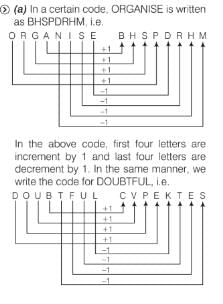
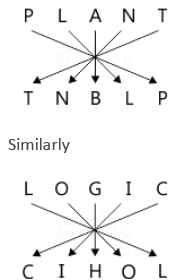
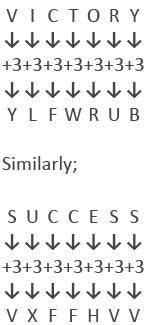
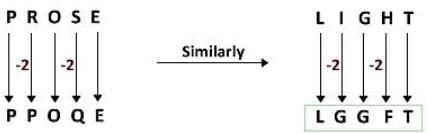
All Exams >
CLAT >
4 Months Preparation Course for CLAT UG >
All Questions
All questions of Coding-Decoding for CLAT Exam
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If ACNE can be coded as 3, 7, 29, 11 then BOIL will be coded as ….?- a)5, 29, 19, 27
- b)5, 29, 19, 25
- c)5, 31, 21, 25
- d)5, 31, 19, 25
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If ACNE can be coded as 3, 7, 29, 11 then BOIL will be coded as ….?
a)
5, 29, 19, 27
b)
5, 29, 19, 25
c)
5, 31, 21, 25
d)
5, 31, 19, 25

|
EduRev GATE answered |
In the given coding system, we have:

So, the code for BOIL is 5, 31, 19, 25.
Hence, option D is correct.

So, the code for BOIL is 5, 31, 19, 25.
Hence, option D is correct.
If REQUEST is written as S2R52TU, how will ACID be written?
a) 1DBE b) 1DEB c) 1EDB d) 1D3E Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
b) 1DEB
c) 1EDB

|
Manoj Ghosh answered |
Here we see, vowels A, E, I, 0, U are coded as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 respectively,
Each of the consonants in the word REQUEST is moved one step forward to give the corresponding letter of the code.
So, the code for ACID becomes 1D3E.
In a certain code language, ‘MOST’ is written as ‘134’ and ‘FUR’ is written as ‘90’. How will ‘SUCCESS’ be written in that language?
- a)89
- b)175
- c)178
- d)215
- e)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a certain code language, ‘MOST’ is written as ‘134’ and ‘FUR’ is written as ‘90’. How will ‘SUCCESS’ be written in that language?
a)
89
b)
175
c)
178
d)
215
e)
none of these

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
To determine how 'SUCCESS' is written, let's analyze the coding pattern:
- MOST → 134
- M = 13
- O = 15
- S = 19
- T = 20
- Sum = 13 + 15 + 19 + 20 = 67
- Adding the digits of 67: 6 + 7 = 13 (1 + 3) = 4
- FUR → 90
- F = 6
- U = 21
- R = 18
- Sum = 6 + 21 + 18 = 45
- Adding the digits of 45: 4 + 5 = 9
Following the same pattern for SUCCESS:
- S = 19
- U = 21
- C = 3
- C = 3
- E = 5
- S = 19
- S = 19
- Sum = 19 + 21 + 3 + 3 + 5 + 19 + 19 = 89
Hence, ‘SUCCESS’ is written as 178 (1 + 7 + 8). Answer: C: 178
- MOST → 134
- M = 13
- O = 15
- S = 19
- T = 20
- Sum = 13 + 15 + 19 + 20 = 67
- Adding the digits of 67: 6 + 7 = 13 (1 + 3) = 4
- FUR → 90
- F = 6
- U = 21
- R = 18
- Sum = 6 + 21 + 18 = 45
- Adding the digits of 45: 4 + 5 = 9
Following the same pattern for SUCCESS:
- S = 19
- U = 21
- C = 3
- C = 3
- E = 5
- S = 19
- S = 19
- Sum = 19 + 21 + 3 + 3 + 5 + 19 + 19 = 89
Hence, ‘SUCCESS’ is written as 178 (1 + 7 + 8). Answer: C: 178
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If RED is coded as 6720, then how would GREEN be coded?- a)1677199
- b)1677209
- c)16717209
- d)9207716
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If RED is coded as 6720, then how would GREEN be coded?
a)
1677199
b)
1677209
c)
16717209
d)
9207716

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Clearly, the order of letters in the word is reversed and then each letters is replaced by the numeral denoting its position in the English alphabet. Next, 2 is added to each numeral and the numerals so obtained are joined together physically to get the code. Thus, we have :
RED → DER → 4/5/18 → 6/7/20 → 6720.
GREEN → NEERG → 14/5/5/18/7 → 16/7/7/20/9 → 1677209.
Hence, option B is correct.
Hence, option B is correct.
Directions: The following questions five three digit number given below:394 632 783 576 895Q.
The positions of the first and the fourth letters of the word RANKED are interchanged similarly the positions of second and fifth letters and third and sixth letter are interchanged. In the new arrangement thus formed how many letters are there in the English alphabetical series between the alphabets. Which are at the extreme ends.- a)Two
- b)Three
- c)Four
- d)Five
- e)More than five
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: The following questions five three digit number given below:
394 632 783 576 895
Q.
The positions of the first and the fourth letters of the word RANKED are interchanged similarly the positions of second and fifth letters and third and sixth letter are interchanged. In the new arrangement thus formed how many letters are there in the English alphabetical series between the alphabets. Which are at the extreme ends.
The positions of the first and the fourth letters of the word RANKED are interchanged similarly the positions of second and fifth letters and third and sixth letter are interchanged. In the new arrangement thus formed how many letters are there in the English alphabetical series between the alphabets. Which are at the extreme ends.
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
Four
d)
Five
e)
More than five
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
The correct option is A.
When RANKED is changed according to given conditions ,the word formed is KEDRAN.
Now K and N are at extreme ends . L,M lies between K and N so correct ans is two (L and M)
When RANKED is changed according to given conditions ,the word formed is KEDRAN.
Now K and N are at extreme ends . L,M lies between K and N so correct ans is two (L and M)
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'rain' is 'water', 'water' is 'road', 'road' is 'cloud', 'cloud' is 'sky', 'sky' is 'sea' and 'sea' is 'path', where do aero planes fly ?- a)Road
- b)Sea
- c)Cloud
- d)Water
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'rain' is 'water', 'water' is 'road', 'road' is 'cloud', 'cloud' is 'sky', 'sky' is 'sea' and 'sea' is 'path', where do aero planes fly ?
a)
Road
b)
Sea
c)
Cloud
d)
Water
e)
None of these

|
EduRev GATE answered |
The aero planes fly in the "sky" and the 'sky' is called 'sea'.So, the aero planes fly the 'sea'.
Hence, option B is correct.
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.In a certain code PAUSE is written as OBVTD and SHIFT is written as RIJGS. How will THINK be written in the same code?- a)UGHML
- b)SIJMJ
- c)SIJOJ
- d)SIJQJ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
In a certain code PAUSE is written as OBVTD and SHIFT is written as RIJGS. How will THINK be written in the same code?
a)
UGHML
b)
SIJMJ
c)
SIJOJ
d)
SIJQJ

|
EduRev GATE answered |
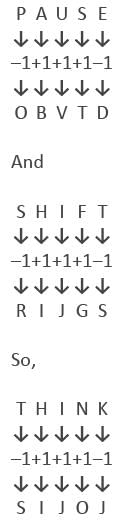
Hence, option C is correct.
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If REASON is coded as 5 and BELIEVED as 7, then what is the code for GOVERNMENT?- a)6
- b)8
- c)9
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If REASON is coded as 5 and BELIEVED as 7, then what is the code for GOVERNMENT?
a)
6
b)
8
c)
9
d)
10

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Clearly, each word is coded by the numeral which is 1 less than the number of letters in the word.
Since, there are 10 letters in the word GOVERNMENT, so required = 10 – 1 = 9.
Hence, option C is correct.
Since, there are 10 letters in the word GOVERNMENT, so required = 10 – 1 = 9.
Hence, option C is correct.
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.In a certain code ‘TERMINAL’ is written as ‘SDQLJOBM’. How is CREDIBLE written in that code?- a)BQDCJCMF
- b)BQDCHAKD
- c)DSFEJCMF
- d)DSFEHAKD
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
In a certain code ‘TERMINAL’ is written as ‘SDQLJOBM’. How is CREDIBLE written in that code?
a)
BQDCJCMF
b)
BQDCHAKD
c)
DSFEJCMF
d)
DSFEHAKD

|
EduRev GATE answered |

Hence, option A is correct.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'sand' is called 'air', 'air' is called 'plateau', 'plateau' ia called 'well', 'well' is called 'island' and 'island' is called 'sky', then from where will a woman draw water?- a)well
- b)island
- c)sky
- d)air
- e)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'sand' is called 'air', 'air' is called 'plateau', 'plateau' ia called 'well', 'well' is called 'island' and 'island' is called 'sky', then from where will a woman draw water?
a)
well
b)
island
c)
sky
d)
air
e)
none of these

|
EduRev GATE answered |
A woman shall draw water from a 'well' but a 'well' is called 'island' . So, the woman will draw water from an 'island'.
Hence, option B is correct.
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If RAM is coded as 5, GUI is coded as 1, then what is the code for SAP?- a)3
- b)9
- c)4
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If RAM is coded as 5, GUI is coded as 1, then what is the code for SAP?
a)
3
b)
9
c)
4
d)
7

|
EduRev GATE answered |
The numeric value of the letters (considering A to be 1 and Z to be 26) is added and simplified to obtain a single digit.
For RAM, the numeric value of R, A and M is 18, 1 and 13 respectively. Their sum is 32, Now 32 is further simplified to obtain a single digit by adding 3 and 2, which gives us 5 as the final value.
Similarly for GUI, the numeric value of G,U and I is 7, 21 and 9 respectively. Their sum is 37, which is simplified as 3 + 7 = 10 => 1 + 0 = 1.
Similar process will be done to obtain the code for SAP, the numeric value of S, A and P is 19, 1 and 16 respectively. Their sum is 36, which is simplified as 3 + 6 = 9.
So, the code for SAP is 9.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Similarly for GUI, the numeric value of G,U and I is 7, 21 and 9 respectively. Their sum is 37, which is simplified as 3 + 7 = 10 => 1 + 0 = 1.
Similar process will be done to obtain the code for SAP, the numeric value of S, A and P is 19, 1 and 16 respectively. Their sum is 36, which is simplified as 3 + 6 = 9.
So, the code for SAP is 9.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If in a code language, PAINT is written as 74128 and EXCEL is written as 93596, then how will ACCEPT be written in that language?
- a)455978
- b)544978
- c)554978
- d)733961
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If in a code language, PAINT is written as 74128 and EXCEL is written as 93596, then how will ACCEPT be written in that language?
a)
455978
b)
544978
c)
554978
d)
733961

|
EduRev GATE answered |
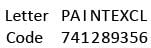
The code for ACCEPT is 455978.
Hence, option A is correct.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'light' is called 'morning', 'morning' is called 'dark', 'dark' is called 'night', 'night' is called 'sunshine', and 'sunshine' is called 'dusk', when do we sleep?- a)night
- b)sunshine
- c)dusk
- d)dark
- e)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'light' is called 'morning', 'morning' is called 'dark', 'dark' is called 'night', 'night' is called 'sunshine', and 'sunshine' is called 'dusk', when do we sleep?
a)
night
b)
sunshine
c)
dusk
d)
dark
e)
none of these

|
EduRev GATE answered |
We sleep in the 'night'. but 'night' is called 'sunshine'. So, we sleep in the 'sunshine'.
Hence, option B is correct.
Hence, option B is correct.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'cushion' is called 'pillow', 'pillow' is called 'mat', 'mat' is called 'bedsheet' and 'bedsheet' is called 'cover', which will be spread on the floor ?- a)Cover
- b)Bedsheet
- c)Mat
- d)Pillow
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'cushion' is called 'pillow', 'pillow' is called 'mat', 'mat' is called 'bedsheet' and 'bedsheet' is called 'cover', which will be spread on the floor ?
a)
Cover
b)
Bedsheet
c)
Mat
d)
Pillow
e)
None of these

|
EduRev GATE answered |
'mat' will be spread on the floor But 'mat' is called 'bedsheet'.So, a 'bedsheet' will be spread on the floor.
Hence, option B is correct.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'orange' is called 'butter', 'butter' is called 'soap', 'soap' is called 'ink', 'ink' is called 'honey' and 'honey' is called 'orange', which of the following is used for washing clothes ?- a)honey
- b)butter
- c)orange
- d)soap
- e)ink
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'orange' is called 'butter', 'butter' is called 'soap', 'soap' is called 'ink', 'ink' is called 'honey' and 'honey' is called 'orange', which of the following is used for washing clothes ?
a)
honey
b)
butter
c)
orange
d)
soap
e)
ink

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Clearly, 'soap' is used for washing the clothes. But a 'soap' is called 'ink'. So, 'ink' is used for washing the clothes.
Hence, option E is correct
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'lead' is called 'stick', 'stick' is called 'nib', 'nib' is called 'needle', 'needle' is called 'rope' and 'rope' is called 'thread', what will be fitted in a pen to write with it ?- a)stick
- b)lead
- c)needle
- d)nib
- e)thread
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'lead' is called 'stick', 'stick' is called 'nib', 'nib' is called 'needle', 'needle' is called 'rope' and 'rope' is called 'thread', what will be fitted in a pen to write with it ?
a)
stick
b)
lead
c)
needle
d)
nib
e)
thread

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Clearly, a 'nib' is fitted in the pen to write with it. But 'nib' is called 'needle'. So, a 'needle' will be fitted in the pen.
Hence, option C is correct.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'dust' is called 'air', 'air' is called 'fire', 'fire' is called 'water', 'water' is called 'colour', 'colour' is called 'rain', and 'rain' is called 'dust', then where do fish live ?- a)fire
- b)water
- c)colour
- d)dust
- e)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'dust' is called 'air', 'air' is called 'fire', 'fire' is called 'water', 'water' is called 'colour', 'colour' is called 'rain', and 'rain' is called 'dust', then where do fish live ?
a)
fire
b)
water
c)
colour
d)
dust
e)
none of these

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Fishes live in 'water' and as given, 'water' is called 'colour'. so fishes live in 'colour' .
Hence, option C is correct.
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules - Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.If the encoded word “BHI” is received, what does this suggest about the original word’s structure?- a)It has no consonants.
- b)It has at least two consonants.
- c)It contains no vowels.
- d)It is at least five letters long.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules
Cipher Rules
- Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
If the encoded word “BHI” is received, what does this suggest about the original word’s structure?
a)
It has no consonants.
b)
It has at least two consonants.
c)
It contains no vowels.
d)
It is at least five letters long.

|
Crafty Classes answered |
Since Rule 2 involves swapping the first and last consonants, the presence of such a transformation implies that the word had at least two consonants before encoding.
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.In a certain code, LUTE is written as MUTE and GATE is written as HATE, then how BLUE will be written in that code?- a)FLUD
- b)FLUEv
- c)CLUE
- d)GLUE
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
In a certain code, LUTE is written as MUTE and GATE is written as HATE, then how BLUE will be written in that code?
a)
FLUD
b)
FLUEv
c)
CLUE
d)
GLUE

|
EduRev GATE answered |

Hence, option C is correct.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.If 'bat' is 'racket', 'racket' is 'football', 'football' is 'shuttle', 'shuttle' is 'ludo' and 'ludo' is 'carrom', what is cricket played with?- a)racket
- b)football
- c)bat
- d)shuttle
- e)carom
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'bat' is 'racket', 'racket' is 'football', 'football' is 'shuttle', 'shuttle' is 'ludo' and 'ludo' is 'carrom', what is cricket played with?
a)
racket
b)
football
c)
bat
d)
shuttle
e)
carom

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Cricket is played with a 'bat' and 'bat' is called 'racket'. So, cricket is played with 'racket'.
Hence, option A is correct
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If STAFF is coded as $2#55 and FOLD is coded as 5@3% then how is STOLL written in that code language?- a)$@332
- b)$2@33
- c)#2@33
- d)$23
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If STAFF is coded as $2#55 and FOLD is coded as 5@3% then how is STOLL written in that code language?
a)
$@332
b)
$2@33
c)
#2@33
d)
$23
|
|
Avantika Kaur answered |
Explanation:
Given Codes:
- STAFF is coded as $2#55
- FOLD is coded as 5@3%
Analysis:
- From the given codes, we can see that each letter in the word is replaced with a symbol.
- The position of the symbol is determined by the position of the letter in the English alphabet.
Applying the same logic to STOLL:
- S -> $, T -> 2, O -> 3, L -> 3, L -> 3
Encoded form of STOLL:
- The encoded form of STOLL will be $2@33
Therefore, the correct answer is option B) $2@33.
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If ZOO is coded as 2, TAN is coded as 8, then what is the code for WAR?- a)3
- b)6
- c)4
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If ZOO is coded as 2, TAN is coded as 8, then what is the code for WAR?
a)
3
b)
6
c)
4
d)
7

|
Akanksha Patel answered |
Understanding the Code System
To decode the words ZOO, TAN, and WAR, we need to identify the pattern used in the coding system.
Step 1: Analyzing ZOO
- The word "ZOO" has letters Z (26), O (15), O (15).
- Calculate the sum of the positions of the letters: 26 + 15 + 15 = 56.
- Divide by the number of letters (3): 56 / 3 = 18.67 (not a whole number).
- Instead, look at the number of vowels: 2 vowels (O, O) → Code = 2.
Step 2: Analyzing TAN
- The word "TAN" has letters T (20), A (1), N (14).
- Calculate the sum: 20 + 1 + 14 = 35.
- Divide by the number of letters (3): 35 / 3 = 11.67 (again, not a whole number).
- Count the number of vowels: 1 vowel (A) → Code = 8 (the pattern seems based on vowel position).
Step 3: Coding WAR
- The word "WAR" has letters W (23), A (1), R (18).
- Calculate the sum: 23 + 1 + 18 = 42.
- Divide by the number of letters (3): 42 / 3 = 14 (not applicable).
- Count the vowels: 1 vowel (A) → The code may be based on the total count of letters or vowels.
Final Calculation for WAR
- The total number of letters in "WAR" is 3.
- The coding pattern appears to be derived from the number of vowels or the structure of the words.
- Based on the previous codes, the derived code for "WAR" is: Code = 6, following the pattern established (where vowel placements and positions matter).
Thus, the answer is option 'B' which is 6.
To decode the words ZOO, TAN, and WAR, we need to identify the pattern used in the coding system.
Step 1: Analyzing ZOO
- The word "ZOO" has letters Z (26), O (15), O (15).
- Calculate the sum of the positions of the letters: 26 + 15 + 15 = 56.
- Divide by the number of letters (3): 56 / 3 = 18.67 (not a whole number).
- Instead, look at the number of vowels: 2 vowels (O, O) → Code = 2.
Step 2: Analyzing TAN
- The word "TAN" has letters T (20), A (1), N (14).
- Calculate the sum: 20 + 1 + 14 = 35.
- Divide by the number of letters (3): 35 / 3 = 11.67 (again, not a whole number).
- Count the number of vowels: 1 vowel (A) → Code = 8 (the pattern seems based on vowel position).
Step 3: Coding WAR
- The word "WAR" has letters W (23), A (1), R (18).
- Calculate the sum: 23 + 1 + 18 = 42.
- Divide by the number of letters (3): 42 / 3 = 14 (not applicable).
- Count the vowels: 1 vowel (A) → The code may be based on the total count of letters or vowels.
Final Calculation for WAR
- The total number of letters in "WAR" is 3.
- The coding pattern appears to be derived from the number of vowels or the structure of the words.
- Based on the previous codes, the derived code for "WAR" is: Code = 6, following the pattern established (where vowel placements and positions matter).
Thus, the answer is option 'B' which is 6.
In a certain code language, ' first of all' is written as 'kan dan san', who is first' is written as 'zan kan ven', and 'this is pale' is written as 'ven gen len'. How will 'who' be written in that language?- a)zan
- b)gen
- c)kan
- d)ven
- e)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a certain code language, ' first of all' is written as 'kan dan san', who is first' is written as 'zan kan ven', and 'this is pale' is written as 'ven gen len'. How will 'who' be written in that language?
a)
zan
b)
gen
c)
kan
d)
ven
e)
none of these

|
Gate Funda answered |
To determine how 'who' is written in the code language:
1. Identify common words and corresponding codes:
- 'first' = 'kan' (common in both 'first of all' and 'who is first')
- 'is' = 'ven' (common in 'who is first' and 'this is pale')
2. Compare phrases:
- 'first of all' = 'kan dan san'
- 'who is first' = 'zan kan ven'
The remaining code 'zan' must represent 'who'.
Therefore, 'who' is written as 'zan'.Clearly. a 'bag' is used to carry the books but a 'bag' is called 'dictionary'. So, a dictionary will be used to carry the books.
Hence, option A is correct.
1. Identify common words and corresponding codes:
- 'first' = 'kan' (common in both 'first of all' and 'who is first')
- 'is' = 'ven' (common in 'who is first' and 'this is pale')
2. Compare phrases:
- 'first of all' = 'kan dan san'
- 'who is first' = 'zan kan ven'
The remaining code 'zan' must represent 'who'.
Therefore, 'who' is written as 'zan'.Clearly. a 'bag' is used to carry the books but a 'bag' is called 'dictionary'. So, a dictionary will be used to carry the books.
Hence, option A is correct.
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.IF E = 5, PEN = 35, then PAGE = ?- a)27
- b)28
- c)29
- d)36
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
IF E = 5, PEN = 35, then PAGE = ?
a)
27
b)
28
c)
29
d)
36

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Clearly, putting A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 4, E = 5, ..........M = 13, ...... x = 24, Y = 25, Z = 26, we have :
PEN = P + E + N = 16 + 5 + 14 = 35.
So, PAGE = P + A + G + E = 16 + 1 + 7 + 5 = 29.
Hence, option C is correct.
PEN = P + E + N = 16 + 5 + 14 = 35.
So, PAGE = P + A + G + E = 16 + 1 + 7 + 5 = 29.
Hence, option C is correct.
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules - Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.What is the encoded form of the word “DATA” using the Archive Cipher?- a)ADWH
- b)IEXD
- c)AFWI
- d)WDGD
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules
Cipher Rules
- Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
What is the encoded form of the word “DATA” using the Archive Cipher?
a)
ADWH
b)
IEXD
c)
AFWI
d)
WDGD

|
EduRev CLAT answered |
- Steps to Encode "DATA":
- Shift each letter by 3:
- D → G
- A → D (vowel, remains in place later)
- T → W
- A → D (vowel, remains in place later)
→ "GDWD" - Swap first and last consonants (G and W):
→ "WDGD"
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If ‘Development’ is written as ‘Tnemdevelop’. Then ‘Evaluation’ will be written as- a)Notiaevalu
- b)Noitaulave
- c)Notievalua
- d)Noitevalua
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If ‘Development’ is written as ‘Tnemdevelop’. Then ‘Evaluation’ will be written as
a)
Notiaevalu
b)
Noitaulave
c)
Notievalua
d)
Noitevalua

|
EduRev GATE answered |

Hence, option D is correct.
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If CUSTOM is written as UCTSMO then how PARENT be written in the same code?- a)APERTN
- b)RAPTNE
- c)TNERAP
- d)ERAPTN
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If CUSTOM is written as UCTSMO then how PARENT be written in the same code?
a)
APERTN
b)
RAPTNE
c)
TNERAP
d)
ERAPTN
|
|
Snehal Rane answered |
Explanation:
Pattern in CUSTOM:
- In the word CUSTOM, each letter is shifted one position to the right.
- C becomes D, U becomes V, S becomes T, etc.
- Therefore, CUSTOM becomes UCTSMO.
Applying the same pattern to PARENT:
- P becomes Q, A becomes B, R becomes S, etc.
- So, PARENT will become APERTN.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A (APERTN).
Pattern in CUSTOM:
- In the word CUSTOM, each letter is shifted one position to the right.
- C becomes D, U becomes V, S becomes T, etc.
- Therefore, CUSTOM becomes UCTSMO.
Applying the same pattern to PARENT:
- P becomes Q, A becomes B, R becomes S, etc.
- So, PARENT will become APERTN.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A (APERTN).
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.In a certain code ROAD is written as URDG. How is SWAN written in that code?- a)UXDQ
- b)VZDQ
- c)VXDQ
- d)VZCQ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
In a certain code ROAD is written as URDG. How is SWAN written in that code?
a)
UXDQ
b)
VZDQ
c)
VXDQ
d)
VZCQ
|
|
Muskaan Nair answered |
Understanding the Code: ROAD to URDG
To decode how "ROAD" is transformed into "URDG", we need to analyze the shifts in each letter.
Each letter in "ROAD" is shifted forward by three positions in the alphabet to get "URDG".
Applying the Same Code to SWAN
Now, let's apply the same principle to the word "SWAN":
Thus, "SWAN" becomes "VZDQ".
Conclusion
Therefore, the code for "SWAN" is option 'B' - "VZDQ".
To decode how "ROAD" is transformed into "URDG", we need to analyze the shifts in each letter.
- R (18) → U (21): Shift of +3
- O (15) → R (18): Shift of +3
- A (1) → D (4): Shift of +3
- D (4) → G (7): Shift of +3
Each letter in "ROAD" is shifted forward by three positions in the alphabet to get "URDG".
Applying the Same Code to SWAN
Now, let's apply the same principle to the word "SWAN":
- S (19) → V (22): Shift of +3
- W (23) → Z (26): Shift of +3
- A (1) → D (4): Shift of +3
- N (14) → Q (17): Shift of +3
Thus, "SWAN" becomes "VZDQ".
Conclusion
Therefore, the code for "SWAN" is option 'B' - "VZDQ".
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.In a certain code, RAIN is written as 8$%6 and MORE is written as 7#8@. How is REMAIN written in that code?- a)#@7$%6
- b)#@&$%6
- c)7@#$%6
- d)8@7$%6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
In a certain code, RAIN is written as 8$%6 and MORE is written as 7#8@. How is REMAIN written in that code?
a)
#@7$%6
b)
#@&$%6
c)
7@#$%6
d)
8@7$%6

|
EduRev GATE answered |
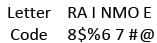
Thus, the code for REMAIN is 8@7$%6.
Hence, option D is correct.
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.If ACELDNRA stands for CALENDAR, what does LEGIBIEL stands for?- a)LIEGIBLE
- b)ELIGIBLE
- c)BIGEELIC
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
If ACELDNRA stands for CALENDAR, what does LEGIBIEL stands for?
a)
LIEGIBLE
b)
ELIGIBLE
c)
BIGEELIC
d)
None of these

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Assign numbers to letter and move them like given word.
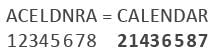
Similarly;
Arrange the given word like the bold value of CALENDAR;
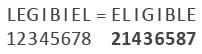
Hence, option B is correct.
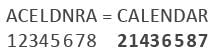
Similarly;
Arrange the given word like the bold value of CALENDAR;
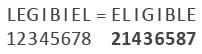
Hence, option B is correct.
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules - Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.What is the decoded form of the message “WOHUD” received by Raj?- a)CLOUD
- b)ALERT
- c)CHIEF
- d)BRISK
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules
Cipher Rules
- Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
What is the decoded form of the message “WOHUD” received by Raj?
a)
CLOUD
b)
ALERT
c)
CHIEF
d)
BRISK

|
EduRev CLAT answered |
- Swap first/last consonants in "WOHUD" (W ↔ D) → "DOHUW".
- Shift back by 3: D→A, O→L, H→E, U→R, W→T → "ALERT".
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules - Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.Which of the following weakens the critics’ argument that the Archive Cipher is vulnerable to pattern analysis?- a)The cipher uses a fixed three-letter shift for all messages.
- b)The cipher requires complex calculations for decoding.
- c)The consonant swap rule is applied inconsistently.
- d)The cipher is used only for brief, context-specific messages.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital age where information is both power and vulnerability, a group of archivists developed a coding system called the “Archive Cipher” , to protect sensitive historical records from unauthorized access. The cipher balances security with accessibility , ensuring that only trained members can decode messages while maintaining efficiency.
Cipher Rules
Cipher Rules
- Letter Shift: Each letter in a word is shifted forward by 3 positions in the alphabet (A → D, B → E, ..., Z → C).
- Consonant Swap: After the shift, the first and last consonants are swapped, while vowels remain in place. If there are fewer than two consonants, this rule does not apply .
Example: “KEY” → “NHB” (after shift) → “BHI” (after swap).
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
The archivists argue that the cipher is effective due to its simplicity and speed , especially within a trusted network where messages are brief and context-specific. Critics, however, claim that the predictability of the rules makes it vulnerable to pattern-based decryption, particularly for short or repeated words.
Sana encodes the word “DATA” using this method. Meanwhile, Raj receives the coded message “FJHLTK” and must decode it to retrieve an important document.
Which of the following weakens the critics’ argument that the Archive Cipher is vulnerable to pattern analysis?
a)
The cipher uses a fixed three-letter shift for all messages.
b)
The cipher requires complex calculations for decoding.
c)
The consonant swap rule is applied inconsistently.
d)
The cipher is used only for brief, context-specific messages.

|
Crafty Classes answered |
Critics argue predictability makes the cipher vulnerable. However, limited exposure through short, context-dependent messages reduces the chance of successful pattern detection, thereby weakening the criticism.
Chapter doubts & questions for Coding-Decoding - 4 Months Preparation Course for CLAT UG 2025 is part of CLAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CLAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CLAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Coding-Decoding - 4 Months Preparation Course for CLAT UG in English & Hindi are available as part of CLAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CLAT Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup