All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg >
All Questions
All questions of Construction Materials & Management for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
Geologically marble is known asa)calcareous rock... moreb)argillaceous rockc)metamorpihic rockd)silicious rockCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Marble is geologically Metamorphic Rock (made from metamorphic action of sedimentary limestone).
Chemically marble is calcareous rock.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A stone is rejected if it absorbs water more than
- A:
5%
- B:
10%
- C:
15%
- D:
20%
The answer is b.
A stone is rejected if it absorbs water more than
5%
10%
15%
20%

|
Partho Jain answered |
Explanation:
When a stone absorbs water, it means that it is porous and can easily get damaged due to water absorption. Therefore, it is important to check the amount of water a stone can absorb before using it for construction purposes.
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that a stone is rejected if it absorbs water more than 10%. This means that if a stone absorbs more than 10% of its weight in water, it is not suitable for construction purposes.
Reasons for rejecting a stone with more than 10% water absorption:
1. Durability: Stones with high water absorption tend to have low durability as they can easily get damaged due to water absorption. This can lead to cracks, fissures, and other structural issues.
2. Weathering: Stones with high water absorption tend to weather faster than stones with low water absorption. This is because water can penetrate deep into the stone and cause damage over time.
3. Maintenance: Stones with high water absorption require more maintenance as they need to be protected from water damage. This can lead to higher maintenance costs over time.
4. Aesthetics: Stones with high water absorption tend to look dull and unattractive due to water damage. This can impact the overall aesthetics of the construction.
Therefore, it is important to check the water absorption capacity of stones before using them for construction purposes. Stones with water absorption more than 10% should be rejected as they can cause structural issues, higher maintenance costs, and impact the overall aesthetics of the construction.
When a stone absorbs water, it means that it is porous and can easily get damaged due to water absorption. Therefore, it is important to check the amount of water a stone can absorb before using it for construction purposes.
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that a stone is rejected if it absorbs water more than 10%. This means that if a stone absorbs more than 10% of its weight in water, it is not suitable for construction purposes.
Reasons for rejecting a stone with more than 10% water absorption:
1. Durability: Stones with high water absorption tend to have low durability as they can easily get damaged due to water absorption. This can lead to cracks, fissures, and other structural issues.
2. Weathering: Stones with high water absorption tend to weather faster than stones with low water absorption. This is because water can penetrate deep into the stone and cause damage over time.
3. Maintenance: Stones with high water absorption require more maintenance as they need to be protected from water damage. This can lead to higher maintenance costs over time.
4. Aesthetics: Stones with high water absorption tend to look dull and unattractive due to water damage. This can impact the overall aesthetics of the construction.
Therefore, it is important to check the water absorption capacity of stones before using them for construction purposes. Stones with water absorption more than 10% should be rejected as they can cause structural issues, higher maintenance costs, and impact the overall aesthetics of the construction.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:... moreThe size of mould for brick is generally keptA:a little large to specified sizeB:a little small to specified sizeC:equal to specified sizeD:10 % larger than specified sizeThe answer is a.
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
During drying process, it shrinks. That's why Mould kept a little large to specified size.
Modular bricks are of nominal size 20 * 10 * 10 cm and 20% of the volume is lost in mortar between joints. Then what is the number of modular bricks required per cubic meter of brickwork ?- a)520
- b)500
- c)485
- d)470
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Modular bricks are of nominal size 20 * 10 * 10 cm and 20% of the volume is lost in mortar between joints. Then what is the number of modular bricks required per cubic meter of brickwork ?
a)
520
b)
500
c)
485
d)
470

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Nominal size of modular brick = 20 x 10 x 10 cm
Actual size of modular brick = 19 x 9 x 9 cm
Mortar required for 1 m^3 brickwork


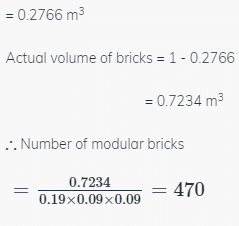
The main ingredient of a good quality brick earth, is
- a)magnesia
- b)lime
- c)silica
- d)aluminum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The main ingredient of a good quality brick earth, is
a)
magnesia
b)
lime
c)
silica
d)
aluminum
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Good brick earth should contain 50 – 60% of silica. It prevents cracking, shrinking, and wrapping of raw bricks. Silica imparts a uniform shape to the bricks. The excess of silica makes the bricks brittle..
Limestone is not a
- a)sedimentary rock
- b)stratified rock
- c)aqueous rock
- d)metamorphic rock
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Limestone is not a
a)
sedimentary rock
b)
stratified rock
c)
aqueous rock
d)
metamorphic rock
|
|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Limestone is not a metamorphic rock. Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed principally of calcium carbonate (calcite) or the double carbonate of calcium and magnesium (dolomite). It is commonly composed of tiny fossils, shell fragments and other fossilized debris.
Second class bricks- a)are of dark brown colours
- b)produce a metalic sound when struck
- c)are well burnt
- d)are under burnt
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Second class bricks
a)
are of dark brown colours
b)
produce a metalic sound when struck
c)
are well burnt
d)
are under burnt
|
|
Vikas Choudhury answered |
These are also fully burnt and give a clear ringing sound when struck together. Slightly irregularities in shape, size or color are accepted.
Its compressive strength shall not be less than 70 kg/cm2 and absorption value should not be greater than 22 percent when soaked for 24 hours in water.
Slight difference in the structure on fractured surfaces is admissible.
Use: For exterior work when plastering is to be done. And can also be used for interior works but they may not be used for flooring.
Note : under burnt brick is 3rd class brick.
Kaolin is chemically classified as
- a)metamorphic rock
- b)argillaceous rock
- c)calcareous rock
- d)silicious rock
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Kaolin is chemically classified as
a)
metamorphic rock
b)
argillaceous rock
c)
calcareous rock
d)
silicious rock

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Kaolin is a type of clay found in nature. It can also be made in a laboratory.
As main constituent is clay so it is argillaceous rock as argillaceous means made up of clay, and kaolin is a clay.
Stones used for ornamental work must be- a)soil
- b)hard
- c)light
- d)heavy
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stones used for ornamental work must be
a)
soil
b)
hard
c)
light
d)
heavy

|
Juhi Choudhary answered |
Stones Used for Ornamental Work Must be Soft
Stones have been used for ornamental work for centuries. However, not all types of stones are suitable for this purpose. Stones used for ornamental work must be soft. Let's understand why.
Properties of Stones Used for Ornamental Work
1. Workability: The stone used for ornamental work must be easy to work with. The stone must be soft enough to be easily carved, cut and polished.
2. Durability: The stone must be durable enough to withstand wear and tear. The ornamental work must be able to withstand the test of time.
3. Texture: The stone must have a fine texture. A fine texture makes it easier to carve intricate designs and patterns.
4. Color: The stone must have an attractive color. A stone with an attractive color makes the ornamental work more visually appealing.
Why Stones Used for Ornamental Work Must be Soft?
1. Workability: Soft stones are easier to carve, cut and polish. Hard stones are difficult to work with, and it takes a lot of effort and time to create intricate designs and patterns.
2. Texture: Soft stones have a finer texture than hard stones. A fine texture makes it easier to carve intricate designs and patterns.
3. Durability: Soft stones are not as durable as hard stones. However, ornamental work is not subjected to heavy wear and tear. Therefore, the durability of soft stones is sufficient for ornamental work.
4. Availability: Soft stones are more widely available than hard stones. This makes them more accessible and affordable.
Examples of Stones Used for Ornamental Work
1. Marble: Marble is a soft stone that is commonly used for ornamental work. It has a fine texture and an attractive color.
2. Soapstone: Soapstone is a soft stone that is easy to work with. It has a smooth texture and is available in a variety of colors.
3. Alabaster: Alabaster is a soft stone that is easy to carve. It has a fine texture and is available in a variety of colors.
Conclusion
Stones used for ornamental work must be soft. Soft stones are easier to work with and have a finer texture. They are not as durable as hard stones, but they are sufficient for ornamental work. Examples of soft stones used for ornamental work include marble, soapstone, and alabaster.
Stones have been used for ornamental work for centuries. However, not all types of stones are suitable for this purpose. Stones used for ornamental work must be soft. Let's understand why.
Properties of Stones Used for Ornamental Work
1. Workability: The stone used for ornamental work must be easy to work with. The stone must be soft enough to be easily carved, cut and polished.
2. Durability: The stone must be durable enough to withstand wear and tear. The ornamental work must be able to withstand the test of time.
3. Texture: The stone must have a fine texture. A fine texture makes it easier to carve intricate designs and patterns.
4. Color: The stone must have an attractive color. A stone with an attractive color makes the ornamental work more visually appealing.
Why Stones Used for Ornamental Work Must be Soft?
1. Workability: Soft stones are easier to carve, cut and polish. Hard stones are difficult to work with, and it takes a lot of effort and time to create intricate designs and patterns.
2. Texture: Soft stones have a finer texture than hard stones. A fine texture makes it easier to carve intricate designs and patterns.
3. Durability: Soft stones are not as durable as hard stones. However, ornamental work is not subjected to heavy wear and tear. Therefore, the durability of soft stones is sufficient for ornamental work.
4. Availability: Soft stones are more widely available than hard stones. This makes them more accessible and affordable.
Examples of Stones Used for Ornamental Work
1. Marble: Marble is a soft stone that is commonly used for ornamental work. It has a fine texture and an attractive color.
2. Soapstone: Soapstone is a soft stone that is easy to work with. It has a smooth texture and is available in a variety of colors.
3. Alabaster: Alabaster is a soft stone that is easy to carve. It has a fine texture and is available in a variety of colors.
Conclusion
Stones used for ornamental work must be soft. Soft stones are easier to work with and have a finer texture. They are not as durable as hard stones, but they are sufficient for ornamental work. Examples of soft stones used for ornamental work include marble, soapstone, and alabaster.
The standard size of masonry bricks, is- a)18 cm × 8 cm × 8cm
- b)19 cm × 9 cm × 8cm
- c)20 cm × 10 cm × 10cm
- d)21 cm × 11 cm × 11cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard size of masonry bricks, is
a)
18 cm × 8 cm × 8cm
b)
19 cm × 9 cm × 8cm
c)
20 cm × 10 cm × 10cm
d)
21 cm × 11 cm × 11cm

