, if PA and PB are tangents to the circle with centre O such that ∠APB = 50°, then ∠PAB is equal to


a)
35°
b)
65°
c)
40°
d)
70°

|
Crafty Classes answered |
In triangle PAB
∠A+∠B+∠P=180
x+x+50=180 [ if tangents are drawn from same point then they are equal so PAB is a isoceles triangle ]
2x=130
x=65
∠A+∠B+∠P=180
x+x+50=180 [ if tangents are drawn from same point then they are equal so PAB is a isoceles triangle ]
2x=130
x=65
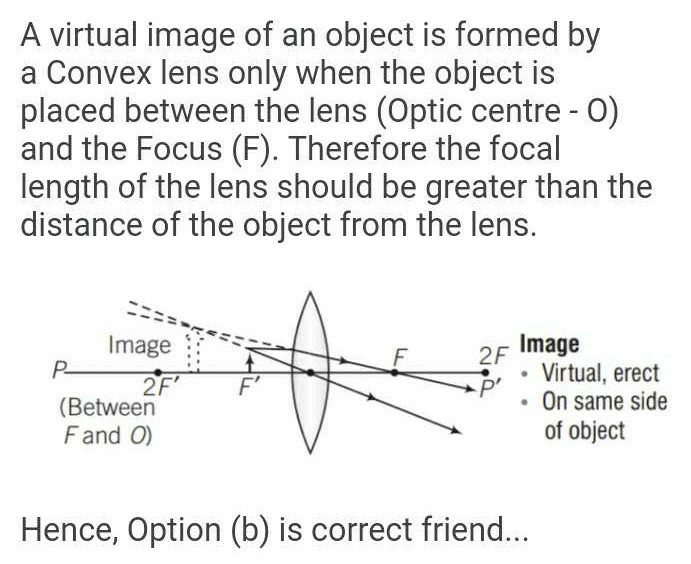
The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is- a)Both convex and concave
- b)Concave lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Convex Lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is
a)
Both convex and concave
b)
Concave lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Convex Lens
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Shortsightedness is corrected using a concave (curved inwards) lens which is placed in front of a myopic eye, moving the image back to the retina and making it clearer.
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
- a)Convex lens
- b)Concave lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
a)
Convex lens
b)
Concave lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Both convex and concave

