All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg >
All Questions
All questions of Highway Development & Planning for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
Consider
1. Creation of Central Road Fund
2. National Highway Act
3. Formation of Indian Road Congress
4. Creation of Highway Research BoardThe correct chronological order of these events is- a)4, 3, 2, 1
- b)2, 1, 3, 4
- c)1 ,3 , 2 , 4
- d)2, 3, 1 ,4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider
1. Creation of Central Road Fund
2. National Highway Act
3. Formation of Indian Road Congress
4. Creation of Highway Research Board
1. Creation of Central Road Fund
2. National Highway Act
3. Formation of Indian Road Congress
4. Creation of Highway Research Board
The correct chronological order of these events is
a)
4, 3, 2, 1
b)
2, 1, 3, 4
c)
1 ,3 , 2 , 4
d)
2, 3, 1 ,4

|
Engineers Adda answered |
Creation of Central Road Fund -1929
National Highway Act -1956
Formation of Indian Road Congress - 1934
Creation of Highway Research Board - 1973
National Highway Act -1956
Formation of Indian Road Congress - 1934
Creation of Highway Research Board - 1973
As per the Nagpur plan the un-surfaced roads were meant for- a)National highway
- b)State highway
- c)Major district road
- d)Other district road and village road
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
As per the Nagpur plan the un-surfaced roads were meant for
a)
National highway
b)
State highway
c)
Major district road
d)
Other district road and village road

|
Sparsh Unni answered |
The Nagpur plan classified the roads into two categories, category one was meant for national highway, state highway and major district road. The un-surfaced roads were meant for other district roads and village roads.
The first 20 year development plan is also called as?- a)Nagpur road plan
- b)Lucknow road plan
- c)Bombay road plan
- d)Delhi road plan
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The first 20 year development plan is also called as?
a)
Nagpur road plan
b)
Lucknow road plan
c)
Bombay road plan
d)
Delhi road plan

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
Accordingly a 20-year plan was drafted by the Roads wing of Government of India, which is popularly known as the Bombay plan. The highlights of the plan were: It was the second 20 year road plan (1961-1981)
The east west corridor of National highway connects which of the following cities?- a)Delhi-Bombay
- b)Bombay-Madras
- c)Kolkata-Vadodara
- d)Porbandar- Silichar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The east west corridor of National highway connects which of the following cities?
a)
Delhi-Bombay
b)
Bombay-Madras
c)
Kolkata-Vadodara
d)
Porbandar- Silichar

|
Sarthak Kulkarni answered |
The National Highways Authority of India initiated the National Highway Development Program (the program) in 1998 to ease chronic capacity constraints by upgrading key arteries of the national highways network. The project, which this validation is reviewing, was the third loan financed by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) for the multiyear lending program for the program. The program upgraded into four lanes the following highway corridors: (i) corridor connecting the major metropolitan cities of Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata—known as the golden quadrilateral; (ii) north–south corridor connecting Srinagar to Kanyakumari (4,000 km); and (iii) east–west corridor that connects Silchar to Porbandar (3,300 km).
The broken stones that were used in construction of roads in macadam’s construction were?- a)10mm and 20mm
- b)20mm and 40mm
- c)30mm and 50mm
- d)50mm and 100mm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The broken stones that were used in construction of roads in macadam’s construction were?
a)
10mm and 20mm
b)
20mm and 40mm
c)
30mm and 50mm
d)
50mm and 100mm

|
Ananya Sharma answered |
The bigger stones that were passing through 100mm sieve were used at the bottom and compacted and the smaller stones that were passing through 50mm were used at the top of the pavement.
The topographic survey is conducted to estimate which of the following characteristics?- a)Engineering
- b)Traffic
- c)Financial
- d)Soil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The topographic survey is conducted to estimate which of the following characteristics?
a)
Engineering
b)
Traffic
c)
Financial
d)
Soil

|
Rajat Sen answered |
Topographic Survey for Estimating Engineering Characteristics
A Topographic Survey is a type of land survey that involves the measurement and mapping of the natural and man-made features of a piece of land. This survey is conducted to estimate the engineering characteristics of the land. The following are the characteristics estimated through a Topographic Survey:
1. Elevation: The survey helps to determine the elevation of the land, which is the height above sea level. This information is important for designing buildings, roads, and drainage systems.
2. Slope: The survey helps to determine the slope of the land, which is the angle of inclination of the land surface. This information is important for designing roads, railways, and other transportation systems.
3. Contour lines: The survey helps to create contour lines, which are lines that connect points of equal elevation. These lines are used to create topographic maps that provide information about the shape and features of the land.
4. Drainage: The survey helps to identify natural drainage patterns on the land, which is important for designing drainage systems.
5. Soil conditions: The survey helps to identify soil conditions on the land, which is important for designing foundations for buildings and other structures.
In conclusion, a Topographic Survey is an important tool for estimating the engineering characteristics of a piece of land. It helps to determine the elevation, slope, contour lines, drainage, and soil conditions of the land, which are all important factors in designing buildings, roads, and other infrastructure projects.
A Topographic Survey is a type of land survey that involves the measurement and mapping of the natural and man-made features of a piece of land. This survey is conducted to estimate the engineering characteristics of the land. The following are the characteristics estimated through a Topographic Survey:
1. Elevation: The survey helps to determine the elevation of the land, which is the height above sea level. This information is important for designing buildings, roads, and drainage systems.
2. Slope: The survey helps to determine the slope of the land, which is the angle of inclination of the land surface. This information is important for designing roads, railways, and other transportation systems.
3. Contour lines: The survey helps to create contour lines, which are lines that connect points of equal elevation. These lines are used to create topographic maps that provide information about the shape and features of the land.
4. Drainage: The survey helps to identify natural drainage patterns on the land, which is important for designing drainage systems.
5. Soil conditions: The survey helps to identify soil conditions on the land, which is important for designing foundations for buildings and other structures.
In conclusion, a Topographic Survey is an important tool for estimating the engineering characteristics of a piece of land. It helps to determine the elevation, slope, contour lines, drainage, and soil conditions of the land, which are all important factors in designing buildings, roads, and other infrastructure projects.
The determination of optimum length is based on- a)Saturation system
- b)Geometric design
- c)Type of highway
- d)Length of highway
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The determination of optimum length is based on
a)
Saturation system
b)
Geometric design
c)
Type of highway
d)
Length of highway

|
Sasikumar Nuthalapati answered |
The determination of optimum length is based on saturation system based on U.S system of highway planning.
The Indian Roads Congress was formed in the year?- a)1928
- b)1934
- c)1929
- d)1930
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Indian Roads Congress was formed in the year?
a)
1928
b)
1934
c)
1929
d)
1930
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The Indian Roads Congress was formed in the year 1934 after recommendation from the jayakar committee after a meeting in year 1928 and CRF was formed in 1929.
The roads that connect the district headquarters to important city of other state is called- a)National Highway
- b)State Highway
- c)Major district road
- d)Other district road
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The roads that connect the district headquarters to important city of other state is called
a)
National Highway
b)
State Highway
c)
Major district road
d)
Other district road

|
Prerna Menon answered |
A State Highway is a highway that connects the district headquarters to other important cities in another state.
The main features of the roman road do not include the following?- a)They were built straight
- b)They were strong
- c)They excavated soft soil till hard strata was obtained
- d)The total thickness was 0.75m to 1.2m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The main features of the roman road do not include the following?
a)
They were built straight
b)
They were strong
c)
They excavated soft soil till hard strata was obtained
d)
The total thickness was 0.75m to 1.2m
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
The romans built roads by excavating till the hard strata they were much stronger than required for animal drawn carts that time.
Primary system of roads consists of?- a)National highway
- b)Expressway
- c)National highway and Expressway
- d)State highway
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Primary system of roads consists of?
a)
National highway
b)
Expressway
c)
National highway and Expressway
d)
State highway

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
Roads consist of one or two roadways (British English: carriageways), each with one or more lanes and any associated sidewalks (British English: pavement) and road verges. ... Other names for roads include parkways, avenues, freeways, tollways, interstates, highways, or primary, secondary, and tertiary local roads.
The length of National Highways as per 3rd 20 year (Lucknow) road plan is given by- a)area of the country/75
- b)area of the country/50
- c)area of the country/40
- d)area of the country/25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of National Highways as per 3rd 20 year (Lucknow) road plan is given by
a)
area of the country/75
b)
area of the country/50
c)
area of the country/40
d)
area of the country/25

|
Tanishq Rane answered |
(i) Length of National Highways (NH) - Area of the country/50
(ii) Length of State Highways (SH) = Area of the state/25 = 62.5 x number of towns in the state - Area of the state/50
(iii) Length of the Major District Roads (MDR) = Area of the State/12.5 = 90 x number of towns in the state
(iv) Total length of all categories of roads in a district i.e.
NH + SH + MDR + ODR + VR
= Area of District x 0.82
(ii) Length of State Highways (SH) = Area of the state/25 = 62.5 x number of towns in the state - Area of the state/50
(iii) Length of the Major District Roads (MDR) = Area of the State/12.5 = 90 x number of towns in the state
(iv) Total length of all categories of roads in a district i.e.
NH + SH + MDR + ODR + VR
= Area of District x 0.82
The maximum number of cities and towns are connected by which type of highway- a)National highway
- b)State highway
- c)Major district road
- d)Village road
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum number of cities and towns are connected by which type of highway
a)
National highway
b)
State highway
c)
Major district road
d)
Village road

|
Sonal Tiwari answered |
The national highway connects most of the cities and towns in the country.
State highway connects in the state, village road in villages and other roads connect the remote areas.
State highway connects in the state, village road in villages and other roads connect the remote areas.
The second 20 year development plan conference was held in which city?- a)Nagpur
- b)Bombay
- c)Madras
- d)Lucknow
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The second 20 year development plan conference was held in which city?
a)
Nagpur
b)
Bombay
c)
Madras
d)
Lucknow

|
Milan Ghosh answered |
The second 20 year development plan conference was held in Bombay,
Their target was to achieve road length of 32km but they achieved 34.8km.
Their target was to achieve road length of 32km but they achieved 34.8km.
The accident cost analysis is estimated by conducting- a)Origin and destination
- b)Traffic survey
- c)Transportation facilities
- d)Geometric design
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The accident cost analysis is estimated by conducting
a)
Origin and destination
b)
Traffic survey
c)
Transportation facilities
d)
Geometric design

|
Lekshmi Rane answered |
The accident cost analysis, trends in road accidents and facilities all are estimated by conducting traffic survey, origin and destination studies are for trips and geometry for facility.
The estimates are studied in which type of studies?- a)Economic studies
- b)Financial studies
- c)Traffic studies
- d)Engineering studies
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The estimates are studied in which type of studies?
a)
Economic studies
b)
Financial studies
c)
Traffic studies
d)
Engineering studies
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
The details to be collected during economic studies are useful in estimating the requirements, cost involved in the project and economic justification.
Planning is based on- a)Factual data
- b)Analysis
- c)Scientific data
- d)Factual data and analysis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Planning is based on
a)
Factual data
b)
Analysis
c)
Scientific data
d)
Factual data and analysis

|
Sravya Tiwari answered |
Planning based on factual data and analysis may be considered scientific and sound.
The ‘rural road development plan: Vision 2025’ aims to provide basic access to villages in how many phases?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ‘rural road development plan: Vision 2025’ aims to provide basic access to villages in how many phases?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four
|
|
Rajeev Masand answered |
The Vision: 2025 aims at providing accessible facilities to villages in 3 phases by giving priority to the population in the village.
A locomotive has four pairs of driving wheels carrying an axle load of 24 x 104 N The maximum load that can be pulled if the coefficient of friction is 1/6, is- a)32 x 104 N
- b)16 x 104 N
- c)8 x 104 N
- d)4 x 104 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A locomotive has four pairs of driving wheels carrying an axle load of 24 x 104 N The maximum load that can be pulled if the coefficient of friction is 1/6, is
a)
32 x 104 N
b)
16 x 104 N
c)
8 x 104 N
d)
4 x 104 N

|
Devansh Banerjee answered |
Maximum load pulled
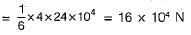
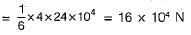
The utility unit as per saturation system for a population of less 1001 to 2000 is- a)0.25
- b)0.50
- c)1.00
- d)2.00
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The utility unit as per saturation system for a population of less 1001 to 2000 is
a)
0.25
b)
0.50
c)
1.00
d)
2.00

|
Simran Mukherjee answered |
Population-based Utility Units:
In a saturation system, the utility units refer to the number of utilities (such as water supply, electricity, etc.) that are required to meet the needs of a specific population. These units are determined based on the size of the population being served.
Given Information:
According to the given information, we are dealing with a population range of 1001 to 2000. And we need to determine the utility unit for this population range.
Determining the Utility Unit:
To determine the utility unit for a given population range, we need to divide the total population by a certain factor. This factor is determined based on various factors such as average consumption, demand patterns, and availability of resources.
In this case, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that the utility unit is 1.00. This means that for a population range of 1001 to 2000, only one utility unit is required.
Explanation:
The utility unit of 1.00 for a population range of 1001 to 2000 indicates that the needs of this population can be met by a single utility unit. This means that the existing infrastructure and resources are sufficient to cater to the requirements of this population range.
The determination of utility units is based on factors such as the average consumption of utilities per person, the availability of resources, and the capacity of the infrastructure. These factors are carefully considered to ensure that the utility units are adequate to meet the needs of the population.
It is important to note that the utility unit can vary for different population ranges. For larger populations, multiple utility units may be required to meet the increased demand. Similarly, for smaller populations, a fraction of a utility unit may be sufficient.
In conclusion, the utility unit of 1.00 for a population range of 1001 to 2000 indicates that a single utility unit is adequate to meet the needs of this population range.
In a saturation system, the utility units refer to the number of utilities (such as water supply, electricity, etc.) that are required to meet the needs of a specific population. These units are determined based on the size of the population being served.
Given Information:
According to the given information, we are dealing with a population range of 1001 to 2000. And we need to determine the utility unit for this population range.
Determining the Utility Unit:
To determine the utility unit for a given population range, we need to divide the total population by a certain factor. This factor is determined based on various factors such as average consumption, demand patterns, and availability of resources.
In this case, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that the utility unit is 1.00. This means that for a population range of 1001 to 2000, only one utility unit is required.
Explanation:
The utility unit of 1.00 for a population range of 1001 to 2000 indicates that the needs of this population can be met by a single utility unit. This means that the existing infrastructure and resources are sufficient to cater to the requirements of this population range.
The determination of utility units is based on factors such as the average consumption of utilities per person, the availability of resources, and the capacity of the infrastructure. These factors are carefully considered to ensure that the utility units are adequate to meet the needs of the population.
It is important to note that the utility unit can vary for different population ranges. For larger populations, multiple utility units may be required to meet the increased demand. Similarly, for smaller populations, a fraction of a utility unit may be sufficient.
In conclusion, the utility unit of 1.00 for a population range of 1001 to 2000 indicates that a single utility unit is adequate to meet the needs of this population range.
The master plan may not be prepared for- a)Village
- b)City
- c)State
- d)Country
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The master plan may not be prepared for
a)
Village
b)
City
c)
State
d)
Country

|
Yash Joshi answered |
The master plan is prepared after interpretation of small plans in different phases. It may be prepared for a city, district ,state or even country.
The final step after fixing the optimum length of the road- a)Financing
- b)Construction
- c)Phasing
- d)Preparation of master plan
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The final step after fixing the optimum length of the road
a)
Financing
b)
Construction
c)
Phasing
d)
Preparation of master plan
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The final step after fixing the optimum length is phasing of the road program before the construction, after financing and master plan the construction is under taken.
Effective stress is- a)the stress at particles contact
- b)a physical parameter that can be measured
- c)important because it is a function of engineering properties of soil
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Effective stress is
a)
the stress at particles contact
b)
a physical parameter that can be measured
c)
important because it is a function of engineering properties of soil
d)
all of the above

|
Siddharth Bajaj answered |
Effective stress is a defined property which cannot be measured and is calculated by measuring the total stress and pore water pressure in the field.
Effective Stress= Total Stress- Pore water Pressure
It is not the true contact stress between particles because it uses area for division as gross area rather than Area of actual contact between particles
The load on each axle of a locomotive is 22 tonnes. If the coefficient of friction is 0.2 then the hauling capacity due to 3 pairs of driving wheels will be- a)26.4t
- b)19.8t
- c)13.2t
- d)6.6t
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The load on each axle of a locomotive is 22 tonnes. If the coefficient of friction is 0.2 then the hauling capacity due to 3 pairs of driving wheels will be
a)
26.4t
b)
19.8t
c)
13.2t
d)
6.6t

|
Rishika Sen answered |
Hauling capacity = 0.2 x 22 x 3 = 13.2t
In 1927, Jayakar committee was set up-to examine and report on road development in India, based on which certain institutions were subsequently set up. Which of the following were the direct out come of Jayakar committee recommendations.
1. Indian Road Congress
2. Central Road Fund
3. CRRI
4. National Highway Act- a)1,2 and 3
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1,3 and 4
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1927, Jayakar committee was set up-to examine and report on road development in India, based on which certain institutions were subsequently set up. Which of the following were the direct out come of Jayakar committee recommendations.
1. Indian Road Congress
2. Central Road Fund
3. CRRI
4. National Highway Act
1. Indian Road Congress
2. Central Road Fund
3. CRRI
4. National Highway Act
a)
1,2 and 3
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1,3 and 4
d)
All the above
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
After the first World War, motor vehicle using the roads increases. Jaykar Committee was thus, formed and recommended-
Road development should be a national interest.
An extra tax should be levied on petrol from road users to create the road development fund Central Road Fund
To establish a semi-official, technical institution to pool technical knowledge, sharing of ideas to act as an advisory body Indian Road Congress
To create a national level institution to carry research, development works and constitution CRRI (Central Road Research Institute)
Road development should be a national interest.
An extra tax should be levied on petrol from road users to create the road development fund Central Road Fund
To establish a semi-official, technical institution to pool technical knowledge, sharing of ideas to act as an advisory body Indian Road Congress
To create a national level institution to carry research, development works and constitution CRRI (Central Road Research Institute)
The total length of highways in 2001 in km was- a)56000
- b)56756
- c)56750
- d)57000
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The total length of highways in 2001 in km was
a)
56000
b)
56756
c)
56750
d)
57000

|
Rajat Patel answered |
The total length of NH achieved in 2001 was 5700km against a planned length of 66000km.
The total length of the first category roads was calculated by adding up the sum of- a)NH+SH+MDR
- b)NH+SH
- c)SH*2
- d)NH+2SH+MDR
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The total length of the first category roads was calculated by adding up the sum of
a)
NH+SH+MDR
b)
NH+SH
c)
SH*2
d)
NH+2SH+MDR

|
Akshat Datta answered |
The category one type of roads consisted of national highway, state highway and major district roads. The length was calculated by adding all the three types of roads.
The tresaguet method of laying roads was developed in the year?- a)1764
- b)1774
- c)1800
- d)1796
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The tresaguet method of laying roads was developed in the year?
a)
1764
b)
1774
c)
1800
d)
1796

|
Sreemoyee Chauhan answered |
The tresaguet method was developed in 1764 AD in France after the fall of Roman Empire, in later years better methods were developed.
Nagpur road plan has recommended the use of road pattern type of- a)star and circular pattern
- b)star and block pattern
- c)star and grid pattern
- d)star and hexagonal pattern
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nagpur road plan has recommended the use of road pattern type of
a)
star and circular pattern
b)
star and block pattern
c)
star and grid pattern
d)
star and hexagonal pattern

|
Bhavya Ahuja answered |
Road Plan for Nagpur
Introduction:
The road plan for Nagpur has recommended the use of a specific road pattern type. This road pattern type is crucial for the efficient flow of traffic and the reduction of congestion on the roads.
Road Pattern Type:
The recommended road pattern type for Nagpur is the star and grid pattern. This road pattern type is a combination of two different patterns that work together to provide efficient traffic flow.
Star Pattern:
The star pattern is a type of road pattern that branches out from a central point like the spokes of a wheel. This type of pattern is suitable for areas where there is a high volume of traffic that needs to move quickly in and out of a central location.
Grid Pattern:
The grid pattern is a type of road pattern that uses a series of intersecting roads to create a network of streets. This type of pattern is suitable for areas where there is a lower volume of traffic that needs to move around different parts of the city.
Combination of Star and Grid Pattern:
The combination of the star and grid pattern is ideal for Nagpur because it allows for both high volume and low volume traffic to move efficiently throughout the city. The central point of the star pattern can be used for important locations like the city center or major transportation hubs, while the grid pattern can be used for residential areas and other parts of the city.
Benefits of Star and Grid Pattern:
The star and grid pattern has several benefits for Nagpur, including:
1. Efficient traffic flow: The combination of the star and grid pattern allows for efficient traffic flow throughout the city.
2. Reduced congestion: By using the star and grid pattern, Nagpur can reduce congestion on the roads and improve air quality.
3. Improved safety: The star and grid pattern can improve safety on the roads by reducing the number of accidents and improving visibility.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the recommended road pattern type for Nagpur is the star and grid pattern. This pattern will help to improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve safety on the roads.
Introduction:
The road plan for Nagpur has recommended the use of a specific road pattern type. This road pattern type is crucial for the efficient flow of traffic and the reduction of congestion on the roads.
Road Pattern Type:
The recommended road pattern type for Nagpur is the star and grid pattern. This road pattern type is a combination of two different patterns that work together to provide efficient traffic flow.
Star Pattern:
The star pattern is a type of road pattern that branches out from a central point like the spokes of a wheel. This type of pattern is suitable for areas where there is a high volume of traffic that needs to move quickly in and out of a central location.
Grid Pattern:
The grid pattern is a type of road pattern that uses a series of intersecting roads to create a network of streets. This type of pattern is suitable for areas where there is a lower volume of traffic that needs to move around different parts of the city.
Combination of Star and Grid Pattern:
The combination of the star and grid pattern is ideal for Nagpur because it allows for both high volume and low volume traffic to move efficiently throughout the city. The central point of the star pattern can be used for important locations like the city center or major transportation hubs, while the grid pattern can be used for residential areas and other parts of the city.
Benefits of Star and Grid Pattern:
The star and grid pattern has several benefits for Nagpur, including:
1. Efficient traffic flow: The combination of the star and grid pattern allows for efficient traffic flow throughout the city.
2. Reduced congestion: By using the star and grid pattern, Nagpur can reduce congestion on the roads and improve air quality.
3. Improved safety: The star and grid pattern can improve safety on the roads by reducing the number of accidents and improving visibility.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the recommended road pattern type for Nagpur is the star and grid pattern. This pattern will help to improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve safety on the roads.
The planning survey consists of how many numbers of studies?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The planning survey consists of how many numbers of studies?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four

|
Tanishq Menon answered |
The planning survey consists of the four studies namely
Economic studies
Financial studies
Traffic studies
Engineering studies.
Economic studies
Financial studies
Traffic studies
Engineering studies.
The phases of highway planning do not include the following- a)Assessment of road length requirement
- b)Preparation of master plan
- c)Showing the phasing of a plan in five year plan
- d)Financing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The phases of highway planning do not include the following
a)
Assessment of road length requirement
b)
Preparation of master plan
c)
Showing the phasing of a plan in five year plan
d)
Financing

|
Arnab Saini answered |
Financing of the highway is done after the planning of highway after getting approval from the government, before the assessment, preparation and DPR are prepared.
The method of providing a definite cross slope by varying thickness of foundations under roads was proposed by?- a)Tresauguet
- b)Metcalf
- c)Telford
- d)Macadam
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The method of providing a definite cross slope by varying thickness of foundations under roads was proposed by?
a)
Tresauguet
b)
Metcalf
c)
Telford
d)
Macadam

|
Pallabi Bajaj answered |
Telford insisted to provide a definitely varying cross slope by varying the thickness under the foundation of stones.
The cross slopes provided for drainage water under Macadam’s construction road is?- a)1 in 10
- b)1 in 20
- c)1 in 36
- d)1 in 40
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cross slopes provided for drainage water under Macadam’s construction road is?
a)
1 in 10
b)
1 in 20
c)
1 in 36
d)
1 in 40

|
Nidhi Patel answered |
The slope provided is 1 in 36, it was proposed by Macadam. He also completely changed the construction methods that were used earlier.
The Nagpur plan formulae assumed which type of pattern?- a)Star and grid
- b)Star and circular
- c)Hexagonal
- d)Circular
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Nagpur plan formulae assumed which type of pattern?
a)
Star and grid
b)
Star and circular
c)
Hexagonal
d)
Circular

|
Shraddha Datta answered |
The Nagpur plan formulae assumed a star and grid pattern.
The Nagpur plan formulae were developed by architect Charles Correa for the city of Nagpur in India. These formulae aimed to provide a comprehensive and flexible approach to urban planning that could accommodate the rapid growth and changing needs of the city.
Star Pattern:
The star pattern refers to a layout in which major roads radiate outwards from a central point, like the spokes of a wheel. This pattern is often used in urban planning to create a well-connected and easily navigable road network. The Nagpur plan formulae assumed a star pattern as a basis for the city's road network.
Grid Pattern:
The grid pattern, on the other hand, refers to a layout in which streets intersect at right angles, forming a rectangular grid. This pattern is commonly used in urban planning to create a regular and organized street network. While the Nagpur plan formulae did not assume a grid pattern as the primary layout, it incorporated elements of both the star and grid patterns to create a hybrid approach.
Combination of Star and Grid:
The Nagpur plan formulae combined the star and grid patterns to create a unique urban planning strategy. The central area of the city was organized in a star pattern, with major roads radiating out from a central point. This allowed for efficient connectivity and easy access to key destinations within the city.
At the same time, the Nagpur plan formulae incorporated a grid-like structure in the outer areas of the city. This grid pattern served as a framework for future development and expansion, ensuring that new developments could be easily integrated into the existing road network.
The combination of the star and grid patterns in the Nagpur plan formulae provided a balance between efficient connectivity and future flexibility. It allowed for the growth and evolution of the city while maintaining a cohesive and well-planned urban environment.
In conclusion, the Nagpur plan formulae assumed a star and grid pattern, combining the strengths of both layouts to create a comprehensive and adaptable urban planning strategy for the city of Nagpur.
The Nagpur plan formulae were developed by architect Charles Correa for the city of Nagpur in India. These formulae aimed to provide a comprehensive and flexible approach to urban planning that could accommodate the rapid growth and changing needs of the city.
Star Pattern:
The star pattern refers to a layout in which major roads radiate outwards from a central point, like the spokes of a wheel. This pattern is often used in urban planning to create a well-connected and easily navigable road network. The Nagpur plan formulae assumed a star pattern as a basis for the city's road network.
Grid Pattern:
The grid pattern, on the other hand, refers to a layout in which streets intersect at right angles, forming a rectangular grid. This pattern is commonly used in urban planning to create a regular and organized street network. While the Nagpur plan formulae did not assume a grid pattern as the primary layout, it incorporated elements of both the star and grid patterns to create a hybrid approach.
Combination of Star and Grid:
The Nagpur plan formulae combined the star and grid patterns to create a unique urban planning strategy. The central area of the city was organized in a star pattern, with major roads radiating out from a central point. This allowed for efficient connectivity and easy access to key destinations within the city.
At the same time, the Nagpur plan formulae incorporated a grid-like structure in the outer areas of the city. This grid pattern served as a framework for future development and expansion, ensuring that new developments could be easily integrated into the existing road network.
The combination of the star and grid patterns in the Nagpur plan formulae provided a balance between efficient connectivity and future flexibility. It allowed for the growth and evolution of the city while maintaining a cohesive and well-planned urban environment.
In conclusion, the Nagpur plan formulae assumed a star and grid pattern, combining the strengths of both layouts to create a comprehensive and adaptable urban planning strategy for the city of Nagpur.
During the development of the roads maximum priority is given to which type of road?- a)National highway
- b)State highway
- c)Major district road
- d)Village road
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During the development of the roads maximum priority is given to which type of road?
a)
National highway
b)
State highway
c)
Major district road
d)
Village road

|
Gitanjali Menon answered |
The maximum priority during construction of any road is given to national highway as they connect across length and breadth of the entire country.
The arterial roads are a classification of which type of roads?- a)Rural roads
- b)Urban Rods
- c)National highway
- d)State highway
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The arterial roads are a classification of which type of roads?
a)
Rural roads
b)
Urban Rods
c)
National highway
d)
State highway

|
Anmol Menon answered |
Urban roads are classified into Arterial roads, Sub arterial roads, Collector streets and Local streets.
Select the correct statement.- a)Nagpur road plan formulae take into account the towns with very large population
- b)Nagpur road plan has a target road length of 32 km per 100 square km
- c)Second 20 year plan has provided 1600 km of expressways out of the proposed National highway
- d)Second 20 year plan allowed deduction of length of railway track in the area while calculating the length of roads
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement.
a)
Nagpur road plan formulae take into account the towns with very large population
b)
Nagpur road plan has a target road length of 32 km per 100 square km
c)
Second 20 year plan has provided 1600 km of expressways out of the proposed National highway
d)
Second 20 year plan allowed deduction of length of railway track in the area while calculating the length of roads
|
|
C.p Yadav answered |
B
The rectangular pattern of roads has been adopted in which Indian city?- a)New Delhi
- b)Chandigarh
- c)Hyderabad
- d)Mumbai
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The rectangular pattern of roads has been adopted in which Indian city?
a)
New Delhi
b)
Chandigarh
c)
Hyderabad
d)
Mumbai
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Chandigarh city was planned by assuming rectangular pattern. But by this pattern operation of traffic has been a problem.
The Nagpur plan conference was held in which year?- a)1941
- b)1942
- c)1943
- d)1947
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Nagpur plan conference was held in which year?
a)
1941
b)
1942
c)
1943
d)
1947

|
Manasa Sen answered |
The Nagpur plan conference was held in 1943 which was the first 20 year development plan. The main target of the plan was to achieve 16km road density per 100sq.km.
What was the development allowance assumed in the Nagpur plan?- a)10%
- b)20%
- c)15%
- d)25%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the development allowance assumed in the Nagpur plan?
a)
10%
b)
20%
c)
15%
d)
25%

|
Bhargavi Sarkar answered |
The development allowance was assumed as 15% and in this plan the length of the railway track also was deducted, this was not like the previous 20 year plan.
Expressways should be constructed along- a)Congested cities
- b)Major traffic corridors
- c)Along with highways
- d)Small cities
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Expressways should be constructed along
a)
Congested cities
b)
Major traffic corridors
c)
Along with highways
d)
Small cities

|
Deepika Saha answered |
Expressways should be constructed along major traffic corridors for convenience of passengers to travel safely and comfortably.
The highway research Board was set up in the year- a)1947
- b)1953
- c)1963
- d)1973
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The highway research Board was set up in the year
a)
1947
b)
1953
c)
1963
d)
1973

|
Yash Joshi answered |
The highway research board was set up in the year 1973 by IRC to give good guidance for road development in India.
Which type of roads can be utilized during monsoon?- a)Unpaved roads
- b)Gravel roads
- c)Fair weather roads
- d)Bituminous roads
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of roads can be utilized during monsoon?
a)
Unpaved roads
b)
Gravel roads
c)
Fair weather roads
d)
Bituminous roads

|
Harshad Iyer answered |
Bituminous roads are convenient to use compared to the other roads because they can easily drain off the water and are comfortable to use during rainy season.
The Nagpur plan classified the roads based on- a)Location
- b)Function
- c)Location and function
- d)Annual daily traffic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Nagpur plan classified the roads based on
a)
Location
b)
Function
c)
Location and function
d)
Annual daily traffic

|
Mira Sharma answered |
The Nagpur plan is a classification system for roads that was developed in Nagpur, India. It categorizes roads based on their location and function. The correct answer for this question is option 'C' which means that roads are classified based on both location and function.
Location and Function as Classification Criteria:
1. Location: The Nagpur plan considers the location of the road as one of the criteria for classification. The location refers to the area or region where the road is situated. This criterion takes into account the surrounding land use, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or rural areas. The location of the road can have a significant impact on its design, capacity, and traffic flow.
2. Function: The function of a road refers to its purpose or role within the transportation network. The Nagpur plan recognizes that different roads serve different functions and have varying levels of importance. For example, some roads may primarily serve as arterial routes, carrying high volumes of traffic between major destinations. Others may serve as local access roads, providing connectivity within neighborhoods or smaller areas.
Classification of Roads:
Based on the combination of location and function, the Nagpur plan classifies roads into different categories:
1. National Highways: These are major roads that connect different states or important cities within the country. They serve as the backbone of the national transportation network and cater to long-distance travel.
2. State Highways: These roads connect important cities and towns within a state. They serve as a link between national highways and district-level roads.
3. District Roads: District roads connect various parts of a district, including towns, villages, and other important locations. They provide connectivity within a specific administrative region.
4. Village Roads: Village roads connect rural areas and provide access to villages and agricultural land. These roads play a crucial role in rural development and transportation of agricultural produce.
5. Urban Roads: Urban roads are further classified based on their location and function within a city or town. They include arterial roads, sub-arterial roads, collector roads, local access roads, and other specialized roads like ring roads or bypasses.
The classification of roads based on location and function helps in planning and designing the road network, allocating resources, and managing traffic efficiently. It allows for a systematic approach to meet the diverse transportation needs of different areas and ensures that roads are designed and maintained appropriately.
Location and Function as Classification Criteria:
1. Location: The Nagpur plan considers the location of the road as one of the criteria for classification. The location refers to the area or region where the road is situated. This criterion takes into account the surrounding land use, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or rural areas. The location of the road can have a significant impact on its design, capacity, and traffic flow.
2. Function: The function of a road refers to its purpose or role within the transportation network. The Nagpur plan recognizes that different roads serve different functions and have varying levels of importance. For example, some roads may primarily serve as arterial routes, carrying high volumes of traffic between major destinations. Others may serve as local access roads, providing connectivity within neighborhoods or smaller areas.
Classification of Roads:
Based on the combination of location and function, the Nagpur plan classifies roads into different categories:
1. National Highways: These are major roads that connect different states or important cities within the country. They serve as the backbone of the national transportation network and cater to long-distance travel.
2. State Highways: These roads connect important cities and towns within a state. They serve as a link between national highways and district-level roads.
3. District Roads: District roads connect various parts of a district, including towns, villages, and other important locations. They provide connectivity within a specific administrative region.
4. Village Roads: Village roads connect rural areas and provide access to villages and agricultural land. These roads play a crucial role in rural development and transportation of agricultural produce.
5. Urban Roads: Urban roads are further classified based on their location and function within a city or town. They include arterial roads, sub-arterial roads, collector roads, local access roads, and other specialized roads like ring roads or bypasses.
The classification of roads based on location and function helps in planning and designing the road network, allocating resources, and managing traffic efficiently. It allows for a systematic approach to meet the diverse transportation needs of different areas and ensures that roads are designed and maintained appropriately.
The total area of a state is 2500km .calculate the length of MDR- a)100 km
- b)200 km
- c)300 km
- d)400 km
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The total area of a state is 2500km .calculate the length of MDR
a)
100 km
b)
200 km
c)
300 km
d)
400 km

|
Nidhi Patel answered |
Length of MDR=Area of the state/12.5=2500/12.5=200km.
The revenue from road transport sector is studied in which type of studies?- a)Economic
- b)Financial
- c)Traffic
- d)Engineering
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The revenue from road transport sector is studied in which type of studies?
a)
Economic
b)
Financial
c)
Traffic
d)
Engineering

|
Lekshmi Das answered |
The sources of income, excise duty, registration charges and tax all are studied in financial studies only.
The tertiary road system consists of- a)National highway
- b)State highway
- c)Major district road
- d)Other district road and village road
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The tertiary road system consists of
a)
National highway
b)
State highway
c)
Major district road
d)
Other district road and village road

|
Mira Mishra answered |
As per the 2nd 20 year road development plan the primary system consist of national highway and state highway. The secondary system consists of state highway .the tertiary system consists of other district road and village road.
The semiofficial body set up for controlling and standardization of roads and bridges in India is - a)Highway Research
- b)National Highways Act Committee
- c)Central Road Fund
- d)Indian Road congress
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The semiofficial body set up for controlling and standardization of roads and bridges in India is
a)
Highway Research
b)
National Highways Act Committee
c)
Central Road Fund
d)
Indian Road congress

|
Rashi Shah answered |
**Explanation:**
The semiofficial body set up for controlling and standardization of roads and bridges in India is the Indian Road Congress (IRC). The IRC is the premier technical body of highway engineers in the country and is responsible for the development and maintenance of the road infrastructure in India.
**Role and Functions of Indian Road Congress (IRC):**
1. **Standardization of Guidelines:** IRC formulates and standardizes the guidelines for the design, construction, and maintenance of roads, bridges, and other transportation infrastructure in India. These guidelines cover various aspects such as geometric design, pavement design, traffic engineering, and road safety.
2. **Publication of Codes and Manuals:** IRC publishes codes and manuals that serve as reference documents for highway engineers and professionals. These codes and manuals provide detailed specifications and guidelines for different aspects of road and bridge construction, helping ensure uniformity and quality in the infrastructure projects.
3. **Research and Development:** IRC conducts research and development activities to promote innovation and improvement in the field of highway engineering. It collaborates with various research institutions, universities, and industry experts to undertake research projects related to road and bridge engineering, materials, and technologies.
4. **Capacity Building:** IRC organizes training programs, workshops, and seminars to enhance the technical knowledge and skills of highway engineers and professionals. These capacity-building initiatives help disseminate the latest advancements and best practices in the field of road and bridge engineering.
5. **Policy Advocacy:** IRC works closely with the government and other stakeholders to provide technical inputs and recommendations for policy formulation related to road and bridge infrastructure. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that the road network in India is developed and maintained as per international standards and practices.
6. **Networking and Collaboration:** IRC facilitates networking and collaboration among highway engineers, professionals, and organizations involved in the road and bridge sector. It provides a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices through conferences, symposiums, and technical meetings.
In conclusion, the Indian Road Congress (IRC) is the semiofficial body responsible for controlling and standardizing roads and bridges in India. It plays a vital role in developing and maintaining the road infrastructure by formulating guidelines, publishing codes and manuals, conducting research, capacity building, policy advocacy, and facilitating networking and collaboration in the field of highway engineering.
The semiofficial body set up for controlling and standardization of roads and bridges in India is the Indian Road Congress (IRC). The IRC is the premier technical body of highway engineers in the country and is responsible for the development and maintenance of the road infrastructure in India.
**Role and Functions of Indian Road Congress (IRC):**
1. **Standardization of Guidelines:** IRC formulates and standardizes the guidelines for the design, construction, and maintenance of roads, bridges, and other transportation infrastructure in India. These guidelines cover various aspects such as geometric design, pavement design, traffic engineering, and road safety.
2. **Publication of Codes and Manuals:** IRC publishes codes and manuals that serve as reference documents for highway engineers and professionals. These codes and manuals provide detailed specifications and guidelines for different aspects of road and bridge construction, helping ensure uniformity and quality in the infrastructure projects.
3. **Research and Development:** IRC conducts research and development activities to promote innovation and improvement in the field of highway engineering. It collaborates with various research institutions, universities, and industry experts to undertake research projects related to road and bridge engineering, materials, and technologies.
4. **Capacity Building:** IRC organizes training programs, workshops, and seminars to enhance the technical knowledge and skills of highway engineers and professionals. These capacity-building initiatives help disseminate the latest advancements and best practices in the field of road and bridge engineering.
5. **Policy Advocacy:** IRC works closely with the government and other stakeholders to provide technical inputs and recommendations for policy formulation related to road and bridge infrastructure. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that the road network in India is developed and maintained as per international standards and practices.
6. **Networking and Collaboration:** IRC facilitates networking and collaboration among highway engineers, professionals, and organizations involved in the road and bridge sector. It provides a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices through conferences, symposiums, and technical meetings.
In conclusion, the Indian Road Congress (IRC) is the semiofficial body responsible for controlling and standardizing roads and bridges in India. It plays a vital role in developing and maintaining the road infrastructure by formulating guidelines, publishing codes and manuals, conducting research, capacity building, policy advocacy, and facilitating networking and collaboration in the field of highway engineering.
In India, in station yards a minimum gradient of 1 in 1000 is provided for- a)avoiding movement of standing wagons due to heavy wind blows
- b)easy starting of trains as minimum extra pull will be required for such gradients
- c)easy stopping of trains running at high speeds
- d)easy draining of water of station yards
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In India, in station yards a minimum gradient of 1 in 1000 is provided for
a)
avoiding movement of standing wagons due to heavy wind blows
b)
easy starting of trains as minimum extra pull will be required for such gradients
c)
easy stopping of trains running at high speeds
d)
easy draining of water of station yards

|
Crack Gate answered |
In India, station yards are designed with a minimum gradient of 1 in 1000 primarily for drainage purposes. This gradient ensures that rainwater and other water accumulation can easily drain away, preventing waterlogging and maintaining the operational efficiency of the station yard.
Correct Answer:
d) easy draining of water of station yards
d) easy draining of water of station yards
A train is hauled by 2-8-2 locomotive with 22.5 tonnes load on each driving axle. Assuming the coefficient of rail-wheel friction to be 0.25, what would be the hauling capacity of the locomotive?- a)15.0 tonnes
- b)22.5 tonnes
- c)45.0 tonnes
- d)90.0 tonnes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A train is hauled by 2-8-2 locomotive with 22.5 tonnes load on each driving axle. Assuming the coefficient of rail-wheel friction to be 0.25, what would be the hauling capacity of the locomotive?
a)
15.0 tonnes
b)
22.5 tonnes
c)
45.0 tonnes
d)
90.0 tonnes

|
Gate Funda answered |
Given: Type of Locomotive: 2-8-2
Load on each driving axle: 22.5 tonnes
Coefficient of rail-wheel friction: 0.25
Load on each driving axle: 22.5 tonnes
Coefficient of rail-wheel friction: 0.25
To find: Hauling capacity of the locomotive
Assumptions:
- The locomotive is moving on a level track.
- The weight of other parts of the train (like wagons) is negligible compared to the weight on the driving axles of the locomotive.
Formula: Hauling capacity = (Load per driving axle) x (Number of driving axles) x (Coefficient of friction)
Calculation: Load per driving axle = 22.5 tonnes
Number of driving axles = 4 (2 in front and 2 at the back)
Coefficient of friction = 0.25
Number of driving axles = 4 (2 in front and 2 at the back)
Coefficient of friction = 0.25
Hauling capacity = 22.5 x 4 x 0.25 = 22.5 tonnes
Therefore, the hauling capacity of the locomotive is 22.5 tonnes.
Explanation: The hauling capacity of a locomotive is the maximum load it can pull on a level track, without slipping or losing traction. The formula for hauling capacity takes into account the load on each driving axle, the number of driving axles, and the coefficient of friction between the rail and the wheel. In this case, the locomotive has 4 driving axles, each with a load of 22.5 tonnes, and the coefficient of friction is 0.25. Plugging these values into the formula gives the hauling capacity of the locomotive as 22.5 tonnes.
Chapter doubts & questions for Highway Development & Planning - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Highway Development & Planning - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg
488 videos|1261 docs|878 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