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
For India, a brick of standard size 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm is recommended by the BIS. With mortar thickness, the size of such a brick becomes 200 mm x 100 mm x 100 mm and it is known as the nominal size of the modular brick. Thus the nominal size of brick includes the mortar thickness. (1 cm = 10 mm)
A good quality stone absorbs water less than- a)5%
- b)10%
- c)15%
- d)20%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A good quality stone absorbs water less than
a)
5%
b)
10%
c)
15%
d)
20%

|
Puja Sharma answered |
Properties of a Good Quality Stone
Water Absorption
Water absorption is one of the most important properties of a good quality stone. A good quality stone should absorb a minimal amount of water.
Options Given
a)5%
b)10%
c)15%
d)20%
Correct answer
Option 'A' (5%) is the correct answer as a good quality stone should absorb water less than 5%.
Explanation
When a stone has a high water absorption rate, it can lead to various problems such as:
- Reduced durability: The stone may start to break down or decay over time due to the presence of water.
- Staining: The stone may absorb water that contains impurities or chemicals, leading to stains and discoloration.
- Cracking: When a stone absorbs water and then freezes, it can cause the stone to crack due to the expansion of the water.
Therefore, it is important to choose a stone with a low water absorption rate to ensure its durability and longevity. A good quality stone should absorb water less than 5%.
Water Absorption
Water absorption is one of the most important properties of a good quality stone. A good quality stone should absorb a minimal amount of water.
Options Given
a)5%
b)10%
c)15%
d)20%
Correct answer
Option 'A' (5%) is the correct answer as a good quality stone should absorb water less than 5%.
Explanation
When a stone has a high water absorption rate, it can lead to various problems such as:
- Reduced durability: The stone may start to break down or decay over time due to the presence of water.
- Staining: The stone may absorb water that contains impurities or chemicals, leading to stains and discoloration.
- Cracking: When a stone absorbs water and then freezes, it can cause the stone to crack due to the expansion of the water.
Therefore, it is important to choose a stone with a low water absorption rate to ensure its durability and longevity. A good quality stone should absorb water less than 5%.
Good quality stones must- a)be durable
- b)be free from clay
- c)resist action of acids
- d)all the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Good quality stones must
a)
be durable
b)
be free from clay
c)
resist action of acids
d)
all the above

|
Swara Dasgupta answered |
The following are the requirements of good building stones:
(i) Strength: The stone should be able to resist the load coming on it. Ordinarilly this is not of
primary concern since all stones are having good strength. However in case of large structure, it may be necessary to check the strength.
(ii) Durability: Stones selected should be capable of resisting adverse effects of natural forces
like wind, rain and heat.
(iii) Hardness: The stone used in floors and pavements should be able to resist abrasive forces
caused by movement of men and materials over them.
(iv) Toughness: Building stones should be tough enough to sustain stresses developed due to vibrations. The vibrations may be due to the machinery mounted over them or due to the loads moving over them. The stone aggregates used in the road constructions should be tough.
(v) Specific Gravity: Heavier variety of stones should be used for the construction of dams,
retaining walls, docks and harbours. The specific gravity of good building stone is between 2.4 and 2.8.
(vi) Porosity and Absorption: Building stone should not be porous. If it is porous rain water enters into the pour and reacts with stone and crumbles it. In higher altitudes, the freezing of water in pores takes place and it results into the disintegration of the stone.
(vii) Dressing: Giving required shape to the stone is called dressing. It should be easy to dress so that the cost of dressing is reduced. However the care should be taken so that, this is not be at the cost of the required strength and the durability.
(viii) Appearance: In case of the stones to be used for face works, where appearance is a primary requirement, its colour and ability to receive polish is an important factor.
(ix) Seasoning: Good stones should be free from the quarry sap. Laterite stones should not be used for 6 to 12 months after quarrying. They are allowed to get rid of quarry sap by the action of nature. This process of removing quarry sap is called seasoning.
(x) Cost: Cost is an important consideration in selecting a building material. Proximity of the quarry to building site brings down the cost of transportation and hence the cost of stones comes down.
The rocks formed by gradual deposition, are called
- a)sedimentary rocks
- b)igneous rocks
- c)metamorphic rocks
- d)none of these.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The rocks formed by gradual deposition, are called
a)
sedimentary rocks
b)
igneous rocks
c)
metamorphic rocks
d)
none of these.

|
Bhagirath Jalwaniya answered |
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock types, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". ... The protolith may be a sedimentary, igneous, or existing metamorphic rock.Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface.
A 1st class brick immersed in water for 24 hours, should not absorb water (by weight) more than
- a)10%
- b)20%
- c)15%
- d)25%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 1st class brick immersed in water for 24 hours, should not absorb water (by weight) more than
a)
10%
b)
20%
c)
15%
d)
25%

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
Water absorption should be 12-15% of its dry weight when immersed in cold water for 24 hours. The crushing strength of the brick should not be less than 10 N/mm2. This limit varies with different Government organizations around the country.
A bull nose brick is not used for- a)rounding off sharp corners
- b)pillars
- c)decoration purpose
- d)arches
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A bull nose brick is not used for
a)
rounding off sharp corners
b)
pillars
c)
decoration purpose
d)
arches

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
CORRECT OPTION IS D Because bullnose brick in arches only one side will be rounded leading to the unaesthetic structure.
The softest rock is- a)marble
- b)diamond
- c)talc
- d)quartz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The softest rock is
a)
marble
b)
diamond
c)
talc
d)
quartz

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
mineral talc
I guess the honor for the softest crystal will have to go to the mineral talc, which has a hardness of one (1) on the Mohs Hardness Scale. Talc is a silicate (like many of the earth's most important minerals), and contains magnesium and a bit of water along with the silica and oxygen.
The rock generally used for roofing, is
- a)granite
- b)basalt
- c)slate
- d)pumice
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The rock generally used for roofing, is
a)
granite
b)
basalt
c)
slate
d)
pumice

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
Slate can be made into roofing slates, which are installed by a Slater. And, are a type of roof shingle, or more specifically a type of roof tile. Slate has two lines of break ability "Cleavage and grain" which make it possible to split the stone into thin sheets. When broken, slate retains a natural appearance while remaining relatively flat and easy to stack.
Clay and silt content in a good brick earth must be at least- a)50%
- b)40%
- c)30%
- d)25%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Clay and silt content in a good brick earth must be at least
a)
50%
b)
40%
c)
30%
d)
25%
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Silica (sand) " 50% to 60% by weight.
Alumina (clay) " 20% to 30% by weight.
Lime " 2 to 5% by weight.
Iron oxide "7% by weight.
Magnesia " less than 1% by weight.
Laterite is a/an- a)volcanic rock
- b)argillaceour rock
- c)calcareour rock
- d)silicious rock
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Laterite is a/an
a)
volcanic rock
b)
argillaceour rock
c)
calcareour rock
d)
silicious rock

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Laterite is a soil and rock type rich in iron and aluminium, and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and prolonged weathering of the underlying parent rock.
In stone masonry, if stones are so placed that their layers are parallel to the direction of load, they- a)split easily
- b)are affected by moisture
- c)both (A) and (B)
- d)none of these.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In stone masonry, if stones are so placed that their layers are parallel to the direction of load, they
a)
split easily
b)
are affected by moisture
c)
both (A) and (B)
d)
none of these.

|
Arnab Saini answered |
Stone masonry and its properties:
Stone masonry is the process of building structures using individual stones. Stones used in masonry construction have natural features such as grain, texture, color, and durability.
Parallel placement of stone layers:
When stones are placed parallel to the direction of load, they become vulnerable to splitting and moisture penetration. This is because the load, which is the weight or pressure that the structure is subjected to, is not distributed evenly across the stone layers. Instead, the weight of the structure is concentrated on individual stones or layers, causing them to split easily.
Effects of moisture:
Moisture penetration in stone masonry can lead to several problems. Moisture can cause stones to expand, contract, or crack, leading to structural damage. Moisture can also cause the growth of mold, mildew, and other bacteria, which can weaken the stone and cause it to deteriorate over time.
Conclusion:
In summary, stones placed parallel to the direction of load are more susceptible to splitting and moisture penetration, which can lead to structural damage and deterioration. Therefore, it is important to ensure that stones are placed perpendicular to the direction of load and that proper measures are taken to prevent moisture penetration.
Stone masonry is the process of building structures using individual stones. Stones used in masonry construction have natural features such as grain, texture, color, and durability.
Parallel placement of stone layers:
When stones are placed parallel to the direction of load, they become vulnerable to splitting and moisture penetration. This is because the load, which is the weight or pressure that the structure is subjected to, is not distributed evenly across the stone layers. Instead, the weight of the structure is concentrated on individual stones or layers, causing them to split easily.
Effects of moisture:
Moisture penetration in stone masonry can lead to several problems. Moisture can cause stones to expand, contract, or crack, leading to structural damage. Moisture can also cause the growth of mold, mildew, and other bacteria, which can weaken the stone and cause it to deteriorate over time.
Conclusion:
In summary, stones placed parallel to the direction of load are more susceptible to splitting and moisture penetration, which can lead to structural damage and deterioration. Therefore, it is important to ensure that stones are placed perpendicular to the direction of load and that proper measures are taken to prevent moisture penetration.
Chemically, marble is known as- a)metamorphic rock
- b)argillaceous rock
- c)calcareous rock
- d)silicious rock
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Chemically, marble is known as
a)
metamorphic rock
b)
argillaceous rock
c)
calcareous rock
d)
silicious rock
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated, although there are exceptions. In geology, the term "marble" refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone.Chemically, marble is known as calcareous rock.
Pegmatite is a/an
- a)intrusive igneous rock
- b)extrusive igneous rock
- c)sedimentary rock
- d)metamorphic rock
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pegmatite is a/an
a)
intrusive igneous rock
b)
extrusive igneous rock
c)
sedimentary rock
d)
metamorphic rock

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Pegmatite is an intrusive igneous rock with extremely large crystals sometimes greater than 10cm. Pegmatites are usually composed of feldspars, quartz and micas but may also contain minerals such as tourmaline (a silicate mineral that contains boron).
In stone masonry, stones (stratified rocks) are so placed that the direction of pressure to the plane of bedding is- a)right angles
- b)45°
- c)60°
- d)parallel
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In stone masonry, stones (stratified rocks) are so placed that the direction of pressure to the plane of bedding is
a)
right angles
b)
45°
c)
60°
d)
parallel

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
Stratified rocks are weaker when we put force parallel to the stratified layer of rocks it makes the rock break in parallel layer, however when we apply force perpendicular to the stratified layer of rock, it dose not break because it has numerous thin layer in that direction.
Stratified means naturally combination of parallel sheet of rocks due to metamorphic action, however we usually avoid stratified rocks for load bearing structure, instead we use non stratified rocks for load bearing structure.
Basalt is
- a)sedimentary rock
- b)metamorphic rock
- c)extrusive igneous rock
- d)intrusive igneous rock
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Basalt is
a)
sedimentary rock
b)
metamorphic rock
c)
extrusive igneous rock
d)
intrusive igneous rock

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Extrusive igneous rocks erupt onto the surface, where they cool quickly to form small crystals. Some cool so quickly that they form an amorphous glass. These rocks include andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria, and tuff.
Consider the following statements:
The critical path in a network plan of a project
1. helps in planning efficient time schedule
2. indicates the shortest path in time
3. helps in crashing the project judiciously
4. helps in encouraging-discipline in execution
Which of these statements are correct?
- a)1, 3 and 4
- b)1, 2, 3 and 4
- c)1 and 4
- d)2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
The critical path in a network plan of a project
1. helps in planning efficient time schedule
2. indicates the shortest path in time
3. helps in crashing the project judiciously
4. helps in encouraging-discipline in execution
Which of these statements are correct?
The critical path in a network plan of a project
1. helps in planning efficient time schedule
2. indicates the shortest path in time
3. helps in crashing the project judiciously
4. helps in encouraging-discipline in execution
Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1, 3 and 4
b)
1, 2, 3 and 4
c)
1 and 4
d)
2 and 3
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
-
Helps in planning efficient time schedule:
- The critical path method (CPM) is used to identify the longest sequence of tasks in a project that must be completed on time for the project to be finished by its deadline. Knowing the critical path helps in planning an efficient time schedule by focusing on these critical tasks.
-
Indicates the shortest path in time:
- This statement is incorrect. The critical path actually represents the longest path through the project, not the shortest. It determines the minimum project duration by identifying the sequence of dependent tasks that have the longest total duration.
-
Helps in crashing the project judiciously:
- Crashing a project involves adding resources to critical path tasks to complete them more quickly, thus reducing the project duration. Identifying the critical path is crucial for effective crashing, as only tasks on the critical path will affect the overall project completion time.
-
Helps in encouraging discipline in execution:
- By highlighting the tasks that cannot be delayed without affecting the project completion date, the critical path helps enforce discipline in execution. Project managers and team members can focus their attention on critical tasks to ensure they stay on track.
Therefore, the correct answer is: 1, 3 and 4
The presence of original rounded surface on the manufactured piece of timber, is called- a)Wane
- b)Torn grain
- c)Diagonal grain
- d)Chipmark.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The presence of original rounded surface on the manufactured piece of timber, is called
a)
Wane
b)
Torn grain
c)
Diagonal grain
d)
Chipmark.
|
|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
TYPES OF DEFECTS IN TIMBER: DEFECTS DUE TO CONVERSION
During the process of converting timber to commercial form, the following defects may occur.
1. Chip mark: mark or sign placed by chip on finished surface of timber
2. Diagonal grain: Due to improper sawing of timber
3. Torn grain: Due to falling of tool small impression is formed
4. Wane: Presence of original rounded surface on the manufactured piece of timber
Dolomite is a lime stone which contains carbonate of magnesia upto
- a)15%
- b)20%
- c)25%
- d)45%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dolomite is a lime stone which contains carbonate of magnesia upto
a)
15%
b)
20%
c)
25%
d)
45%

|
Ishani Basu answered |
Limestone Composition
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It forms from the accumulation of shells, coral, and other organic remains over millions of years. However, limestone can also contain other minerals and compounds that contribute to its composition.
Dolomite Composition
Dolomite is a type of limestone that contains a high concentration of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) as well as calcium carbonate. The chemical formula for dolomite is CaMg(CO3)2, indicating that it contains one calcium atom, one magnesium atom, and two carbonate ions.
Dolomite Percentage of Carbonate of Magnesia
The percentage of carbonate of magnesia in dolomite can vary depending on the specific composition of the rock. However, dolomite typically contains between 45% and 50% carbonate of magnesia. This means that for every 100 grams of dolomite, approximately 45 to 50 grams will be magnesium carbonate.
Correct Answer
In the given options, the correct answer is option 'D', which states that dolomite contains carbonate of magnesia up to 45%. This aligns with the typical composition range of dolomite.
Importance of Dolomite
Dolomite is an important rock in various industries due to its unique properties. It is commonly used as a construction and building material, as it can be easily crushed and shaped. Additionally, dolomite is used in the production of cement, glass, ceramics, and fertilizers.
Conclusion
Dolomite is a type of limestone that contains a significant percentage of carbonate of magnesia. It is commonly found in nature and has various industrial applications. The correct answer for the percentage of carbonate of magnesia in dolomite is option 'D', which states that it can be up to 45%.
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It forms from the accumulation of shells, coral, and other organic remains over millions of years. However, limestone can also contain other minerals and compounds that contribute to its composition.
Dolomite Composition
Dolomite is a type of limestone that contains a high concentration of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) as well as calcium carbonate. The chemical formula for dolomite is CaMg(CO3)2, indicating that it contains one calcium atom, one magnesium atom, and two carbonate ions.
Dolomite Percentage of Carbonate of Magnesia
The percentage of carbonate of magnesia in dolomite can vary depending on the specific composition of the rock. However, dolomite typically contains between 45% and 50% carbonate of magnesia. This means that for every 100 grams of dolomite, approximately 45 to 50 grams will be magnesium carbonate.
Correct Answer
In the given options, the correct answer is option 'D', which states that dolomite contains carbonate of magnesia up to 45%. This aligns with the typical composition range of dolomite.
Importance of Dolomite
Dolomite is an important rock in various industries due to its unique properties. It is commonly used as a construction and building material, as it can be easily crushed and shaped. Additionally, dolomite is used in the production of cement, glass, ceramics, and fertilizers.
Conclusion
Dolomite is a type of limestone that contains a significant percentage of carbonate of magnesia. It is commonly found in nature and has various industrial applications. The correct answer for the percentage of carbonate of magnesia in dolomite is option 'D', which states that it can be up to 45%.
For one cubic metre of brick masonry, number of bricks required, is- a)400
- b)425
- c)450
- d)500
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For one cubic metre of brick masonry, number of bricks required, is
a)
400
b)
425
c)
450
d)
500

|
Ashwin Gupta answered |
Number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry
To calculate the number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry, we need to consider the following factors:
1. Size of brick: The standard size of a brick is 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm.
2. Size of mortar joint: The standard size of a mortar joint is 10 mm.
3. Volume of one brick: The volume of one brick can be calculated as follows:
Volume of one brick = Length x Breadth x Height
= 0.19 m x 0.09 m x 0.09 m
= 0.001539 m^3
4. Volume of one brick with mortar joint: The volume of one brick with mortar joint can be calculated as follows:
Volume of one brick with mortar joint = (Length + Thickness of mortar joint) x (Breadth + Thickness of mortar joint) x Height
= (0.19 m + 0.01 m) x (0.09 m + 0.01 m) x 0.09 m
= 0.00198 m^3
5. Volume of one cubic metre of brick masonry: One cubic metre of brick masonry consists of 500 bricks and 0.3 cubic metres of mortar.
Volume of one cubic metre of brick masonry = (500 x 0.00198 m^3) + 0.3 m^3
= 0.99 m^3
6. Number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry: The number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry can be calculated as follows:
Number of bricks required = Volume of one cubic metre of brick masonry / Volume of one brick with mortar joint
= 0.99 m^3 / 0.00198 m^3
= 500
Therefore, the correct option is D, i.e., 500 bricks are required for one cubic metre of brick masonry.
To calculate the number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry, we need to consider the following factors:
1. Size of brick: The standard size of a brick is 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm.
2. Size of mortar joint: The standard size of a mortar joint is 10 mm.
3. Volume of one brick: The volume of one brick can be calculated as follows:
Volume of one brick = Length x Breadth x Height
= 0.19 m x 0.09 m x 0.09 m
= 0.001539 m^3
4. Volume of one brick with mortar joint: The volume of one brick with mortar joint can be calculated as follows:
Volume of one brick with mortar joint = (Length + Thickness of mortar joint) x (Breadth + Thickness of mortar joint) x Height
= (0.19 m + 0.01 m) x (0.09 m + 0.01 m) x 0.09 m
= 0.00198 m^3
5. Volume of one cubic metre of brick masonry: One cubic metre of brick masonry consists of 500 bricks and 0.3 cubic metres of mortar.
Volume of one cubic metre of brick masonry = (500 x 0.00198 m^3) + 0.3 m^3
= 0.99 m^3
6. Number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry: The number of bricks required for one cubic metre of brick masonry can be calculated as follows:
Number of bricks required = Volume of one cubic metre of brick masonry / Volume of one brick with mortar joint
= 0.99 m^3 / 0.00198 m^3
= 500
Therefore, the correct option is D, i.e., 500 bricks are required for one cubic metre of brick masonry.
The tendency of a stone is, to split along- a)texture
- b)fracture
- c)cleavage
- d)structure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The tendency of a stone is, to split along
a)
texture
b)
fracture
c)
cleavage
d)
structure
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
Cleavage - The tendency of a mineral to break along flat planar surfaces as determined by the structure of its crystal lattice.
jumb brick are- a)under burnt
- b)over burnt
- c)kutcha
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
jumb brick are
a)
under burnt
b)
over burnt
c)
kutcha
d)
none of these

|
Aditya Jain answered |
Explanation:
Jhumb bricks are a type of bricks which are traditionally made in India by hand-molding clay with the use of water and then drying them in the sun. These bricks are often used in rural areas for constructing houses and other buildings. However, the quality of these bricks can vary depending on the skill of the maker and the conditions in which they are fired.
Option B is the correct answer because jhumb bricks are often over-burnt, meaning that they are fired at too high a temperature for too long, causing them to become brittle and prone to cracking. This can result in a lower quality brick which is not suitable for construction.
Other options:
A) Under-burnt: Jhumb bricks can also be under-burnt, meaning that they are not fired at a high enough temperature for long enough. This can result in a brick which is too soft and weak to be used for construction.
C) Kutcha: Kutcha is a term used to describe building materials which are not permanent, such as mud or straw. Jhumb bricks are not considered kutcha as they are a permanent building material.
D) None of these: This is incorrect as option B is the correct answer.
Jhumb bricks are a type of bricks which are traditionally made in India by hand-molding clay with the use of water and then drying them in the sun. These bricks are often used in rural areas for constructing houses and other buildings. However, the quality of these bricks can vary depending on the skill of the maker and the conditions in which they are fired.
Option B is the correct answer because jhumb bricks are often over-burnt, meaning that they are fired at too high a temperature for too long, causing them to become brittle and prone to cracking. This can result in a lower quality brick which is not suitable for construction.
Other options:
A) Under-burnt: Jhumb bricks can also be under-burnt, meaning that they are not fired at a high enough temperature for long enough. This can result in a brick which is too soft and weak to be used for construction.
C) Kutcha: Kutcha is a term used to describe building materials which are not permanent, such as mud or straw. Jhumb bricks are not considered kutcha as they are a permanent building material.
D) None of these: This is incorrect as option B is the correct answer.
The frog of a brick is normally made on its- a)top face
- b)bottom face
- c)longer face
- d)shorter side
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The frog of a brick is normally made on its
a)
top face
b)
bottom face
c)
longer face
d)
shorter side

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
Frog is a depression made on the face of bricks during moulding.
Functions served by frog in bricks are:
The mortar accumulated in the frog forms a very good key for subsequent course of brick above it.
Manufacturers generally engrave their trade name in the frog which is a very good advertisement for the manufacturer.
Consider the following statements regarding AON diagram:
1. Each activity is represented by a circle.
2. The successor of the activity is connected by a directed arrow.
3. The number of the activity and the amount of time required for its completion are inserted in the job node.
4. An AON network contains a node for the start and a node for a finish of the project.Which of these statements are correct?- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1,3 and 4
- d)1,2, and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding AON diagram:
1. Each activity is represented by a circle.
2. The successor of the activity is connected by a directed arrow.
3. The number of the activity and the amount of time required for its completion are inserted in the job node.
4. An AON network contains a node for the start and a node for a finish of the project.
1. Each activity is represented by a circle.
2. The successor of the activity is connected by a directed arrow.
3. The number of the activity and the amount of time required for its completion are inserted in the job node.
4. An AON network contains a node for the start and a node for a finish of the project.
Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1,3 and 4
d)
1,2, and 4

|
Constructing Careers answered |
Activity 'G'
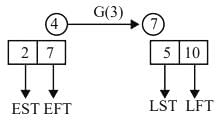
LFT of activity 'G' = 10 hours
The rocks which are formed due to cooling of magma at a considerable depth from earth's surface are called- a)Plutonic rocks
- b)Hypabyssal rocks
- c)Volcanic rocks
- d)Igneous rocks.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The rocks which are formed due to cooling of magma at a considerable depth from earth's surface are called
a)
Plutonic rocks
b)
Hypabyssal rocks
c)
Volcanic rocks
d)
Igneous rocks.
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Plutonic rocks are the igneous rocks formed at considerable depths, generally between 7-10 km below the surface of the earth. Explanation: Because of a very slow rate of cooling at the depths, the rocks resulting from magma are coarse grained.
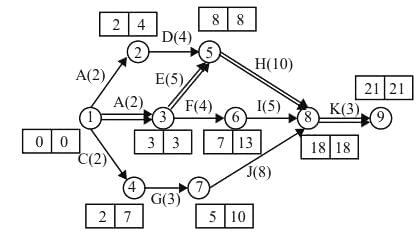
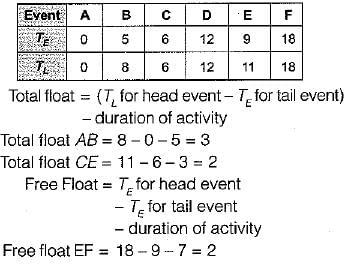
A network of seven activities is shown in the diagram given above. The respective activity durations are shown beside the arrows. Which one of the following is the total float in AB, the total float in CE and free float in EF, respectively?
- a)2, 2, 3
- b)3, 3, 2
- c)3, 2, 2
- d)2, 3, 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A network of seven activities is shown in the diagram given above. The respective activity durations are shown beside the arrows. Which one of the following is the total float in AB, the total float in CE and free float in EF, respectively?


a)
2, 2, 3
b)
3, 3, 2
c)
3, 2, 2
d)
2, 3, 2

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Solving the network will give earliest occurrence time (TE) and latest finish time (TL) as below:

The minimum compressive strength of Ist class bricks should be- a)75 kg/cm2
- b)90 kg/cm2
- c)100 kg/ cm2
- d)120 kg/cm2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum compressive strength of Ist class bricks should be
a)
75 kg/cm2
b)
90 kg/cm2
c)
100 kg/ cm2
d)
120 kg/cm2
|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
The minimum crushing / compressive strengths of burnt bricks tested flat-wise prescribed are:
(i) Common building bricks—35 kg/sq. cm,
(ii) Second class bricks—70 kg/sq. cm,
(iii) First class bricks— 100-105 kg/sq. cm.
The colour of statuary marble used for sculptor’s work is- a)red
- b)blue
- c)white
- d)green
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The colour of statuary marble used for sculptor’s work is
a)
red
b)
blue
c)
white
d)
green
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
White Statuary Marble is the most precious and sought-after marble in the World and it has always been prefered by the artists and especially sculptors for their masterpieces. Known worldwide, white statuary marble has been employed since ancient times in sculpture, being much appreciated for its shininess, gleam and compact structure, characteristics that make it particularly suitable for being carved with the cold chisel. Incredibly luxurious are the floors, fireplaces, interior design elements and special design fittings in which Statuary was used. All the objects made using statuary marble guarantee the visual and aestetic luxury of all the spaces in a property; Statuary Marble is the natural stone that best expresses the beauty of the Italian Apuan Alps. A type of marble that belongs to the category of the statuary marbles is the one called veined statuary marble that is white with important grey veins, very much used in interior design projects. Veined Statuary Marble can be combined with a lot of other types of other marbles as the black ones, pink, green marbles or red ones, creating beautiful lights and shadows effects, unforgettable chromatic themes. Thanks to the beauty of the Apuan Alps and Furrer’s extensive tradition in statuary marble processing, many important projects come to life.It’s the attention to every single detail that distinguishes Furrer’s works. The experience and professionalism of Furrer’s skilled engineers and the quality of our natural stones makes us stand out in each and every project.
In a CPM network the activity is non critical if- a)EST = LST & EFT = LFT
- b)EST < LST & EFT < LFT
- c)EST > LST & EFT > LFT
- d)EST < LST & EFT > LFT
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a CPM network the activity is non critical if
a)
EST = LST & EFT = LFT
b)
EST < LST & EFT < LFT
c)
EST > LST & EFT > LFT
d)
EST < LST & EFT > LFT

|
Divya Mehta answered |
B)EST < lst="" />
c)EST > LST
d)None of the above
Answer: b) EST < />
Explanation: In a CPM network, EST (Earliest Start Time) is the earliest possible time an activity can start and LST (Latest Start Time) is the latest possible time an activity can start without delaying the project completion time. If EST is less than LST, it means the activity can start earlier than its latest start time without affecting the project completion time, hence the activity is non-critical. If EST is equal to LST, it means the activity is critical as any delay in its start time will delay the project completion time. If EST is greater than LST, it is not possible for the activity to start within the project timeline, hence it is not a valid scenario. Therefore, the correct answer is EST < lst.="" />
c)EST > LST
d)None of the above
Answer: b) EST < />
Explanation: In a CPM network, EST (Earliest Start Time) is the earliest possible time an activity can start and LST (Latest Start Time) is the latest possible time an activity can start without delaying the project completion time. If EST is less than LST, it means the activity can start earlier than its latest start time without affecting the project completion time, hence the activity is non-critical. If EST is equal to LST, it means the activity is critical as any delay in its start time will delay the project completion time. If EST is greater than LST, it is not possible for the activity to start within the project timeline, hence it is not a valid scenario. Therefore, the correct answer is EST < lst.="" />
In arches, stratified stones are placed so that their lanes are- a)parallel
- b)perpendicular
- c)radial
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In arches, stratified stones are placed so that their lanes are
a)
parallel
b)
perpendicular
c)
radial
d)
none of these

|
Srestha Datta answered |
Arches are architectural structures that rely on the placement of carefully arranged stones to support weight and distribute stress. The stones are typically arranged in a specific pattern to help maintain the structure's stability and durability. One of the key characteristics of arches is the placement of stratified stones in a radial pattern.
Radial Placement of Stratified Stones
- The term "stratified stones" refers to stones that have been cut or shaped to fit together in a particular pattern.
- In an arch, these stones are typically placed in a radial pattern, meaning that they fan out from the center of the arch.
- This pattern helps to evenly distribute weight and stress across the entire structure, which is important for maintaining stability and preventing collapse.
- The stones are often arranged in a series of concentric rings, with each ring made up of stones that are slightly smaller than the ones below it.
Benefits of Radial Placement
- One of the main benefits of placing stratified stones in a radial pattern is that it helps to distribute weight and stress evenly across the arch.
- This can help to prevent the arch from collapsing or sagging under the weight of the structure above it.
- Additionally, the radial pattern can help to create a more visually appealing structure, as the stones are arranged in a symmetrical pattern that draws the eye inward toward the center of the arch.
Conclusion
Overall, the radial placement of stratified stones is an important feature of arches, helping to ensure their stability and durability over time. This pattern of stone placement is carefully designed to evenly distribute weight and stress, while also creating a visually appealing structure.
Radial Placement of Stratified Stones
- The term "stratified stones" refers to stones that have been cut or shaped to fit together in a particular pattern.
- In an arch, these stones are typically placed in a radial pattern, meaning that they fan out from the center of the arch.
- This pattern helps to evenly distribute weight and stress across the entire structure, which is important for maintaining stability and preventing collapse.
- The stones are often arranged in a series of concentric rings, with each ring made up of stones that are slightly smaller than the ones below it.
Benefits of Radial Placement
- One of the main benefits of placing stratified stones in a radial pattern is that it helps to distribute weight and stress evenly across the arch.
- This can help to prevent the arch from collapsing or sagging under the weight of the structure above it.
- Additionally, the radial pattern can help to create a more visually appealing structure, as the stones are arranged in a symmetrical pattern that draws the eye inward toward the center of the arch.
Conclusion
Overall, the radial placement of stratified stones is an important feature of arches, helping to ensure their stability and durability over time. This pattern of stone placement is carefully designed to evenly distribute weight and stress, while also creating a visually appealing structure.
Stones used for the construction of retaining walls must be- a)soft
- b)hard
- c)light
- d)heavy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stones used for the construction of retaining walls must be
a)
soft
b)
hard
c)
light
d)
heavy

|
Sakshi Basak answered |
Why do retaining walls need heavy stones?
Retaining walls are structures that are built to hold back soil and prevent it from eroding, sliding or collapsing. These walls are typically constructed using a variety of materials, including concrete, wood, steel, and stones. However, when it comes to the stones used for retaining walls, they must be heavy.
Here are some reasons why retaining walls need heavy stones:
1. Stability: Retaining walls need to be able to withstand the weight of the soil that they are holding back. If the stones used for the wall are too light, they may not be able to provide the necessary stability to keep the wall from collapsing.
2. Durability: Retaining walls are typically built to last for decades, if not centuries. Stones that are too soft or too light may deteriorate over time, which could compromise the structural integrity of the wall.
3. Aesthetics: Retaining walls are often built for both functional and aesthetic purposes. Heavy stones can be used to create a more visually appealing wall, as they provide a more natural and organic look.
4. Availability: Heavy stones are often readily available in many areas, making them a practical choice for retaining wall construction.
In summary, heavy stones are necessary for the construction of retaining walls because they provide the stability, durability, and aesthetics required for these structures to be effective and long-lasting.
Retaining walls are structures that are built to hold back soil and prevent it from eroding, sliding or collapsing. These walls are typically constructed using a variety of materials, including concrete, wood, steel, and stones. However, when it comes to the stones used for retaining walls, they must be heavy.
Here are some reasons why retaining walls need heavy stones:
1. Stability: Retaining walls need to be able to withstand the weight of the soil that they are holding back. If the stones used for the wall are too light, they may not be able to provide the necessary stability to keep the wall from collapsing.
2. Durability: Retaining walls are typically built to last for decades, if not centuries. Stones that are too soft or too light may deteriorate over time, which could compromise the structural integrity of the wall.
3. Aesthetics: Retaining walls are often built for both functional and aesthetic purposes. Heavy stones can be used to create a more visually appealing wall, as they provide a more natural and organic look.
4. Availability: Heavy stones are often readily available in many areas, making them a practical choice for retaining wall construction.
In summary, heavy stones are necessary for the construction of retaining walls because they provide the stability, durability, and aesthetics required for these structures to be effective and long-lasting.
Black marble is generally found in the district of- a)Jodhpur
- b)Jaipur
- c)Jabalpur
- d)Jaisalmer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Black marble is generally found in the district of
a)
Jodhpur
b)
Jaipur
c)
Jabalpur
d)
Jaisalmer

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
Generally, white marble is found in Jabalpur district (M.P) & Black marble in Jaipur.
Choose the main objectives of estimating analysis of rates at construction.
1. To determine the actual cost of items on location
2. To finalize the labor contract rates
3. To find out the quantity of materials and labor required for specific work
4. To know the alternatives to optimize the resources - a)1, 2, 3 statements are correct
- b)2, 3, 4 statements are correct
- c)1, 3, 4 statements are correct
- d)1, 2, 3, 4 statements are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the main objectives of estimating analysis of rates at construction.
1. To determine the actual cost of items on location
2. To finalize the labor contract rates
3. To find out the quantity of materials and labor required for specific work
4. To know the alternatives to optimize the resources
1. To determine the actual cost of items on location
2. To finalize the labor contract rates
3. To find out the quantity of materials and labor required for specific work
4. To know the alternatives to optimize the resources
a)
1, 2, 3 statements are correct
b)
2, 3, 4 statements are correct
c)
1, 3, 4 statements are correct
d)
1, 2, 3, 4 statements are correct

|
Ishan Kapoor answered |
Main Objectives of Estimating Analysis of Rates at Construction
Estimating analysis of rates is an essential process in construction projects to determine the cost, quantity, and resources required for specific work. The main objectives of estimating analysis of rates at construction include:
1. To determine the actual cost of items on location:
- Estimating analysis of rates helps in determining the actual cost of various items required for construction, such as materials, equipment, and labor.
- It involves analyzing the market rates, prices, and specifications of the items to accurately calculate their cost.
- This objective ensures that the project budget is realistic, and the construction activities can be carried out within the allocated funds.
2. To finalize the labor contract rates:
- Estimating analysis of rates helps in finalizing the labor contract rates for various construction activities.
- It involves studying the labor market, considering factors such as skill level, availability, and demand, to determine the appropriate rates for different types of labor.
- Finalizing the labor contract rates ensures that the project budget includes the necessary labor costs and helps in managing the labor resources effectively.
3. To find out the quantity of materials and labor required for specific work:
- Another objective of estimating analysis of rates is to determine the quantity of materials and labor required for specific construction activities.
- This involves studying the project plans, specifications, and drawings to identify the materials and labor needed.
- By accurately estimating the quantity of materials and labor, the project team can procure the necessary resources and plan the construction activities efficiently.
4. To know the alternatives to optimize the resources:
- Estimating analysis of rates also aims to explore alternatives to optimize the use of resources.
- This involves analyzing different methods, techniques, and materials to identify cost-effective and efficient options.
- By considering alternatives, the project team can make informed decisions to optimize the resources, reduce costs, and improve productivity.
Conclusion:
The main objectives of estimating analysis of rates at construction include determining the actual cost of items, finalizing labor contract rates, finding out the quantity of materials and labor required, and exploring alternatives to optimize resources. These objectives help in ensuring accurate cost estimation, effective resource management, and successful completion of construction projects.
Estimating analysis of rates is an essential process in construction projects to determine the cost, quantity, and resources required for specific work. The main objectives of estimating analysis of rates at construction include:
1. To determine the actual cost of items on location:
- Estimating analysis of rates helps in determining the actual cost of various items required for construction, such as materials, equipment, and labor.
- It involves analyzing the market rates, prices, and specifications of the items to accurately calculate their cost.
- This objective ensures that the project budget is realistic, and the construction activities can be carried out within the allocated funds.
2. To finalize the labor contract rates:
- Estimating analysis of rates helps in finalizing the labor contract rates for various construction activities.
- It involves studying the labor market, considering factors such as skill level, availability, and demand, to determine the appropriate rates for different types of labor.
- Finalizing the labor contract rates ensures that the project budget includes the necessary labor costs and helps in managing the labor resources effectively.
3. To find out the quantity of materials and labor required for specific work:
- Another objective of estimating analysis of rates is to determine the quantity of materials and labor required for specific construction activities.
- This involves studying the project plans, specifications, and drawings to identify the materials and labor needed.
- By accurately estimating the quantity of materials and labor, the project team can procure the necessary resources and plan the construction activities efficiently.
4. To know the alternatives to optimize the resources:
- Estimating analysis of rates also aims to explore alternatives to optimize the use of resources.
- This involves analyzing different methods, techniques, and materials to identify cost-effective and efficient options.
- By considering alternatives, the project team can make informed decisions to optimize the resources, reduce costs, and improve productivity.
Conclusion:
The main objectives of estimating analysis of rates at construction include determining the actual cost of items, finalizing labor contract rates, finding out the quantity of materials and labor required, and exploring alternatives to optimize resources. These objectives help in ensuring accurate cost estimation, effective resource management, and successful completion of construction projects.
Shingle is
- a)water bound pebbles
- b)crushed granite
- c)decomposed laterite
- d)air weathered rock
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Shingle is
a)
water bound pebbles
b)
crushed granite
c)
decomposed laterite
d)
air weathered rock
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Correct Answer :- a
Explanation : The shingle is water bound pebble.
In civil engineering, Shingle is a thin piece of building material, usually with a butt end thicker than the other. Shingles are widely used as roof covering on residential buildings and sometimes for siding. They are of stock sizes and various materials—including wood, asphalt, and slate. They are attached in overlapping courses, or rows.
The term frog means- a)an apparatus to lift the stone
- b)a depression on a face of brick
- c)vertical joint in a brick work
- d)soaking brick in water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The term frog means
a)
an apparatus to lift the stone
b)
a depression on a face of brick
c)
vertical joint in a brick work
d)
soaking brick in water

|
Sreemoyee Deshpande answered |
Explanation:
In bricklaying, a frog is a depression or indentation on the top face of a brick or block.
Bricklayers create this indentation on one or more faces of the brick to reduce the weight of the brick and to create a better bond with mortar.
The frog can also be used to hold a small amount of mortar, allowing for better adhesion between bricks.
Overall, the frog is an essential part of bricklaying and is used to create a more secure and stable structure.
In bricklaying, a frog is a depression or indentation on the top face of a brick or block.
Bricklayers create this indentation on one or more faces of the brick to reduce the weight of the brick and to create a better bond with mortar.
The frog can also be used to hold a small amount of mortar, allowing for better adhesion between bricks.
Overall, the frog is an essential part of bricklaying and is used to create a more secure and stable structure.
The minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks should be- a)75 kg/cm2
- b)90 kg/cm2
- c)100 kg/ cm2
- d)120 kg/cm2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks should be
a)
75 kg/cm2
b)
90 kg/cm2
c)
100 kg/ cm2
d)
120 kg/cm2

|
Bhaskar Rane answered |
Minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks
IInd class bricks are commonly used for construction purposes. They are cheaper compared to Ist class bricks and have a lower compressive strength. Their minimum compressive strength is specified as per IS 1077-1976.
According to IS 1077-1976, the minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks should be 75 kg/cm2.
Factors affecting the compressive strength of bricks
The compressive strength of bricks depends on various factors such as:
1. Raw materials: The quality of raw materials used in brick-making affects the compressive strength of the bricks. The clay used should have a proper balance of plasticity and shrinkage, and should be free from impurities.
2. Method of manufacturing: The method of manufacturing also affects the compressive strength of bricks. The bricks should be properly moulded and dried before firing.
3. Firing temperature: The temperature at which the bricks are fired affects their compressive strength. Over-firing or under-firing can lead to a reduction in the compressive strength of the bricks.
4. Age of the bricks: The compressive strength of bricks increases with age. The bricks should be allowed to age for a minimum of 28 days before testing.
Uses of IInd class bricks
IInd class bricks are commonly used for non-load-bearing walls, foundations, and other construction purposes. They are not suitable for load-bearing structures as their compressive strength is relatively low.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks should be 75 kg/cm2 as per IS 1077-1976. The compressive strength of bricks is affected by various factors such as raw materials, method of manufacturing, firing temperature, and age of the bricks. IInd class bricks are commonly used for non-load-bearing structures and foundations.
IInd class bricks are commonly used for construction purposes. They are cheaper compared to Ist class bricks and have a lower compressive strength. Their minimum compressive strength is specified as per IS 1077-1976.
According to IS 1077-1976, the minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks should be 75 kg/cm2.
Factors affecting the compressive strength of bricks
The compressive strength of bricks depends on various factors such as:
1. Raw materials: The quality of raw materials used in brick-making affects the compressive strength of the bricks. The clay used should have a proper balance of plasticity and shrinkage, and should be free from impurities.
2. Method of manufacturing: The method of manufacturing also affects the compressive strength of bricks. The bricks should be properly moulded and dried before firing.
3. Firing temperature: The temperature at which the bricks are fired affects their compressive strength. Over-firing or under-firing can lead to a reduction in the compressive strength of the bricks.
4. Age of the bricks: The compressive strength of bricks increases with age. The bricks should be allowed to age for a minimum of 28 days before testing.
Uses of IInd class bricks
IInd class bricks are commonly used for non-load-bearing walls, foundations, and other construction purposes. They are not suitable for load-bearing structures as their compressive strength is relatively low.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the minimum compressive strength of IInd class bricks should be 75 kg/cm2 as per IS 1077-1976. The compressive strength of bricks is affected by various factors such as raw materials, method of manufacturing, firing temperature, and age of the bricks. IInd class bricks are commonly used for non-load-bearing structures and foundations.
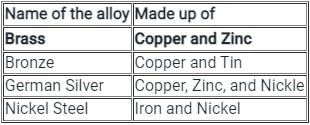
The alloy of copper and zinc is known as ________- a)brass
- b)nickle
- c)bronze
- d)duralumin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The alloy of copper and zinc is known as ________
a)
brass
b)
nickle
c)
bronze
d)
duralumin
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
- An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or nonmetals.
- Alloys are metal mixtures with other elements and the combination of both is governed by the properties required.
- The following table shows some metals with there alloys.
Important Points
Duralumin: It is an aluminium alloy. It contains 3.5 to 4.5% copper, 0.4 to 0.7% manganese, 0.4 to 0.7% magnesium and the remaining being aluminium. It is widely used in the aircraft industry for forging, stamping, bars, sheets, rivets, and so on.
Hindalium: It contains 5% copper and the rest aluminium. It is used for containers, utensils, tubes, rivets, etc.
What is printed list of rates of various items of work maintained by the engineering department?- a)Schedule of rates
- b)Analysis of rates
- c)Item rates
- d)Market rates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is printed list of rates of various items of work maintained by the engineering department?
a)
Schedule of rates
b)
Analysis of rates
c)
Item rates
d)
Market rates

|
Sanchita Pillai answered |
Schedule of rates
The printed list of rates of various items of work maintained by the engineering department is known as the schedule of rates. It is a comprehensive document that provides the details of the rates for different types of construction works and materials used in a project. The schedule of rates is an important tool for estimating the cost of a project and for preparing tender documents.
Importance of the schedule of rates
The schedule of rates serves as a reference for contractors, engineers, and other stakeholders involved in the construction industry. It provides a standardized and transparent system for determining the rates of various construction activities. This helps in ensuring fairness and consistency in pricing, as well as in minimizing disputes and conflicts during the execution of a project.
Components of the schedule of rates
The schedule of rates typically includes the following components:
1. Description of items: It provides a detailed description of each item of work, such as excavation, concrete work, brickwork, plastering, painting, etc. This ensures clarity and understanding of the work to be executed.
2. Unit of measurement: It specifies the unit of measurement for each item of work, such as cubic meter (m³), square meter (m²), or number of units. This helps in quantifying and measuring the work accurately.
3. Rate per unit: It mentions the rate per unit of measurement for each item of work. This rate is usually determined based on market rates, previous experience, and other factors. It is important to regularly update these rates to reflect changes in market conditions and material costs.
4. Specifications: It includes the specifications and standards to be followed for executing each item of work. This ensures uniformity in quality and performance.
5. Schedule of quantities: It provides the estimated quantities of each item of work required for a project. This helps in calculating the total cost of the project.
6. Terms and conditions: It includes any special terms and conditions related to the rates or execution of the work. This may include clauses related to variations, escalation, penalties, etc.
Benefits of the schedule of rates
The schedule of rates offers several benefits, including:
1. Cost estimation: It helps in accurately estimating the cost of a project by providing standardized rates for various items of work.
2. Benchmarking: It serves as a benchmark for comparing rates quoted by contractors during the tendering process. This helps in evaluating the reasonableness of the rates and in selecting the most competitive bidder.
3. Variation analysis: It facilitates the analysis of variations in rates during the execution of a project. Any changes in rates can be tracked and justified based on the variations in market conditions or project requirements.
4. Budget control: It assists in controlling the project budget by providing a reference for comparing the actual cost of work with the estimated cost.
5. Legal documentation: It serves as a legal document that can be used as evidence in case of disputes or claims related to rates or work execution.
Overall, the schedule of rates is an essential document in the construction industry as it provides a systematic and transparent framework for determining the rates of various construction activities. It helps in ensuring fairness, accuracy, and consistency in pricing, which ultimately contributes to the successful execution of a project.
The printed list of rates of various items of work maintained by the engineering department is known as the schedule of rates. It is a comprehensive document that provides the details of the rates for different types of construction works and materials used in a project. The schedule of rates is an important tool for estimating the cost of a project and for preparing tender documents.
Importance of the schedule of rates
The schedule of rates serves as a reference for contractors, engineers, and other stakeholders involved in the construction industry. It provides a standardized and transparent system for determining the rates of various construction activities. This helps in ensuring fairness and consistency in pricing, as well as in minimizing disputes and conflicts during the execution of a project.
Components of the schedule of rates
The schedule of rates typically includes the following components:
1. Description of items: It provides a detailed description of each item of work, such as excavation, concrete work, brickwork, plastering, painting, etc. This ensures clarity and understanding of the work to be executed.
2. Unit of measurement: It specifies the unit of measurement for each item of work, such as cubic meter (m³), square meter (m²), or number of units. This helps in quantifying and measuring the work accurately.
3. Rate per unit: It mentions the rate per unit of measurement for each item of work. This rate is usually determined based on market rates, previous experience, and other factors. It is important to regularly update these rates to reflect changes in market conditions and material costs.
4. Specifications: It includes the specifications and standards to be followed for executing each item of work. This ensures uniformity in quality and performance.
5. Schedule of quantities: It provides the estimated quantities of each item of work required for a project. This helps in calculating the total cost of the project.
6. Terms and conditions: It includes any special terms and conditions related to the rates or execution of the work. This may include clauses related to variations, escalation, penalties, etc.
Benefits of the schedule of rates
The schedule of rates offers several benefits, including:
1. Cost estimation: It helps in accurately estimating the cost of a project by providing standardized rates for various items of work.
2. Benchmarking: It serves as a benchmark for comparing rates quoted by contractors during the tendering process. This helps in evaluating the reasonableness of the rates and in selecting the most competitive bidder.
3. Variation analysis: It facilitates the analysis of variations in rates during the execution of a project. Any changes in rates can be tracked and justified based on the variations in market conditions or project requirements.
4. Budget control: It assists in controlling the project budget by providing a reference for comparing the actual cost of work with the estimated cost.
5. Legal documentation: It serves as a legal document that can be used as evidence in case of disputes or claims related to rates or work execution.
Overall, the schedule of rates is an essential document in the construction industry as it provides a systematic and transparent framework for determining the rates of various construction activities. It helps in ensuring fairness, accuracy, and consistency in pricing, which ultimately contributes to the successful execution of a project.
The unit mass (kg/cum) of structural steel as prescribed by IS 800 is:- a)7650
- b)7750
- c)7950
- d)7850
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The unit mass (kg/cum) of structural steel as prescribed by IS 800 is:
a)
7650
b)
7750
c)
7950
d)
7850

|
Sanskriti Datta answered |
The unit mass of structural steel is an important parameter in designing and constructing buildings and structures. It is crucial to know the weight of steel components to ensure structural stability and calculate loads accurately. In the context of Indian standards, IS 800 provides guidelines for the design of steel structures. According to IS 800, the unit mass of structural steel is 7850 kg/cum.
Explanation:
- Importance of unit mass in structural design:
The unit mass of structural steel refers to the weight of steel per unit volume. It is an essential parameter used in structural design calculations to determine the loads, stresses, and forces acting on the structure. By knowing the unit mass, engineers can accurately estimate the weight of steel components and design the structure accordingly.
- IS 800: Indian Standard for steel design:
IS 800 is the Indian Standard Code of Practice for general construction in steel. It provides guidelines and specifications for the design, fabrication, and erection of steel structures. This code covers various aspects, including loads, material properties, design criteria, and safety measures.
- Determination of unit mass of structural steel:
IS 800 specifies that the unit mass of structural steel is 7850 kg/cum. This value is based on the average density of steel, which is approximately 7850 kg/m^3. It is important to note that the unit mass may vary slightly depending on the specific type and grade of steel used.
- Significance of unit mass in design calculations:
Knowing the unit mass of structural steel allows engineers to accurately determine the self-weight of steel components such as beams, columns, and plates. This information is crucial in calculating the dead load, which is a permanent and constant load acting on the structure. The dead load, along with other loads such as live loads and wind loads, forms the basis for structural analysis and design.
- Other factors influencing steel weight:
While the unit mass of structural steel is fixed at 7850 kg/cum according to IS 800, it is important to consider other factors that may affect the actual weight of steel components. These factors can include additional coatings, attachments, and structural configurations.
In conclusion, the unit mass of structural steel as prescribed by IS 800 is 7850 kg/cum. It is an important parameter used in the design of steel structures to accurately estimate the weight of steel components and calculate loads.
Explanation:
- Importance of unit mass in structural design:
The unit mass of structural steel refers to the weight of steel per unit volume. It is an essential parameter used in structural design calculations to determine the loads, stresses, and forces acting on the structure. By knowing the unit mass, engineers can accurately estimate the weight of steel components and design the structure accordingly.
- IS 800: Indian Standard for steel design:
IS 800 is the Indian Standard Code of Practice for general construction in steel. It provides guidelines and specifications for the design, fabrication, and erection of steel structures. This code covers various aspects, including loads, material properties, design criteria, and safety measures.
- Determination of unit mass of structural steel:
IS 800 specifies that the unit mass of structural steel is 7850 kg/cum. This value is based on the average density of steel, which is approximately 7850 kg/m^3. It is important to note that the unit mass may vary slightly depending on the specific type and grade of steel used.
- Significance of unit mass in design calculations:
Knowing the unit mass of structural steel allows engineers to accurately determine the self-weight of steel components such as beams, columns, and plates. This information is crucial in calculating the dead load, which is a permanent and constant load acting on the structure. The dead load, along with other loads such as live loads and wind loads, forms the basis for structural analysis and design.
- Other factors influencing steel weight:
While the unit mass of structural steel is fixed at 7850 kg/cum according to IS 800, it is important to consider other factors that may affect the actual weight of steel components. These factors can include additional coatings, attachments, and structural configurations.
In conclusion, the unit mass of structural steel as prescribed by IS 800 is 7850 kg/cum. It is an important parameter used in the design of steel structures to accurately estimate the weight of steel components and calculate loads.
Which of the following is not a weakness of bar chart?- a)Suitable only for small job
- b)Cost control can not be achieved
- c)Optimum use of men and machines can not be done
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a weakness of bar chart?
a)
Suitable only for small job
b)
Cost control can not be achieved
c)
Optimum use of men and machines can not be done
d)
None of these

|
Madhurima Banerjee answered |
Drawbacks of bar charts are:
Suitable only for small job, no inter-dependency between the activities can be determined, cost control cannot be achieved and optimum use of machines and men cannot be done.
Suitable only for small job, no inter-dependency between the activities can be determined, cost control cannot be achieved and optimum use of machines and men cannot be done.
A cylinder with diameter D, length L, and P be the compressive load applied on cylinder, then split tensile strength is given by _______.- a)P / πLD
- b)2P / πLD
- c)4P / πLD
- d)16P / πLD
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylinder with diameter D, length L, and P be the compressive load applied on cylinder, then split tensile strength is given by _______.
a)
P / πLD
b)
2P / πLD
c)
4P / πLD
d)
16P / πLD

|
Anshul Kumar answered |
Understanding Split Tensile Strength
Split tensile strength is an important property in assessing the behavior of concrete and cylindrical structures under compressive loads. In this context, we are looking at a cylinder with a given diameter (D), length (L), and a compressive load (P) applied to it.
Formula Derivation
To derive the split tensile strength, we start by understanding the forces acting on the cylinder. When a compressive load (P) is applied, it generates tensile stresses along the diameter of the cylinder. The split tensile strength can be expressed using the following relationship:
- The tensile stress developed in the cylinder due to the applied load can be calculated by considering the cross-sectional area and the length.
Cross-sectional Area
- The cross-sectional area (A) of the cylinder is given by the formula:
A = (π/4) * D²
Tensile Stress Calculation
- The tensile stress (σ) is calculated as:
σ = P / A
Therefore, substituting for A:
σ = 4P / (πD²)
Considering Length Factor
- However, we need to consider the length (L) of the cylinder as well. The split tensile strength is derived considering the length as a factor affecting the distribution of stress.
- The final equation for split tensile strength becomes:
σ = 2P / (πLD)
Thus, the correct answer to the question is option b) 2P / πLD. This formula encapsulates how the tensile strength is influenced by the compressive load, cylinder dimensions, and length.
Conclusion
Understanding this relationship is crucial for engineers when evaluating the structural integrity of cylindrical components under load.
Split tensile strength is an important property in assessing the behavior of concrete and cylindrical structures under compressive loads. In this context, we are looking at a cylinder with a given diameter (D), length (L), and a compressive load (P) applied to it.
Formula Derivation
To derive the split tensile strength, we start by understanding the forces acting on the cylinder. When a compressive load (P) is applied, it generates tensile stresses along the diameter of the cylinder. The split tensile strength can be expressed using the following relationship:
- The tensile stress developed in the cylinder due to the applied load can be calculated by considering the cross-sectional area and the length.
Cross-sectional Area
- The cross-sectional area (A) of the cylinder is given by the formula:
A = (π/4) * D²
Tensile Stress Calculation
- The tensile stress (σ) is calculated as:
σ = P / A
Therefore, substituting for A:
σ = 4P / (πD²)
Considering Length Factor
- However, we need to consider the length (L) of the cylinder as well. The split tensile strength is derived considering the length as a factor affecting the distribution of stress.
- The final equation for split tensile strength becomes:
σ = 2P / (πLD)
Thus, the correct answer to the question is option b) 2P / πLD. This formula encapsulates how the tensile strength is influenced by the compressive load, cylinder dimensions, and length.
Conclusion
Understanding this relationship is crucial for engineers when evaluating the structural integrity of cylindrical components under load.
Chapter doubts & questions for Construction Materials & Management - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Construction Materials & Management - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Civil Engg
488 videos|1261 docs|878 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









