All Exams >
Class 6 >
Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT) >
All Questions
All questions of Water (Old Syllabus) for Class 6 Exam
Which one is not a natural source of water- a)River
- b)Lake
- c)Canal
- d)Pond
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a natural source of water
a)
River
b)
Lake
c)
Canal
d)
Pond

|
Kunal Mehta answered |
Correct option is (c) .
Dams, wells, tube wells, hand-pumps, canals, etc, are man-made sources of water.
Dams, wells, tube wells, hand-pumps, canals, etc, are man-made sources of water.
Which of the following substance is found in all three states in nature?- a)Ether
- b)Water
- c)Petrol
- d)Kerosene oil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following substance is found in all three states in nature?
a)
Ether
b)
Water
c)
Petrol
d)
Kerosene oil
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
Water is the only substance on Earth that is present in all three states of matter – as a solid, liquid or gas. (And Earth is the only planet where water is abundantly present in all three states.
Evaporation of water takes place faster in- a)Temperate condition
- b)Humid condition
- c)Hot condition
- d)Cold condition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaporation of water takes place faster in
a)
Temperate condition
b)
Humid condition
c)
Hot condition
d)
Cold condition

|
Arshiya Mehta answered |
The water molecules move rapidly when the water is heated. This makes the molecules escape faster. Higher temperatures lead to increase in vaporization as more molecules get kinetic energy to convert into vapor. For example, boiling water evaporates faster than fresh tap water.
Most of the water available to us as- a)Ground water
- b)Sea water
- c)Glacial water
- d)Ocean water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the water available to us as
a)
Ground water
b)
Sea water
c)
Glacial water
d)
Ocean water

|
Arjun Desai answered |
About 71 percent of the Earth's surface is water-covered, and the oceans hold about 96.5 percent of all Earth's water. Water also exists in the air as water vapor, in rivers and lakes, in icecaps and glaciers, in the ground as soil moisture and in aquifers, and even in you and your dog. Water is never sitting still.
Cyclic flow of water in different state is called- a)Water change
- b)Water cycle
- c)Water range
- d)Water life
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cyclic flow of water in different state is called
a)
Water change
b)
Water cycle
c)
Water range
d)
Water life

|
Sagnik Chatterjee answered |
Cyclic flow of water in different state is called water cycle that includes, evaporation, condensation and raining.
Rain is also known as- a)Condensation
- b)Transpiration
- c)Precipitation
- d)Evaporation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain is also known as
a)
Condensation
b)
Transpiration
c)
Precipitation
d)
Evaporation
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
Rain is when water falls from clouds in droplets that are bigger than 0.5 mm. Droplets of water that are about 0.2mm to 0.45mm big are called drizzle. Rain is a kind of precipitation. Precipitation is any kind of water that falls from clouds in the sky, like rain, hail, sleet and snow. precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor, so that the water condenses and "precipitates". Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but suspensions, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called "showers.
Loss of water by plants is called- a)Transpiration
- b)Transportation
- c)Evaporation
- d)Condensation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Loss of water by plants is called
a)
Transpiration
b)
Transportation
c)
Evaporation
d)
Condensation

|
Rajveer Choudhury answered |
Loss of water in form of water vapour by plants is called as transpiration.
Water is a /an- a)Solution
- b)Element
- c)Compound
- d)Mixture
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is a /an
a)
Solution
b)
Element
c)
Compound
d)
Mixture

|
Arshiya Mehta answered |
It's a compound because it combines two elements (H-Hydrogen and O-Oxygen) to form water (H2O), which is a compound. ... The 2 elements are hydrogen and oxygen. In a water molecule their are 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atoms attached by covalent bonds .
Of the total amount of water present on the earth, the water available for human use is about- a)20%
- b)2%
- c)1%
- d)10%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the total amount of water present on the earth, the water available for human use is about
a)
20%
b)
2%
c)
1%
d)
10%
|
|
Sagar Roy answered |
Of the total amount of water present on the earth, the water available for human use is about 1% only.
The process of changing water vapour into water is called- a)Condensation
- b)Sedimentation
- c)Evaporation
- d)Boiling
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of changing water vapour into water is called
a)
Condensation
b)
Sedimentation
c)
Evaporation
d)
Boiling
|
|
V. lihitha reddy answered |
The water are evaporated by the sun and then the water vapour is changed into clouds.
Water is __________ of hydrogen and oxygen element.- a)Mixture
- b)Solution
- c)Suspension
- d)Compound
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is __________ of hydrogen and oxygen element.
a)
Mixture
b)
Solution
c)
Suspension
d)
Compound

|
Swara Mukherjee answered |
Water is compound and not mixture. Its because compounds are always formed in definite ratio of constituent elements. To say it more simply, when two atoms of Hydrogen and one atom of Oxygen react together, they form one molecule of Water.
In early winter mornings, we can see drops of water on the grass. This is because of- a)photosynthesis.
- b)transpiration.
- c)condensation.
- d)water cycle.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In early winter mornings, we can see drops of water on the grass. This is because of
a)
photosynthesis.
b)
transpiration.
c)
condensation.
d)
water cycle.

|
Janhavi Kumar answered |
Due to the sunrays, the water vapour present in the atmosphere condenses to form dew drops which fall on the blades of grass, leaves of plants etc., during early winter mornings.
Water above the 1000C is in- a)Liquid state
- b)Gaseous state
- c)Semi-liquid state
- d)Solid state
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water above the 1000C is in
a)
Liquid state
b)
Gaseous state
c)
Semi-liquid state
d)
Solid state

|
Anshika Singh answered |
Water above the 1000C is in gaseous state in form of water vapour.
Fast moving air is called- a)Rain
- b)Tornado
- c)Wind
- d)Cyclone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fast moving air is called
a)
Rain
b)
Tornado
c)
Wind
d)
Cyclone

|
Prisha Choudhary answered |
Fast moving air is called Wind
At high humidity, evaporation occurs- a)Same rate
- b)Slower
- c)Change with time
- d)Faster
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At high humidity, evaporation occurs
a)
Same rate
b)
Slower
c)
Change with time
d)
Faster

|
Anjali Yadav answered |
At high humidity, evaporation occurs slower which increase with increase in temperature or surface area.
The purest form of water is- a)Rain water
- b)Subsoil water
- c)Spring water
- d)Hand pump water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The purest form of water is
a)
Rain water
b)
Subsoil water
c)
Spring water
d)
Hand pump water
|
|
Aruna Singh answered |
Rain water is considered the purest form of water. Impurities and salts present in water on earth are left behind during vaporisation by the sun. However, the rain water we receive on earth is not necessarily pure, as it brings down impurities and particles present in the atmosphere along with it.
No rain or very less rain causes- a)Soil fertile
- b)Soil unfertile
- c)Flood
- d)Drought
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
No rain or very less rain causes
a)
Soil fertile
b)
Soil unfertile
c)
Flood
d)
Drought

|
Pankaj Kumar answered |
No rain or very less rain in an area causes drought.
In a small town, the number of water pumps, concrete houses and roads increased. What happens to the water table of that place?- a)It becomes lower
- b)It becomes higher
- c)It remains unaffected
- d)It first becomes lower and then higher.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a small town, the number of water pumps, concrete houses and roads increased. What happens to the water table of that place?
a)
It becomes lower
b)
It becomes higher
c)
It remains unaffected
d)
It first becomes lower and then higher.

|
Athira Sengupta answered |
The water table of that place becomes lower.
Which one is a common source of drinking water?- a)Ocean water
- b)Spring water
- c)River and lake
- d)Sea water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is a common source of drinking water?
a)
Ocean water
b)
Spring water
c)
River and lake
d)
Sea water

|
Gayatri Chavan answered |
There are two main sources of water: surface water and groundwater. Surface Water is found in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs. Groundwater lies under the surface of the land, where it travels through and fills openings in the rocks. The rocks that store and transmit groundwater are called aquifers.
Wet clothes dry up in sun due to- a)Exclamation
- b)Evaporation
- c)Boiling
- d)Condensation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Wet clothes dry up in sun due to
a)
Exclamation
b)
Evaporation
c)
Boiling
d)
Condensation

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
Clothes dry up in sun due to evaporation of water by solar energy.
Ground water gets recharged by the process of- a)aquification.
- b)transpiration.
- c)infiltration.
- d)transportation.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ground water gets recharged by the process of
a)
aquification.
b)
transpiration.
c)
infiltration.
d)
transportation.
|
|
Bibek Verma answered |
Ground water gets recharged by the process of infiltration.
Dew is the- a)Melting of ice on mountain peaks
- b)Freezing of water in river and ponds
- c)Condensation of water vapour in atmosphere
- d)Condensation of water vapour near the earth surface
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dew is the
a)
Melting of ice on mountain peaks
b)
Freezing of water in river and ponds
c)
Condensation of water vapour in atmosphere
d)
Condensation of water vapour near the earth surface

|
K.L Institute answered |
Dew is the condensation of water vapour near the earth’s surface due to low temperature.
The falling of water drops of clouds is known as- a)Snow hail
- b)Freezing
- c)Condensation
- d)Precipitation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The falling of water drops of clouds is known as
a)
Snow hail
b)
Freezing
c)
Condensation
d)
Precipitation

|
Amar Menon answered |
The falling of water drops of clouds is known as precipitation.
Gaseous state of water is- a)Ice
- b)Cloud
- c)Vapour
- d)Rain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gaseous state of water is
a)
Ice
b)
Cloud
c)
Vapour
d)
Rain

|
Prachi Singh answered |
Vapour is gaseous state of a water
An example of underground water is- a)River
- b)Well
- c)Sea
- d)Lake
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of underground water is
a)
River
b)
Well
c)
Sea
d)
Lake

|
Rajat Menon answered |
Well is underground source of water while river, lake and sea are surface source of water.
Changing of water into water vapour is called- a)Freezing
- b)Melting
- c)Condensation
- d)Evaporation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Changing of water into water vapour is called
a)
Freezing
b)
Melting
c)
Condensation
d)
Evaporation

|
Amar Menon answered |
Changing of water into water vapour is called as evaporation, it occurs at all temperature.
Which one is a renewable natural source?- a)Water
- b)Coal
- c)Forest
- d)Petrol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is a renewable natural source?
a)
Water
b)
Coal
c)
Forest
d)
Petrol

|
Anshika Singh answered |
Water is a renewable natural resource as it can be recycled naturally and can be reused again and again.
Cloud seeding is a technique that induces rain. What does the process involve?- a)Adopting an agricultural practice that depends on clouds
- b)Introducing particles in clouds to facilitate condensation
- c)Making clouds and placing them in the sky
- d)Scattering clouds to form seed like structures
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cloud seeding is a technique that induces rain. What does the process involve?
a)
Adopting an agricultural practice that depends on clouds
b)
Introducing particles in clouds to facilitate condensation
c)
Making clouds and placing them in the sky
d)
Scattering clouds to form seed like structures

|
Meghana Iyer answered |
Cloud seeding is an artificial method of introducing particles in clouds to cause rains by initiating condensation of water vapour present in the clouds.
Why do you feel cool after you start sweating?- a)Evaporation of water droplets
- b)Condensation of water droplets
- c)Freezing of water droplets
- d)Solidification of salts in the water droplets
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why do you feel cool after you start sweating?
a)
Evaporation of water droplets
b)
Condensation of water droplets
c)
Freezing of water droplets
d)
Solidification of salts in the water droplets

|
Deepika Basu answered |
During summer, water, from our body as sweat. Evaporation causes cooling because water droplets present on the skin require some heat to evaporate, which they take from the body.
Water is natural resource which is
- a)Exhaustible
- b)Exhaustible as well as inexhaustible
- c)Inexhaustible
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is natural resource which is
a)
Exhaustible
b)
Exhaustible as well as inexhaustible
c)
Inexhaustible
d)
All of above
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
Water is a natural resource that can be considered both exhaustible and inexhaustible depending on context:
-
Inexhaustible: In the broadest sense, water is considered inexhaustible because it is part of the Earth's hydrological cycle, where it is continuously recycled through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
-
Exhaustible: Locally or in specific regions, water can be exhausted or depleted due to overuse, pollution, or mismanagement, leading to water scarcity.
Therefore, the best choice is:
Exhaustible as well as inexhaustible
Water is ___________ for life.- a)Needed in small
- b)Not necessary
- c)Essential
- d)Non-essential
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is ___________ for life.
a)
Needed in small
b)
Not necessary
c)
Essential
d)
Non-essential
|
|
Charvi Chauhan answered |
Importance of Water for Life
Water is commonly referred to as the essence of life. It plays a vital role in almost every biological process. Here’s why water is considered essential:
1. Fundamental Component of Cells
- Water constitutes about 70% of the human body.
- It is a major component of cells, helping to maintain their structure and function.
2. Facilitates Biological Reactions
- Water acts as a solvent, allowing various biochemical reactions to occur.
- It helps in the transport of nutrients, hormones, and waste products within and between cells.
3. Temperature Regulation
- Water helps regulate body temperature through sweating and respiration.
- It absorbs heat, preventing drastic temperature changes in the body.
4. Hydration and Metabolism
- Proper hydration is crucial for metabolic processes, including digestion and energy production.
- Water aids in the absorption of nutrients and helps in the elimination of toxins.
5. Ecosystem Support
- Water is essential for all living organisms, including plants and animals.
- It supports ecosystems, providing habitats and maintaining biodiversity.
In conclusion, water is not just needed in small amounts but is an essential element for survival. It supports crucial life processes, making it indispensable for all forms of life on Earth.
Water is commonly referred to as the essence of life. It plays a vital role in almost every biological process. Here’s why water is considered essential:
1. Fundamental Component of Cells
- Water constitutes about 70% of the human body.
- It is a major component of cells, helping to maintain their structure and function.
2. Facilitates Biological Reactions
- Water acts as a solvent, allowing various biochemical reactions to occur.
- It helps in the transport of nutrients, hormones, and waste products within and between cells.
3. Temperature Regulation
- Water helps regulate body temperature through sweating and respiration.
- It absorbs heat, preventing drastic temperature changes in the body.
4. Hydration and Metabolism
- Proper hydration is crucial for metabolic processes, including digestion and energy production.
- Water aids in the absorption of nutrients and helps in the elimination of toxins.
5. Ecosystem Support
- Water is essential for all living organisms, including plants and animals.
- It supports ecosystems, providing habitats and maintaining biodiversity.
In conclusion, water is not just needed in small amounts but is an essential element for survival. It supports crucial life processes, making it indispensable for all forms of life on Earth.
During transpiration, plants lose water in form of- a)Liquid water
- b)Water vapour
- c)Ice water
- d)Cold water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During transpiration, plants lose water in form of
a)
Liquid water
b)
Water vapour
c)
Ice water
d)
Cold water
|
|
Nishanth Majumdar answered |
Understanding Transpiration in Plants
Transpiration is a vital process in plants, where they lose water primarily through their leaves. This mechanism plays a crucial role in their overall health and functioning.
What is Transpiration?
- Transpiration is the process by which water evaporates from the surface of leaves.
- It mainly occurs through small openings called stomata, which are found on the underside of leaves.
Water Loss in the Form of Vapour
- During transpiration, plants lose water in the form of water vapour.
- This process is essential for maintaining the plant's internal water balance and temperature.
Importance of Water Vapour Loss
- Cooling Effect: The evaporation of water vapour helps cool the plant, preventing overheating.
- Nutrient Transport: As water is lost, it creates a negative pressure that helps pull water and nutrients from the roots through the xylem to various parts of the plant.
- Photosynthesis: The process also aids in the uptake of carbon dioxide, which is crucial for photosynthesis.
Conclusion
In summary, during transpiration, plants lose water in the form of water vapour (option B). This process is vital for their survival, aiding in cooling, nutrient transport, and gas exchange, making it an essential aspect of plant physiology.
Transpiration is a vital process in plants, where they lose water primarily through their leaves. This mechanism plays a crucial role in their overall health and functioning.
What is Transpiration?
- Transpiration is the process by which water evaporates from the surface of leaves.
- It mainly occurs through small openings called stomata, which are found on the underside of leaves.
Water Loss in the Form of Vapour
- During transpiration, plants lose water in the form of water vapour.
- This process is essential for maintaining the plant's internal water balance and temperature.
Importance of Water Vapour Loss
- Cooling Effect: The evaporation of water vapour helps cool the plant, preventing overheating.
- Nutrient Transport: As water is lost, it creates a negative pressure that helps pull water and nutrients from the roots through the xylem to various parts of the plant.
- Photosynthesis: The process also aids in the uptake of carbon dioxide, which is crucial for photosynthesis.
Conclusion
In summary, during transpiration, plants lose water in the form of water vapour (option B). This process is vital for their survival, aiding in cooling, nutrient transport, and gas exchange, making it an essential aspect of plant physiology.
Excessive rain cause- a)Flood
- b)Disease
- c)Drought
- d)Deforestation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Excessive rain cause
a)
Flood
b)
Disease
c)
Drought
d)
Deforestation

|
Deepak Verma answered |
Excessive rain cause flood in a particular area to submerge the large area.
What is the main source of water for inland lakes?- a)Snow
- b)Sea water
- c)Ground water
- d)Springs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main source of water for inland lakes?
a)
Snow
b)
Sea water
c)
Ground water
d)
Springs

|
Devika Nair answered |
The inland lakes depend on rains or the water table (ground water).
Why does the water table of a place become lower?- a)When trees are planted
- b)When there is a drought
- c)When there is a cyclone and flood
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why does the water table of a place become lower?
a)
When trees are planted
b)
When there is a drought
c)
When there is a cyclone and flood
d)
All of the above

|
Uday Gupta answered |
The water table of a place where droughts prolong for a long period of time becomes lower because of lesser water seeping into the ground.
Which of the following statements is true?- a)The salinity of sea increases tremendously in a short time.
- b)The salinity of rivers decreases with time.
- c)The salinity of seas increases with time.
- d)The salinity of seas remains constant with time.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true?
a)
The salinity of sea increases tremendously in a short time.
b)
The salinity of rivers decreases with time.
c)
The salinity of seas increases with time.
d)
The salinity of seas remains constant with time.
|
|
Riya Sahu answered |
Evaporation of ocean water and formation of sea ice both increase the salinity of the ocean.
Identify the source of ground water.- a)Sub-soil water
- b)River water
- c)Rainwater
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the source of ground water.
a)
Sub-soil water
b)
River water
c)
Rainwater
d)
All of the above

|
Rajveer Choudhury answered |
Rain water is the source of ground water.
A Observe the figure given below and identify the process.
- a)Water cycle
- b)Torrential rain causing floods
- c)Soil erosion
- d)Rain water harvesting
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A Observe the figure given below and identify the process.

a)
Water cycle
b)
Torrential rain causing floods
c)
Soil erosion
d)
Rain water harvesting

|
Janhavi Kumar answered |
The process of water cycle is shown in the given figure.
Rain water harvesting is a method employed to- a)stop soil erosion in a place.
- b)raise the water table of a place.
- c)decrease drought at a place.
- d)decrease floods at a place.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain water harvesting is a method employed to
a)
stop soil erosion in a place.
b)
raise the water table of a place.
c)
decrease drought at a place.
d)
decrease floods at a place.

|
Rajveer Choudhury answered |
Rain water is collected in a special type of arrangement. This water is used which in turn helps to raise the water table of a place.
Why is water useful to life on the earth?
(i) It maintains ecological balance.
(ii) It sustains life.
(iii) It is necessary for respiration in aquatic organisms.- a)Only (i) and (ii)
- b)Only (ii) and (iii)
- c)Only (i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is water useful to life on the earth?
(i) It maintains ecological balance.
(ii) It sustains life.
(iii) It is necessary for respiration in aquatic organisms.
(i) It maintains ecological balance.
(ii) It sustains life.
(iii) It is necessary for respiration in aquatic organisms.
a)
Only (i) and (ii)
b)
Only (ii) and (iii)
c)
Only (i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)

|
Janani Mukherjee answered |
Water is useful to life on the earth. To maintain ecological balance, for sustaining life and it is also necessary for respiration in aquatic organisms.
Which of the following is the primary source of water on land?- a)Lakes
- b)Tanks
- c)Ponds
- d)Rain water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the primary source of water on land?
a)
Lakes
b)
Tanks
c)
Ponds
d)
Rain water

|
Prasad Chawla answered |
Rain water forms the primary source of water on the land.
Given in the figure are four containers that contain the same amount of water.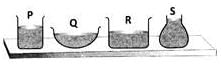 In which of the following containers will water evaporate the slowest?
In which of the following containers will water evaporate the slowest?- a)Q
- b)R
- c)P
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given in the figure are four containers that contain the same amount of water.

In which of the following containers will water evaporate the slowest?
a)
Q
b)
R
c)
P
d)
S

|
Janani Mukherjee answered |
Container S (a flask) has the smallest surface area of water exposed to the atmosphere. Thus, the rate of evaporation will be the slowest in flask S.
Why is water scarcity increasing day by day?
- a)Water cycle has stopped functioning.
- b)The total amount of water on earth has decreased.
- c)The amount of potable water is decreasing because of over usage.
- d)There is an increasing frequency of floods.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is water scarcity increasing day by day?
a)
Water cycle has stopped functioning.
b)
The total amount of water on earth has decreased.
c)
The amount of potable water is decreasing because of over usage.
d)
There is an increasing frequency of floods.

|
Moumita Roy answered |
The amount of potable water is decreasing because of over usage. Water scarcity is the lack of sufficient available water resources to meet the demands of water usage within a region.
What causes the formation of salt from sea water?- a)Evaporation
- b)Condensation
- c)Transpiration
- d)Transformation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What causes the formation of salt from sea water?
a)
Evaporation
b)
Condensation
c)
Transpiration
d)
Transformation

|
Sanskriti Tiwari answered |
Sea water contains a lot of dissolved salts and when the evaporation of the sea water occurs, these salts are left behind.
Which of the following are changed when water boils?
(i) Temperature
(ii) State
(iii) Colour- a)Only (i) and (ii)
- b)Only (ii) and (iii)
- c)Only (i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are changed when water boils?
(i) Temperature
(ii) State
(iii) Colour
(i) Temperature
(ii) State
(iii) Colour
a)
Only (i) and (ii)
b)
Only (ii) and (iii)
c)
Only (i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)

|
Raksha Roy answered |
When water boils, there will be a change in its temperature and state.
Clouds are formed due to- a)only evaporation.
- b)only condensation.
- c)both evaporation and condensation.
- d)only vaporization.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Clouds are formed due to
a)
only evaporation.
b)
only condensation.
c)
both evaporation and condensation.
d)
only vaporization.

|
Rishika Chopra answered |
Clouds are formed due to evaporation and condensation.
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of floods?- a)Crop loss, leading to financial losses for farmers
- b)Increased soil fertility due to nutrient-rich floodwaters
- c)Waterlogging, creating breeding grounds for mosquitoes
- d)Damage to infrastructure such as buildings, roads, and bridges
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of floods?
a)
Crop loss, leading to financial losses for farmers
b)
Increased soil fertility due to nutrient-rich floodwaters
c)
Waterlogging, creating breeding grounds for mosquitoes
d)
Damage to infrastructure such as buildings, roads, and bridges

|
Nclex Coaching Centre answered |
Answer:
b) Increased soil fertility due to nutrient-rich floodwaters
Floods typically cause soil erosion rather than increasing soil fertility. The force of floodwaters often washes away the topsoil, removing valuable nutrients and reducing the fertility of the land. Other consequences of floods include crop loss, waterlogging (which can lead to disease outbreaks), and damage to infrastructure.
b) Increased soil fertility due to nutrient-rich floodwaters
Floods typically cause soil erosion rather than increasing soil fertility. The force of floodwaters often washes away the topsoil, removing valuable nutrients and reducing the fertility of the land. Other consequences of floods include crop loss, waterlogging (which can lead to disease outbreaks), and damage to infrastructure.
Which of the following is potable water?- a)A glass of water fit for drinking
- b)Water in a pot
- c)Sea water
- d)Water with bacteria and chemicals
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is potable water?
a)
A glass of water fit for drinking
b)
Water in a pot
c)
Sea water
d)
Water with bacteria and chemicals

|
Nandita Choudhary answered |
Water which is fit for drinking is called potable water.
Chapter doubts & questions for Water (Old Syllabus) - Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT) 2025 is part of Class 6 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 6 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Water (Old Syllabus) - Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT) in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 6 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT)
297 videos|1066 docs|204 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









