All Exams >
NEET >
JIPMER: Subject wise Tests & Practice Mock Tests 2025 >
All Questions
All questions of Chemistry for NEET Exam
For principle quatum number n = 4, the total number of orbitals having l = 3 is- a)3
- b)5
- c)7
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
5
c)
7
d)
9
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Total number of orbital having n= 4, l = 3 is 7. n = 4, l= 3 means 4f. f- sub-shell has 7 orbitals.
Most stable alkene is :- a)CH2 ═ CH2
- b)CH3CH ═ CH2
- c)
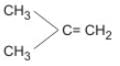
- d)
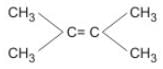
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most stable alkene is :
a)
CH2 ═ CH2
b)
CH3CH ═ CH2
c)

d)


|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Hi I am ishika
I think increase no of carbon ..
I think increase no of carbon ..
The maximum number of electrons in p-orbital with n = 6 ; m = 0 is- a)2
- b)6
- c)10
- d)14
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum number of electrons in p-orbital with n = 6 ; m = 0 is
a)
2
b)
6
c)
10
d)
14
|
|
Sonal Yadav answered |
Maximum Number of Electrons in p-orbital with n=6;m=0
The electronic configuration of an atom is the distribution of electrons in its atomic orbitals. The p-orbital is one of the three types of orbitals - s, p, and d - that are present in the valence shell of an atom. The maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital with n=6 and m=0 is determined by the quantum numbers n, l, and m.
Quantum Numbers
The quantum numbers are used to describe the electronic configuration of an atom. There are four quantum numbers: n, l, m, and s.
- Principal Quantum Number (n) - It determines the size and energy of the orbital.
- Azimuthal Quantum Number (l) - It determines the shape of the orbital.
- Magnetic Quantum Number (m) - It determines the orientation of the orbital.
- Spin Quantum Number (s) - It determines the spin of the electron.
The p-orbital has l=1, which means it has three sub-orbitals: px, py, and pz. Each sub-orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. The magnetic quantum number (m) can have values of -1, 0, or 1, which means there are three p-orbitals. The value of m=0 corresponds to the pz orbital.
Maximum Number of Electrons in p-orbital
The maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital is determined by the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. Therefore, the maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital with n=6 and m=0 is 2.
Conclusion
The maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital with n=6 and m=0 is 2. This is because the pz sub-orbital has only one possible orientation, which means it can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
The electronic configuration of an atom is the distribution of electrons in its atomic orbitals. The p-orbital is one of the three types of orbitals - s, p, and d - that are present in the valence shell of an atom. The maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital with n=6 and m=0 is determined by the quantum numbers n, l, and m.
Quantum Numbers
The quantum numbers are used to describe the electronic configuration of an atom. There are four quantum numbers: n, l, m, and s.
- Principal Quantum Number (n) - It determines the size and energy of the orbital.
- Azimuthal Quantum Number (l) - It determines the shape of the orbital.
- Magnetic Quantum Number (m) - It determines the orientation of the orbital.
- Spin Quantum Number (s) - It determines the spin of the electron.
The p-orbital has l=1, which means it has three sub-orbitals: px, py, and pz. Each sub-orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. The magnetic quantum number (m) can have values of -1, 0, or 1, which means there are three p-orbitals. The value of m=0 corresponds to the pz orbital.
Maximum Number of Electrons in p-orbital
The maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital is determined by the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. Therefore, the maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital with n=6 and m=0 is 2.
Conclusion
The maximum number of electrons that can be present in a p-orbital with n=6 and m=0 is 2. This is because the pz sub-orbital has only one possible orientation, which means it can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
The homologue of ethyne is- a) C2H6
- b) C3H8
- c) C3H4
- d) None of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
C2H6
b)
C3H8
c)
C3H4
d)
None of these
|
|
Baishali Desai answered |
C2H2 is Ethyne (homologue of alkyne)
C3H4 is propyne (homologue of alkyne)
C3H8 → propane (homologue of alkane)
C2H6 → Ethane (homologue of alkane)
C3H4 is propyne (homologue of alkyne)
C3H8 → propane (homologue of alkane)
C2H6 → Ethane (homologue of alkane)
Among the following compounds, which has a dipole moment greater than zero?- a)CCl₄
- b)BF₃
- c)HF
- d)C₆H₆
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds, which has a dipole moment greater than zero?
a)
CCl₄
b)
BF₃
c)
HF
d)
C₆H₆
|
|
Janani Bose answered |
Explanation:
Dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a molecule. It is defined as the product of the distance between the charges and the magnitude of the charge.
CCl and BF are nonpolar molecules because they have a symmetrical structure and the electronegativity difference between the atoms is very small.
CH is a polar molecule because the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is significant. However, the dipole moment of CH is zero because the molecule has a linear shape, and the bond dipoles cancel out each other.
HF is a polar molecule because of the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and fluorine. The bond between hydrogen and fluorine is covalent, but the electrons are not shared equally due to the higher electronegativity of fluorine. Therefore, the molecule has a dipole moment.
Hence, the correct option is (c) HF.
Dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a molecule. It is defined as the product of the distance between the charges and the magnitude of the charge.
CCl and BF are nonpolar molecules because they have a symmetrical structure and the electronegativity difference between the atoms is very small.
CH is a polar molecule because the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is significant. However, the dipole moment of CH is zero because the molecule has a linear shape, and the bond dipoles cancel out each other.
HF is a polar molecule because of the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and fluorine. The bond between hydrogen and fluorine is covalent, but the electrons are not shared equally due to the higher electronegativity of fluorine. Therefore, the molecule has a dipole moment.
Hence, the correct option is (c) HF.
Which of the following metal oxides is anti-ferromagnetic in nature ?- a)MnO₂
- b)TiO₂
- c)VO₂
- d)CrO₂
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following metal oxides is anti-ferromagnetic in nature ?
a)
MnO₂
b)
TiO₂
c)
VO₂
d)
CrO₂
|
|
Vivek Dwivedi answered |
Pure Mno2 is antiferromagnetic ...
Read NCERT carefully.
Read NCERT carefully.
12 litre of hydrogen and 11.2 litre of chlorine are mixed and exploded. The composition in volume of the mixture will be- a)0.8 litre of hydrogen and 22.4 litre of HCl
- b)24 litre of HCl
- c)22.4 litre of HCl
- d)0.8 litre of chlorine and 20.8 litre of HCl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
12 litre of hydrogen and 11.2 litre of chlorine are mixed and exploded. The composition in volume of the mixture will be
a)
0.8 litre of hydrogen and 22.4 litre of HCl
b)
24 litre of HCl
c)
22.4 litre of HCl
d)
0.8 litre of chlorine and 20.8 litre of HCl
|
|
User5881746 answered |
Which of the following is a pseudohalide?- a)CN⁻
- b)ICI
- c)I₃
- d)IF₅
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a pseudohalide?
a)
CN⁻
b)
ICI
c)
I₃
d)
IF₅
|
|
Chirag Unni answered |
Pseudohalides
Pseudohalides are a class of compounds that resemble halides in their reactivity and chemical properties but differ in their composition. They are also known as false halides or pseudo-halides.
Examples of Pseudohalides
Some examples of pseudohalides include:
1. Cyanide (CN-)
2. Thiocyanate (SCN-)
3. Azide (N3-)
4. Selenocyanate (SeCN-)
5. Tellurocyanate (TeCN-)
Explanation
Among the given options, only CN- (cyanide) is a pseudohalide. It is considered a pseudohalide because it has similar chemical properties to halides, such as chloride (Cl-) and bromide (Br-), but it is composed of different elements (carbon and nitrogen).
On the other hand, ICI (iodine chloride), I (iodine), and IF (iodine fluoride) are halides, which means they are composed of a halogen and another element. ICI is composed of iodine and chlorine, I is composed of iodine, and IF is composed of iodine and fluorine.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, CN.
Pseudohalides are a class of compounds that resemble halides in their reactivity and chemical properties but differ in their composition. They are also known as false halides or pseudo-halides.
Examples of Pseudohalides
Some examples of pseudohalides include:
1. Cyanide (CN-)
2. Thiocyanate (SCN-)
3. Azide (N3-)
4. Selenocyanate (SeCN-)
5. Tellurocyanate (TeCN-)
Explanation
Among the given options, only CN- (cyanide) is a pseudohalide. It is considered a pseudohalide because it has similar chemical properties to halides, such as chloride (Cl-) and bromide (Br-), but it is composed of different elements (carbon and nitrogen).
On the other hand, ICI (iodine chloride), I (iodine), and IF (iodine fluoride) are halides, which means they are composed of a halogen and another element. ICI is composed of iodine and chlorine, I is composed of iodine, and IF is composed of iodine and fluorine.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, CN.
If 0.75 mole of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally at 27oC from 15 litres to 25 litres, then work done by the gas during this process is (R = 8.314J-K-1-mol-1)- a)-894.2J
- b)-954.2J
- c)-1054.2J
- d)-1154.2J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If 0.75 mole of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally at 27oC from 15 litres to 25 litres, then work done by the gas during this process is (R = 8.314J-K-1-mol-1)
a)
-894.2J
b)
-954.2J
c)
-1054.2J
d)
-1154.2J
|
|
Siddiq Zayeda answered |
W = 2.303×nRT×10gV2/V1
W = - 954.2J......
W = - 954.2J......
Dow's reaction involves- a)Electrophilic addition
- b)Nucleophilic addition
- c)Electrophilic substitution
- d)Nucleophilic substitution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dow's reaction involves
a)
Electrophilic addition
b)
Nucleophilic addition
c)
Electrophilic substitution
d)
Nucleophilic substitution

|
Veerendra Kuruva answered |
As in dows reaction involves chlorine, it involves Nucleophilic substitution reaction
When iron or zinc is added to CuSO₄ solution, copper is precipitated. It is due to- a)Oxidation of Cu+2
- b)Reduction of Cu+2
- c)Hydrolysis of CuSO₄
- d)Ionization of CuSO₄
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When iron or zinc is added to CuSO₄ solution, copper is precipitated. It is due to
a)
Oxidation of Cu+2
b)
Reduction of Cu+2
c)
Hydrolysis of CuSO₄
d)
Ionization of CuSO₄

|
Anchal Maurya answered |
It forms ZnSO4 +Cu
in CuSO4 oxidation no.Cu is +2
in rxn it change +2 to 0
so reduction of Cu2+ occurs.
in CuSO4 oxidation no.Cu is +2
in rxn it change +2 to 0
so reduction of Cu2+ occurs.
In its reaction with silver nitrate acetylene shows- a)Oxidising property
- b)Reducing property
- c)Basic property
- d)Acidic property
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In its reaction with silver nitrate acetylene shows
a)
Oxidising property
b)
Reducing property
c)
Basic property
d)
Acidic property

|
Syed Ashraf answered |
Its aqueous solution was acidic (pH = 5~6). Silver nitrate, in the aqueous solution of ammonia, meets glucose and formaldehyde can be reduced to generate "silver mirror." Zinc, cadmium, tin, lead, copper and other metals are easy to replace the metallic silver in the nitrate silver solution. Silver nitrate, when being mixed with sulfur, can lead to explosion upon being beaten by hammer.
Gold number is minimum in case of- a)Gelatin
- b)Egg albumin
- c)Gum arabic
- d)Starch
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gold number is minimum in case of
a)
Gelatin
b)
Egg albumin
c)
Gum arabic
d)
Starch
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Gold number is minimum in case of gelatin..which is of range 0.005 - 0.01..so option A
Consider the following reaction : 6 NaOH + 3 Cl₂ → 5 NaCl + A + 3 H₂O.
What is the oxidation number of chlorine in "A"?- a)+ 5
- b)- 1
- c)+ 3
- d)+ 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction : 6 NaOH + 3 Cl₂ → 5 NaCl + A + 3 H₂O.
What is the oxidation number of chlorine in "A"?
What is the oxidation number of chlorine in "A"?
a)
+ 5
b)
- 1
c)
+ 3
d)
+ 1
|
|
Dhivya Pooja answered |
Here the molecule "A" is "NaClO3" so the oxidation state is + 5
Which of the following has the maximum acidic strength?- a)o-Nitrobenzoic acid
- b)m-Nitrobenzoic acid
- c)p-Nitrobenzoic acid
- d)p-Nitrophenol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has the maximum acidic strength?
a)
o-Nitrobenzoic acid
b)
m-Nitrobenzoic acid
c)
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
d)
p-Nitrophenol
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Ortho isomer is the strongest one because in this case --- 1.ortho effect..2... the -I effect of the -No2 grp is the most powerful because distance from the -COOH grp is minimum ...3...the corresponding Carboxylic ion is stabilised by intramolecular electrostatic interaction between the carboxyl and the nitro group...So...the correct answer is option A..
Titanium shows magnetic moment of 1.73 B.M. in its compound. What is the oxidation number of titanium in the compound ?- a)+ 1
- b)+ 4
- c)+ 3
- d)+ 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Titanium shows magnetic moment of 1.73 B.M. in its compound. What is the oxidation number of titanium in the compound ?
a)
+ 1
b)
+ 4
c)
+ 3
d)
+ 2

|
Kanak Agrawal answered |
As M.M=1.73 i.e it have 1 unpair e so Ti^+3 should be present .as in normal state 3d2,4s2 condition present in +3 form. 3d1 form.
Which of the following ions has the maximum magnetic moment?- a)Mn2+
- b)Fe2+
- c)Ti2+
- d)Cr2+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ions has the maximum magnetic moment?
a)
Mn2+
b)
Fe2+
c)
Ti2+
d)
Cr2+
|
|
Mayank Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Magnetic moment is the measure of the strength of a magnetic field. It is denoted by the symbol μ and its unit is joule per tesla (J/T) or ampere meter squared (A m²).
Factors affecting magnetic moment:
The magnetic moment of an ion depends on the following factors:
1. Number of unpaired electrons: The magnetic moment of an ion increases with an increase in the number of unpaired electrons.
2. Spin-only magnetic moment: The spin-only magnetic moment is the magnetic moment of an ion if all the electrons are unpaired. It is given by the formula:
μspin = √n(n+2) BM
where n is the number of unpaired electrons and BM is the Bohr magneton (9.27 x 10^-24 J/T).
3. Ligand field splitting: The magnetic moment of an ion is affected by the ligand field splitting (LFS) of the complex in which it is present. The LFS is the energy difference between the d-orbitals in the presence of ligands. The higher the LFS, the lower the magnetic moment of the ion.
Analysis of options:
a) Mn2: Mn2+ has 5 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √5(5+2) BM = 5.92 BM
Hence, Mn2+ has the maximum magnetic moment among the given options.
b) Fe2: Fe2+ has 4 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √4(4+2) BM = 4.90 BM
c) Ti2: Ti2+ has 2 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √2(2+2) BM = 2.83 BM
d) Cr2: Cr2+ has 3 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √3(3+2) BM = 3.87 BM
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is (a) Mn2+ as it has the maximum number of unpaired electrons and hence the maximum magnetic moment.
Magnetic moment is the measure of the strength of a magnetic field. It is denoted by the symbol μ and its unit is joule per tesla (J/T) or ampere meter squared (A m²).
Factors affecting magnetic moment:
The magnetic moment of an ion depends on the following factors:
1. Number of unpaired electrons: The magnetic moment of an ion increases with an increase in the number of unpaired electrons.
2. Spin-only magnetic moment: The spin-only magnetic moment is the magnetic moment of an ion if all the electrons are unpaired. It is given by the formula:
μspin = √n(n+2) BM
where n is the number of unpaired electrons and BM is the Bohr magneton (9.27 x 10^-24 J/T).
3. Ligand field splitting: The magnetic moment of an ion is affected by the ligand field splitting (LFS) of the complex in which it is present. The LFS is the energy difference between the d-orbitals in the presence of ligands. The higher the LFS, the lower the magnetic moment of the ion.
Analysis of options:
a) Mn2: Mn2+ has 5 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √5(5+2) BM = 5.92 BM
Hence, Mn2+ has the maximum magnetic moment among the given options.
b) Fe2: Fe2+ has 4 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √4(4+2) BM = 4.90 BM
c) Ti2: Ti2+ has 2 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √2(2+2) BM = 2.83 BM
d) Cr2: Cr2+ has 3 unpaired electrons, so its spin-only magnetic moment is:
μspin = √3(3+2) BM = 3.87 BM
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is (a) Mn2+ as it has the maximum number of unpaired electrons and hence the maximum magnetic moment.
Number of atoms in one molecule of sulphur is- a)8
- b)4
- c)3
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of atoms in one molecule of sulphur is
a)
8
b)
4
c)
3
d)
None
|
|
Kirti Kulkarni answered |
Molecule of Sulphur
Sulphur is a non-metallic element with the atomic number 16. Its chemical symbol is S. Sulphur exists in nature in various forms such as elemental sulphur, sulphides, and sulphates.
Number of Atoms in One Molecule of Sulphur
The atomic mass of sulphur is 32.06 u. Sulphur molecule is formed by the covalent bonding of two sulphur atoms. Therefore, the number of atoms in one molecule of sulphur is 2.
Mathematically, the calculation can be done as follows:
- The molecular formula of sulphur is S2.
- The molecular mass of sulphur is 2 x 32.06 u = 64.12 u.
- Therefore, one molecule of sulphur contains 2 atoms.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A', i.e., 8.
Sulphur is a non-metallic element with the atomic number 16. Its chemical symbol is S. Sulphur exists in nature in various forms such as elemental sulphur, sulphides, and sulphates.
Number of Atoms in One Molecule of Sulphur
The atomic mass of sulphur is 32.06 u. Sulphur molecule is formed by the covalent bonding of two sulphur atoms. Therefore, the number of atoms in one molecule of sulphur is 2.
Mathematically, the calculation can be done as follows:
- The molecular formula of sulphur is S2.
- The molecular mass of sulphur is 2 x 32.06 u = 64.12 u.
- Therefore, one molecule of sulphur contains 2 atoms.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A', i.e., 8.
Piezoelectric crystals are used in- a)TV
- b)radio
- c)refrigerator
- d)record-player
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Piezoelectric crystals are used in
a)
TV
b)
radio
c)
refrigerator
d)
record-player
|
|
Poulomi Choudhury answered |
Piezoelectric Crystals in Record-Players
Piezoelectric crystals are materials that generate an electric charge when a mechanical stress is applied to them. This property makes them useful in various applications, including in record-players.
How Piezoelectric Crystals Work in Record-Players
In record-players, a stylus is used to read the grooves in a vinyl record. When the stylus moves along the grooves, it creates mechanical vibrations that are transferred to a piezoelectric crystal. The crystal converts these vibrations into an electrical signal that can be amplified and played through speakers.
Advantages of Using Piezoelectric Crystals in Record-Players
There are several advantages to using piezoelectric crystals in record-players. These include:
- High output: Piezoelectric crystals have a high output compared to other types of pickups, which means they produce a stronger electrical signal. This results in a louder and clearer sound.
- Durability: Piezoelectric crystals are more durable than other types of pickups, such as magnetic pickups. They are less susceptible to damage from dust and dirt, and they don't require as much maintenance.
- Low noise: Piezoelectric crystals produce a low amount of noise compared to other types of pickups. This results in a cleaner and more accurate sound.
Conclusion
Piezoelectric crystals are an important component in record-players. They provide a reliable and high-quality signal that can be amplified and played through speakers. Their durability and low noise make them an ideal choice for this application.
Piezoelectric crystals are materials that generate an electric charge when a mechanical stress is applied to them. This property makes them useful in various applications, including in record-players.
How Piezoelectric Crystals Work in Record-Players
In record-players, a stylus is used to read the grooves in a vinyl record. When the stylus moves along the grooves, it creates mechanical vibrations that are transferred to a piezoelectric crystal. The crystal converts these vibrations into an electrical signal that can be amplified and played through speakers.
Advantages of Using Piezoelectric Crystals in Record-Players
There are several advantages to using piezoelectric crystals in record-players. These include:
- High output: Piezoelectric crystals have a high output compared to other types of pickups, which means they produce a stronger electrical signal. This results in a louder and clearer sound.
- Durability: Piezoelectric crystals are more durable than other types of pickups, such as magnetic pickups. They are less susceptible to damage from dust and dirt, and they don't require as much maintenance.
- Low noise: Piezoelectric crystals produce a low amount of noise compared to other types of pickups. This results in a cleaner and more accurate sound.
Conclusion
Piezoelectric crystals are an important component in record-players. They provide a reliable and high-quality signal that can be amplified and played through speakers. Their durability and low noise make them an ideal choice for this application.
In a hydrocarbon, mass ratio of hydrogen and carbon is 1:3, the empirical formula of hydrocarbon is- a)CH
- b)CH₂
- c)C₂H
- d)CH₄
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a hydrocarbon, mass ratio of hydrogen and carbon is 1:3, the empirical formula of hydrocarbon is
a)
CH
b)
CH₂
c)
C₂H
d)
CH₄
|
|
Nishtha Joshi answered |
Explanation:
- The mass ratio of hydrogen and carbon is 1:3 in the given hydrocarbon.
- This means that for every 1 gram of hydrogen, there are 3 grams of carbon in the hydrocarbon.
- Let's assume that we have 100 grams of the hydrocarbon.
- Out of these 100 grams, the mass of hydrogen would be 25 grams (1/4th of 100) and the mass of carbon would be 75 grams (3/4th of 100).
- Now, we need to find the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon.
- The empirical formula gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound.
- To find the empirical formula, we need to find the ratio of atoms in the given hydrocarbon.
- For this, we need to find the number of moles of hydrogen and carbon in the hydrocarbon.
- The number of moles of hydrogen can be found using its mass and molar mass.
- The molar mass of hydrogen is 1 g/mol.
- Therefore, the number of moles of hydrogen in the hydrocarbon is 25/1 = 25.
- The number of moles of carbon can be found using its mass and molar mass.
- The molar mass of carbon is 12 g/mol.
- Therefore, the number of moles of carbon in the hydrocarbon is 75/12 = 6.25.
- Now, we need to find the ratio of atoms by dividing the number of moles by the smallest number of moles.
- The smallest number of moles is 6.25, so we divide the number of moles of hydrogen and carbon by 6.25.
- Number of moles of hydrogen = 25/6.25 = 4
- Number of moles of carbon = 6.25/6.25 = 1
- Therefore, the ratio of hydrogen to carbon in the given hydrocarbon is 4:1.
- The empirical formula of the hydrocarbon can be written as CH4 since the ratio of hydrogen to carbon is 4:1.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option D (CH).
A 2.5 mol sample of hydrazine, N₂H₄ loses 25 mol of electrons in being converted to a new compound X. Assuming that all of the nitrogen appears in the new compound, what is the oxidation state of nitrogen in compound X ?- a)-1
- b)-2
- c)+3
- d)+4
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 2.5 mol sample of hydrazine, N₂H₄ loses 25 mol of electrons in being converted to a new compound X. Assuming that all of the nitrogen appears in the new compound, what is the oxidation state of nitrogen in compound X ?
a)
-1
b)
-2
c)
+3
d)
+4
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
2.5 mol of N2H4 loses 25 mol electrons,
∴ 1 mole of N2H4 loses 10 mol electrons.
∴ 1 mole of N2H4 loses 10 mol electrons.
The substance not likely to contain CaCO₃ is- a)dolomite
- b)calcined gypsum
- c)a marble statue
- d)sea shells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The substance not likely to contain CaCO₃ is
a)
dolomite
b)
calcined gypsum
c)
a marble statue
d)
sea shells

|
Rocky Handsome answered |
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4.2H2O
. It does not have CaCO3.
Marble is composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or dolomite (CaMa(CO3)2).
The correct option is b
Under what conditions of temperature and pressure the formation of atomic hydrogen from molecular hydrogen will be favoured- a)high temperature and high pressure
- b)low temperature and low pressure
- c)high temperature and low pressure
- d)low temperature and high pressure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Under what conditions of temperature and pressure the formation of atomic hydrogen from molecular hydrogen will be favoured
a)
high temperature and high pressure
b)
low temperature and low pressure
c)
high temperature and low pressure
d)
low temperature and high pressure

|
Safeena H A answered |
According to Le - Chatellier's principle, the forward reaction is favoured by low pressure and high temperature.
Which of the following is an electrophile?- a)H₂O
- b)NH₃
- c)AlCl₃
- d)C₂H₅NH₂
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an electrophile?
a)
H₂O
b)
NH₃
c)
AlCl₃
d)
C₂H₅NH₂
|
|
Anshu Kaur answered |
Electrophiles
An electrophile is a molecule or ion that is attracted to a region of high electron density (i.e., an electron-rich atom or group) and accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond. Electrophiles are commonly involved in reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, addition, and aromatic substitution.
AlCl as an Electrophile
Among the given choices, AlCl is the only electrophile. This is because it has an electron-deficient aluminum atom that is attracted to the electron-rich regions of other molecules. Specifically, AlCl acts as an electrophile in Friedel-Crafts reactions, where it reacts with an aromatic compound to form a new carbon-carbon bond.
Examples of Friedel-Crafts Reactions
Here are some examples of Friedel-Crafts reactions, where AlCl acts as an electrophile:
1. Benzene + AlCl3 → chlorobenzene + HCl
In this reaction, AlCl3 accepts a pair of electrons from the benzene ring, forming a complex that is attacked by a chloride ion. The resulting product is chlorobenzene.
2. Toluene + AlCl3 → benzyl chloride + HCl
In this reaction, toluene is first activated by AlCl3 to form an intermediate carbocation. The carbocation is then attacked by a chloride ion, resulting in the formation of benzyl chloride.
Conclusion
In summary, AlCl is an electrophile because it has an electron-deficient aluminum atom that is attracted to electron-rich regions of other molecules. In particular, AlCl acts as an electrophile in Friedel-Crafts reactions, which involve the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond.
An electrophile is a molecule or ion that is attracted to a region of high electron density (i.e., an electron-rich atom or group) and accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond. Electrophiles are commonly involved in reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, addition, and aromatic substitution.
AlCl as an Electrophile
Among the given choices, AlCl is the only electrophile. This is because it has an electron-deficient aluminum atom that is attracted to the electron-rich regions of other molecules. Specifically, AlCl acts as an electrophile in Friedel-Crafts reactions, where it reacts with an aromatic compound to form a new carbon-carbon bond.
Examples of Friedel-Crafts Reactions
Here are some examples of Friedel-Crafts reactions, where AlCl acts as an electrophile:
1. Benzene + AlCl3 → chlorobenzene + HCl
In this reaction, AlCl3 accepts a pair of electrons from the benzene ring, forming a complex that is attacked by a chloride ion. The resulting product is chlorobenzene.
2. Toluene + AlCl3 → benzyl chloride + HCl
In this reaction, toluene is first activated by AlCl3 to form an intermediate carbocation. The carbocation is then attacked by a chloride ion, resulting in the formation of benzyl chloride.
Conclusion
In summary, AlCl is an electrophile because it has an electron-deficient aluminum atom that is attracted to electron-rich regions of other molecules. In particular, AlCl acts as an electrophile in Friedel-Crafts reactions, which involve the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond.
Glass reacts with HF to produce- a)Na₃AlF₆
- b)H₂SiO₃
- c)SiF₄
- d)H₂SiF₆
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Na₃AlF₆
b)
H₂SiO₃
c)
SiF₄
d)
H₂SiF₆
|
|
Ujwal Sen answered |
Reaction between Glass and HF
Introduction: Glass is an amorphous solid material that is commonly used in the manufacturing of various products, such as windows, bottles, and mirrors. Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a highly corrosive acid that can react with many materials, including glass.
Reaction: When glass comes into contact with HF, it reacts to produce silicon fluoride (SiF). This reaction occurs because HF is a strong acid that can dissolve the silica (SiO2) that makes up the glass.
Chemical equation: The chemical equation for the reaction between glass and HF can be written as follows:
SiO2 (s) + 4HF (aq) → SiF4 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Products: The products of this reaction are silicon fluoride (SiF4) and water (H2O). Silicon fluoride is a colorless gas that is highly reactive and can be used in the manufacturing of various products, such as semiconductors and optical fibers.
Dangers: It is important to note that the reaction between glass and HF can be extremely dangerous. HF is a highly corrosive acid that can cause severe burns and tissue damage. Therefore, proper safety precautions must be taken when handling HF and any materials that may react with it.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the reaction between glass and HF produces silicon fluoride (SiF). This reaction occurs because HF is a strong acid that can dissolve the silica (SiO2) that makes up the glass. It is important to handle HF and any materials that may react with it with extreme caution due to its highly corrosive nature.
Introduction: Glass is an amorphous solid material that is commonly used in the manufacturing of various products, such as windows, bottles, and mirrors. Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a highly corrosive acid that can react with many materials, including glass.
Reaction: When glass comes into contact with HF, it reacts to produce silicon fluoride (SiF). This reaction occurs because HF is a strong acid that can dissolve the silica (SiO2) that makes up the glass.
Chemical equation: The chemical equation for the reaction between glass and HF can be written as follows:
SiO2 (s) + 4HF (aq) → SiF4 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Products: The products of this reaction are silicon fluoride (SiF4) and water (H2O). Silicon fluoride is a colorless gas that is highly reactive and can be used in the manufacturing of various products, such as semiconductors and optical fibers.
Dangers: It is important to note that the reaction between glass and HF can be extremely dangerous. HF is a highly corrosive acid that can cause severe burns and tissue damage. Therefore, proper safety precautions must be taken when handling HF and any materials that may react with it.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the reaction between glass and HF produces silicon fluoride (SiF). This reaction occurs because HF is a strong acid that can dissolve the silica (SiO2) that makes up the glass. It is important to handle HF and any materials that may react with it with extreme caution due to its highly corrosive nature.
CuCl₂ and CuBr₂ exist as- a)Monomer
- b)Dimer
- c)Trimer
- d)Polymer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Monomer
b)
Dimer
c)
Trimer
d)
Polymer
|
|
Navya Tiwari answered |
Polymerization of CuCl and CuBr
CuCl and CuBr are transition metal halides that exist as polymers rather than monomers or dimers. The polymerization of CuCl and CuBr occurs due to the bridging of halogen atoms.
Polymerization of CuCl
In the case of CuCl, the bridging occurs through the formation of bridging chlorine atoms. Each Cu atom is bonded to two Cl atoms, with one Cl atom bridging the two Cu atoms. The resulting polymer is a one-dimensional chain.
Polymerization of CuBr
Similarly, CuBr also undergoes polymerization through the bridging of bromine atoms. Each Cu atom is bonded to two Br atoms, with one Br atom bridging the two Cu atoms. The resulting polymer is also a one-dimensional chain.
Comparison with other transition metal halides
In comparison to other transition metal halides, CuCl and CuBr have a lower tendency to form dimers or trimers. For example, FeCl3 exists as a dimer, while FeCl2 exists as a monomer. Similarly, TiCl4 exists as a polymer, but its structure is different from that of CuCl and CuBr.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CuCl and CuBr exist as polymers due to the bridging of halogen atoms. The resulting polymers are one-dimensional chains. This is in contrast to other transition metal halides, which may exist as monomers, dimers, trimers, or polymers with different structures.
CuCl and CuBr are transition metal halides that exist as polymers rather than monomers or dimers. The polymerization of CuCl and CuBr occurs due to the bridging of halogen atoms.
Polymerization of CuCl
In the case of CuCl, the bridging occurs through the formation of bridging chlorine atoms. Each Cu atom is bonded to two Cl atoms, with one Cl atom bridging the two Cu atoms. The resulting polymer is a one-dimensional chain.
Polymerization of CuBr
Similarly, CuBr also undergoes polymerization through the bridging of bromine atoms. Each Cu atom is bonded to two Br atoms, with one Br atom bridging the two Cu atoms. The resulting polymer is also a one-dimensional chain.
Comparison with other transition metal halides
In comparison to other transition metal halides, CuCl and CuBr have a lower tendency to form dimers or trimers. For example, FeCl3 exists as a dimer, while FeCl2 exists as a monomer. Similarly, TiCl4 exists as a polymer, but its structure is different from that of CuCl and CuBr.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CuCl and CuBr exist as polymers due to the bridging of halogen atoms. The resulting polymers are one-dimensional chains. This is in contrast to other transition metal halides, which may exist as monomers, dimers, trimers, or polymers with different structures.
Which of the following is isoelectronic as well as has the same structure as that of N₂O?- a)N3H
- b)H₂O
- c)NO₂
- d)CO₂
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is isoelectronic as well as has the same structure as that of N₂O?
a)
N3H
b)
H₂O
c)
NO₂
d)
CO₂

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
CO2 and N2O are isoelectronic with 22 electrons and isostructural with linear geometry.
Structure of nitrous oxide:
Structure of carbon di-oxide:
Structure of nitrous oxide:
Structure of carbon di-oxide:
If three electrons are lost by a metal ion M3+, its final oxidation number would be- a)zero
- b)+6
- c)+2
- d)+3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If three electrons are lost by a metal ion M3+, its final oxidation number would be
a)
zero
b)
+6
c)
+2
d)
+3

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
When M3+ losses 3 electrons,
It becomes M6+.
Hence the oxidation number of M will be +6.
A mixture of carbon monoxide, hydrogen and hydrocarbons is known as- a)Water gas
- b)Carburetted water gas
- c)Semi water gas
- d)Producer gas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mixture of carbon monoxide, hydrogen and hydrocarbons is known as
a)
Water gas
b)
Carburetted water gas
c)
Semi water gas
d)
Producer gas
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
No, the correct answer is an option (A).
Methanol is known as water gas and it is obtained from synthesis gas. Water gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen (not water).
Water gas is produced by passing steam (water)over a red-hot carbon fuel such as coke. SO it is called water gas because the source is water which produced water gas.
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ----> CH3OH(g) {Methanol}
When the product of pressure and volume is plotted against pressure for a given amount of the gas, the line obtained is- a)Parallel to X-axis
- b)Parallel to Y-axis
- c)Linear with positive slope
- d)Linear with negative slope
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the product of pressure and volume is plotted against pressure for a given amount of the gas, the line obtained is
a)
Parallel to X-axis
b)
Parallel to Y-axis
c)
Linear with positive slope
d)
Linear with negative slope
|
|
Sarita Koturwar answered |
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Hence the product of pressure and volume is constant which is parallel to X-axis.
Plaster of Paris hardens by- a)Giving off CO₂
- b)Changing into CaCO₃
- c)Combining with water
- d)Giving out water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Plaster of Paris hardens by
a)
Giving off CO₂
b)
Changing into CaCO₃
c)
Combining with water
d)
Giving out water

|
Rocky Handsome answered |
Plaster of Paris caso4.½H2O
.H2o is an important compound which is prepared by heating gypsum(CaSO4)2.2H2O.In order to hardened it and solidifying it,it is mixes with water.This mixing of water with plaster causes an exothermic chemical reaction that releases heat. This heat helps to harden the Plaster of Paris allowing it to set.
The type of hybridisation of boron in diborane is- a)sp3
- b)sp2
- c)sp2d
- d)sp3d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of hybridisation of boron in diborane is
a)
sp3
b)
sp2
c)
sp2d
d)
sp3d

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
B2H6 is diborane so hyb. Is Sp3 due to banana bonding.
If NaOH is added to an aqueous solution of zinc ions a white precipitate appears and on adding excess of NaOH, the precipitate dissolves. In this solution, zinc exists in the- a)Cationic part
- b)Anionic part
- c)Both in the cationic and anionic parts
- d)There is no zinc ion in the solution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If NaOH is added to an aqueous solution of zinc ions a white precipitate appears and on adding excess of NaOH, the precipitate dissolves. In this solution, zinc exists in the
a)
Cationic part
b)
Anionic part
c)
Both in the cationic and anionic parts
d)
There is no zinc ion in the solution

|
Syed Ashraf answered |
Sodium hydroxide NaOH, is comprised of a positive sodium cation Na+ and a polyatomic hydroxide anion OH− . In solution hydroxide OH− is is typically insoluble but with a group IA alkali metal like sodium Na+ the ions will dissociate in solution.
The most probable radius (in pm) for finding the electron in He⁺ is- a)0.0
- b)52.9
- c)26.5
- d)105.8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most probable radius (in pm) for finding the electron in He⁺ is
a)
0.0
b)
52.9
c)
26.5
d)
105.8
|
|
Anjali Chauhan answered |
The most probable radius for finding the electron in a helium atom can be determined using the concept of electron density and the radial probability distribution function.
1. Electron Density:
The electron density is a measure of the probability of finding an electron at a specific location around the nucleus of an atom. It is given by the square of the wave function, which describes the behavior of the electron in the atom. In the case of helium, the electron density is the highest at the nucleus and decreases as we move away from the nucleus.
2. Radial Probability Distribution Function:
The radial probability distribution function (RPDF) gives the probability of finding the electron within a certain radial distance from the nucleus. It is obtained by integrating the square of the wave function over all angles and dividing by the total probability of finding the electron. The RPDF provides information about the most probable locations of the electron in the atom.
3. The Most Probable Radius:
The most probable radius is the distance from the nucleus where the RPDF is highest, indicating the highest probability of finding the electron at that distance. In the case of helium, the most probable radius is equal to the first peak in the RPDF curve.
4. Explanation of Option C (26.5 pm):
Based on calculations and experimental data, the most probable radius for finding the electron in a helium atom is approximately 26.5 picometers (pm). This means that there is a higher probability of finding the electron at this distance from the nucleus compared to other distances.
5. Justification:
The justification for option C (26.5 pm) being the correct answer lies in the theoretical calculations and experimental observations of the electron density and RPDF for helium. These calculations and observations have been done using advanced mathematical models and spectroscopic techniques. The value of 26.5 pm has been determined as the most probable radius based on these studies.
In conclusion, the correct answer for the most probable radius for finding the electron in a helium atom is option C (26.5 pm). This value is obtained through theoretical calculations and experimental observations of the electron density and RPDF for helium.
1. Electron Density:
The electron density is a measure of the probability of finding an electron at a specific location around the nucleus of an atom. It is given by the square of the wave function, which describes the behavior of the electron in the atom. In the case of helium, the electron density is the highest at the nucleus and decreases as we move away from the nucleus.
2. Radial Probability Distribution Function:
The radial probability distribution function (RPDF) gives the probability of finding the electron within a certain radial distance from the nucleus. It is obtained by integrating the square of the wave function over all angles and dividing by the total probability of finding the electron. The RPDF provides information about the most probable locations of the electron in the atom.
3. The Most Probable Radius:
The most probable radius is the distance from the nucleus where the RPDF is highest, indicating the highest probability of finding the electron at that distance. In the case of helium, the most probable radius is equal to the first peak in the RPDF curve.
4. Explanation of Option C (26.5 pm):
Based on calculations and experimental data, the most probable radius for finding the electron in a helium atom is approximately 26.5 picometers (pm). This means that there is a higher probability of finding the electron at this distance from the nucleus compared to other distances.
5. Justification:
The justification for option C (26.5 pm) being the correct answer lies in the theoretical calculations and experimental observations of the electron density and RPDF for helium. These calculations and observations have been done using advanced mathematical models and spectroscopic techniques. The value of 26.5 pm has been determined as the most probable radius based on these studies.
In conclusion, the correct answer for the most probable radius for finding the electron in a helium atom is option C (26.5 pm). This value is obtained through theoretical calculations and experimental observations of the electron density and RPDF for helium.
A compound A has a molecular formula C₂Cl₃OH. It reduces Fehling solution and on oxidation give a monocarboxylic acid B. A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl alcohol. A is- a)methyl chloride
- b)monchloroacetic acid
- c)chloral
- d)Chloroform
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A compound A has a molecular formula C₂Cl₃OH. It reduces Fehling solution and on oxidation give a monocarboxylic acid B. A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl alcohol. A is
a)
methyl chloride
b)
monchloroacetic acid
c)
chloral
d)
Chloroform
|
|
Niharika Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
The compound A has a molecular formula CClOH, which means it contains carbon (C), chlorine (Cl), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms.
Reduction of Fehling Solution:
Compound A is capable of reducing Fehling solution. Fehling solution is a mixture of copper sulfate (CuSO4) and alkaline tartrate, which is used to test for the presence of reducing sugars. When a reducing sugar is present, such as in compound A, it reacts with Fehling solution to form a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide (Cu2O). This indicates the presence of an aldehyde or a reducing sugar.
Oxidation to Monocarboxylic Acid:
Compound A can be oxidized to form a monocarboxylic acid, which means it can be converted into a compound containing a carboxyl group (COOH). This indicates the presence of an aldehyde group (CHO) in compound A.
Action of Chlorine on Ethyl Alcohol:
Compound A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl alcohol. Chlorine (Cl2) reacts with ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) to form a compound with the formula CClOH. This compound is called chloral (trichloroacetaldehyde).
Conclusion:
Based on the information given, compound A with the molecular formula CClOH is chloral. Chloral is formed by the reaction of chlorine with ethyl alcohol and it possesses an aldehyde group that allows it to reduce Fehling solution. On oxidation, chloral can be converted into a monocarboxylic acid. Therefore, the correct answer is option C, chloral.
The compound A has a molecular formula CClOH, which means it contains carbon (C), chlorine (Cl), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms.
Reduction of Fehling Solution:
Compound A is capable of reducing Fehling solution. Fehling solution is a mixture of copper sulfate (CuSO4) and alkaline tartrate, which is used to test for the presence of reducing sugars. When a reducing sugar is present, such as in compound A, it reacts with Fehling solution to form a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide (Cu2O). This indicates the presence of an aldehyde or a reducing sugar.
Oxidation to Monocarboxylic Acid:
Compound A can be oxidized to form a monocarboxylic acid, which means it can be converted into a compound containing a carboxyl group (COOH). This indicates the presence of an aldehyde group (CHO) in compound A.
Action of Chlorine on Ethyl Alcohol:
Compound A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl alcohol. Chlorine (Cl2) reacts with ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) to form a compound with the formula CClOH. This compound is called chloral (trichloroacetaldehyde).
Conclusion:
Based on the information given, compound A with the molecular formula CClOH is chloral. Chloral is formed by the reaction of chlorine with ethyl alcohol and it possesses an aldehyde group that allows it to reduce Fehling solution. On oxidation, chloral can be converted into a monocarboxylic acid. Therefore, the correct answer is option C, chloral.
Which has highest radii ?- a)Cr3+
- b)Mn3+
- c)Fe3+
- d)Co3+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has highest radii ?
a)
Cr3+
b)
Mn3+
c)
Fe3+
d)
Co3+

|
User4427873 answered |
Fe 3+ has highest radii because by going left to right in the periodic table , the size get decreased so ..
Fe 3+ >Co3+ >Cr3+ >Mn3+ .
Fe 3+ >Co3+ >Cr3+ >Mn3+ .
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemistry - JIPMER: Subject wise Tests & Practice Mock Tests 2025 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemistry - JIPMER: Subject wise Tests & Practice Mock Tests 2025 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup







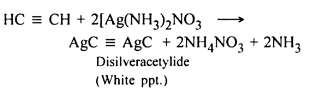

 is
is