All Exams >
Computer Science Engineering (CSE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE >
All Questions
All questions of Hashing for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
Which one of the following hash functions on integers will distribute keys most uniformly over 10 buckets numbered 0 to 9 for i ranging from 0 to 2020?- a)h(i) =i2 mod 10
- b)h(i) =i3 mod 10
- c)h(i) = (11 ∗ i2) mod 10
- d)h(i) = (12 ∗ i) mod 10
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following hash functions on integers will distribute keys most uniformly over 10 buckets numbered 0 to 9 for i ranging from 0 to 2020?
a)
h(i) =i2 mod 10
b)
h(i) =i3 mod 10
c)
h(i) = (11 ∗ i2) mod 10
d)
h(i) = (12 ∗ i) mod 10
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
Since mod 10 is used, the last digit matters. If you do cube all numbers from 0 to 9, you get following
Therefore all numbers from 0 to 2020 are equally divided in 10 buckets. If we make a table for square, we don't get equal distribution. In the following table. 1, 4, 6 and 9 are repeated, so these buckets would have more entries and buckets 2, 3, 7 and 8 would be empty.
Consider a hash table with 100 slots. Collisions are resolved using chaining. Assuming simple uniform hashing, what is the probability that the first 3 slots are unfilled after the first 3 insertions?- a)(97 × 97 × 97)/1003
- b)(99 × 98 × 97)/1003
- c)(97 × 96 × 95)/1003
- d)(97 × 96 × 95)/(3! × 1003)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a hash table with 100 slots. Collisions are resolved using chaining. Assuming simple uniform hashing, what is the probability that the first 3 slots are unfilled after the first 3 insertions?
a)
(97 × 97 × 97)/1003
b)
(99 × 98 × 97)/1003
c)
(97 × 96 × 95)/1003
d)
(97 × 96 × 95)/(3! × 1003)
|
|
Mayank Malik answered |
Simple Uniform hashing function is a hypothetical hashing function that evenly distributes items into the slots of a hash table. Moreover, each item to be hashed has an equal probability of being placed into a slot, regardless of the other elements already placed.
Probability that the first 3 slots are unfilled after the first 3 insertions =
(probability that first item doesn't go in any of the first 3 slots)*
(probability that second item doesn't go in any of the first 3 slots)*
(probability that third item doesn't go in any of the first 3 slots)
(probability that first item doesn't go in any of the first 3 slots)*
(probability that second item doesn't go in any of the first 3 slots)*
(probability that third item doesn't go in any of the first 3 slots)
= (97/100) * (97/100) * (97/100)
Consider a hash function that distributes keys uniformly. The hash table size is 20. After hashing of how many keys will the probability that any new key hashed collides with an existing one exceed 0.5.- a)5
- b)6
- c)7
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a hash function that distributes keys uniformly. The hash table size is 20. After hashing of how many keys will the probability that any new key hashed collides with an existing one exceed 0.5.
a)
5
b)
6
c)
7
d)
10
|
|
Ishaan Saini answered |
For each entry probability of collision is 1/20 {as possible total spaces =20, and an entry will go into only 1 place}
Say after inserting x values probability becomes ½
(1/20).x = ½
X=10
Say after inserting x values probability becomes ½
(1/20).x = ½
X=10
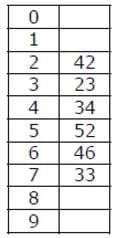 How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
- a)10
- b)20
- c)30
- d)40
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
a)
10
b)
20
c)
30
d)
40

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
In a valid insertion sequence, the elements 42, 23 and 34 must appear before 52 and 33, and 46 must appear before 33.
Total number of different sequences = 3! x 5 = 30
In the above expression, 3! is for elements 42, 23 and 34 as they can appear in any order, and 5 is for element 46 as it can appear at 5 different places.
Consider a hash table of size seven, with starting index zero, and a hash function (3x + 4)mod7. Assuming the hash table is initially empty, which of the following is the contents of the table when the sequence 1, 3, 8, 10 is inserted into the table using closed hashing? Note that ‘_’ denotes an empty location in the table.- a)8, _, _, _, _, _, 10
- b)1, 8, 10, _, _, _, 3
- c)1, _, _, _, _, _,3
- d)1, 10, 8, _, _, _, 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a hash table of size seven, with starting index zero, and a hash function (3x + 4)mod7. Assuming the hash table is initially empty, which of the following is the contents of the table when the sequence 1, 3, 8, 10 is inserted into the table using closed hashing? Note that ‘_’ denotes an empty location in the table.
a)
8, _, _, _, _, _, 10
b)
1, 8, 10, _, _, _, 3
c)
1, _, _, _, _, _,3
d)
1, 10, 8, _, _, _, 3
|
|
Palak Khanna answered |
Let us put values 1, 3, 8, 10 in the hash of size 7. Initially, hash table is empty
The value of function (3x + 4)mod 7 for 1 is 0, so let us put the value at 0
The value of function (3x + 4)mod 7 for 3 is 6, so let us put the value at 6
The value of function (3x + 4)mod 7 for 8 is 0, but 0 is already occupied, let us put the value(8) at next available space(1)
The value of function (3x + 4)mod 7 for 10 is 6, but 6 is already occupied, let us put the value(10) at next available space(2)
Which of the following statement(s) is TRUE? - A hash function takes a message of arbitrary length and generates a fixed length code.
- A hash function takes a message of fixed length and generates a code of variable length.
- A hash function may give the same hash value for distinct messages.
- a)I only
- b)II and III only
- c)I and III only
- d)II only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement(s) is TRUE?
- A hash function takes a message of arbitrary length and generates a fixed length code.
- A hash function takes a message of fixed length and generates a code of variable length.
- A hash function may give the same hash value for distinct messages.
a)
I only
b)
II and III only
c)
I and III only
d)
II only
|
|
Nilanjan Chavan answered |
Hash function is defined as any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size of data to a fixed size data.. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, digests, or simply hashes : Statement 1 is correct Yes, it is possible that a Hash Function maps a value to a same location in the memmory that's why collision occurs and we have different technique to handle this problem : Statement 3 is coorect. eg : we have hash function, h(x) = x mod 3 Acc to Statement 1, no matter what the value of 'x' is h(x) results in a fixed mapping location. Acc. to Statement 3, h(x) can result in same mapping mapping location for different value of 'x' e.g. if x = 4 or x = 7 , h(x) = 1 in both the cases, although collision occurs.
Given the following input (4322, 1334, 1471, 9679, 1989, 6171, 6173, 4199) and the hash function x mod 10, which of the following statements are true?
i. 9679, 1989, 4199 hash to the same value
ii. 1471, 6171 has to the same value
iii. All elements hash to the same value
iv. Each element hashes to a different value- a)i only
- b)ii only
- c)i and ii only
- d)iii or iv
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given the following input (4322, 1334, 1471, 9679, 1989, 6171, 6173, 4199) and the hash function x mod 10, which of the following statements are true?
i. 9679, 1989, 4199 hash to the same value
ii. 1471, 6171 has to the same value
iii. All elements hash to the same value
iv. Each element hashes to a different value
i. 9679, 1989, 4199 hash to the same value
ii. 1471, 6171 has to the same value
iii. All elements hash to the same value
iv. Each element hashes to a different value
a)
i only
b)
ii only
c)
i and ii only
d)
iii or iv
|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
Hash function given is mod(10).
9679, 1989 and 4199 all these give same hash value i.e 9
1471 and 6171 give hash value 1
Given a hash table T with 25 slots that stores 2000 elements, the load factor α for T is __________- a)80
- b)0.0125
- c)8000
- d)1.25
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given a hash table T with 25 slots that stores 2000 elements, the load factor α for T is __________
a)
80
b)
0.0125
c)
8000
d)
1.25
|
|
Mahi Chavan answered |
Load Factor of a Hash Table
The load factor of a hash table is the ratio of the number of elements stored in the table to the number of slots available in the table.
Load Factor = Number of elements / Number of slots
Given Information
- Hash table T with 25 slots
- Stores 2000 elements
Calculation
Load Factor = Number of elements / Number of slots
Load Factor = 2000 / 25
Load Factor = 80
Therefore, the load factor for T is 80.
Explanation
- The load factor of a hash table is used to measure its efficiency.
- A load factor of 1 indicates that the hash table is full, while a load factor of 0 means that the hash table is empty.
- In this case, the load factor is calculated by dividing the number of elements stored in the hash table by the number of slots available in the hash table.
- As per the given information, the hash table T has 25 slots and stores 2000 elements. Therefore, the load factor is 80.
- A high load factor indicates that the hash table is densely populated, which can lead to collisions and performance issues.
The load factor of a hash table is the ratio of the number of elements stored in the table to the number of slots available in the table.
Load Factor = Number of elements / Number of slots
Given Information
- Hash table T with 25 slots
- Stores 2000 elements
Calculation
Load Factor = Number of elements / Number of slots
Load Factor = 2000 / 25
Load Factor = 80
Therefore, the load factor for T is 80.
Explanation
- The load factor of a hash table is used to measure its efficiency.
- A load factor of 1 indicates that the hash table is full, while a load factor of 0 means that the hash table is empty.
- In this case, the load factor is calculated by dividing the number of elements stored in the hash table by the number of slots available in the hash table.
- As per the given information, the hash table T has 25 slots and stores 2000 elements. Therefore, the load factor is 80.
- A high load factor indicates that the hash table is densely populated, which can lead to collisions and performance issues.
The keys 12, 18, 13, 2, 3, 23, 5 and 15 are inserted into an initially empty hash table of length 10 using open addressing with hash function h(k) = k mod 10 and linear probing. What is the resultant hash table?- a)
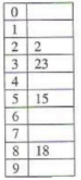
- b)
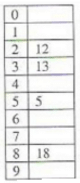
- c)
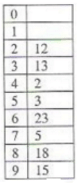
- d)
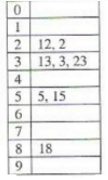
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The keys 12, 18, 13, 2, 3, 23, 5 and 15 are inserted into an initially empty hash table of length 10 using open addressing with hash function h(k) = k mod 10 and linear probing. What is the resultant hash table?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Soumya Dey answered |
To get the idea of open addressing concept, you can go through below lines from Wikipedia . Open addressing, or closed hashing, is a method of collision resolution in hash tables. With this method a hash collision is resolved by probing, or searching through alternate locations in the array (the probe sequence) until either the target record is found, or an unused array slot is found, which indicates that there is no such key in the table. Well known probe sequences include: linear probing in which the interval between probes is fixed--often at 1. quadratic probing in which the interval between probes increases linearly (hence, the indices are described by a quadratic function). double hashing in which the interval between probes is fixed for each record but is computed by another hash function.
Chapter doubts & questions for Hashing - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Hashing - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE
453 videos|1305 docs|700 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