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
A concave lens (also known as a diverging lens) is thinner in the center and thicker at the edges. When light rays pass through a concave lens, they diverge (spread out), causing the rays to appear to come from a single point on the same side of the lens as the object. This results in the formation of a virtual image.
Key characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens:
- Diminished: The image is smaller than the actual object.
- Erect: The image is upright, meaning it has the same orientation as the object.
- Virtual: The image cannot be projected on a screen because the light rays do not actually meet but only appear to do so when extended backward.
Because of these properties, a concave lens always forms a diminished, erect, and virtual image, no matter where the object is placed in front of the lens.
On the other hand, a convex lens (also known as a converging lens) can form different types of images (real and inverted or virtual and erect) depending on the position of the object relative to the lens. But it does not always form a diminished and erect image, unlike the concave lens.
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?- a)Between F and 2F
- b)At focus (F)
- c)At 2F on the other side
- d)At 2F on the same side
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?
a)
Between F and 2F
b)
At focus (F)
c)
At 2F on the other side
d)
At 2F on the same side
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
At the 2F point, the object distance equals the image distance and the object height equals the image height. As the object distance approaches one focal length, the image distance and image height approaches infinity.
Two parallel lines touch the circle at points A and B respectively, If area of the circle is 25πcm2, then AB is equal to- a)5 cm
- b)8 cm
- c)10 cm
- d)25 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two parallel lines touch the circle at points A and B respectively, If area of the circle is 25πcm2, then AB is equal to
a)
5 cm
b)
8 cm
c)
10 cm
d)
25 cm
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Let radius of circle = R
∴ πR2 = 25π
⇒ R = 5cm
∴ Distance between two parallel tangents
= diameter = 2 x 5 = 10 cm.
∴ πR2 = 25π
⇒ R = 5cm
∴ Distance between two parallel tangents
= diameter = 2 x 5 = 10 cm.
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens) - a)2.5 f
- b)2 f
- c)4 f
- d)f
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens)
a)
2.5 f
b)
2 f
c)
4 f
d)
f
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Let the distance between the object and its real image formed by convex lens be d1.
Let the distance of the object from lens be x,so,the image distance from the lens is (d-x)
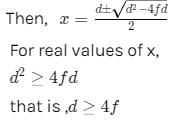
Let the distance of the object from lens be x,so,the image distance from the lens is (d-x)
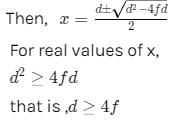
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f.
hence,option C is correct.
.
hence,option C is correct.
.
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a- a)Can be convex or concave
- b)Convex lens
- c)Diverging lens
- d)Concave lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a
a)
Can be convex or concave
b)
Convex lens
c)
Diverging lens
d)
Concave lens
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The focal length of convex lens is always positive. Image obtained can be either real or virtual.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?- a)At infinity
- b)At twice the focal length
- c)Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
- d)At the principal focus of the lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?
a)
At infinity
b)
At twice the focal length
c)
Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
d)
At the principal focus of the lens
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
At twice the focal length the image formed by convex lens is real and of the same size as object.
Drop of water behaves likes a- a)Diverging lens
- b)Concave lens
- c)Convex lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Drop of water behaves likes a
a)
Diverging lens
b)
Concave lens
c)
Convex lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The surface of a water drop curves outward to make a dome. This outward, or convex, curvature bends light rays inward. will act as a concave lens that bends the light rays outward. As a result, letters seen through the layer of water in a cup appear smaller than they are.
A magnifying glass is a- a)Both convex and concave
- b)Concave lens
- c)Diverging lens
- d)Convex Lens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnifying glass is a
a)
Both convex and concave
b)
Concave lens
c)
Diverging lens
d)
Convex Lens
|
|
Ꭰꮰ Ꮥꮑꭿꮶꭼ answered |
A magnifying glass is a convex lens used to make an object appear much larger than it actually is. This works when the object is placed at a distance less than the focal length from the lens.
Which lens always forms a virtual image ?- a)Concave lens
- b)Convex lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which lens always forms a virtual image ?
a)
Concave lens
b)
Convex lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Nandini nair answered |
Explanation:
A virtual image is an image that cannot be projected onto a screen. It is always located on the opposite side of the lens from the object and is always upright. Virtual images are formed when light rays appear to come from a point behind the lens, rather than actually converging at that point.
Concave Lens:
- A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a concave lens, they diverge or spread out.
- As a result, a concave lens always forms a virtual image that is upright, smaller in size, and located between the lens and the object.
Convex Lens:
- A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a convex lens, they converge or come together.
- Depending on the placement of the object, a convex lens can form either a real or virtual image.
Converging Lens:
- A converging lens is another name for a convex lens.
- As discussed above, a converging lens can form both real and virtual images.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it can be concluded that a concave lens always forms a virtual image.
A virtual image is an image that cannot be projected onto a screen. It is always located on the opposite side of the lens from the object and is always upright. Virtual images are formed when light rays appear to come from a point behind the lens, rather than actually converging at that point.
Concave Lens:
- A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a concave lens, they diverge or spread out.
- As a result, a concave lens always forms a virtual image that is upright, smaller in size, and located between the lens and the object.
Convex Lens:
- A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a convex lens, they converge or come together.
- Depending on the placement of the object, a convex lens can form either a real or virtual image.
Converging Lens:
- A converging lens is another name for a convex lens.
- As discussed above, a converging lens can form both real and virtual images.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it can be concluded that a concave lens always forms a virtual image.
A ray of light incident on the optical centre of a spherical lens, after refraction passes through:- a)Radius of curvature
- b)Optical centre
- c)Twice the focal length
- d)Principal focus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light incident on the optical centre of a spherical lens, after refraction passes through:
a)
Radius of curvature
b)
Optical centre
c)
Twice the focal length
d)
Principal focus
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
A ray of light passes through optical centre of a lens is refracted back along the same path ie. through optical centre itself.
In the given figure, point P is 26 cm away from the centre O of a circle and the length PT of the tangent drawn from P to the circle is 24 cm. Then the radius of the circle is
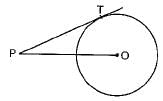
- a)25 cm
- b)26 cm
- c)24 cm
- d)10 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure, point P is 26 cm away from the centre O of a circle and the length PT of the tangent drawn from P to the circle is 24 cm. Then the radius of the circle is


a)
25 cm
b)
26 cm
c)
24 cm
d)
10 cm
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
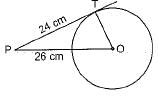
∵ OT is radius and PT is tangent
∴ OT ⊥ PT
Now, in ΔOTP,
OP2 = PT2 + OT2
⇒ 262 = 242 + OT2
⇒ 676 - 576 -OT2
⇒ 100 = OT2 ⇒ 10 cm = OT
The image formed by a convex lens is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Then the position of the object should be- a)beyond the centre of curvature
- b)at the centre of curvature
- c)between the focus and the centre of curvature
- d)between the pole and focus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The image formed by a convex lens is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Then the position of the object should be
a)
beyond the centre of curvature
b)
at the centre of curvature
c)
between the focus and the centre of curvature
d)
between the pole and focus
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
The image formed by a convex lens is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Then the position of the object should be. If the object is placed between the pole and focus, then the image formed will be virtual, erect and enlarged.
A lens which forms a virtual and enlarged image is- a)Convex lens
- b)Concave lens
- c)Diverging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A lens which forms a virtual and enlarged image is
a)
Convex lens
b)
Concave lens
c)
Diverging lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Vedashree V answered |
A lens that forms a virtual and enlarged image is Çôñvëx lèñs.....
If a lens has a focal length, f = -12 cm. then it is a- a)Concave lens
- b)Convex lens
- c)Can be convex or concave
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a lens has a focal length, f = -12 cm. then it is a
a)
Concave lens
b)
Convex lens
c)
Can be convex or concave
d)
none of these

|
Saksham answered |
Because concave lens has negative focal length according to sign conventions. convex lens has positive focal length
C (O, r1) and C (O, r2) are two concentric circles with r1 > r2. AB is a chord of C (O, r1) touching C (O, r2) at C then- a)AB = r1
- b)AB = r2
- c)AC = BC
- d) AB = r1 + r2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
C (O, r1) and C (O, r2) are two concentric circles with r1 > r2. AB is a chord of C (O, r1) touching C (O, r2) at C then
a)
AB = r1
b)
AB = r2
c)
AC = BC
d)
AB = r1 + r2

|
Arjun Dasgupta answered |
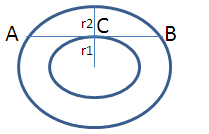
Given that AB is chord of bigger circle and it is tangent to a smaller circle touching at C.
Then AB is perpendicular to OC. C is mid point of AB then AC = BC.
What is one reason why caste alone cannot determine election results in India?- a)All political parties have equal representation of different castes.
- b)Caste-based voting patterns are not significant in urban areas.
- c)Many voters consider factors other than caste, such as party ideology and candidate credibility.
- d)Caste identities are legally prohibited from influencing elections.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
All political parties have equal representation of different castes.
b)
Caste-based voting patterns are not significant in urban areas.
c)
Many voters consider factors other than caste, such as party ideology and candidate credibility.
d)
Caste identities are legally prohibited from influencing elections.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Many voters in India consider factors beyond caste when casting their votes, such as the party’s ideology, candidate's credibility, and local issues. This diversity in voting considerations means that caste alone cannot determine election outcomes, as electoral decisions are influenced by a range of political and social factors.
Is the optical centre always at the centre of lens?- a)Never
- b)Only if both the curved surfaces are asymmetrical
- c)Only if both the curved surfaces are symmetrical
- d)Yes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Is the optical centre always at the centre of lens?
a)
Never
b)
Only if both the curved surfaces are asymmetrical
c)
Only if both the curved surfaces are symmetrical
d)
Yes

|
Vivek R answered |
1)take a convex lens 2)take a small slice of convex lens away from optical axis(from any of the either side) 3)the small part of the lens now would still act as a lens but the optical centre is outside the body. hence it is necessary that the convex and the concave curves of a convex lens be symmetrical and only then the optical centre would be at the centre of the lens.
To determine the focal length of convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object we generally follow the following steps which are not in proper sequence.
(a) Hold the lens between the object and the screen
(b) Measure the distance between the lens and the screen
(c) Select a well lit distant object
(d) Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image
The correct sequence will be:- a)c, a, d, b
- b)c, d, b, a
- c)a, c, d, b
- d)c, d, a, b
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
To determine the focal length of convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object we generally follow the following steps which are not in proper sequence.
(a) Hold the lens between the object and the screen
(b) Measure the distance between the lens and the screen
(c) Select a well lit distant object
(d) Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image
The correct sequence will be:
(a) Hold the lens between the object and the screen
(b) Measure the distance between the lens and the screen
(c) Select a well lit distant object
(d) Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image
The correct sequence will be:
a)
c, a, d, b
b)
c, d, b, a
c)
a, c, d, b
d)
c, d, a, b
|
|
Harsiddhi Parmar answered |
A
Which lens has a virtual focus?- a)Concave lens
- b)Convex lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which lens has a virtual focus?
a)
Concave lens
b)
Convex lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Concave lenses are thinner at the middle. Rays of light that pass through the lens are spread out (they diverge). A concave lens is a diverging lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens the refracted rays diverge so that they appear to come from one point called the principal focus.
In the given figure, AB and AC are tangents to the circle with centre O such that ∠BAC = 40°, then ∠BOC is equal to
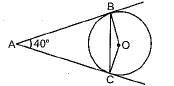
- a)40°
- b)50°
- c)140°
- d)150°
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure, AB and AC are tangents to the circle with centre O such that ∠BAC = 40°, then ∠BOC is equal to


a)
40°
b)
50°
c)
140°
d)
150°

|
Avi Mukherjee answered |
The raddi to the tangents of contact make right and so the sum of the two angles will be 180degree
In a quadrilateral, the sum of the angles is 360degree
so the other two angles add up to 180degree
∠ACO = ∠ABO = 90degree
find ∠BOC = ?
∵∠BAC = 40degree
∠BAC +∠BOC = 180degree
∠BOC = (180degree 40degree)
∠BOC = 140degree
Chapter doubts & questions for November Week 2 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of November Week 2 - Weekly Tests for Class 10 Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily