All Exams >
JEE >
VITEEE: Subject Wise and Full Length MOCK Tests >
All Questions
All questions of Full Length (PCME) Mock Tests for JEE Exam
Two moles of an aldehyde react with concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide and produce one mole of acid and one mole of alcohol. The aldehyde is- a)Acetaldehyde, CH₃CHO
- b)Formaldehyde, HCHO
- c)Propionaldehyde, CH₃CH₂CHO
- d)All the three above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two moles of an aldehyde react with concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide and produce one mole of acid and one mole of alcohol. The aldehyde is
a)
Acetaldehyde, CH₃CHO
b)
Formaldehyde, HCHO
c)
Propionaldehyde, CH₃CH₂CHO
d)
All the three above.

|
Beyond the Horizon answered |
Its Cannizaro reaction that uses concentrated NaOH. And we also need aldehyde without alpha-H. So, answer is B
How much of the original radioactive parent material would be left in a rock sample after three half- lives ?- a)1/2
- b)1/3
- c)1/6
- d)1/8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How much of the original radioactive parent material would be left in a rock sample after three half- lives ?
a)
1/2
b)
1/3
c)
1/6
d)
1/8

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
To understand the answer to this question, we need to have a basic understanding of radioactive decay and half-life.
Radioactive decay is the process by which unstable atomic nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation. The parent material refers to the original radioactive substance that undergoes decay, while the daughter material refers to the stable product of the decay process.
The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time it takes for half of the parent material to decay into daughter material. After one half-life, half of the parent material will have decayed, leaving behind half of the original amount. After two half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay, leaving behind a quarter of the original amount. Similarly, after three half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay, leaving behind an eighth of the original amount.
Now, let's break down the answer in detail:
1) First Half-Life:
- After one half-life, half of the original parent material will have decayed into daughter material.
- This means that only half of the original radioactive substance remains in the rock sample.
2) Second Half-Life:
- After two half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay.
- Since only half of the original parent material was left after the first half-life, half of that remaining half will decay.
- This results in only a quarter (1/2 * 1/2 = 1/4) of the original parent material remaining in the rock sample.
3) Third Half-Life:
- After three half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay.
- Since only a quarter of the original parent material was left after the second half-life, half of that remaining quarter will decay.
- This results in only an eighth (1/4 * 1/2 = 1/8) of the original parent material remaining in the rock sample.
Therefore, after three half-lives, only 1/8 (or 1 out of 8) of the original radioactive parent material would be left in the rock sample. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D' - 1/8.
Radioactive decay is the process by which unstable atomic nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation. The parent material refers to the original radioactive substance that undergoes decay, while the daughter material refers to the stable product of the decay process.
The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time it takes for half of the parent material to decay into daughter material. After one half-life, half of the parent material will have decayed, leaving behind half of the original amount. After two half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay, leaving behind a quarter of the original amount. Similarly, after three half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay, leaving behind an eighth of the original amount.
Now, let's break down the answer in detail:
1) First Half-Life:
- After one half-life, half of the original parent material will have decayed into daughter material.
- This means that only half of the original radioactive substance remains in the rock sample.
2) Second Half-Life:
- After two half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay.
- Since only half of the original parent material was left after the first half-life, half of that remaining half will decay.
- This results in only a quarter (1/2 * 1/2 = 1/4) of the original parent material remaining in the rock sample.
3) Third Half-Life:
- After three half-lives, half of the remaining parent material will decay.
- Since only a quarter of the original parent material was left after the second half-life, half of that remaining quarter will decay.
- This results in only an eighth (1/4 * 1/2 = 1/8) of the original parent material remaining in the rock sample.
Therefore, after three half-lives, only 1/8 (or 1 out of 8) of the original radioactive parent material would be left in the rock sample. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D' - 1/8.
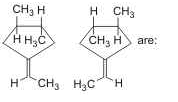
- a)enantiomers
- b)diastereomers
- c)geometrical isomers
- d)same structure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
enantiomers
b)
diastereomers
c)
geometrical isomers
d)
same structure

|
Shobha Pagadala answered |
Enantiomers are mirror images which are non superimposing( means not identical)
In an AC circuit, the potential across an inductance and resistance joined in series are respectively 16 V and 20 V. The total potential difference across the circuit is,
- a)20.0 V
- b)25.6 V
- c)31.9 V
- d)33.6 V
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer??
In an AC circuit, the potential across an inductance and resistance joined in series are respectively 16 V and 20 V. The total potential difference across the circuit is,
a)
20.0 V
b)
25.6 V
c)
31.9 V
d)
33.6 V
|
|
Keerthana Bose answered |
Total Potential in an AC Circuit
In an AC circuit with components such as inductors and resistors, the total potential difference can be calculated using the concept of impedance and the phase difference between the voltage across the inductor and the resistor.
Given Values:
- Voltage across the inductor (V_L) = 16V
- Voltage across the resistor (V_R) = 20V
Understanding the Circuit:
- In a series AC circuit, the total voltage (V_total) is not simply the sum of the voltages across the components due to the phase difference.
- The voltages across the inductor and resistor are perpendicular to each other in the phasor representation.
Calculating Total Potential:
- The total potential can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
V_total = √(V_R^2 + V_L^2)
- Substituting the given values:
V_total = √(20^2 + 16^2)
V_total = √(400 + 256)
V_total = √656
V_total ≈ 25.6V
Conclusion:
- Therefore, the total potential difference across the circuit is approximately 25.6V.
- The correct answer is option B) 25.6 V.
This calculation highlights the importance of considering both the resistive and inductive components in AC circuits to determine the total voltage accurately.
In an AC circuit with components such as inductors and resistors, the total potential difference can be calculated using the concept of impedance and the phase difference between the voltage across the inductor and the resistor.
Given Values:
- Voltage across the inductor (V_L) = 16V
- Voltage across the resistor (V_R) = 20V
Understanding the Circuit:
- In a series AC circuit, the total voltage (V_total) is not simply the sum of the voltages across the components due to the phase difference.
- The voltages across the inductor and resistor are perpendicular to each other in the phasor representation.
Calculating Total Potential:
- The total potential can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
V_total = √(V_R^2 + V_L^2)
- Substituting the given values:
V_total = √(20^2 + 16^2)
V_total = √(400 + 256)
V_total = √656
V_total ≈ 25.6V
Conclusion:
- Therefore, the total potential difference across the circuit is approximately 25.6V.
- The correct answer is option B) 25.6 V.
This calculation highlights the importance of considering both the resistive and inductive components in AC circuits to determine the total voltage accurately.
A wave front travels- a)Parallel to the rays
- b)Perpendicular to the rays
- c)Both A and B
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A wave front travels
a)
Parallel to the rays
b)
Perpendicular to the rays
c)
Both A and B
d)
None of these
|
|
Subham Goyal answered |
Explanation:
- Wave Front: A wave front is an imaginary surface that contains all the points in a medium that are in the same phase of oscillation. It represents the locus of all the particles vibrating in the same phase at any instant.
- Travel Direction: When a wave front travels, it moves in a direction perpendicular to the rays. This means that the wave front propagates at right angles to the direction of energy transfer.
- Perpendicular to the Rays: The rays represent the direction of energy transfer in a wave. The wave front, being perpendicular to the rays, indicates the direction in which the wave is moving.
- Relationship: The wave front and rays are related in such a way that the wave front always moves perpendicular to the rays. This relationship helps in understanding the propagation of waves in a medium.
- Key Point: Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B' - Perpendicular to the rays. This relationship between wave fronts and rays is crucial in understanding the behavior of waves in different mediums.
Understanding this relationship can help in solving problems related to wave propagation and interference, making it an important concept to grasp in the study of wave physics.
- Wave Front: A wave front is an imaginary surface that contains all the points in a medium that are in the same phase of oscillation. It represents the locus of all the particles vibrating in the same phase at any instant.
- Travel Direction: When a wave front travels, it moves in a direction perpendicular to the rays. This means that the wave front propagates at right angles to the direction of energy transfer.
- Perpendicular to the Rays: The rays represent the direction of energy transfer in a wave. The wave front, being perpendicular to the rays, indicates the direction in which the wave is moving.
- Relationship: The wave front and rays are related in such a way that the wave front always moves perpendicular to the rays. This relationship helps in understanding the propagation of waves in a medium.
- Key Point: Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B' - Perpendicular to the rays. This relationship between wave fronts and rays is crucial in understanding the behavior of waves in different mediums.
Understanding this relationship can help in solving problems related to wave propagation and interference, making it an important concept to grasp in the study of wave physics.
During extraction of silver, which of the following is formed ?- a)Na[Ag(CN)₂]
- b)Na₂[Ag(CN)₂]
- c)Na₄[Ag(CN)₂]
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During extraction of silver, which of the following is formed ?
a)
Na[Ag(CN)₂]
b)
Na₂[Ag(CN)₂]
c)
Na₄[Ag(CN)₂]
d)
None of the above
|
|
Neha Pillai answered |
Extraction of Silver
Silver is extracted from its ore by the following steps:
1. Crushing and grinding: The ore is first crushed into small pieces and then ground to a fine powder.
2. Concentration: The ore is then concentrated by froth flotation process.
3. Roasting: The concentrated ore is roasted in a furnace to convert it into silver oxide.
4. Reduction: The silver oxide is then reduced to silver by heating it with a reducing agent such as charcoal or coke.
5. Purification: The impure silver thus obtained is purified by electrolytic refining.
Formation of Na[Ag(CN)2]
During the extraction of silver, the silver is dissolved in a solution of sodium cyanide (NaCN) to form sodium argentocyanide (Na[Ag(CN)2]). This complex compound is soluble in water and is used as the main intermediate in the extraction of silver from its ores.
The chemical reaction involved in the formation of Na[Ag(CN)2] is as follows:
Ag(s) + 2NaCN(aq) → Na[Ag(CN)2](aq)
In this reaction, silver (Ag) is oxidized to form the complex ion [Ag(CN)2]^- and sodium (Na) acts as a reducing agent.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer as Na[Ag(CN)2] is formed during the extraction of silver.
Silver is extracted from its ore by the following steps:
1. Crushing and grinding: The ore is first crushed into small pieces and then ground to a fine powder.
2. Concentration: The ore is then concentrated by froth flotation process.
3. Roasting: The concentrated ore is roasted in a furnace to convert it into silver oxide.
4. Reduction: The silver oxide is then reduced to silver by heating it with a reducing agent such as charcoal or coke.
5. Purification: The impure silver thus obtained is purified by electrolytic refining.
Formation of Na[Ag(CN)2]
During the extraction of silver, the silver is dissolved in a solution of sodium cyanide (NaCN) to form sodium argentocyanide (Na[Ag(CN)2]). This complex compound is soluble in water and is used as the main intermediate in the extraction of silver from its ores.
The chemical reaction involved in the formation of Na[Ag(CN)2] is as follows:
Ag(s) + 2NaCN(aq) → Na[Ag(CN)2](aq)
In this reaction, silver (Ag) is oxidized to form the complex ion [Ag(CN)2]^- and sodium (Na) acts as a reducing agent.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer as Na[Ag(CN)2] is formed during the extraction of silver.
The blue complex formed on addition of conc. NH₄OH solution to a Cu2+ salt solution has the structure?- a)[Cu(NH₄]₄]2+
- b)[Cu(NH₃]₂]2+
- c)[Cu(NH₃]₄]2+
- d)[Cu(NH₄]₂]2+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The blue complex formed on addition of conc. NH₄OH solution to a Cu2+ salt solution has the structure?
a)
[Cu(NH₄]₄]2+
b)
[Cu(NH₃]₂]2+
c)
[Cu(NH₃]₄]2+
d)
[Cu(NH₄]₂]2+
|
|
Anagha Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Formation of the blue complex:
- When concentrated NH3 solution is added to a Cu2+ salt solution, a deep blue complex is formed due to the formation of [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ complex ion.
Structure of the complex:
- The complex ion [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ consists of a central copper ion surrounded by four ammonia molecules and two water molecules.
- The ammonia molecules act as ligands and coordinate with the central copper ion through coordinate covalent bonds.
- The two water molecules are also coordinated to the central copper ion.
Correct answer:
- The correct structure of the blue complex formed is [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+, which corresponds to option 'c' [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+.
Formation of the blue complex:
- When concentrated NH3 solution is added to a Cu2+ salt solution, a deep blue complex is formed due to the formation of [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ complex ion.
Structure of the complex:
- The complex ion [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ consists of a central copper ion surrounded by four ammonia molecules and two water molecules.
- The ammonia molecules act as ligands and coordinate with the central copper ion through coordinate covalent bonds.
- The two water molecules are also coordinated to the central copper ion.
Correct answer:
- The correct structure of the blue complex formed is [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+, which corresponds to option 'c' [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+.
Ga As is- a)element semiconductor
- b)alloy semiconductor
- c)bad conductor
- d)metallic semiconductor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ga As is
a)
element semiconductor
b)
alloy semiconductor
c)
bad conductor
d)
metallic semiconductor
|
|
Palak Nair answered |
Alloy Semiconductor:
GaAs is classified as an alloy semiconductor.
Explanation:
Element Semiconductor vs. Alloy Semiconductor:
- Element semiconductors are made up of a single element, such as silicon or germanium. Alloy semiconductors, on the other hand, are composed of two or more elements.
- GaAs is an alloy semiconductor because it is made up of gallium (Ga) and arsenic (As), combining properties of both elements to create a unique semiconductor material.
Properties of GaAs:
- GaAs exhibits properties that make it a suitable material for use in electronic devices.
- It has a direct bandgap, allowing it to efficiently emit light, making it useful in optoelectronic applications.
- GaAs also has high electron mobility, which is beneficial for high-frequency applications such as in microwave devices.
Applications of GaAs:
- GaAs is commonly used in the production of LEDs (light-emitting diodes), lasers, solar cells, and high-frequency electronic devices.
- Its properties make it a preferred material for applications where high performance is required.
In conclusion, GaAs is an alloy semiconductor composed of gallium and arsenic, exhibiting properties that make it suitable for a variety of electronic applications.
If a star is moving towards earth, then the lines are shifted towards- a)red
- b)infra-red
- c)blue
- d)green
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a star is moving towards earth, then the lines are shifted towards
a)
red
b)
infra-red
c)
blue
d)
green
|
|
Srestha Basak answered |
Doppler Effect
The phenomenon of changing the frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source is called the Doppler effect. This effect can be observed in sound waves, light waves, and other types of waves.
Doppler Effect in Light Waves
When a star is moving towards earth, the light waves emitted by the star are compressed or squeezed. This compression results in a shift of the lines towards the blue end of the spectrum. This shift is called the blue shift.
Explanation
The light waves emitted by a star have a certain frequency and wavelength. When the star moves towards the earth, the distance between the source of the light waves and the observer decreases. This results in a compression of the light waves, which increases the frequency of the wave. The increase in frequency results in a shift towards the blue end of the spectrum.
The blue shift is observed in the spectral lines of the star. These spectral lines are dark lines that are observed when the light from the star is passed through a prism or a diffraction grating. These lines are produced by the absorption of certain frequencies of light by the gases in the outer layers of the star.
The blue shift is an indication that the star is moving towards the observer. The amount of blue shift is proportional to the speed of the star relative to the observer.
Conclusion
When a star is moving towards the earth, the spectral lines are shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum. This shift is called the blue shift and is a result of the Doppler effect. The blue shift is an indication that the star is moving towards the observer.
The phenomenon of changing the frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source is called the Doppler effect. This effect can be observed in sound waves, light waves, and other types of waves.
Doppler Effect in Light Waves
When a star is moving towards earth, the light waves emitted by the star are compressed or squeezed. This compression results in a shift of the lines towards the blue end of the spectrum. This shift is called the blue shift.
Explanation
The light waves emitted by a star have a certain frequency and wavelength. When the star moves towards the earth, the distance between the source of the light waves and the observer decreases. This results in a compression of the light waves, which increases the frequency of the wave. The increase in frequency results in a shift towards the blue end of the spectrum.
The blue shift is observed in the spectral lines of the star. These spectral lines are dark lines that are observed when the light from the star is passed through a prism or a diffraction grating. These lines are produced by the absorption of certain frequencies of light by the gases in the outer layers of the star.
The blue shift is an indication that the star is moving towards the observer. The amount of blue shift is proportional to the speed of the star relative to the observer.
Conclusion
When a star is moving towards the earth, the spectral lines are shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum. This shift is called the blue shift and is a result of the Doppler effect. The blue shift is an indication that the star is moving towards the observer.
Chapter doubts & questions for Full Length (PCME) Mock Tests - VITEEE: Subject Wise and Full Length MOCK Tests 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Full Length (PCME) Mock Tests - VITEEE: Subject Wise and Full Length MOCK Tests in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup