All questions of Acceleration for Grade 9 Exam
If the signs of the velocity and acceleration of a particle are the same, the speed of the particle ______________.- a)Remains same
- b)Increases
- c)Decreases
- d)Cannot conclude anything
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the signs of the velocity and acceleration of a particle are the same, the speed of the particle ______________.
a)
Remains same
b)
Increases
c)
Decreases
d)
Cannot conclude anything
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
In this question, it has been asked about the signs of velocity and acceleration not about the values of velocity and acceleration.
So, if both the entities have same the signs, then the speed of the object will increase.
If it is accelerating in the positive direction, the negative velocity is decreasing, and the object is slowing down.
On acceleration-time graph, a horizontal line indicates:- a)zero displacement
- b)zero acceleration
- c)constant velocity
- d)constant acceleration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On acceleration-time graph, a horizontal line indicates:
a)
zero displacement
b)
zero acceleration
c)
constant velocity
d)
constant acceleration
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
A horizontal line on a acceleration- time graph indicates that object has constant acceleration.
The dimensions of (change in velocity / time) is- a)[LT-2]
- b)[LT-1]
- c)[L/T-1]
- d)[L/T-2]
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dimensions of (change in velocity / time) is
a)
[LT-2]
b)
[LT-1]
c)
[L/T-1]
d)
[L/T-2]
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
We know that change in velocity / time is acceleration.
And dimension of acceleration is LT-2
A boy throws up a ball in a stationary lift and the ball returns to his hands in 10 s. Now if the lift starts moving up at a speed of 5 m/s. The time taken for a ball thrown straight up to return to his hands is:- a)more than 10 s
- b)Less than 10 s
- c)insufficient information given
- d)equal to 10 s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy throws up a ball in a stationary lift and the ball returns to his hands in 10 s. Now if the lift starts moving up at a speed of 5 m/s. The time taken for a ball thrown straight up to return to his hands is:
a)
more than 10 s
b)
Less than 10 s
c)
insufficient information given
d)
equal to 10 s
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Lift moving with Uniform speed = 5m / s
Ball is thrown inside the lift
The uniform velocity of the lift does not affect the relative velocity of the ball with respect to the boy.
Relative velocity of ball = 49m/s
⇒ Relative acceleration = 9.8
Thus, u(relative) = velocity of bell
t = 2ur / gr
= (2 × 49) / 9.8
⇒ t = 10s
so, the ball will still return in 10 secs
The dimensions of instantaneous acceleration is:- a)[ LT-2]
- b)[L/T2]
- c)[L/T-1]
- d)[LT-1]
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dimensions of instantaneous acceleration is:
a)
[ LT-2]
b)
[L/T2]
c)
[L/T-1]
d)
[LT-1]
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Instantaneous acceleration is rate of change of instantaneous velocity with time or velocity upon total time, hence we get its dimension is same as of acceleration i.e. LT-2
What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object?
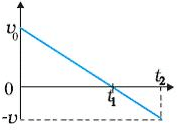
- a)Object is moving in positive direction with positive acceleration
- b)Object is moving in negative direction with negative acceleration
- c)An object is moving in positive direction till time t1, and then turns back with the same Velocity
- d)Object is moving in positive direction with negative acceleration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object?
a)
Object is moving in positive direction with positive acceleration
b)
Object is moving in negative direction with negative acceleration
c)
An object is moving in positive direction till time t1, and then turns back with the same Velocity
d)
Object is moving in positive direction with negative acceleration

|
Top Rankers answered |
Through the given graph we get that:
Velocity is decreasing from a positive constant to some negative number with zero at t1
Velocity is decreasing from a positive constant to some negative number with zero at t1
Distance from the original point increases from zero to t1 and then it decreases afterwards.
The object is moving in a positive direction at first and after time t1 it moves in a negative direction.
What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object ?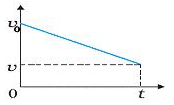
- a)object is moving in negative direction with positive acceleration
- b)object is moving in negative direction with negative acceleration
- c)object is moving in positive direction with negative acceleration
- d)object is moving in positive direction with positive acceleration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does this graph indicate about the motion of an object ?
a)
object is moving in negative direction with positive acceleration
b)
object is moving in negative direction with negative acceleration
c)
object is moving in positive direction with negative acceleration
d)
object is moving in positive direction with positive acceleration
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Velocity is decreasing so, acceleration is negative. Velocity is positive so direction is positive.
Hence option (C) is correct.
The position x of a particle varies with time (t) as x = 3t2 – 2t3 .The acceleration of the particle will be zero at time- a)1
- b)3/2
- c)0
- d)1/2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The position x of a particle varies with time (t) as x = 3t2 – 2t3 .The acceleration of the particle will be zero at time
a)
1
b)
3/2
c)
0
d)
1/2
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
We know that acceleration is the second derivative of change in displacement wrt time, hence we get a = 6 - 12t
When a = 0 = 6 -12t ;
We get t = ½
When a = 0 = 6 -12t ;
We get t = ½
The displacement of a particle along x-axis is given by x = 4 + 6t + 5t2. Its acceleration at t = 2s- a)2 m/s2
- b)10 m/s2
- c)1000 m/s2
- d)100 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The displacement of a particle along x-axis is given by x = 4 + 6t + 5t2. Its acceleration at t = 2s
a)
2 m/s2
b)
10 m/s2
c)
1000 m/s2
d)
100 m/s2
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
usingdifferentiation
x = 18t + 5t^2
dx/dt = 18 + 10t
v = 18 + 10t
at t = 2s
v = 18 + 10x2
= 18 + 20 =38m/s
at t = 3s
v = 18 + 10x3
= 18 + 20 = 48m/s
vav= 38+48/2= 43m/s
dv/dt = 10
a = 10
a =10m/s^2
On acceleration-time graph the area under the curve equals the:- a)Meaningless
- b)Change in velocity
- c)Displacement
- d)Change in acceleration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On acceleration-time graph the area under the curve equals the:
a)
Meaningless
b)
Change in velocity
c)
Displacement
d)
Change in acceleration
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The area under an acceleration graph represents the change in velocity. In other words, the area under the acceleration graph for a certain time interval is equal to the change in velocity during that time interval.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. The acceleration due to gravity:- a)is in the upward direction
- b)is in the downward direction
- c)is in the horizontal direction
- d)always in the direction of motion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. The acceleration due to gravity:
a)
is in the upward direction
b)
is in the downward direction
c)
is in the horizontal direction
d)
always in the direction of motion
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. The acceleration due to gravity is in the downward direction.
The value of acceleration due to gravity on earth is.- a)9.8ms−2.
- b)15376
- c)227004
- d)127008
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of acceleration due to gravity on earth is.
a)
9.8ms−2.
b)
15376
c)
227004
d)
127008
|
|
Ishan Ghosh answered |
Understanding Acceleration Due to Gravity
The acceleration due to gravity (g) is a fundamental constant that defines the acceleration experienced by an object when it is in free fall near the Earth's surface.
Value of g
- The standard value of acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s².
- This means that, neglecting air resistance, an object will increase its velocity by 9.8 meters per second for every second it is falling.
Why g is Approximately 9.8 m/s²
- Earth's Mass and Radius: The value of g is influenced by the mass of the Earth and its radius. The more massive the Earth, the stronger the gravitational pull. Similarly, the closer you are to the Earth's center (i.e., the smaller the radius), the stronger the gravitational force.
- Universal Law of Gravitation: According to this law, every mass attracts every other mass. The force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Variations of g
- It's important to note that the value of g can vary slightly depending on where you are on Earth, due to factors such as altitude and the Earth's rotation. For instance, g is slightly less at the equator compared to the poles.
Conclusion
- Among the options provided, 9.8 m/s² is the only correct and scientifically accepted value for the acceleration due to gravity on Earth, making option 'A' the right choice. Other values like 15376, 227004, and 127008 are incorrect and do not represent the gravitational acceleration experienced on our planet.
The acceleration due to gravity (g) is a fundamental constant that defines the acceleration experienced by an object when it is in free fall near the Earth's surface.
Value of g
- The standard value of acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s².
- This means that, neglecting air resistance, an object will increase its velocity by 9.8 meters per second for every second it is falling.
Why g is Approximately 9.8 m/s²
- Earth's Mass and Radius: The value of g is influenced by the mass of the Earth and its radius. The more massive the Earth, the stronger the gravitational pull. Similarly, the closer you are to the Earth's center (i.e., the smaller the radius), the stronger the gravitational force.
- Universal Law of Gravitation: According to this law, every mass attracts every other mass. The force of gravity is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Variations of g
- It's important to note that the value of g can vary slightly depending on where you are on Earth, due to factors such as altitude and the Earth's rotation. For instance, g is slightly less at the equator compared to the poles.
Conclusion
- Among the options provided, 9.8 m/s² is the only correct and scientifically accepted value for the acceleration due to gravity on Earth, making option 'A' the right choice. Other values like 15376, 227004, and 127008 are incorrect and do not represent the gravitational acceleration experienced on our planet.
The earth's gravitational force at someplace in space causes an acceleration of 7m/s2 in a 1kg mass.What will be the acceleration of a 5kg mass at the same place?- a)7m/s2
- b)35m/s2
- c)1.4m/s2
- d)3.5m/s2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The earth's gravitational force at someplace in space causes an acceleration of 7m/s2 in a 1kg mass.What will be the acceleration of a 5kg mass at the same place?
a)
7m/s2
b)
35m/s2
c)
1.4m/s2
d)
3.5m/s2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The acceleration due to gravity does not vary with the change in the mass of the object as it is a dimensionless quantity representing the amount of matter in a particle or object.
Therefore, the acceleration of a 5 kg mass at the same place is 7m/s2.
Therefore, the acceleration of a 5 kg mass at the same place is 7m/s2.
Two balls are dropped from the same height from places A and B. The body at B takes two seconds less to reach the ground at B strikes the ground with a velocity greater than at A by 10m/s. The product of the acceleration due to gravity at the two places A and B is:- a)5
- b)25
- c)125
- d)12.5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two balls are dropped from the same height from places A and B. The body at B takes two seconds less to reach the ground at B strikes the ground with a velocity greater than at A by 10m/s. The product of the acceleration due to gravity at the two places A and B is:
a)
5
b)
25
c)
125
d)
12.5
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The diameters of two planets are in the ratio 4:1 and their mean densities in the ratio 1:2. The acceleration due to gravity on the planets will be in ratio
- a)2:1
- b)2:3
- c)1:2
- d)4:1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The diameters of two planets are in the ratio 4:1 and their mean densities in the ratio 1:2. The acceleration due to gravity on the planets will be in ratio
a)
2:1
b)
2:3
c)
1:2
d)
4:1
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Acceleration due to gravity is given by the equation g = GM/R2 (at surface)
so g1 = GM1 /R12 and g2 = GM2 /R22 (gravities at planets 1 and 2)
also M1/M2 = V1p1/V2p2 = R13 p1/ R23 p2 (as V = 4/3 π r3
Therefore, g1/g2 = R1 ρ1 / R2 ρ2 = (4/1) x (1/2) = 2:1
Radius of planet A is twice that of planet B and the dencity of A is one third that of B . The ratio of the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of A to that at the surface of B is.-- a)2:3
- b)3:2
- c)3:4
- d)4:3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Radius of planet A is twice that of planet B and the dencity of A is one third that of B . The ratio of the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of A to that at the surface of B is.-
a)
2:3
b)
3:2
c)
3:4
d)
4:3
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Radius of planet A is twice that of planet B and the density of A is one-third that of B.
so, the radius is
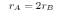
The density is
We know that,
The acceleration due to gravity
The ratio of the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of A to that at the surface of B is
We know,
Mass = density X Volume
Hence, the ratio of the acceleration due to gravity is 2:3.
Force of gravity is least at- a)The equator
- b)The poles
- c)A point in between equator and any pole
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Force of gravity is least at
a)
The equator
b)
The poles
c)
A point in between equator and any pole
d)
None of these
|
|
Bhargavi Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
Gravity is the force that attracts two bodies towards each other. The force of gravity depends on the mass of the two bodies and the distance between them. The closer the two bodies are, the stronger the force of gravity between them.
Gravity at Equator, Poles and in between:
- The Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator due to its rotation. This means that the distance from the center of the Earth to a point on the equator is greater than the distance from the center of the Earth to a point on the poles.
- As the force of gravity depends on the distance between two bodies, it is least at the equator where the distance from the center of the Earth is the greatest.
- At the poles, the force of gravity is the greatest as the distance from the center of the Earth is the least.
- The force of gravity at a point in between the equator and any pole would be somewhere in between the force of gravity at the equator and the force of gravity at the poles.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' as the force of gravity is the least at the equator due to the greater distance from the center of the Earth.
Gravity is the force that attracts two bodies towards each other. The force of gravity depends on the mass of the two bodies and the distance between them. The closer the two bodies are, the stronger the force of gravity between them.
Gravity at Equator, Poles and in between:
- The Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator due to its rotation. This means that the distance from the center of the Earth to a point on the equator is greater than the distance from the center of the Earth to a point on the poles.
- As the force of gravity depends on the distance between two bodies, it is least at the equator where the distance from the center of the Earth is the greatest.
- At the poles, the force of gravity is the greatest as the distance from the center of the Earth is the least.
- The force of gravity at a point in between the equator and any pole would be somewhere in between the force of gravity at the equator and the force of gravity at the poles.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' as the force of gravity is the least at the equator due to the greater distance from the center of the Earth.
The mass of a planet is 5 times the mass of the earth but its diameter is the same as that of the earth. How much work is done in lifting a stone of mass 3 kg through a distance of 1 m on this planet?- a)100 j
- b)150 j
- c)175 j
- d)200 j
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of a planet is 5 times the mass of the earth but its diameter is the same as that of the earth. How much work is done in lifting a stone of mass 3 kg through a distance of 1 m on this planet?
a)
100 j
b)
150 j
c)
175 j
d)
200 j
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
We know that g∝Mp, Where Mp is mass of planet.
So, gp=5×10=50 m/s2
So work done in lifting a 3 kg stone by 1m =50×3×1=150J
The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on the surface of the earth, the acceleration due to gravity :- a)will be directed towards the centre but not the same everywhere.
- b)will have the same value everywhere but not directed towards the centre.
- c)will be same everywhere in magnitude directed towards the centre.
- d)cannot be zero at at point.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on the surface of the earth, the acceleration due to gravity :
a)
will be directed towards the centre but not the same everywhere.
b)
will have the same value everywhere but not directed towards the centre.
c)
will be same everywhere in magnitude directed towards the centre.
d)
cannot be zero at at point.
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
There's no such thing as zero gravity. Weightlessness and zero gravity are two different things. The earth's gravity keeps the moon in orbit. And astronauts are generally much closer to earth than the moon is, which means that the earth's pull on them has to be much stronger.
Chapter doubts & questions for Acceleration - Physics 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Acceleration - Physics in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Physics
307 videos|482 docs|202 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










