All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Progress Test for NEET Exam
A body starts from rest. If the body travels with an acceleration of 2 m/s², its displacement after 3 seconds is- a)9 m
- b)12 m
- c)16 m
- d)10 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A body starts from rest. If the body travels with an acceleration of 2 m/s², its displacement after 3 seconds is
a)
9 m
b)
12 m
c)
16 m
d)
10 m

|
Ambition Institute answered |
We can use the kinematic equation to find the displacement (s):
s = ut +1/2at2
In this case, the body starts from rest (u = 0m/s), and the acceleration (a) is given as 2m/s2. The time (t) is 3 seconds.
s = 0⋅3 + 1/2(2)(3)2
s= 0 + 1/2(2)(9)
s = 9m
So, the correct answer is (a) 9 m.
The epithelial tissue on the inner surface of bronchioles and fallopian tubes is
- a)cuboidal
- b)glandular
- c)squamous
- d)Ciliated
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The epithelial tissue on the inner surface of bronchioles and fallopian tubes is
a)
cuboidal
b)
glandular
c)
squamous
d)
Ciliated

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The epithelium of the bronchioles and fallopian tubes is ciliated, meaning it is covered in tiny hair-like structures called cilia that are involved in the movement. The cilia help to move air or mucus through the tubes.
Assertion (A): Bryophytes are more differentiated than algae and possess structures resembling roots, stems, and leaves.Reason (R): Bryophytes are primarily aquatic and require water for their entire life cycle.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Bryophytes are more differentiated than algae and possess structures resembling roots, stems, and leaves.
Reason (R): Bryophytes are primarily aquatic and require water for their entire life cycle.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- Assertion: True. Bryophytes, unlike algae, show a higher level of structural differentiation and have distinct organ-like structures that resemble roots, stems, and leaves, known as rhizoids, caules, and phylloids respectively.
- Reason: False. Bryophytes are not primarily aquatic. Although they require water for sexual reproduction, particularly for the transfer of sperm, they predominantly live in moist terrestrial environments, not in aquatic settings.
- Thus, while the Assertion is correct, the Reason is incorrect, making Option C the correct choice.
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100 m. With the same effort, he throws the ball vertically upwards. The maximum height attained by the ball is- a)100 m
- b)80 m
- c)60 m
- d)50 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100 m. With the same effort, he throws the ball vertically upwards. The maximum height attained by the ball is
a)
100 m
b)
80 m
c)
60 m
d)
50 m
|
|
Anushka Das answered |
Understanding the Problem
The problem states that a cricketer can throw a ball horizontally to a maximum distance of 100 m. We need to find the maximum height the ball can attain when thrown vertically with the same effort.
Key Concepts
- Projectile Motion: The ball thrown horizontally and vertically can be analyzed using the principles of projectile motion.
- Energy Conservation: The initial kinetic energy when throwing the ball is conserved in both horizontal and vertical throws.
Horizontal Throw
- When the ball is thrown horizontally, it covers a horizontal distance of 100 m.
- The range (horizontal distance) formula for projectile motion is given by R = (v^2 * sin(2θ)) / g, where θ is the angle of projection.
- For a horizontal throw, θ = 0°, which means the vertical component of velocity is zero.
Vertical Throw
- When throwing vertically, all the initial kinetic energy is converted into potential energy at the maximum height.
- The potential energy at height h is given by PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is height.
Energy Equivalence
- The kinetic energy when the ball is thrown horizontally can be equated to the potential energy at maximum height for the vertical throw.
- For the horizontal throw: KE = (1/2)mv^2.
- For the vertical throw: KE = mgh.
Calculating Maximum Height
- Since the range is 100 m, we can deduce the initial velocity (v) using the range formula.
- By conservation of energy and rearranging terms, for the vertical throw:
h = v^2 / (2g).
- Solving this gives us h = 50 m, which is the maximum height attained when thrown vertically.
Conclusion
- The maximum height attained by the ball when thrown vertically upwards with the same effort is 50 m (Option D).
The problem states that a cricketer can throw a ball horizontally to a maximum distance of 100 m. We need to find the maximum height the ball can attain when thrown vertically with the same effort.
Key Concepts
- Projectile Motion: The ball thrown horizontally and vertically can be analyzed using the principles of projectile motion.
- Energy Conservation: The initial kinetic energy when throwing the ball is conserved in both horizontal and vertical throws.
Horizontal Throw
- When the ball is thrown horizontally, it covers a horizontal distance of 100 m.
- The range (horizontal distance) formula for projectile motion is given by R = (v^2 * sin(2θ)) / g, where θ is the angle of projection.
- For a horizontal throw, θ = 0°, which means the vertical component of velocity is zero.
Vertical Throw
- When throwing vertically, all the initial kinetic energy is converted into potential energy at the maximum height.
- The potential energy at height h is given by PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is height.
Energy Equivalence
- The kinetic energy when the ball is thrown horizontally can be equated to the potential energy at maximum height for the vertical throw.
- For the horizontal throw: KE = (1/2)mv^2.
- For the vertical throw: KE = mgh.
Calculating Maximum Height
- Since the range is 100 m, we can deduce the initial velocity (v) using the range formula.
- By conservation of energy and rearranging terms, for the vertical throw:
h = v^2 / (2g).
- Solving this gives us h = 50 m, which is the maximum height attained when thrown vertically.
Conclusion
- The maximum height attained by the ball when thrown vertically upwards with the same effort is 50 m (Option D).
Which one of the following groups is called 'amphibians of plant kingdom'?- a)Bryophytes
- b)Thallophytes
- c)Pteridophytes
- d)Gymnosperms
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following groups is called 'amphibians of plant kingdom'?
a)
Bryophytes
b)
Thallophytes
c)
Pteridophytes
d)
Gymnosperms

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- Bryophytes include the various mosses and liverworts.
- These are non-vascular embryophytes, characterized by the presence of an independent gametophyte and parasitic sporophyte.
- Bryophytes commonly grow in moist, shaded areas in hills.
- These are called amphibians of the plant Kingdom because, these can live in soil, but are dependent on water for sexual reproduction.
- However, their sperms, known as antherozoids, are flagellate and require water to swim and reach the eggs in order to fertilize them. As a result, they require water for sexual reproduction.
- The plant body of bryophytes is more differentiated than that of algae.
- Ecological importance:
- Some mosses provide food for herbaceous mammals, birds, and other animals.
- Mosses along with lichens are the first organisms to colonize rocks. Hence, these help in biological succession.
- Mosses form dense mats on the soil.
- Marchantia has medicinal properties to cure lungs and liver infections. It also has anti-tumor properties.
The wavelength of a photon is 400 nm. What is the energy of the photon? (Planck’s constant, h=6.626×10−34 J⋅s; speed of light, c=3×108 m/s- a)3.1eV
- b)2.48eV
- c)4.96eV
- d)5.0eV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The wavelength of a photon is 400 nm. What is the energy of the photon? (Planck’s constant, h=6.626×10−34 J⋅s; speed of light, c=3×108 m/s
a)
3.1eV
b)
2.48eV
c)
4.96eV
d)
5.0eV

