All questions of Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction for Grade 9 Exam
A typical angiospemic embryo sac is though 8 nucleate is 7-celled. 8 nuclei includes______.
- a)2 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
- b)Either (a) or (b)
- c)3 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 2 antipodal
- d)3 egg apparatus, 2 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical angiospemic embryo sac is though 8 nucleate is 7-celled. 8 nuclei includes______.
a)
2 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
b)
Either (a) or (b)
c)
3 egg apparatus, 3 polar nuclei and 2 antipodal
d)
3 egg apparatus, 2 polar nuclei and 3 antipodal
|
|
Swati Malkani answered |
Option B is correct.
Which of the following is an example of false fruit?- a)Apple
- b)Coconut
- c)Mango
- d)Papaya
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of false fruit?
a)
Apple
b)
Coconut
c)
Mango
d)
Papaya
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Apple - An accessory fruit (also called false fruit or spurious fruit) is a fruit in which some of the flesh is derived not from the ovary but from some adjacent tissue exterior to the carpel. Examples of accessory tissue are the receptacle of strawberries, figs, or mulberries, Pomes, such as apples and pears.
Which of the following plant is not pollinated by water?- a)Hydrilla
- b)Zostera
- c)Lotus
- d)Vallisneria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plant is not pollinated by water?
a)
Hydrilla
b)
Zostera
c)
Lotus
d)
Vallisneria
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Lotus is an aquatic plant but the flower of lotus is outside and above the water surface. So, it cannot be pollinated by water. It is generally pollinated by insects.
In meiosis, the daughter cells are not similar to the parent because of- a)Crossing over
- b)Synapsis
- c)Both 1 and 2 above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In meiosis, the daughter cells are not similar to the parent because of
a)
Crossing over
b)
Synapsis
c)
Both 1 and 2 above
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Meiosis is basically an extended and complex version of mitosis. The term “Reductional division” gives this process the underlying definition, a sequence of events that results in reduction of the total number of chromosomes (from a diploid state of 46 to a haploid state of 23; in general, from ‘2n’ to ‘n’).
However, in the initial steps of meiosis, there is an eventful period wherein the previously duplicated chromosomes (in the S-Phase or Synthesis phase of cell cycle) exchange a part of their respective genetic material, a process termed as Recombination through crossing over (of the genetic material). The further steps are the same as in mitosis, but because of the exchange, the daughter chromosomes will have a different identity than their parents.
A bilobed dithecous anther had 100 microspore mother cells per microsporangium. How many male gametes this anther can produce?
- a)400
- b)1600
- c)100
- d)200
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bilobed dithecous anther had 100 microspore mother cells per microsporangium. How many male gametes this anther can produce?
a)
400
b)
1600
c)
100
d)
200

|
Swara Desai answered |
Each microsporangium has 100 microspore mother cells which by meiosis form 400 microspores ( 100 × 4). In an anther there are four microsporangia , so, total number of microspores will be 4 × 400 = 1600 4 × 400 = 1600 . As each microspore forms one male gametophyte, hence , 1600 male gametophytes can be produced.
The cotyledon of maize grain is technically called as? - a)Funicle
- b)Dicots
- c)Scutellum
- d)Testa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cotyledon of maize grain is technically called as?
a)
Funicle
b)
Dicots
c)
Scutellum
d)
Testa

|
Anand Jain answered |
The cotyledons are known as seed leaves, they are attached to the embryonic axis. Dicotyledons typically have two cotyledons and monocotyledons have oly one cotyledon. The single shield-shaped cotyledon in grains known as scutellum. Cotyledon of maize grain is called scutellum.
The meiocyte of an onion plant contains 32 chromosomes. Calculate the number of chromosomes found in its endosperm?- a)96 chromosomes
- b)32 chromosomes
- c)16 chromosomes
- d)48 chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The meiocyte of an onion plant contains 32 chromosomes. Calculate the number of chromosomes found in its endosperm?
a)
96 chromosomes
b)
32 chromosomes
c)
16 chromosomes
d)
48 chromosomes

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
If the number of chromosomes in meiocytes of onion is 32, then the number of chromosomes in gamete cells will be 16. Furthermore, as endosperm is formed after fusion of one sperm nucleus with two egg nucleus called triple fusion, then its chromosome number will be 48.
Crossing over may result in- a)Addition of genetic material
- b)Deletion of genetic material
- c)Exchange of genetic material
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Crossing over may result in
a)
Addition of genetic material
b)
Deletion of genetic material
c)
Exchange of genetic material
d)
All of the above
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Crossing over is the exchange of genes between two chromosomes, resulting in non-identical chromatids that comprise the genetic material of gametes. This process occurs during Prophase I of Meiosis, just prior to chromosome alignment and splitting of the cell.
Meiosis results in
- a)Production of gametes
- b)Reduction in Chromosome number
- c)Introduction of variation
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis results in
a)
Production of gametes
b)
Reduction in Chromosome number
c)
Introduction of variation
d)
All of the above
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
As previously mentioned, the first round of nuclear division that occurs during the formation of gametes is called meiosis I. It is also known as the reduction division because it results in cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Pollen grain of large number of species can be stored in: - a)Liquid oxygen
- b)Liquid carbon dioxide
- c)Liquid sulphur dioxide
- d)Liquid nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pollen grain of large number of species can be stored in:
a)
Liquid oxygen
b)
Liquid carbon dioxide
c)
Liquid sulphur dioxide
d)
Liquid nitrogen
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Pollen grain consists of hard covering of exine but their viability may lost with time. For Hybridisation pollen grains are collected and stored in liquid nitrogen below -196 degree Celsius temperature.
Endosperm type in which first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent division are not accompanied by wall formation is called?- a)Cellular type
- b)Micropylar type
- c)Free nuclear type
- d)Helobial type
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Endosperm type in which first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent division are not accompanied by wall formation is called?
a)
Cellular type
b)
Micropylar type
c)
Free nuclear type
d)
Helobial type
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Nuclear type:
In nuclear type of endosperm the first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent nuclear divisions are not accompanied by wall formation. The nuclei produced are free in the cytoplasm of the embryo sac and they may remain free indefinitely or wall formation takes place later. In the coconut, cell wall formation of endosperm is never found complete. In Areca and Phoenix the endosperm becomes very hard .
Match List I and List II, and select the correct answer.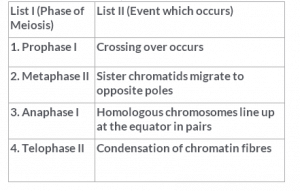
- a)1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- b)1 and 3 are correct.
- c)2 and 4 are correct.
- d)Only 1 is correct.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List I and List II, and select the correct answer.

a)
1, 2 and 3 are correct.
b)
1 and 3 are correct.
c)
2 and 4 are correct.
d)
Only 1 is correct.

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : Genetic variation comes from crossing over, which may occur during prophase I of meiosis.
In prophase I of meiosis, the replicated homologous pair of chromosomes comes together in the process called synapsis, and sections of the chromosomes are exchanged.
Inside the ovary the ovule is attached to placenta by means of- - a)Chalaza
- b)Micropyle
- c)Hilum
- d)Funicle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Inside the ovary the ovule is attached to placenta by means of-
a)
Chalaza
b)
Micropyle
c)
Hilum
d)
Funicle
|
|
Anjali Patel answered |
The ovule is the female reproductive structure of the flower and it is located inside the ovary. The ovule contains the female gametophyte and is attached to the placenta by means of the funicle.
Explanation:
- The ovary is the part of the flower that contains the ovules. It is the female reproductive organ of the flower.
- The ovule is a structure that contains the female gametophyte, the egg cell, and the surrounding protective layers.
- The placenta is the tissue inside the ovary that provides nutrients and support to the developing ovules.
- The funicle is the stalk-like structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta. It is also known as the stalk or the seed stalk.
- The funicle is responsible for transporting nutrients and water from the placenta to the developing ovule.
- The funicle also provides the pathway for the sperm cells to reach the egg cell during fertilization.
- The funicle is usually located at the base of the ovule and is often visible as a small, thin stalk.
In summary, the funicle is the structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta inside the ovary. It plays a vital role in the development and fertilization of the female reproductive structure in the flower.
Explanation:
- The ovary is the part of the flower that contains the ovules. It is the female reproductive organ of the flower.
- The ovule is a structure that contains the female gametophyte, the egg cell, and the surrounding protective layers.
- The placenta is the tissue inside the ovary that provides nutrients and support to the developing ovules.
- The funicle is the stalk-like structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta. It is also known as the stalk or the seed stalk.
- The funicle is responsible for transporting nutrients and water from the placenta to the developing ovule.
- The funicle also provides the pathway for the sperm cells to reach the egg cell during fertilization.
- The funicle is usually located at the base of the ovule and is often visible as a small, thin stalk.
In summary, the funicle is the structure that attaches the ovule to the placenta inside the ovary. It plays a vital role in the development and fertilization of the female reproductive structure in the flower.
Dormancy is the____.- a)State of hyperactivity
- b)Condition of senescence
- c)State of maturity
- d)State of inactivity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dormancy is the____.
a)
State of hyperactivity
b)
Condition of senescence
c)
State of maturity
d)
State of inactivity
|
|
Sandy Naaz answered |
Dormancy is a period in an organism's life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolic activity and therefore helps an organism to conserve energy. Dormancy tends to be closely associated with environmental conditions
In which of the following plants fruit contain larger number of seed?- a)Neem fruits
- b)Orchid fruits
- c)Lemon fruits
- d)Mango fruits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following plants fruit contain larger number of seed?
a)
Neem fruits
b)
Orchid fruits
c)
Lemon fruits
d)
Mango fruits

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
The number of ovule present in ovary determine the number of seeds produced inside the fruit. Mango and neem produce single seed in each fruit. Lemon contain a number of seeds but orchid contain many small size seeds.
Synaptonemal complex is observed during cell division in- a)Meiotic prophase
- b)Mitotic prophase
- c)Meiotic metaphase
- d)Mitotic telophase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Synaptonemal complex is observed during cell division in
a)
Meiotic prophase
b)
Mitotic prophase
c)
Meiotic metaphase
d)
Mitotic telophase

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
The formation of tetrad is a special characteristic of Prophase 1 of meiosis 1.
The homologous pair aligns with each other and gets ready for crossing over.
So, the correct option is 'Meiotic Prophase'.
The homologous pair aligns with each other and gets ready for crossing over.
So, the correct option is 'Meiotic Prophase'.
Synapsis occurs in which of the following stages of meiosis?- a)Diakinesis
- b)Pachytene
- c)Leptotene
- d)Zygotene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Synapsis occurs in which of the following stages of meiosis?
a)
Diakinesis
b)
Pachytene
c)
Leptotene
d)
Zygotene
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Most of the events that function to differentiate meiosis from mitosis occur in Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes form bivalents (or tetrads) and crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids
Prophase I is divided into 5 distinctive sub-stages:
1. Leptotene – The chromosomes begin to condense and are attached to the nuclear membrane via their telomeres
2. Zygotene – Synapsis begins with a synaptonemal complex forming between homologous chromosomes
3. Pachytene – Crossing over of genetic material occurs between non-sister chromatids
4. Diplotene – Synapsis ends with disappearance of synaptonemal complex; homologous pairs remain attached at chiasmata
5. Diakinesis – Chromosomes become fully condensed and nuclear membrane disintegrates prior to metaphase I
Placenta is located inside the-------.- a)Micropyle
- b)Funicle
- c)Ovule cavity
- d)Ovarian cavity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Placenta is located inside the-------.
a)
Micropyle
b)
Funicle
c)
Ovule cavity
d)
Ovarian cavity
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Inside the ovary is the ovarian cavity (locule). The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity. Arising from the placenta are the megasporangia, commonly called ovules.
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called- a)Diakinesis
- b)Zygotene
- c)Diplotene
- d)Pachytene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called
a)
Diakinesis
b)
Zygotene
c)
Diplotene
d)
Pachytene
|
|
Surbhi Dasgupta answered |
Pachytene Stage in Meiosis
The process of meiosis is divided into several stages, one of which is the Pachytene stage. This stage occurs during the first meiotic division or meiosis I. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. The Pachytene stage is characterized by the following events:
Synapsis
During the Pachytene stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. This process is called synapsis. The synaptonemal complex plays a crucial role in this process. The complex is composed of proteins that hold the homologous chromosomes together.
Crossing over
Crossing over occurs during the Pachytene stage. It is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process results in the creation of new combinations of genes, which contributes to genetic diversity.
Chiasmata formation
During the Pachytene stage, the homologous chromosomes that have paired up undergo crossing over. This process results in the formation of chiasmata, which are visible under a microscope. Chiasmata are the points where the homologous chromosomes crisscross and exchange genetic material.
Conclusion
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called Pachytene. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form bivalents or tetrads. Synapsis, crossing over, and chiasmata formation occur during this stage. The Pachytene stage is an essential process in meiosis as it contributes to the genetic diversity of offspring.
The process of meiosis is divided into several stages, one of which is the Pachytene stage. This stage occurs during the first meiotic division or meiosis I. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. The Pachytene stage is characterized by the following events:
Synapsis
During the Pachytene stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. This process is called synapsis. The synaptonemal complex plays a crucial role in this process. The complex is composed of proteins that hold the homologous chromosomes together.
Crossing over
Crossing over occurs during the Pachytene stage. It is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process results in the creation of new combinations of genes, which contributes to genetic diversity.
Chiasmata formation
During the Pachytene stage, the homologous chromosomes that have paired up undergo crossing over. This process results in the formation of chiasmata, which are visible under a microscope. Chiasmata are the points where the homologous chromosomes crisscross and exchange genetic material.
Conclusion
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called Pachytene. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form bivalents or tetrads. Synapsis, crossing over, and chiasmata formation occur during this stage. The Pachytene stage is an essential process in meiosis as it contributes to the genetic diversity of offspring.
Number of nuclei participating in double fertilisation is?- a)2
- b)5
- c)4
- d)3
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of nuclei participating in double fertilisation is?
a)
2
b)
5
c)
4
d)
3

|
Sadiya Siddique answered |
The two polar nuclei, 2 male gamates nuclei and an egg cell nucleus participates in double fertilization.thus, op B.
In most of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at_______.- a)4-celled stage
- b)3-celled stage
- c)2-celled stage
- d)8-celled stage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In most of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at_______.
a)
4-celled stage
b)
3-celled stage
c)
2-celled stage
d)
8-celled stage
|
|
Satakshi Kumari answered |
Generally pollengrain has two cells one vegetative and the other generative
so in many of the angiosperms about 60% of them shed off from anther at this two celled stage
and in remaining 40% of angiosperms the generative cell divides into two cells called as male gamets when present in the anther and at this three celled stage of the pollen grain they shed out..... three cells means one vegetative ,two male gametes
so in many of the angiosperms about 60% of them shed off from anther at this two celled stage
and in remaining 40% of angiosperms the generative cell divides into two cells called as male gamets when present in the anther and at this three celled stage of the pollen grain they shed out..... three cells means one vegetative ,two male gametes
If an endosperm cell of angiosperm contain 24 chromosome, the number of chromosome in each cell of root is? - a)24
- b)16
- c)8
- d)48
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an endosperm cell of angiosperm contain 24 chromosome, the number of chromosome in each cell of root is?
a)
24
b)
16
c)
8
d)
48

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Endosperm of angiosperms is triploid (3n) While as root cell is diploid(2n). Hence, number of chromosomes in each root cell = 2n = 2 x 8 = 16.
Seed of castor is- a)non-endospermic, exalbuminous
- b)endospermic, albuminous
- c)endospermic, exalbuminous
- d)non-endospermic, albuminous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Seed of castor is
a)
non-endospermic, exalbuminous
b)
endospermic, albuminous
c)
endospermic, exalbuminous
d)
non-endospermic, albuminous

|
Infinity Academy answered |
- Endospermic: Castor seeds contain endosperm, which is the tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
- Albuminous: The endosperm in castor seeds remains in the mature seed and is not consumed during seed development, so it is termed albuminous.
Topic in NCERT: Seed
Line in NCERT: "Albuminous seeds retain a part of endosperm as it is not completely used up during embryo development (e.g., wheat, maize, barley, castor)."
The anther is a four sided structure consisting of four------------ located at the corner. - a)Microsporangia
- b)Megasporangia
- c)Macrosoporangia
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The anther is a four sided structure consisting of four------------ located at the corner.
a)
Microsporangia
b)
Megasporangia
c)
Macrosoporangia
d)
None of these

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Anther is bilobed structure at the tips of stamen. Each lobe consists of two theca. Each theca change into microsporangium. Anther forms four sided structure having four microsporangia in which pollen grains are formed.
Identify “A” and “B” in the T.S of mature anther: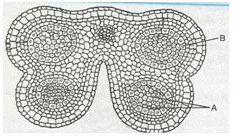
- a)Middle layer and Tapetum
- b)Microspore mother cell and Tapetum
- c)Epidermis and tapetum
- d)Stomium and microspore mother cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify “A” and “B” in the T.S of mature anther:
a)
Middle layer and Tapetum
b)
Microspore mother cell and Tapetum
c)
Epidermis and tapetum
d)
Stomium and microspore mother cell
|
|
Anirban Nambiar answered |
The mature anther consists of four microsporangia which contain four layers. The inner most layer is called tapetum that provide nutrient to growing microspores and tissues inside it are called microspore mother cell that produce pollen grain.
Which of the following is the correct sequence for a meiotic cell cycle?
S → G1 → G2 → M → S
G1 → S → G2 → M → G1
G2 → G1 → S → M → G2
G1 → G2 → S → M → G2- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct sequence for a meiotic cell cycle?
S → G1 → G2 → M → S
G1 → S → G2 → M → G1
G2 → G1 → S → M → G2
G1 → G2 → S → M → G2
S → G1 → G2 → M → S
G1 → S → G2 → M → G1
G2 → G1 → S → M → G2
G1 → G2 → S → M → G2
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Sagar Singh answered |
Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Cytokinesis, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, Cytokinesis
A typical angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is_______.- a)2 nucleate
- b)7 nucleate
- c)4 nucleate
- d)8 nucleate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is_______.
a)
2 nucleate
b)
7 nucleate
c)
4 nucleate
d)
8 nucleate

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Angiospermic embryo sac is 8-nucleate but 7-celled at maturity. This includes 3- celled egg Synergids, 3 antipodal cells and 2 polar nuclei.
Cross-like configurations when non-sister chromatids of a bivalent come in contact during the first meiotic division are- a)Chiasmata
- b)Chromomeres
- c)Bivalents
- d)Centromeres
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cross-like configurations when non-sister chromatids of a bivalent come in contact during the first meiotic division are
a)
Chiasmata
b)
Chromomeres
c)
Bivalents
d)
Centromeres
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Chiasmata) is the point of contact, the physical link, between two (non-sister) chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes. At a given chiasma, an exchange of genetic material can occur between both chromatids, what is called a chromosomal crossover, but this is much more frequent during meiosis than mitosis.
What is the correct sequence of the formation of female gametophyte in angiosperms?- a)Nucellus, megaspore tetrad, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
- b)Megaspore tetrad, nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
- c)Nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, female gametophyte
- d)Megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, nucellus, female gametophyte
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct sequence of the formation of female gametophyte in angiosperms?
a)
Nucellus, megaspore tetrad, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
b)
Megaspore tetrad, nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore, female gametophyte
c)
Nucellus, megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, female gametophyte
d)
Megaspore mother cell, megaspore tetrad, megaspore, nucellus, female gametophyte
|
|
Lakshmi Bose answered |
Formation of Female Gametophyte in Angiosperms
The development of the female gametophyte in angiosperms follows a specific sequence, which can be outlined as follows:
1. Nucellus
- The nucellus is the tissue within the ovule that contains the megasporangium.
- It provides nourishment and support for the developing gametophyte.
2. Megaspore Mother Cell
- The megaspore mother cell (megasporocyte) is located within the nucellus.
- This diploid cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores.
3. Megaspore Tetrad
- After meiosis, the four megaspores form a tetrad.
- Typically, three of the megaspores degenerate, leaving one functional megaspore.
4. Megaspore
- The surviving megaspore undergoes mitotic divisions.
- It divides to form the female gametophyte, also known as the embryo sac.
5. Female Gametophyte
- The final structure is the mature female gametophyte, which usually contains seven cells and eight nuclei.
- This structure is crucial for fertilization, as it will eventually form the egg cell, synergids, and polar nuclei.
Conclusion
The correct sequence of formation of the female gametophyte is:
Nucellus → Megaspore Mother Cell → Megaspore Tetrad → Megaspore → Female Gametophyte
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C'. Understanding this sequence is vital for comprehending the reproductive processes in flowering plants, which is essential for NEET aspirants.
The development of the female gametophyte in angiosperms follows a specific sequence, which can be outlined as follows:
1. Nucellus
- The nucellus is the tissue within the ovule that contains the megasporangium.
- It provides nourishment and support for the developing gametophyte.
2. Megaspore Mother Cell
- The megaspore mother cell (megasporocyte) is located within the nucellus.
- This diploid cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores.
3. Megaspore Tetrad
- After meiosis, the four megaspores form a tetrad.
- Typically, three of the megaspores degenerate, leaving one functional megaspore.
4. Megaspore
- The surviving megaspore undergoes mitotic divisions.
- It divides to form the female gametophyte, also known as the embryo sac.
5. Female Gametophyte
- The final structure is the mature female gametophyte, which usually contains seven cells and eight nuclei.
- This structure is crucial for fertilization, as it will eventually form the egg cell, synergids, and polar nuclei.
Conclusion
The correct sequence of formation of the female gametophyte is:
Nucellus → Megaspore Mother Cell → Megaspore Tetrad → Megaspore → Female Gametophyte
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C'. Understanding this sequence is vital for comprehending the reproductive processes in flowering plants, which is essential for NEET aspirants.
Which one of the following statements is false in respect of flowering plants?
1. Parthenocarpy can be induced through the application of growth hormones
2. Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where a small opening called the germ pore is organized
3. Endosperm development precedes embryo development
4. Apomicts have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture
- a)Statement 1
- b)Statement 2
- c)Statement 3
- d)Statement 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is false in respect of flowering plants?
1. Parthenocarpy can be induced through the application of growth hormones
2. Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where a small opening called the germ pore is organized
3. Endosperm development precedes embryo development
4. Apomicts have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture
a)
Statement 1
b)
Statement 2
c)
Statement 3
d)
Statement 4

|
Bs Academy answered |
Statement 1: Parthenocarpy, the development of fruit without fertilization, can indeed be induced through the application of growth hormones.
Statement 2: Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where there is an opening called the micropyle, not the germ pore. The germ pore is found in pollen grains, not ovules.
Statement 3: Endosperm development typically precedes embryo development in most flowering plants.
Statement 4: Apomicts, plants that can reproduce without fertilization, have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture, such as maintaining desirable traits without genetic variation.
Therefore, Statement 2 is false because the correct term for the opening at the tip of the ovule is the micropyle, not the germ pore.
Statement 2: Integuments encircle the ovule except at the tip where there is an opening called the micropyle, not the germ pore. The germ pore is found in pollen grains, not ovules.
Statement 3: Endosperm development typically precedes embryo development in most flowering plants.
Statement 4: Apomicts, plants that can reproduce without fertilization, have several advantages in horticulture and agriculture, such as maintaining desirable traits without genetic variation.
Therefore, Statement 2 is false because the correct term for the opening at the tip of the ovule is the micropyle, not the germ pore.
While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant?- a) Bagging of the female flower
- b)Dusting of pollen on the stigma
- c) Emasculation
- d)Collection of pollen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant?
a)
Bagging of the female flower
b)
Dusting of pollen on the stigma
c)
Emasculation
d)
Collection of pollen

|
Ambition Institute answered |
In an artificial hybridization program with dioecious plants:
- Bagging of the female flower: Relevant to prevent unwanted pollen contamination.
- Dusting of pollen on the stigma: Essential for pollination to occur.
- Emasculation: Not relevant because dioecious plants have separate sexes; emasculation is for monoecious plants.
- Collection of pollen: Necessary for controlled pollination process.
Therefore, in this context, the step that would not be relevant is C: Emasculation.
Topic in NCERT: Artificial Hybridization Techniques
Line in NCERT: "Emasculated flowers have to be covered with a bag of suitable size, generally made up of butter paper, to prevent contamination of its stigma with unwanted pollen."
- Bagging of the female flower: Relevant to prevent unwanted pollen contamination.
- Dusting of pollen on the stigma: Essential for pollination to occur.
- Emasculation: Not relevant because dioecious plants have separate sexes; emasculation is for monoecious plants.
- Collection of pollen: Necessary for controlled pollination process.
Therefore, in this context, the step that would not be relevant is C: Emasculation.
Topic in NCERT: Artificial Hybridization Techniques
Line in NCERT: "Emasculated flowers have to be covered with a bag of suitable size, generally made up of butter paper, to prevent contamination of its stigma with unwanted pollen."
At the _______ end, embryogenesis happens.- a)Hilum
- b)Hypophysis
- c)Microplylar
- d)Axis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At the _______ end, embryogenesis happens.
a)
Hilum
b)
Hypophysis
c)
Microplylar
d)
Axis

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Embryogeny is the study of the changes that take place when an embryo develops from a zygote.
- It occurs near the embryo sac’s micropylar end.
- The nucellus and integuments unite at the base of the ovule, or chalaza, in plants.
- It can be found on an ovule opposite the micropylar end.
- Chalaza is the pathway via which plant nutrients are delivered to the nucellus.
- Three antipodal cells form from the chalazal end of the embryo sac’s cells.
Topic in NCERT: Embryo
Line in NCERT: "Embryo develops at the micropylar end of the embryo sac where the zygote is situated."
During meiosis, crossover occurs between- a)Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
- b)Sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
- c)Sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
- d)Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During meiosis, crossover occurs between
a)
Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
b)
Sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
c)
Sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
d)
Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes

|
Shibashish Das answered |
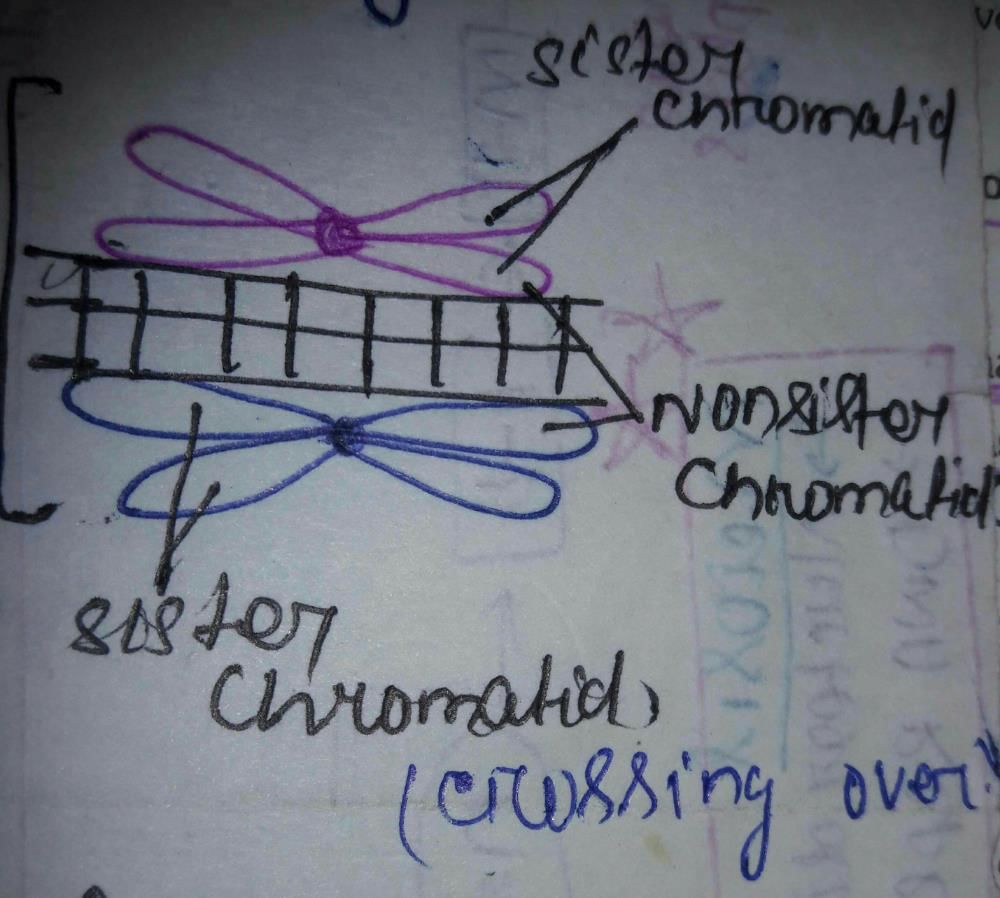
From the statements given below choose the option that are not true for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant:
(i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity
(ii) It is cellular during the development
(iii) It is situated inside the nucellus
(iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end- a)i and iv
- b)ii and iii
- c)i and ii
- d)ii and iv
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
(i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity
(ii) It is cellular during the development
(iii) It is situated inside the nucellus
(iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end
a)
i and iv
b)
ii and iii
c)
i and ii
d)
ii and iv
|
|
Deepak Sharma answered |
Understanding Female Gametophyte in Flowering Plants
The female gametophyte of flowering plants, also known as the embryo sac, has specific characteristics. Let's analyze the given statements to identify which are not true.
Statement Analysis
- (i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity:
This statement is true. The typical female gametophyte develops into an 8-nucleate structure, resulting in 7 cells at maturity: one egg cell, two synergids, three antipodal cells, and one central cell.
- (ii) It is cellular during the development:
This statement is false. The female gametophyte is initially formed as a single cell, and it undergoes nuclear divisions before cellularization occurs.
- (iii) It is situated inside the nucellus:
This statement is true. The embryo sac is located within the nucellus of the ovule.
- (iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end:
This statement is false. The egg apparatus, consisting of the egg cell and synergids, is located at the micropylar end, not the chalazal end.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' because statements (ii) and (iv) are not true for a typical female gametophyte. The female gametophyte is initially a single cell and cellularization occurs later, while the egg apparatus is indeed situated at the micropylar end, not the chalazal end. This understanding is crucial for NEET aspirants focusing on plant reproductive biology.
The female gametophyte of flowering plants, also known as the embryo sac, has specific characteristics. Let's analyze the given statements to identify which are not true.
Statement Analysis
- (i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity:
This statement is true. The typical female gametophyte develops into an 8-nucleate structure, resulting in 7 cells at maturity: one egg cell, two synergids, three antipodal cells, and one central cell.
- (ii) It is cellular during the development:
This statement is false. The female gametophyte is initially formed as a single cell, and it undergoes nuclear divisions before cellularization occurs.
- (iii) It is situated inside the nucellus:
This statement is true. The embryo sac is located within the nucellus of the ovule.
- (iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end:
This statement is false. The egg apparatus, consisting of the egg cell and synergids, is located at the micropylar end, not the chalazal end.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' because statements (ii) and (iv) are not true for a typical female gametophyte. The female gametophyte is initially a single cell and cellularization occurs later, while the egg apparatus is indeed situated at the micropylar end, not the chalazal end. This understanding is crucial for NEET aspirants focusing on plant reproductive biology.
Which among the following statement is incorrect with respect to tapetum?- a)Cells have single nucleus only.
- b)It has dense cytoplasm.
- c)It is the innermost wall layer of microsporangia.
- d)It nourishes developing pollen grains.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following statement is incorrect with respect to tapetum?
a)
Cells have single nucleus only.
b)
It has dense cytoplasm.
c)
It is the innermost wall layer of microsporangia.
d)
It nourishes developing pollen grains.

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The innermost wall layer is the tapetum. It nourishes the developing pollen grains. Cells of the tapetum possess dense cytoplasm and generally have more than one nucleus.
Topic in NCERT: Tapetum
Line in NCERT: "Cells of the tapetum possess dense cytoplasm and generally have more than one nucleus."
Abundant occurrence of fossilized pollen grain is due to resistant: - a)Pectocellulose
- b)Pectolignin
- c)Sporopollenin
- d)Lignocellulose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Abundant occurrence of fossilized pollen grain is due to resistant:
a)
Pectocellulose
b)
Pectolignin
c)
Sporopollenin
d)
Lignocellulose

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
Large amount of fossilized pollen grain are found during excavation process of older parts due to tough covering of Sporopollenin that make the outer wall of pollen grain, exine. This substance cannot be hydrolyzed by any enzyme known.
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): An apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction.
Reason (R): There is no fertilisation in apomicts plants and they do not produce any seeds.- a)(A) is True but (R) is False.
- b)Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is False but (R) is True.
- d)Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): An apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction.
Reason (R): There is no fertilisation in apomicts plants and they do not produce any seeds.
Assertion (A): An apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction.
Reason (R): There is no fertilisation in apomicts plants and they do not produce any seeds.
a)
(A) is True but (R) is False.
b)
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is False but (R) is True.
d)
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
|
|
Lakshmi Bose answered |
Understanding Apomixis and Its Characteristics
Apomixis is an intriguing reproductive strategy in plants that raises questions about its classification as asexual reproduction. Let's break down the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) to see why option 'A' is the correct choice.
Assertion (A):
- Apomixis is indeed a form of asexual reproduction.
- It mimics sexual reproduction by producing seeds without fertilization.
Reason (R):
- In apomicts, there is no fertilization.
- These plants do not produce fertilized seeds but can still produce viable seeds that develop without fertilization.
Analysis of Assertion and Reason
- Assertion Validity:
- The assertion is True because apomixis allows plants to produce seeds asexually, resembling sexual reproduction.
- Reason Validity:
- The reason is also True since apomictic plants do not undergo fertilization, which is a key aspect of apomixis.
Conclusion on Relationship
- While both statements are true, the reason does not correctly explain the assertion. The assertion focuses on the mimicry of sexual reproduction, while the reason highlights the lack of fertilization, which is a characteristic but not an explanation for why apomixis mimics sexual reproduction.
Final Answer
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': (A) is True but (R) is False. The reason, while factual, does not serve as an appropriate explanation for the assertion made.
Apomixis is an intriguing reproductive strategy in plants that raises questions about its classification as asexual reproduction. Let's break down the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) to see why option 'A' is the correct choice.
Assertion (A):
- Apomixis is indeed a form of asexual reproduction.
- It mimics sexual reproduction by producing seeds without fertilization.
Reason (R):
- In apomicts, there is no fertilization.
- These plants do not produce fertilized seeds but can still produce viable seeds that develop without fertilization.
Analysis of Assertion and Reason
- Assertion Validity:
- The assertion is True because apomixis allows plants to produce seeds asexually, resembling sexual reproduction.
- Reason Validity:
- The reason is also True since apomictic plants do not undergo fertilization, which is a key aspect of apomixis.
Conclusion on Relationship
- While both statements are true, the reason does not correctly explain the assertion. The assertion focuses on the mimicry of sexual reproduction, while the reason highlights the lack of fertilization, which is a characteristic but not an explanation for why apomixis mimics sexual reproduction.
Final Answer
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': (A) is True but (R) is False. The reason, while factual, does not serve as an appropriate explanation for the assertion made.
A typical anther is
(a) Tetrasporangiate
(b) Tetragonal
(c) Trilobed
(d) Surrounded by four wall layers- a)Only (a) and (d)
- b)Only (a), (b) and (d)
- c)Only (b) and (c)
- d)All (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical anther is
(a) Tetrasporangiate
(b) Tetragonal
(c) Trilobed
(d) Surrounded by four wall layers
(a) Tetrasporangiate
(b) Tetragonal
(c) Trilobed
(d) Surrounded by four wall layers
a)
Only (a) and (d)
b)
Only (a), (b) and (d)
c)
Only (b) and (c)
d)
All (a), (b), (c) and (d)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
(a) Tetrasporangiate: Correct. A typical anther has four pollen sacs or microsporangia.
(b) Tetragonal: Correct - The anther is a four-sided (tetragonal) structure consisting of four microsporangia located at the corners, two in each lobe.
(c) Trilobed: No, anthers are typically bilobed, not trilobed
(d) Surrounded by four wall layers: Correct. The anther is surrounded by four distinct wall layers: the epidermis, endothecium, middle layer, and tapetum.
Topic in NCERT: Anther Structure and Function
Line in NCERT: "A typical anther is bilobed, dithecous and tetrasporangiate. Four wall layers, the epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and the tapetum surround the microsporangium."
(b) Tetragonal: Correct - The anther is a four-sided (tetragonal) structure consisting of four microsporangia located at the corners, two in each lobe.
(c) Trilobed: No, anthers are typically bilobed, not trilobed
(d) Surrounded by four wall layers: Correct. The anther is surrounded by four distinct wall layers: the epidermis, endothecium, middle layer, and tapetum.
Topic in NCERT: Anther Structure and Function
Line in NCERT: "A typical anther is bilobed, dithecous and tetrasporangiate. Four wall layers, the epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and the tapetum surround the microsporangium."
Label the part marked with a blue arrow.

- a)Chalaza
- b)Micropyle
- c)Nucellus
- d)Egg
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Label the part marked with a blue arrow.


a)
Chalaza
b)
Micropyle
c)
Nucellus
d)
Egg

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- It’s the nucellus. Nucellus is the place where the embryo sac rests.
- It is made up of cushiony cells called parenchymatous cells.
- Nucellus helps in the nourishment of the embryo sac.
Topic in NCERT: Ovule Structure and Development
Line in NCERT: "Enclosed within the integuments is a mass of cells called the nucellus."
Label the part marked by the blue arrow.
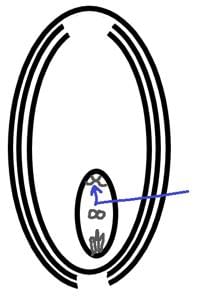
- a)Antipodal cells
- b)Synergids
- c)Polar nuclei
- d)Funicle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Label the part marked by the blue arrow.


a)
Antipodal cells
b)
Synergids
c)
Polar nuclei
d)
Funicle

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- They are the 3 mature cells in the embryo sac present opposite to the micropylar end.
- The function of the antipodal cells is to provide nutrition and nourishment to the embryo sac.
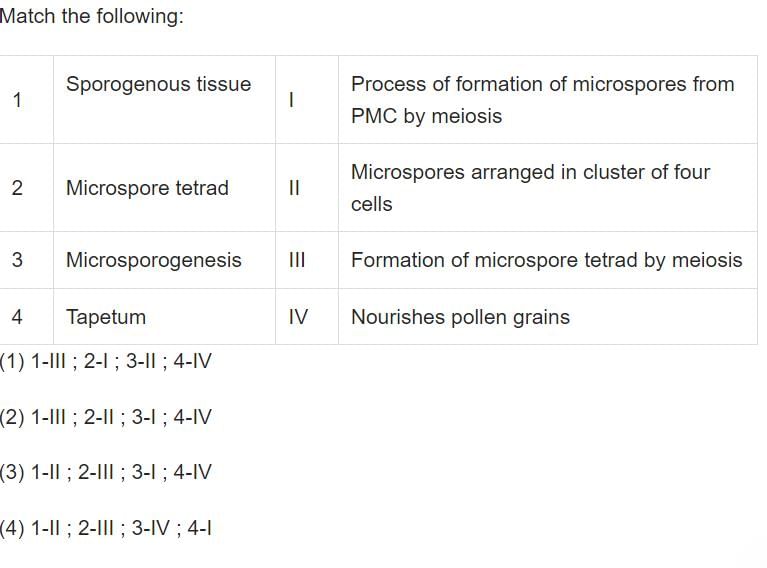
- a)1.
- b)2.
- c)3.
- d)4.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

a)
1.
b)
2.
c)
3.
d)
4.

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- Sporogenous tissue - Formation of microspore tetrad by meiosis
- Microspore tetrad - Microspores arranged in clusters of four cells
- Microsporogenesis - Process of formation of microspore PMC by meiosis
- Tapetum - Nourishes pollen grains
In the given diagram:
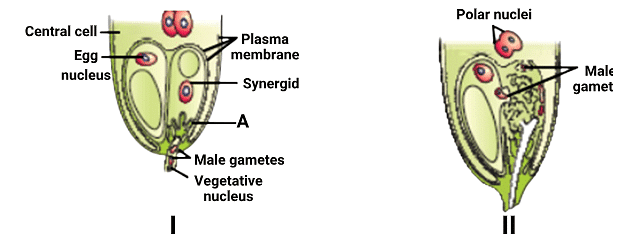
Statement I:I shows the entry of the pollen tube into a synergid under the guidance of A.
Statement II:II shows the discharge of male gametes into a synergid.- a)Statement I is correct, Statement II is correct
- b)Statement I is incorrect, Statement II is correct
- c)Statement I is correct, Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement I is incorrect, Statement II is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given diagram:

Statement I:I shows the entry of the pollen tube into a synergid under the guidance of A.
Statement II:II shows the discharge of male gametes into a synergid.

Statement I:I shows the entry of the pollen tube into a synergid under the guidance of A.
Statement II:II shows the discharge of male gametes into a synergid.
a)
Statement I is correct, Statement II is correct
b)
Statement I is incorrect, Statement II is correct
c)
Statement I is correct, Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement I is incorrect, Statement II is incorrect

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
(A) To determine the correctness of the statements regarding the given diagram:
- Statement I: The pollen tube enters a synergid under guidance from A, which is correct.
- Statement II: Male gametes are discharged into a synergid, which is correct
Statement I is correct, Statement II is correct SO OPTION (A)
Topic in NCERT: DOUBLE FERTILISATION
Line in NCERT: "the pollen tube releases the two male gametes into the cytoplasm of the synergid."
- Statement I: The pollen tube enters a synergid under guidance from A, which is correct.
- Statement II: Male gametes are discharged into a synergid, which is correct
Statement I is correct, Statement II is correct SO OPTION (A)
Topic in NCERT: DOUBLE FERTILISATION
Line in NCERT: "the pollen tube releases the two male gametes into the cytoplasm of the synergid."
What happen to haploid megaspores formed by megaspore mother cell in an angiospermic plant?
- a) three megaspores degenerate and one produce embryo sac
- b) 2 megaspores degenerate and two produce embryo sac
- c) 3 megaspores produce embryo and 1 degenerate
- d)All four megaspores produce 4 embryo sac
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer??
What happen to haploid megaspores formed by megaspore mother cell in an angiospermic plant?
a)
three megaspores degenerate and one produce embryo sac
b)
2 megaspores degenerate and two produce embryo sac
c)
3 megaspores produce embryo and 1 degenerate
d)
All four megaspores produce 4 embryo sac
|
|
Prisha Chavan answered |
Understanding Megaspores in Angiosperms
In angiospermic plants, the process of megasporogenesis leads to the formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell (megasporocyte). This process is crucial for the development of the female gametophyte, known as the embryo sac.
Formation of Megaspores
- The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis, producing four haploid megaspores.
- These megaspores are genetically distinct due to the process of meiosis.
Fate of Megaspores
- Out of the four megaspores formed, typically three degenerate.
- One megaspore survives and undergoes mitotic divisions.
Development of the Embryo Sac
- The surviving megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions, resulting in an eight-nucleate structure.
- This structure develops into the embryo sac, which contains the egg cell, synergids, polar nuclei, and antipodal cells.
Significance of the Process
- The degeneration of three megaspores ensures that resources are concentrated on the development of a single, viable embryo sac.
- This strategy enhances the efficiency of fertilization and subsequent seed development.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option A: three megaspores degenerate, and one produces the embryo sac, which is essential for successful fertilization and seed formation in angiospermic plants.
In angiospermic plants, the process of megasporogenesis leads to the formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell (megasporocyte). This process is crucial for the development of the female gametophyte, known as the embryo sac.
Formation of Megaspores
- The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis, producing four haploid megaspores.
- These megaspores are genetically distinct due to the process of meiosis.
Fate of Megaspores
- Out of the four megaspores formed, typically three degenerate.
- One megaspore survives and undergoes mitotic divisions.
Development of the Embryo Sac
- The surviving megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions, resulting in an eight-nucleate structure.
- This structure develops into the embryo sac, which contains the egg cell, synergids, polar nuclei, and antipodal cells.
Significance of the Process
- The degeneration of three megaspores ensures that resources are concentrated on the development of a single, viable embryo sac.
- This strategy enhances the efficiency of fertilization and subsequent seed development.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option A: three megaspores degenerate, and one produces the embryo sac, which is essential for successful fertilization and seed formation in angiospermic plants.
Chapter doubts & questions for Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction - Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction - Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology
153 videos|283 docs|127 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