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Energy (E) = (Planck’s constant × speed of light) / wavelength.
- Convert wavelength: 400 nm = 400 × 10⁻⁹ m.
- E = (6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ × 3 × 10⁸) / (400 × 10⁻⁹).
- E = 4.97 × 10⁻¹⁹ J. Convert to eV: E = 4.97 × 10⁻¹⁹ / 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ ≈ 3.1 eV.
A boy starts at location A, walks 1.5 kilometres to point B, and then returns to point A. If it takes one hour for this, his average velocity is- a)3 km/h
- b)zero
- c)1.5 km/h
- d)2 km/h
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy starts at location A, walks 1.5 kilometres to point B, and then returns to point A. If it takes one hour for this, his average velocity is
a)
3 km/h
b)
zero
c)
1.5 km/h
d)
2 km/h

|
Bs Academy answered |
The average velocity (vavg) is given by the formula:
vavg = total displacement / total time
In this case, the total displacement is zero because the boy starts at point A, walks to point B, and then returns to point A, so his net displacement is zero.
The total time is given as one hour.
vavg = 0km / 1h = 0km/h
So, the correct answer is (b) zero.
The qualities of eka-aluminium predicted by Mendeleev are the same as the properties of the element aluminium, which was discovered later.- a)scandium
- b)germanium
- c)Gallium
- d)Aluminium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The qualities of eka-aluminium predicted by Mendeleev are the same as the properties of the element aluminium, which was discovered later.
a)
scandium
b)
germanium
c)
Gallium
d)
Aluminium

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Eka-aluminium and gallium are the same elements because the properties of Eka-Aluminium are almost identical to the qualities of the gallium element. Eka-Aluminium is a chemical element that has nearly identical properties to the gallium element. The properties of the elements, such as their atomic mass, density, melting temperature, the formula of chloride, and the formula of oxide, are nearly identical to those anticipated by Mendeleev in his theory.
If an element A atom has 18 protons, it follows that A has 18 electrons. So, the number of electrons in an A+ will be -- a)21
- b)20
- c)19
- d)17
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If an element A atom has 18 protons, it follows that A has 18 electrons. So, the number of electrons in an A+ will be -
a)
21
b)
20
c)
19
d)
17
|
|
Dishani Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Number of Electrons in A+ ion:
- An element A with 18 protons will have 18 electrons in its neutral state.
- When an element loses one electron to form a +1 ion, it will have one less electron than its neutral state.
- Therefore, the number of electrons in A+ ion will be 18 - 1 = 17 electrons.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - 17.
Number of Electrons in A+ ion:
- An element A with 18 protons will have 18 electrons in its neutral state.
- When an element loses one electron to form a +1 ion, it will have one less electron than its neutral state.
- Therefore, the number of electrons in A+ ion will be 18 - 1 = 17 electrons.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - 17.
Which of the following is the correct order of increasing first ionization energy?- a)Li < B < Be < C
- b)B < Be < Li < C
- c)Li < Be < B < C
- d)Be < Li < C < B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct order of increasing first ionization energy?
a)
Li < B < Be < C
b)
B < Be < Li < C
c)
Li < Be < B < C
d)
Be < Li < C < B

|
Top Rankers answered |
Answer: Option A
Along the period IE increases but Be has higher IE than B owing to its stable fully filled orbital configuration.
Hence the order will be Li < B < Be.
Hence the order will be Li < B < Be.
Diatoms belong to the following classifications: _________- a)Chrysophytes
- b)Protozoans
- c)Dianoflagelletes
- d)Euglenoids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Diatoms belong to the following classifications: _________
a)
Chrysophytes
b)
Protozoans
c)
Dianoflagelletes
d)
Euglenoids

|
Top Rankers answered |
Chrysophytes are a category that includes diatoms. Chrysophytes include golden algae, diatoms, and protists that resemble plants, among others. They are called Chrysophytes because of the species’ golden-yellow color.
Planck's constant has the same unit as:- a)force × time
- b)force × speed
- c)force × distance × time
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Planck's constant has the same unit as:
a)
force × time
b)
force × speed
c)
force × distance × time
d)
None of the above
|
|
Bhavya Menon answered |
B) angular momentum
c) energy
d) velocity
c) energy
d) velocity
If time of flight of a projectile is 10 seconds. Range is 500 m. The maximum height attained by it will be - a)125 m
- b)50 m
- c)100 m
- d)150 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If time of flight of a projectile is 10 seconds. Range is 500 m. The maximum height attained by it will be
a)
125 m
b)
50 m
c)
100 m
d)
150 m
|
|
Janani Mishra answered |
Understanding Projectile Motion
In projectile motion, the time of flight, range, and maximum height are interrelated. Let's analyze the given data to find the maximum height.
Given Data
- Time of Flight (T) = 10 seconds
- Range (R) = 500 m
Key Formulas
1. Time of Flight Formula:
T = 2 * (Initial Velocity * sin(θ)) / g
Here, g = 9.8 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity).
2. Range Formula:
R = (Initial Velocity² * sin(2θ)) / g
3. Maximum Height Formula:
H = (Initial Velocity² * (sin(θ))²) / (2g)
Step 1: Finding Initial Velocity
Using the time of flight formula:
- Rearranging gives us:
Initial Velocity = (g * T) / 2
= (9.8 * 10) / 2
= 49 m/s
Step 2: Finding the Angle of Projection
Using the range formula:
R = (Initial Velocity² * sin(2θ)) / g
Plugging in the values:
500 = (49² * sin(2θ)) / 9.8
Solving for sin(2θ) gives:
sin(2θ) = (500 * 9.8) / (49²)
= 0.98
Step 3: Maximum Height Calculation
Using the maximum height formula:
H = (49² * (sin(θ))²) / (2 * 9.8)
Using sin²(θ) from sin(2θ):
H = (49² * 0.5) / (2 * 9.8)
Calculating yields:
H = 125 m
Conclusion
Thus, the maximum height attained by the projectile is 125 m, confirming that the correct answer is option 'A'.
In projectile motion, the time of flight, range, and maximum height are interrelated. Let's analyze the given data to find the maximum height.
Given Data
- Time of Flight (T) = 10 seconds
- Range (R) = 500 m
Key Formulas
1. Time of Flight Formula:
T = 2 * (Initial Velocity * sin(θ)) / g
Here, g = 9.8 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity).
2. Range Formula:
R = (Initial Velocity² * sin(2θ)) / g
3. Maximum Height Formula:
H = (Initial Velocity² * (sin(θ))²) / (2g)
Step 1: Finding Initial Velocity
Using the time of flight formula:
- Rearranging gives us:
Initial Velocity = (g * T) / 2
= (9.8 * 10) / 2
= 49 m/s
Step 2: Finding the Angle of Projection
Using the range formula:
R = (Initial Velocity² * sin(2θ)) / g
Plugging in the values:
500 = (49² * sin(2θ)) / 9.8
Solving for sin(2θ) gives:
sin(2θ) = (500 * 9.8) / (49²)
= 0.98
Step 3: Maximum Height Calculation
Using the maximum height formula:
H = (49² * (sin(θ))²) / (2 * 9.8)
Using sin²(θ) from sin(2θ):
H = (49² * 0.5) / (2 * 9.8)
Calculating yields:
H = 125 m
Conclusion
Thus, the maximum height attained by the projectile is 125 m, confirming that the correct answer is option 'A'.
A rocket of mass 120 kg is fired in the gravity free space. It ejects gases with velocity 600 m/s at the rate of 1 kg/s. What will be the initial acceleration of the rocket ?- a)1 m/s2
- b)5 m/s2
- c)10 m/s2
- d)15 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A rocket of mass 120 kg is fired in the gravity free space. It ejects gases with velocity 600 m/s at the rate of 1 kg/s. What will be the initial acceleration of the rocket ?
a)
1 m/s2
b)
5 m/s2
c)
10 m/s2
d)
15 m/s2

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Θ Thrust force on the rocket,
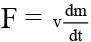
= 600 x 1
= 600 N
∴ Acceleration of rocket, a = F / N
= 600 / 120 = 5 m/s2
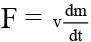
= 600 x 1
= 600 N
∴ Acceleration of rocket, a = F / N
= 600 / 120 = 5 m/s2
The element having tetra-atomic atomicity is ______ .- a)Helium
- b)Nitrogen
- c)Phosphorous
- d)Chlorine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The element having tetra-atomic atomicity is ______ .
a)
Helium
b)
Nitrogen
c)
Phosphorous
d)
Chlorine

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Key Points
- The present number of atoms in any molecule of an element is called its atomicity.
- Tetra atomic elements are those which are made up of four atoms.
- Phosphorous exists as molecules made up of four atoms in a tetrahedral structure.
- Each phosphorus molecule consists of four atoms of phosphorus.
Alkali metals are assigned which group in the Modern Periodic Table?- a)Second group
- b)Eighteenth group
- c)Third group
- d)First group
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Alkali metals are assigned which group in the Modern Periodic Table?
a)
Second group
b)
Eighteenth group
c)
Third group
d)
First group

|
Ambition Institute answered |
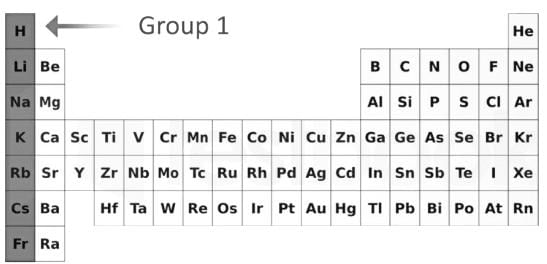
- Group 1 elements in the Periodic table are known as Alkali metals
- They have ns1 outermost configuration and belong to the S-block Elements.
- They also have a strong tendency to donate their valence electrons in the outermost shell to form strong ionic bonds.
- It contains elements from Lithium (Li) to Francium (Fr).
Bacteria multiply by ___________.- a)Asexual reproduction
- b)Sort of Sexual reproduction only
- c)buds
- d)Both a and b
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bacteria multiply by ___________.
a)
Asexual reproduction
b)
Sort of Sexual reproduction only
c)
buds
d)
Both a and b
|
|
Roshni Ahuja answered |
Understanding Bacterial Reproduction
Bacteria are fascinating microorganisms that reproduce primarily through a process known as binary fission, which is a form of asexual reproduction. However, they also exhibit mechanisms that can be considered as a sort of sexual reproduction. Let’s delve deeper into this topic.
Asexual Reproduction in Bacteria
- Binary Fission: This is the most common method of bacterial reproduction. In binary fission, a single bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The process includes:
- Replication of the bacterial DNA.
- Elongation of the cell.
- Division of the cell membrane and wall, resulting in two separate cells.
- Advantages: Asexual reproduction allows for rapid population growth under favorable conditions, leading to exponential increases in bacterial numbers.
Sort of Sexual Reproduction in Bacteria
- Horizontal Gene Transfer: While bacteria do not reproduce sexually in the traditional sense, they can exchange genetic material through:
- Conjugation: Transfer of DNA via direct cell-to-cell contact.
- Transformation: Uptake of free DNA from the environment.
- Transduction: Transfer of DNA by bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria).
- Importance: These processes enhance genetic diversity and adaptability, allowing bacteria to survive in changing environments.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'D' because bacteria primarily multiply through asexual reproduction (binary fission) but can also engage in mechanisms that facilitate genetic exchange, resembling a sort of sexual reproduction. This combination allows them to thrive and adapt effectively in various environments.
Bacteria are fascinating microorganisms that reproduce primarily through a process known as binary fission, which is a form of asexual reproduction. However, they also exhibit mechanisms that can be considered as a sort of sexual reproduction. Let’s delve deeper into this topic.
Asexual Reproduction in Bacteria
- Binary Fission: This is the most common method of bacterial reproduction. In binary fission, a single bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The process includes:
- Replication of the bacterial DNA.
- Elongation of the cell.
- Division of the cell membrane and wall, resulting in two separate cells.
- Advantages: Asexual reproduction allows for rapid population growth under favorable conditions, leading to exponential increases in bacterial numbers.
Sort of Sexual Reproduction in Bacteria
- Horizontal Gene Transfer: While bacteria do not reproduce sexually in the traditional sense, they can exchange genetic material through:
- Conjugation: Transfer of DNA via direct cell-to-cell contact.
- Transformation: Uptake of free DNA from the environment.
- Transduction: Transfer of DNA by bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria).
- Importance: These processes enhance genetic diversity and adaptability, allowing bacteria to survive in changing environments.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'D' because bacteria primarily multiply through asexual reproduction (binary fission) but can also engage in mechanisms that facilitate genetic exchange, resembling a sort of sexual reproduction. This combination allows them to thrive and adapt effectively in various environments.
What statement regarding the haplontic life cycle is incorrect?
- a)Mitosis in the zygote results in the formation of haploid spores.
- b)Sporophytic generation is represented only by the one-celled zygote.
- c)There is no free-living sporophyte.
- d)The haploid spores divide mitotically and form the gametophyte.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What statement regarding the haplontic life cycle is incorrect?
a)
Mitosis in the zygote results in the formation of haploid spores.
b)
Sporophytic generation is represented only by the one-celled zygote.
c)
There is no free-living sporophyte.
d)
The haploid spores divide mitotically and form the gametophyte.

|
Bs Academy answered |
Gametophytes are the predominant stage in this life cycle, which is why the answer is (a). Sporophytes cannot live a life of their own free will. Spores are naturally haploid and develop into gametophytes during mitotic division. A zygote produces spores in the role of a sporophyte.
A man in a balloon rising vertically with an acceleration of 4.9 m/sec2 releases a ball 2 sec after the balloon is let go from the ground. The greatest height above the ground reached by the ball is (g = 9.8 m/sec2)- a)14.7 m
- b)19.6 m
- c)9.8 m
- d)24.5 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A man in a balloon rising vertically with an acceleration of 4.9 m/sec2 releases a ball 2 sec after the balloon is let go from the ground. The greatest height above the ground reached by the ball is (g = 9.8 m/sec2)
a)
14.7 m
b)
19.6 m
c)
9.8 m
d)
24.5 m
|
|
Manoj Kulkarni answered |
Understanding the Problem
The problem involves a balloon rising with a constant upward acceleration, and a ball being released from the balloon after 2 seconds. We need to calculate the maximum height reached by the ball after its release.
Key Information
- Acceleration of the balloon (a) = 4.9 m/s²
- Time before ball is released (t) = 2 s
- Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s²
Calculating the Height of the Balloon
- The balloon starts from rest, so we use the formula for distance under constant acceleration:
Distance (h) = 0.5 * a * t²
- Substituting the values:
h = 0.5 * 4.9 m/s² * (2 s)²
h = 0.5 * 4.9 * 4
h = 9.8 m
Velocity of the Balloon at Release
- The velocity of the balloon at the time of release can be calculated as:
Velocity (v) = a * t
- Substituting the values:
v = 4.9 m/s² * 2 s
v = 9.8 m/s
Motion of the Ball After Release
- When the ball is released, it inherits the upward velocity of the balloon (9.8 m/s) but is now subject to the downward acceleration of gravity.
Calculating Maximum Height of the Ball
- The ball will rise until its velocity becomes zero. The time (t1) to reach maximum height can be found using:
v_final = v_initial - g * t1
0 = 9.8 m/s - 9.8 m/s² * t1
t1 = 1 s
- The additional height gained by the ball during this time is:
Height (h1) = v_initial * t1 - 0.5 * g * t1²
h1 = 9.8 m/s * 1 s - 0.5 * 9.8 m/s² * (1 s)²
h1 = 9.8 m - 4.9 m
h1 = 4.9 m
Total Height Above Ground
- The total height reached by the ball above ground is:
Total height = Height of the balloon + Height gained by the ball
Total height = 9.8 m + 4.9 m
Total height = 14.7 m
Thus, the greatest height above the ground reached by the ball is 14.7 m (option A).
The problem involves a balloon rising with a constant upward acceleration, and a ball being released from the balloon after 2 seconds. We need to calculate the maximum height reached by the ball after its release.
Key Information
- Acceleration of the balloon (a) = 4.9 m/s²
- Time before ball is released (t) = 2 s
- Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s²
Calculating the Height of the Balloon
- The balloon starts from rest, so we use the formula for distance under constant acceleration:
Distance (h) = 0.5 * a * t²
- Substituting the values:
h = 0.5 * 4.9 m/s² * (2 s)²
h = 0.5 * 4.9 * 4
h = 9.8 m
Velocity of the Balloon at Release
- The velocity of the balloon at the time of release can be calculated as:
Velocity (v) = a * t
- Substituting the values:
v = 4.9 m/s² * 2 s
v = 9.8 m/s
Motion of the Ball After Release
- When the ball is released, it inherits the upward velocity of the balloon (9.8 m/s) but is now subject to the downward acceleration of gravity.
Calculating Maximum Height of the Ball
- The ball will rise until its velocity becomes zero. The time (t1) to reach maximum height can be found using:
v_final = v_initial - g * t1
0 = 9.8 m/s - 9.8 m/s² * t1
t1 = 1 s
- The additional height gained by the ball during this time is:
Height (h1) = v_initial * t1 - 0.5 * g * t1²
h1 = 9.8 m/s * 1 s - 0.5 * 9.8 m/s² * (1 s)²
h1 = 9.8 m - 4.9 m
h1 = 4.9 m
Total Height Above Ground
- The total height reached by the ball above ground is:
Total height = Height of the balloon + Height gained by the ball
Total height = 9.8 m + 4.9 m
Total height = 14.7 m
Thus, the greatest height above the ground reached by the ball is 14.7 m (option A).
If the vectors 6i - 2j + 3k, 2i + 3j- 6k and 3i + 6j- 2k form a triangle, then it is- a)Right angled
- b)Obtuse angled
- c)Equilateral
- d)Isosceles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the vectors 6i - 2j + 3k, 2i + 3j- 6k and 3i + 6j- 2k form a triangle, then it is
a)
Right angled
b)
Obtuse angled
c)
Equilateral
d)
Isosceles
|
|
Sharmila Sengupta answered |
Understanding the Vectors
The given vectors are:
- A = 6i - 2j + 3k
- B = 2i + 3j - 6k
- C = 3i + 6j - 2k
These vectors represent the vertices of a triangle when placed tail-to-head in a coordinate system.
Finding the Lengths of the Sides
To determine the type of triangle formed, we need to calculate the lengths of the sides using the distance formula for vectors.
- Length of side AB:
|AB| = |A - B| = |(6-2)i + (-2-3)j + (3+6)k| = |4i - 5j + 9k|
- Length of side BC:
|BC| = |B - C| = |(2-3)i + (3-6)j + (-6+2)k| = |-1i - 3j - 4k|
- Length of side CA:
|CA| = |C - A| = |(3-6)i + (6+2)j + (-2-3)k| = |-3i + 8j - 5k|
Calculating the Squared Lengths
Instead of calculating the lengths directly, we can compare the squares of the lengths to avoid unnecessary calculations:
- |AB|^2 = (4^2) + (-5^2) + (9^2) = 16 + 25 + 81 = 122
- |BC|^2 = (-1^2) + (-3^2) + (-4^2) = 1 + 9 + 16 = 26
- |CA|^2 = (-3^2) + (8^2) + (-5^2) = 9 + 64 + 25 = 98
Determining the Type of Triangle
To classify the triangle:
- Calculate the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides and compare it to the square of the longest side:
26 + 98 = 124 (sum of squares of shorter sides)
122 (square of the longest side)
Since 124 > 122, the triangle is obtuse.
Conclusion
The triangle formed by the given vectors is obtuse-angled, confirming option 'B' as the correct answer.
The given vectors are:
- A = 6i - 2j + 3k
- B = 2i + 3j - 6k
- C = 3i + 6j - 2k
These vectors represent the vertices of a triangle when placed tail-to-head in a coordinate system.
Finding the Lengths of the Sides
To determine the type of triangle formed, we need to calculate the lengths of the sides using the distance formula for vectors.
- Length of side AB:
|AB| = |A - B| = |(6-2)i + (-2-3)j + (3+6)k| = |4i - 5j + 9k|
- Length of side BC:
|BC| = |B - C| = |(2-3)i + (3-6)j + (-6+2)k| = |-1i - 3j - 4k|
- Length of side CA:
|CA| = |C - A| = |(3-6)i + (6+2)j + (-2-3)k| = |-3i + 8j - 5k|
Calculating the Squared Lengths
Instead of calculating the lengths directly, we can compare the squares of the lengths to avoid unnecessary calculations:
- |AB|^2 = (4^2) + (-5^2) + (9^2) = 16 + 25 + 81 = 122
- |BC|^2 = (-1^2) + (-3^2) + (-4^2) = 1 + 9 + 16 = 26
- |CA|^2 = (-3^2) + (8^2) + (-5^2) = 9 + 64 + 25 = 98
Determining the Type of Triangle
To classify the triangle:
- Calculate the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides and compare it to the square of the longest side:
26 + 98 = 124 (sum of squares of shorter sides)
122 (square of the longest side)
Since 124 > 122, the triangle is obtuse.
Conclusion
The triangle formed by the given vectors is obtuse-angled, confirming option 'B' as the correct answer.
Which of the following divisions of plants does NOT have a well-differentiated body?- a)Bryophyta
- b)Thallophyta
- c)Gymnosperms
- d)Pteridophyta
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following divisions of plants does NOT have a well-differentiated body?
a)
Bryophyta
b)
Thallophyta
c)
Gymnosperms
d)
Pteridophyta

|
Lead Academy answered |
The correct answer is Thallophyta.
Key Points
Key Points
- Thallophyta- The plants in this group are commonly called algae.
- The form and size of algae are highly variable.
- The algae reproduce by vegetative, asexual, and sexual methods.
- Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation.
- Each fragment develops into a thallus.
The order generally ends with- a)ales
- b)aceae
- c)eae
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The order generally ends with
a)
ales
b)
aceae
c)
eae
d)
none of these

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The order generally ends with ales. Order being a higher category is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characters.
Which of the following is an example of a green algae?- a)Laminaria
- b)Sargassum
- c)Chlamydomonas
- d)Fucus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of a green algae?
a)
Laminaria
b)
Sargassum
c)
Chlamydomonas
d)
Fucus
|
|
Shraddha Pillai answered |
Understanding Green Algae
Green algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms primarily found in freshwater, marine, and moist terrestrial environments. They are known for their green color, which comes from the presence of chlorophyll.
Options Breakdown
- Laminaria:
- A type of brown algae, commonly known as kelp.
- It is characterized by its large, leafy structures and is not classified as green algae.
- Sargassum:
- Another brown algae species, often found floating in the ocean.
- It forms mats on the surface of the water and is not part of the green algae group.
- Chlamydomonas:
- A unicellular green algae.
- It belongs to the Chlorophyta division, showcasing a typical green color due to chlorophyll.
- Chlamydomonas is known for its flagella, which aid in movement, and its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- Fucus:
- A type of brown algae, commonly found along rocky shorelines.
- It has a distinct structure with air bladders for buoyancy, making it another example of brown algae.
Conclusion
Given the classifications, Chlamydomonas (option C) is the correct answer as it is a representative of green algae, while Laminaria, Sargassum, and Fucus are all brown algae. This distinction is important for understanding the diversity within algal groups and their ecological roles.
Green algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms primarily found in freshwater, marine, and moist terrestrial environments. They are known for their green color, which comes from the presence of chlorophyll.
Options Breakdown
- Laminaria:
- A type of brown algae, commonly known as kelp.
- It is characterized by its large, leafy structures and is not classified as green algae.
- Sargassum:
- Another brown algae species, often found floating in the ocean.
- It forms mats on the surface of the water and is not part of the green algae group.
- Chlamydomonas:
- A unicellular green algae.
- It belongs to the Chlorophyta division, showcasing a typical green color due to chlorophyll.
- Chlamydomonas is known for its flagella, which aid in movement, and its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- Fucus:
- A type of brown algae, commonly found along rocky shorelines.
- It has a distinct structure with air bladders for buoyancy, making it another example of brown algae.
Conclusion
Given the classifications, Chlamydomonas (option C) is the correct answer as it is a representative of green algae, while Laminaria, Sargassum, and Fucus are all brown algae. This distinction is important for understanding the diversity within algal groups and their ecological roles.
Until what element was the Law of Octaves determined to be applicable?
- a)Cobalt
- b)Calcium
- c)Potassium
- d)Aluminium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Until what element was the Law of Octaves determined to be applicable?
a)
Cobalt
b)
Calcium
c)
Potassium
d)
Aluminium

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The Law of Octaves was only valid up to the element calcium, because beyond calcium, every eighth element did not have properties that are identical to those of the first element.
What is the dimensional formula for the universal gravitational constant - a)M-1L3T-2
- b)M-1L3T-1
- c)M-1L2T-2
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the dimensional formula for the universal gravitational constant
a)
M-1L3T-2
b)
M-1L3T-1
c)
M-1L2T-2
d)
None of the above

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Calculation:
Force = G × m1 × m2 × [r2]-1
⇒ G = Force × r2 × [m1 × m2]-1 --- (1)
Where, G = Universal Gravitational Constant
Now, the dimensions of,
Mass = [M1 L0 T0] --- (2)
Radius (distance) = [M0 L1 T0] --- (3)
Force = [M1 L1 T-2] --- (4)
On substituting equation (2), (3) and (4) in equation (1) we get,
Universal Gravitational Constant = Force × r2 × [m1 × m2]-1
⇒ G = [M1 L1 T-2] × [M0 L1 T0]2 × [M1 L0 T0]-1 × [M1 L0 T0]-1 = [M-1 L3 T-2].
Therefore, the Universal Gravitational Constant is dimensionally represented as [M-1 L3 T-2].
Which of the following elements has the maximum atomic radius?- a)P
- b)Cl
- c)Na
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements has the maximum atomic radius?
a)
P
b)
Cl
c)
Na
d)
S

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The correct answer is Na.
- The decreasing order of atomic radius is Na (227pm) > P (195pm) > S (180pm) > Cl (175pm).
Therefore,
- When two atoms have the same value of n for the valence electrons, the atom with the greater number of protons will generally have a greater effective nuclear charge to draw the valence electrons closer to the nucleus and, thus, decrease the atomic radius.
- Since chlorine's 17 protons are greater than sodium's 11 protons, chlorine will have a greater effective nuclear charge to draw chlorine's valence electrons closer to the nucleus and, thus, chlorine is expected to have a smaller atomic radius.
- While sodium with the lower effective nuclear charge is expected to have a larger atomic radius.
A body starts off at rest and moves in a straight line with a constant acceleration. If its velocity is 8 m/s with a displacement of 32 m, its acceleration is- a)1 m/s2
- b)2 m/s2
- c)3 m/s2
- d)4 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A body starts off at rest and moves in a straight line with a constant acceleration. If its velocity is 8 m/s with a displacement of 32 m, its acceleration is
a)
1 m/s2
b)
2 m/s2
c)
3 m/s2
d)
4 m/s2

|
Bs Academy answered |
We can use the following kinematic equation to relate initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), acceleration (a), and displacement (s):
v2 = u2 + 2as
In this scenario, the body starts at rest, so the initial velocity u is 0 m/s. The final velocity v is given as 8 m/s, and the displacement s is 32 m. We want to find the acceleration a.
82 = 02+ 2a(32)
64 = 64a
a = 1 m/s2
a = 1 m/s2
So, the correct answer is (a) 1 m/s².
The speed of boat is 5 km/h in still water. It crosses a river of width 1 km along shortest possible path in 15 min. The velocity of river water is- a)1 km/h
- b)3 km/h
- c)4 km/h
- d)5 km/h
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The speed of boat is 5 km/h in still water. It crosses a river of width 1 km along shortest possible path in 15 min. The velocity of river water is
a)
1 km/h
b)
3 km/h
c)
4 km/h
d)
5 km/h

|
EduRev NEET answered |
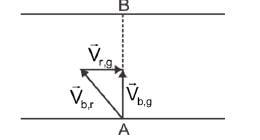
Shortest path is along line AB.
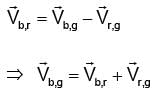
If the boat crosses the river in 15 min
⇒
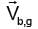 = 4 km/hr ∴
= 4 km/hr ∴ 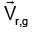 = 3 km/hr
= 3 km/hrTo which block do the elements with atomic number 56 belong?- a)p
- b)f
- c)d
- d)s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To which block do the elements with atomic number 56 belong?
a)
p
b)
f
c)
d
d)
s

|
Top Rankers answered |
- Atomic number 56, Barium belongs to s - block elements.
- Electronic configuration for the Barium [Xe]6s2
- Modern Periodic Table is classified into the following elements - p-block, s-block, d-block, and f-block.
- s-block elements include alkali metals and alkaline earth metals.
Methanogens are found in the ______ of a cow:- a)Mouth
- b)Guts
- c)A cow’s respiratory system
- d)A cow’s ribs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Methanogens are found in the ______ of a cow:
a)
Mouth
b)
Guts
c)
A cow’s respiratory system
d)
A cow’s ribs

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Methane is produced by organisms called methanogens. These are found in marshy places, similar to a cow’s intestines, and they aid in the creation of biogas from cow manure.
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of sponges?- a)Tissue level of organization
- b)Presence of Ostia
- c)Extracellular digestion
- d)Indirect development
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of sponges?
a)
Tissue level of organization
b)
Presence of Ostia
c)
Extracellular digestion
d)
Indirect development

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The characteristic feature of sponges (phylum Porifera) among the options provided is the presence of Ostia. Ostia are tiny pores or openings on the body of a sponge that allow water to enter its central cavity, called the spongocoel. These ostia are responsible for the filtration of water, which is a vital process for sponges to obtain food and oxygen.
Which statement is true regarding taxonomic categories?
- a)The category 'genus' includes organisms from different families.
- b)Species within the same genus share no common characteristics.
- c)Higher taxonomic categories such as phylum include a broader range of organisms than lower categories like species.
- d)The order is the highest level of classification in the biological hierarchy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is true regarding taxonomic categories?
a)
The category 'genus' includes organisms from different families.
b)
Species within the same genus share no common characteristics.
c)
Higher taxonomic categories such as phylum include a broader range of organisms than lower categories like species.
d)
The order is the highest level of classification in the biological hierarchy.

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Answer: C. Higher taxonomic categories such as phylum include a broader range of organisms than lower categories like species.
Solution: Higher taxonomic categories, like phylum, encompass a broader diversity of organisms, sharing more general characteristics compared to the more specific and closely related organisms grouped within lower categories like species and genus. This reflects the hierarchical nature of biological classification, where each ascending level represents a broader grouping based on less specific shared traits.
A body begins at rest and accelerates at a constant rate of 2 m/s2. If its velocity is v with a displacement of 9 m, then v is- a)8 m/s
- b)6 m/s
- c)10 m/s
- d)4 m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body begins at rest and accelerates at a constant rate of 2 m/s2. If its velocity is v with a displacement of 9 m, then v is
a)
8 m/s
b)
6 m/s
c)
10 m/s
d)
4 m/s

|
Lead Academy answered |
We can use the kinematic equation to relate initial velocity (u), acceleration (a), displacement (s), and final velocity (v):
v2 = u2 + 2as
In this case, the body begins at rest, so the initial velocity u is 0 m/s. The acceleration a is given as 2m/s2, and the displacement s is 9 m. We want to find the final velocity v.
v2 = 02 + 2(2)(9)
v2 = 36
v = √36
v = 6m/s
So, the correct answer is (b) 6 m/s.
A boy starts at position A, travels 3 kilometres to point B, and then returns to point A. If it takes two hours for this, his speed is- a)3 km/h
- b)zero
- c)2 km/h
- d)1.5 km/h
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy starts at position A, travels 3 kilometres to point B, and then returns to point A. If it takes two hours for this, his speed is
a)
3 km/h
b)
zero
c)
2 km/h
d)
1.5 km/h

|
Bs Academy answered |
To find the speed of the boy, we can use the formula:
Speed = Distance / Time
In this case, the total distance traveled is 3 kilometers to point B and 3 kilometers back to point A,
so the total distance is 3 + 3 = 6 kilometers.
so the total distance is 3 + 3 = 6 kilometers.
The total time taken is given as 2 hours.
Speed = 6 km / 2 hours=3 km/h
So, the correct answer is (a) 3 km/h.
The elements with atomic numbers 35, 53 and 85 are _________.- a)noble gases
- b)halides
- c)alkaline
- d)halogens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements with atomic numbers 35, 53 and 85 are _________.
a)
noble gases
b)
halides
c)
alkaline
d)
halogens
|
|
Aman Dasgupta answered |
The correct answer is option 'D': halogens.
Halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table that belong to Group 17. They are known for their high reactivity and tendency to form salts. The three elements mentioned in the question, with atomic numbers 35, 53, and 85, are all halogens.
Let's analyze each element individually:
1. Element with atomic number 35:
The element with atomic number 35 is bromine (Br). Bromine is a reddish-brown liquid at room temperature and is the only nonmetallic element that exists in a liquid state. It belongs to the halogen family and is highly reactive. Bromine readily forms compounds with other elements, such as sodium bromide (NaBr) and hydrogen bromide (HBr).
2. Element with atomic number 53:
The element with atomic number 53 is iodine (I). Iodine is a solid at room temperature and appears as shiny purple-black crystals. Like other halogens, iodine is highly reactive and readily forms compounds. It is commonly used as an antiseptic and in the production of iodized salt.
3. Element with atomic number 85:
The element with atomic number 85 is astatine (At). Astatine is a highly radioactive element and is the rarest naturally occurring element on Earth. It is a halogen and exhibits similar chemical properties to the other halogens. Due to its radioactivity and short half-life, astatine is difficult to study and is mainly of scientific interest.
In summary, the elements with atomic numbers 35, 53, and 85 are bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At), respectively. These elements all belong to the halogen group in the periodic table, making option 'D' the correct answer.
Halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table that belong to Group 17. They are known for their high reactivity and tendency to form salts. The three elements mentioned in the question, with atomic numbers 35, 53, and 85, are all halogens.
Let's analyze each element individually:
1. Element with atomic number 35:
The element with atomic number 35 is bromine (Br). Bromine is a reddish-brown liquid at room temperature and is the only nonmetallic element that exists in a liquid state. It belongs to the halogen family and is highly reactive. Bromine readily forms compounds with other elements, such as sodium bromide (NaBr) and hydrogen bromide (HBr).
2. Element with atomic number 53:
The element with atomic number 53 is iodine (I). Iodine is a solid at room temperature and appears as shiny purple-black crystals. Like other halogens, iodine is highly reactive and readily forms compounds. It is commonly used as an antiseptic and in the production of iodized salt.
3. Element with atomic number 85:
The element with atomic number 85 is astatine (At). Astatine is a highly radioactive element and is the rarest naturally occurring element on Earth. It is a halogen and exhibits similar chemical properties to the other halogens. Due to its radioactivity and short half-life, astatine is difficult to study and is mainly of scientific interest.
In summary, the elements with atomic numbers 35, 53, and 85 are bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At), respectively. These elements all belong to the halogen group in the periodic table, making option 'D' the correct answer.
A body’s displacement in metres fluctuates as y = t2 – t – 2 with time t in seconds. The displacement is zero for a value of t equal to- a)1 s
- b)2 s
- c)3 s
- d)4 s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body’s displacement in metres fluctuates as y = t2 – t – 2 with time t in seconds. The displacement is zero for a value of t equal to
a)
1 s
b)
2 s
c)
3 s
d)
4 s

|
Bs Academy answered |
To find when the displacement (y) is zero, we set the displacement equation equal to zero and solve for t:
y = t2 − t − 2
Setting y to zero:
0 = t2 − t − 2
Now, we can factor the quadratic equation or use the quadratic formula to find the values of t when y is zero.
Factoring:
(t − 2)(t + 1) = 0
Setting each factor to zero:
t − 2= 0 or t + 1 = 0
Solving for t:
t = 2 or t = −1
Since time (t) cannot be negative in this context, we discard t = −1.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 2 s. The displacement is zero when t = 2 seconds.
Hardness of water is 400 ppm. The molarity of CaCO3 in this water is:- a)4 × 10-6 M
- b)4 × 10-2 M
- c)4 × 10-3 M
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hardness of water is 400 ppm. The molarity of CaCO3 in this water is:
a)
4 × 10-6 M
b)
4 × 10-2 M
c)
4 × 10-3 M
d)
None of the above
|
|
Palak Basu answered |
Calculation of Molarity of CaCO3
The hardness of water is given as 400 ppm, which means there are 400 mg of CaCO3 present in 1 L of water.
Step 1: Convert ppm to mg/L
- 1 ppm = 1 mg/L
- Therefore, 400 ppm = 400 mg/L
Step 2: Calculate the molar mass of CaCO3
- CaCO3 has a molar mass of 100.09 g/mol
- This is calculated by adding the atomic masses of calcium (40.08), carbon (12.01), and three oxygens (3 x 16.00)
Step 3: Convert mg/L to g/L
- 400 mg = 0.4 g
- Therefore, 400 mg/L = 0.4 g/L
Step 4: Calculate the number of moles of CaCO3
- Number of moles = Mass / Molar mass
- Number of moles = 0.4 g / 100.09 g/mol = 0.003998 mol
Step 5: Calculate the molarity of CaCO3
- Molarity (M) = Number of moles / Volume of solution in L
- Since the volume is 1 L, Molarity = 0.003998 mol / 1 L = 0.003998 M
Therefore, the molarity of CaCO3 in the given water sample is 4 × 10-3 M.
In contrast to other metazoans, coelenterates have
- a)radial symmetry
- b)gemmules
- c)nematocysts
- d)polymorphism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In contrast to other metazoans, coelenterates have
a)
radial symmetry
b)
gemmules
c)
nematocysts
d)
polymorphism

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Coelenterates differ from other metazoans in having radial symmetry. Radial symmetry is a characteristic feature of coelenterates (cnidarians), including organisms such as jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals. These animals typically exhibit a radial body plan with body parts arranged around a central axis, allowing them to have multiple planes of symmetry. In contrast, most other metazoans, such as vertebrates and insects, exhibit bilateral symmetry, where only one plane of symmetry pides the body into left and right halves.
- Nematocysts are specialized stinging cells found in coelenterates, gemmules are a unique reproductive structure found in certain sponges, and polymorphism refers to the presence of different specialized forms within a single species, which is not unique to coelenterates.
Where would you find the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the Modern Periodic Table?- a)Group 8
- b)Group 2
- c)Group 18
- d)Group 10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where would you find the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the Modern Periodic Table?
a)
Group 8
b)
Group 2
c)
Group 18
d)
Group 10

|
Lead Academy answered |
This suggests the presence of a noble gas element. Noble gas elements are found in Group 18 of the modern periodic table, which is the most recent revision. Thus, the element having electronic configuration 2, 8 would be found in group 18 of the Modern Periodic Table, according to this definition. Therefore, option (C) is the most appropriate choice.
Which taxonomic category directly ranks above Species?
- a)Order
- b)Family
- c)Genus
- d)Class
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which taxonomic category directly ranks above Species?
a)
Order
b)
Family
c)
Genus
d)
Class
|
|
Ashutosh Nair answered |
Genus
The taxonomic category directly above Species is Genus. In biological classification, the hierarchy of classification from broadest to most specific goes: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The Genus category groups together species that are closely related and share common characteristics.
Importance of Genus
- Genus helps in organizing and categorizing similar species based on shared characteristics.
- It provides a level of classification above species but below family, allowing for more specific identification and grouping of organisms.
- Scientists use the Genus category to study evolutionary relationships and genetic similarities among related species.
- Genus names are italicized and capitalized in scientific classification, and are always accompanied by a species name to form the binomial name of an organism.
Example
For example, in the scientific name Canis lupus, "Canis" represents the Genus category, while "lupus" represents the Species category. This naming system helps in accurately identifying and distinguishing between different organisms within the same Genus.
In conclusion, the Genus category plays a crucial role in the classification and organization of species, providing a level of specificity above Species but below Family in the taxonomic hierarchy.
The taxonomic category directly above Species is Genus. In biological classification, the hierarchy of classification from broadest to most specific goes: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The Genus category groups together species that are closely related and share common characteristics.
Importance of Genus
- Genus helps in organizing and categorizing similar species based on shared characteristics.
- It provides a level of classification above species but below family, allowing for more specific identification and grouping of organisms.
- Scientists use the Genus category to study evolutionary relationships and genetic similarities among related species.
- Genus names are italicized and capitalized in scientific classification, and are always accompanied by a species name to form the binomial name of an organism.
Example
For example, in the scientific name Canis lupus, "Canis" represents the Genus category, while "lupus" represents the Species category. This naming system helps in accurately identifying and distinguishing between different organisms within the same Genus.
In conclusion, the Genus category plays a crucial role in the classification and organization of species, providing a level of specificity above Species but below Family in the taxonomic hierarchy.
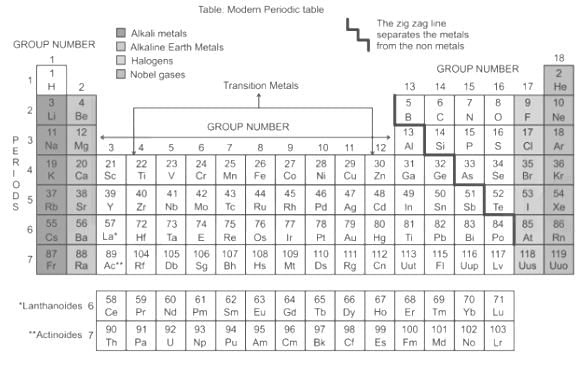
The arrangement of elements in the Modern Periodic Table is based on their\s- a)rising atomic mass in the period\s
- b)increasing atomic number in the horizontal rows
- c)increasing atomic number in the vertical columns
- d)increasing atomic mass in the group
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The arrangement of elements in the Modern Periodic Table is based on their\s
a)
rising atomic mass in the period\s
b)
increasing atomic number in the horizontal rows
c)
increasing atomic number in the vertical columns
d)
increasing atomic mass in the group

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The elements are listed in ascending order of atomic numbers, with heavier elements at the top of the list. The horizontal rows of the periodic table are referred to as Periods, and the vertical columns of the periodic table are referred to as Groups. The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are divided into seven Periods and eighteen Groups, as shown in the diagram below. The chemical elements are arranged from left to right and top to bottom in order of increasing atomic number, or the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which generally corresponds to increasing atomic mass. The elements are arranged from left to right and top to bottom in order of increasing atomic mass.
What is common among Lithium, Sodium and Potassium?- a)These have one electron in their outermost shell
- b)There are alkaline earth metals
- c)These cannot form oxides
- d)These are inert elements
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is common among Lithium, Sodium and Potassium?
a)
These have one electron in their outermost shell
b)
There are alkaline earth metals
c)
These cannot form oxides
d)
These are inert elements
|
|
Bhavya Pillai answered |
One electron in their outermost shell:
- Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium all belong to the alkali metal group in the periodic table.
- They each have one electron in their outermost shell, which makes them highly reactive.
- This outer electron is easily lost, leading to the formation of positively charged ions.
Alkali metals:
- Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium are all classified as alkali metals due to their similar properties.
- They are soft, shiny, highly reactive metals that readily form compounds with other elements.
Reactivity and formation of oxides:
- These elements are highly reactive due to the presence of a single electron in their outer shell.
- When they react with oxygen, they form oxides - Lithium oxide (Li2O), Sodium oxide (Na2O), and Potassium oxide (K2O).
Therefore, the common factor among Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium is that they all have one electron in their outermost shell, leading to their similar reactivity and properties as alkali metals.
- Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium all belong to the alkali metal group in the periodic table.
- They each have one electron in their outermost shell, which makes them highly reactive.
- This outer electron is easily lost, leading to the formation of positively charged ions.
Alkali metals:
- Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium are all classified as alkali metals due to their similar properties.
- They are soft, shiny, highly reactive metals that readily form compounds with other elements.
Reactivity and formation of oxides:
- These elements are highly reactive due to the presence of a single electron in their outer shell.
- When they react with oxygen, they form oxides - Lithium oxide (Li2O), Sodium oxide (Na2O), and Potassium oxide (K2O).
Therefore, the common factor among Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium is that they all have one electron in their outermost shell, leading to their similar reactivity and properties as alkali metals.
Generally, the valency of electropositive elements is ________.- a)2, 1, 0
- b)4, 3, 2
- c)1, 2, 3
- d)0, 1, 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Generally, the valency of electropositive elements is ________.
a)
2, 1, 0
b)
4, 3, 2
c)
1, 2, 3
d)
0, 1, 2

|
Lead Academy answered |
- The general valency of electropositive elements is 1, 2, 3.
- Atoms which tend to donate electrons and converts into a positive ion (M+) are called Electropositive atoms.
- The atoms which have 1, 2, or 3 electrons in their valence shells will lose their electrons to attain a stable electronic configuration.
- Some examples are Sodium, Magnesium, and Aluminium. These 3 elements will lose electrons to attain the configuration of the noble gas Neon.
In 5 seconds, an automobile speeds from 18 km/h to 36 km/h. What is the acceleration of the automobile in m/s?- a)0.5 m/s²
- b)3 m/s²
- c)1 m/s²
- d)2 m/s²
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In 5 seconds, an automobile speeds from 18 km/h to 36 km/h. What is the acceleration of the automobile in m/s?
a)
0.5 m/s²
b)
3 m/s²
c)
1 m/s²
d)
2 m/s²

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The change in velocity (Δv) is the final velocity minus the initial velocity:
Δv = 36km/h − 18km/h = 18km/h
Convert Δv to m/s:
Δv = 18 × 1000 / 3600 m/s ≈ 5m/s
The change in time (Δt) is given as 5 seconds.
Now, use the formula for acceleration:
a = Δv/Δt = 5/5 m/s2 = 1m/s2
So, the acceleration of the automobile is 1m/s2, and the correct answer is (c) 1 m/s².
Binomial nomenclature means- a)one name given by two scientists.
- b)one scientific name consisting of a generic and specific epithet.
- c)two names, one latinized, other of a person.
- d)two names of same plant.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Binomial nomenclature means
a)
one name given by two scientists.
b)
one scientific name consisting of a generic and specific epithet.
c)
two names, one latinized, other of a person.
d)
two names of same plant.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Binomial nomenclature means that the scientific name of any organism consist of a generic epithet and a specific epithet. Binomial nomenclature was developed by Linnaeus.
What distinguishes liverworts from mosses in particular?- a)Mosses have vascular tissue that liverworts lack
- b)In contrast to liverworts, mosses have an intermediate stage known as protonema
- c)Mosses grow taller, whilst liverworts do not
- d)Sporophytes, specialized bodies found only in mosses, are missing in liverworts
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What distinguishes liverworts from mosses in particular?
a)
Mosses have vascular tissue that liverworts lack
b)
In contrast to liverworts, mosses have an intermediate stage known as protonema
c)
Mosses grow taller, whilst liverworts do not
d)
Sporophytes, specialized bodies found only in mosses, are missing in liverworts
|
|
Rajveer Patel answered |
Distinguishing Features of Liverworts and Mosses
Liverworts and mosses are both non-vascular plants belonging to the group of bryophytes, but they exhibit key differences in their life cycles and structures. One of the most significant distinctions is the presence of an intermediate stage known as the protonema in mosses.
Protonema in Mosses
- Definition: The protonema is a filamentous structure that develops from the germinating spore of mosses.
- Function: It serves as the first stage of the gametophyte generation, where it grows into the mature gametophyte, leading to the formation of moss plants.
- Significance: This stage is crucial for nutrient absorption and establishing the plant before it develops into the recognizable leafy structure.
Liverworts Lack Protonema
- Development: Liverworts do not have a protonema stage; they develop directly from the spore into a mature gametophyte.
- Structure: Liverworts typically exhibit a thalloid or leafy structure without the filamentous intermediate form.
Other Distinctions
- Vascular Tissue: Mosses do not have true vascular tissue, but they do have specialized structures for water and nutrient transport.
- Growth Form: Mosses can grow taller compared to liverworts, which tend to be more flat and spread out.
- Sporophytes: Mosses possess sporophytes that are attached to the gametophyte and are specialized structures for spore production, while liverworts have simpler sporophytes.
In summary, the presence of the protonema stage in mosses is a defining characteristic that sets them apart from liverworts, influencing their development and growth patterns.
Liverworts and mosses are both non-vascular plants belonging to the group of bryophytes, but they exhibit key differences in their life cycles and structures. One of the most significant distinctions is the presence of an intermediate stage known as the protonema in mosses.
Protonema in Mosses
- Definition: The protonema is a filamentous structure that develops from the germinating spore of mosses.
- Function: It serves as the first stage of the gametophyte generation, where it grows into the mature gametophyte, leading to the formation of moss plants.
- Significance: This stage is crucial for nutrient absorption and establishing the plant before it develops into the recognizable leafy structure.
Liverworts Lack Protonema
- Development: Liverworts do not have a protonema stage; they develop directly from the spore into a mature gametophyte.
- Structure: Liverworts typically exhibit a thalloid or leafy structure without the filamentous intermediate form.
Other Distinctions
- Vascular Tissue: Mosses do not have true vascular tissue, but they do have specialized structures for water and nutrient transport.
- Growth Form: Mosses can grow taller compared to liverworts, which tend to be more flat and spread out.
- Sporophytes: Mosses possess sporophytes that are attached to the gametophyte and are specialized structures for spore production, while liverworts have simpler sporophytes.
In summary, the presence of the protonema stage in mosses is a defining characteristic that sets them apart from liverworts, influencing their development and growth patterns.
Gaps were left in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table to allow for the discovery of new elements in the future. Which of the following elements did not find a place in the Periodic Table until much later in history?- a)Silicon
- b)Oxygen
- c)Fluorine
- d)Germanium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gaps were left in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table to allow for the discovery of new elements in the future. Which of the following elements did not find a place in the Periodic Table until much later in history?
a)
Silicon
b)
Oxygen
c)
Fluorine
d)
Germanium

|
Top Rankers answered |
Mendeleev himself added these elements to the periodic chart in 1902 as group 0 elements, without altering the fundamental principle of the periodic table in the process. Alfred Werner, a Swiss chemist, was the first to solve the dead zone of Mendeleev’s table, which was discovered in 1905. He came to the conclusion that the rare-earth elements (lanthanides), of which there were 13 known, were contained within that gap.
Assertion (A): Algae are classified into three main classes based on the type of pigment and stored food they possess.Reason (R): Algae reproduce exclusively through vegetative methods, such as fragmentation- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Algae are classified into three main classes based on the type of pigment and stored food they possess.
Reason (R): Algae reproduce exclusively through vegetative methods, such as fragmentation
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Simran Sengupta answered |
Understanding the Assertion and Reason
The assertion and reason provided in the question require a detailed analysis to determine their validity.
Assertion (A):
- Algae are classified into three main classes based on the type of pigment and stored food they possess.
- This statement is true. Algae are commonly categorized into three major groups: Chlorophyta (green algae), Rhodophyta (red algae), and Phaeophyta (brown algae). The classification is indeed based on the pigments they contain (such as chlorophylls and carotenoids) and the type of food they store (like starch or other carbohydrates).
Reason (R):
- Algae reproduce exclusively through vegetative methods, such as fragmentation.
- This statement is false. While algae can reproduce vegetatively through methods such as fragmentation, they also reproduce sexually (through gametes) and asexually (through spores). Therefore, the claim that their reproduction is exclusively vegetative is incorrect.
Conclusion
- Since the assertion is true and the reason is false, the correct option is (c): If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- This distinction is crucial for understanding the classification and reproduction methods of algae, which are diverse and not limited to only vegetative means.
In summary, algae's classification is accurately described, while the reason presented about their reproduction is misleading.
The assertion and reason provided in the question require a detailed analysis to determine their validity.
Assertion (A):
- Algae are classified into three main classes based on the type of pigment and stored food they possess.
- This statement is true. Algae are commonly categorized into three major groups: Chlorophyta (green algae), Rhodophyta (red algae), and Phaeophyta (brown algae). The classification is indeed based on the pigments they contain (such as chlorophylls and carotenoids) and the type of food they store (like starch or other carbohydrates).
Reason (R):
- Algae reproduce exclusively through vegetative methods, such as fragmentation.
- This statement is false. While algae can reproduce vegetatively through methods such as fragmentation, they also reproduce sexually (through gametes) and asexually (through spores). Therefore, the claim that their reproduction is exclusively vegetative is incorrect.
Conclusion
- Since the assertion is true and the reason is false, the correct option is (c): If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- This distinction is crucial for understanding the classification and reproduction methods of algae, which are diverse and not limited to only vegetative means.
In summary, algae's classification is accurately described, while the reason presented about their reproduction is misleading.
On a flat surface, a block of wood is placed) To move the body, a force is provided parallel to the surface. The frictional force develops in the following directions:- a)normal to the surface upwards
- b)normal to the surface downwards
- c)along the applied force’s direction
- d)opposite to the applied force’s direction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On a flat surface, a block of wood is placed) To move the body, a force is provided parallel to the surface. The frictional force develops in the following directions:
a)
normal to the surface upwards
b)
normal to the surface downwards
c)
along the applied force’s direction
d)
opposite to the applied force’s direction

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The frictional force develops in the direction opposite to the applied force's direction.
Therefore, the correct answer is: (d) opposite to the applied force's direction.
Therefore, the correct answer is: (d) opposite to the applied force's direction.
Which of the following developed for the first time in Annelids?- a)Cephalization
- b)Development of a true coelom
- c)Metameric segmentation
- d)Both 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following developed for the first time in Annelids?
a)
Cephalization
b)
Development of a true coelom
c)
Metameric segmentation
d)
Both 2 and 3

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Cephalization, which is the concentration of nerve tissue at the anterior end of an organism, and metameric segmentation, which is the pision of the body into segments, are two significant evolutionary developments that first developed in Annelids. Animal Kingdom’s courses will teach you more about these biological phenomena and their influence on modern species.
Chapter doubts & questions for Progress Test - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Progress Test - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









