All Exams >
Computer Science Engineering (CSE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE >
All Questions
All questions of Computer Networks for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
Which of the following assertions is FALSE about the Internet Protocol (IP)?- a)It is possible for a computer to have multiple IP addresses
- b)IP packets from the same source to the same destination can take different routes in the network
- c)IP ensures that a packet is discarded if it is unable to reach its destination within a given number of hops
- d)The packet source cannot set the route of an outgoing packets; the route is determined only by the routing tables in therouters on the way
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following assertions is FALSE about the Internet Protocol (IP)?
a)
It is possible for a computer to have multiple IP addresses
b)
IP packets from the same source to the same destination can take different routes in the network
c)
IP ensures that a packet is discarded if it is unable to reach its destination within a given number of hops
d)
The packet source cannot set the route of an outgoing packets; the route is determined only by the routing tables in therouters on the way
|
|
Anand Unni answered |
In computer networking, source routing, also called path addressing, allows a sender of a packet to partially or completely specify the route of the packet takes
through the network. In contrast, in non-source routing protocols, routers in the network determine the path based on the packet's destination.
through the network. In contrast, in non-source routing protocols, routers in the network determine the path based on the packet's destination.
Answer-D
Suppose that it takes 1 unit of time to transmit a packet (of fixed size) on a communication link. The link layer uses a window flow control protocol with a window size of N packets. Each packet causes an ack or a nak to be generated by the receiver, and ack/nak transmission times are negligible. Further, the round trip time on the link is equal to N units. Consider time i > N. If only acks have been received till time i(no naks), then the goodput evaluated at the transmitter at time i (in packets per unit time) is- a)1 - N/i
- b) i/(N + i)
- c)1
- d)1 - e(i/N)
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose that it takes 1 unit of time to transmit a packet (of fixed size) on a communication link. The link layer uses a window flow control protocol with a window size of N packets. Each packet causes an ack or a nak to be generated by the receiver, and ack/nak transmission times are negligible. Further, the round trip time on the link is equal to N units. Consider time i > N. If only acks have been received till time i(no naks), then the goodput evaluated at the transmitter at time i (in packets per unit time) is
a)
1 - N/i
b)
i/(N + i)
c)
1
d)
1 - e(i/N)

|
Anushka Bose answered |
In computer networks, goodput is the application level throughput, i.e. the number of useful information bits delivered by
the network to a certain destination per unit of time. (From wikipedia).
So, successful delivery of packet can be assured if ACK has been received for it.
So till time 'i' we would have transmitted 'i' packets but only (i-N) can be acknowledged as minimum time for a packet to
get Acknowledged is N (since RTT is N which is equal to the window size, there is no waiting time for the sender).
So successfully delivered packets = (i-N)
Time for transmission = i
Goodput = Successfully delivered data/ Time = (i-N)/i = 1- N/i
Therefore (A)
the network to a certain destination per unit of time. (From wikipedia).
So, successful delivery of packet can be assured if ACK has been received for it.
So till time 'i' we would have transmitted 'i' packets but only (i-N) can be acknowledged as minimum time for a packet to
get Acknowledged is N (since RTT is N which is equal to the window size, there is no waiting time for the sender).
So successfully delivered packets = (i-N)
Time for transmission = i
Goodput = Successfully delivered data/ Time = (i-N)/i = 1- N/i
Therefore (A)
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A 20 Kbps satellite link has a propagation delay of 400 ms. The transmitter employs the "go back n ARQ" scheme with n setto 10. Assuming that each frame is 100 bytes long, what is the maximum data rate possible?
- A:
5 Kbps
- B:
10 Kbps
- C:
15 Kbps
- D:
20 Kbps
The answer is b.
A 20 Kbps satellite link has a propagation delay of 400 ms. The transmitter employs the "go back n ARQ" scheme with n setto 10. Assuming that each frame is 100 bytes long, what is the maximum data rate possible?
5 Kbps
10 Kbps
15 Kbps
20 Kbps
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
Given Data
Bandwidth = 20 Kbps
Propogation dealy = 400 ms, so RTT = 2 * PD = 800 ms
window size = 10
frame size = 100 bytes of 800 bits
Even though bandwidth is 20kbps, we are restricted with window size here
In 1 RTT we are sending 10 * 800 bits
In 800 ms we are sending 10 * 800 bits
In 1 ms we are sending 10 bits
In 1 sec we are sending 10 * 1000 bits
In 1 sec we are sending 10 Kb
So effective bandwidth = 10 Kb/sec
Which one of the following is not a function of network layer?- a)routing
- b)inter-networking
- c)congestion control
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a function of network layer?
a)
routing
b)
inter-networking
c)
congestion control
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Network Layer :-
The network layer is responsible for the source-to-destination delivery of a packet, possibly across multiple networks (links).
Other functions of the network layer include the following :-
Logical addressing :- In order to identify each device on internetwork uniquely, network layer defines an addressing scheme.
Routing :- The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination.
Consider a simple graph with unit edge costs. Each node in the graph represents a router. Each node maintains a routing table indicating the next hop router to be used to relay a packet to its destination and the cost of the path to the destination through that router. Initially, the routing table is empty. The routing table is synchronously updated as follows. In each updation interval, three tasks are performed.
i. A node determines whether its neighbours in the graph are accessible. If so, it sets the tentative cost to each accessible
neighbour as 1. Otherwise, the cost is set to ∞.
ii. From each accessible neighbour, it gets the costs to relay to other nodes via that neighbour (as the next hop).
iii. Each node updates its routing table based on the information received in the previous two steps by choosing the minimum cost.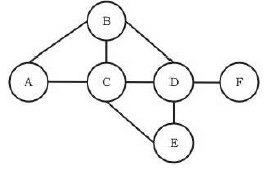 For the graph given above, possible routing tables for various nodes after they have stabilized, are shown in the following options. Identify the correct table.
For the graph given above, possible routing tables for various nodes after they have stabilized, are shown in the following options. Identify the correct table.- a)Table for node A
A - -
B B 1
C C 1
D B 3
E C 3
F C 4 - b)Table for node C
A A 1
B B 1C - -
D D 1
E E 1
F E 3 - c)Table for node B
A A 1
B - -
C C 1
D D 1
E C 2
F D 2 - d)Table for node D
A B 3
B B 1
C C 1
D - -
E E 1
F F 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a simple graph with unit edge costs. Each node in the graph represents a router. Each node maintains a routing table indicating the next hop router to be used to relay a packet to its destination and the cost of the path to the destination through that router. Initially, the routing table is empty. The routing table is synchronously updated as follows. In each updation interval, three tasks are performed.
i. A node determines whether its neighbours in the graph are accessible. If so, it sets the tentative cost to each accessible
neighbour as 1. Otherwise, the cost is set to ∞.
ii. From each accessible neighbour, it gets the costs to relay to other nodes via that neighbour (as the next hop).
iii. Each node updates its routing table based on the information received in the previous two steps by choosing the minimum cost.
i. A node determines whether its neighbours in the graph are accessible. If so, it sets the tentative cost to each accessible
neighbour as 1. Otherwise, the cost is set to ∞.
ii. From each accessible neighbour, it gets the costs to relay to other nodes via that neighbour (as the next hop).
iii. Each node updates its routing table based on the information received in the previous two steps by choosing the minimum cost.
For the graph given above, possible routing tables for various nodes after they have stabilized, are shown in the following options. Identify the correct table.
a)
Table for node A
A - -
B B 1
C C 1
D B 3
E C 3
F C 4
A - -
B B 1
C C 1
D B 3
E C 3
F C 4
b)
Table for node C
A A 1
B B 1
A A 1
B B 1
C - -
D D 1
E E 1
F E 3
D D 1
E E 1
F E 3
c)
Table for node B
A A 1
B - -
C C 1
D D 1
E C 2
F D 2
A A 1
B - -
C C 1
D D 1
E C 2
F D 2
d)
Table for node D
A B 3
B B 1
C C 1
D - -
E E 1
F F 1
A B 3
B B 1
C C 1
D - -
E E 1
F F 1
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
correct table are updated only option C is matching here with given tables
The network layer concerns with- a)bits
- b)frames
- c)packets
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The network layer concerns with
a)
bits
b)
frames
c)
packets
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
The network layer is responsible for routing packets from the source to destination. The routing algorithm is the piece of software that decides where a packet goes next (e.g., which output line, or which node on a broadcast channel).
For connectionless networks, the routing decision is made for each datagram. For connection-oriented networks, the decision is made once, at circuit setup time.
For stop and wait ARQ, for n data packets sent, ______________ acknowledgments are needed.- a)n
- b)2n
- c)n-1
- d)n+1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For stop and wait ARQ, for n data packets sent, ______________ acknowledgments are needed.
a)
n
b)
2n
c)
n-1
d)
n+1
|
|
Pritam Goyal answered |
It n data packets sent we need less than n data packet acknowledgments.
RIP is- a)Protocol used for transmission of IP datagrams across a serial line
- b)Resource information protocol
- c)Protocol used to exchange information between the routers
- d)Protocol used to exchanger information between the layers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RIP is
a)
Protocol used for transmission of IP datagrams across a serial line
b)
Resource information protocol
c)
Protocol used to exchange information between the routers
d)
Protocol used to exchanger information between the layers
|
|
Prisha Sharma answered |
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a routing protocol based on the distance vector algorithm, In this each router periodically shares its knowledge about the entire network with its neighbours.
Which of the following fields of an IP header is NOT modified by a typical IP router?- a)Check sum
- b)Source address
- c)Time to Live (TTL)
- d)Length
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following fields of an IP header is NOT modified by a typical IP router?
a)
Check sum
b)
Source address
c)
Time to Live (TTL)
d)
Length

|
Abhishek Ranjan answered |
Suppose that packet size is more than the Capacity of the forwarding link, at this time fragmentation is to be done at the router. Due to fragmentation Length of the packet changes. TTL value also changes at every router. Due to fragmentation Cheksum also gets changed as any change in IP header also brings change in the checksum.
But source address or origin of packet never changes.
But source address or origin of packet never changes.
In the 4B/5B encoding scheme, every 4 bits of data are encoded in a 5-bit codeword. It is required that the codewords haveat most 1 leading and at most 1 trailing zero. How many such codewords are possible?- a)14
- b)16
- c)18
- d)20
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the 4B/5B encoding scheme, every 4 bits of data are encoded in a 5-bit codeword. It is required that the codewords haveat most 1 leading and at most 1 trailing zero. How many such codewords are possible?
a)
14
b)
16
c)
18
d)
20
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
The possible codewords should not have 00xxx or xxx00
=> Total possible combinations of 5 bits – for (00xxx or xxx00)+ (00*00) {as 00*00 is subtracted twice once each from both cases}
=> 232 – (8+8) +2 = 18
How many 8-bit characters can be transmitted per second over a 9600 baud serial communication link using asynchronousmode of transmission with one start bit, eight data bits, two stop bits and one parity bit?- a)600
- b)800
- c)876
- d)1200
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many 8-bit characters can be transmitted per second over a 9600 baud serial communication link using asynchronousmode of transmission with one start bit, eight data bits, two stop bits and one parity bit?
a)
600
b)
800
c)
876
d)
1200
|
|
Kavya Mukherjee answered |
The baud rate is the rate at which information is transferred in a communication channel. Serial ports use two-level (binary) signaling, so the data rate in bits per second is equal to the symbol rate in bauds.
"9600 baud" means that the serial port is capable of transferring a maximum of 9600 bits per second."
So, transmission rate here = 9600 bps
An eight bit data (which is a char) requires 1 start bit, 2 stop bits and 1 parity bit = 12 bits.
So, number of characters transmitted per second = 9600 / 12 = 800
So, transmission rate here = 9600 bps
An eight bit data (which is a char) requires 1 start bit, 2 stop bits and 1 parity bit = 12 bits.
So, number of characters transmitted per second = 9600 / 12 = 800
An organization has a class B network and wishes to form subnets for 64 departments. The subnet mask would be:- a)255.255.0.0
- b)255.255.64.0
- c)255.255.128.0
- d)255.255.252.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An organization has a class B network and wishes to form subnets for 64 departments. The subnet mask would be:
a)
255.255.0.0
b)
255.255.64.0
c)
255.255.128.0
d)
255.255.252.0
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Firstly, we should know, what a Class B network is and how is it different from Class A network and Class B network.
IP Address Class Network and Host Capacities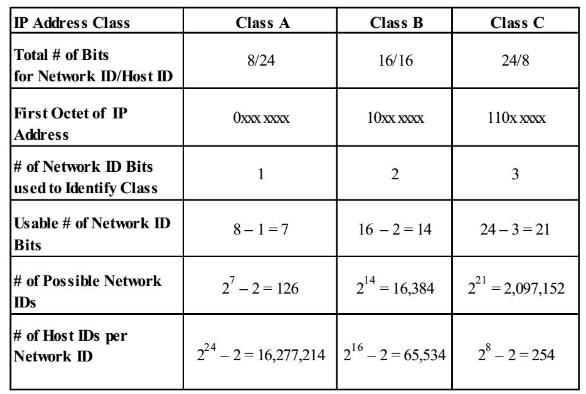

According to the formula number of subnets = 2^n
So, the subnet mask would be = 11111111.11111111.11111100.00000000
Hence, answer is 255. 255. 252. 0
You can go through the course for Computer Science Engineering chapter-wise tests:
Consider the three commands : PROMPT, HEAD and RCPT.Which of the following options indicate a correct association of these commands with protocols where these are used?- a)HTTP, SMTP, FTP
- b)FTP, HTTP, SMTP
- c)HTTP, FTP, SMTP
- d)SMTP, HTTP, FTP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the three commands : PROMPT, HEAD and RCPT.Which of the following options indicate a correct association of these commands with protocols where these are used?
a)
HTTP, SMTP, FTP
b)
FTP, HTTP, SMTP
c)
HTTP, FTP, SMTP
d)
SMTP, HTTP, FTP

|
Kaavya Sengupta answered |
The correct answer is b.
PROMPT- Toggles prompting. Ftp prompts during multiple file transfers to allow you to selectively retrieve or store files //Used for FTP transfers
HEAD- The <head> element can include a title for the document, scripts, styles, meta information, and more //Used in HTML to transfer data across HTTP protocol
RCPT- You tell the mail server who the recipient of your message is by using the RCPT command //Related to mail so,SMTP
In a class A subnet, we know the IP address of one of the hosts and the mask as given below:
IP address = 25.34.12.56
Mask = 255.255.0.0What is the first address (network address)?- a)25.34.12.0
- b)25.34.12.56
- c)25.34.0.0
- d)25.0.0.0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a class A subnet, we know the IP address of one of the hosts and the mask as given below:
IP address = 25.34.12.56
Mask = 255.255.0.0
IP address = 25.34.12.56
Mask = 255.255.0.0
What is the first address (network address)?
a)
25.34.12.0
b)
25.34.12.56
c)
25.34.0.0
d)
25.0.0.0
|
|
Hiral Nair answered |

The subnet mask for a particular network is 255.255.31.0. Which of the following pairs of IP addresses could belong to this network?- a)172.57.88.62 and 172.56.87.23
- b)10.35.28.2 and 10.35.29.4
- c)191.203.31.87 and 191.234.31.88
- d)128.8.129.43 and 128.8.161.55
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The subnet mask for a particular network is 255.255.31.0. Which of the following pairs of IP addresses could belong to this network?
a)
172.57.88.62 and 172.56.87.23
b)
10.35.28.2 and 10.35.29.4
c)
191.203.31.87 and 191.234.31.88
d)
128.8.129.43 and 128.8.161.55
|
|
Anmol Basu answered |
Explanation:
Subnet mask is used to divide an IP address into network and host portions. In this case, the subnet mask is 255.255.31.0, which means that the first 21 bits are used for network identification while the remaining 11 bits are used for host identification.
To find out which pairs of IP addresses could belong to this network, we need to compare the first 21 bits of each IP address with the network portion of the subnet mask.
Option A: 172.57.88.62 and 172.56.87.23
- First IP address: 10101100.00111001.01011000.00111110
- Second IP address: 10101100.00111000.01010111.00010111
- Both IP addresses have different network portions, so they cannot belong to the same network as the given subnet mask.
Option B: 10.35.28.2 and 10.35.29.4
- First IP address: 00001010.00100011.00011100.00000010
- Second IP address: 00001010.00100011.00011101.00000100
- Both IP addresses have the same network portion (00001010.00100011.000111), but the third octet is not within the range of the subnet mask (0-31). Therefore, these IP addresses cannot belong to the given network.
Option C: 191.203.31.87 and 191.234.31.88
- First IP address: 10111111.11001011.00011111.01010111
- Second IP address: 10111111.11101010.00011111.01011000
- Both IP addresses have the same network portion (10111111.11), but the next 10 bits are different, which means they cannot belong to the same network.
Option D: 128.8.129.43 and 128.8.161.55
- First IP address: 10000000.00001000.10000001.00101011
- Second IP address: 10000000.00001000.10100001.00110111
- Both IP addresses have the same network portion (10000000.00001000.10), which matches the network portion of the given subnet mask. Therefore, these IP addresses could belong to the same network as the subnet mask.
Thus, option D is the correct answer.
Subnet mask is used to divide an IP address into network and host portions. In this case, the subnet mask is 255.255.31.0, which means that the first 21 bits are used for network identification while the remaining 11 bits are used for host identification.
To find out which pairs of IP addresses could belong to this network, we need to compare the first 21 bits of each IP address with the network portion of the subnet mask.
Option A: 172.57.88.62 and 172.56.87.23
- First IP address: 10101100.00111001.01011000.00111110
- Second IP address: 10101100.00111000.01010111.00010111
- Both IP addresses have different network portions, so they cannot belong to the same network as the given subnet mask.
Option B: 10.35.28.2 and 10.35.29.4
- First IP address: 00001010.00100011.00011100.00000010
- Second IP address: 00001010.00100011.00011101.00000100
- Both IP addresses have the same network portion (00001010.00100011.000111), but the third octet is not within the range of the subnet mask (0-31). Therefore, these IP addresses cannot belong to the given network.
Option C: 191.203.31.87 and 191.234.31.88
- First IP address: 10111111.11001011.00011111.01010111
- Second IP address: 10111111.11101010.00011111.01011000
- Both IP addresses have the same network portion (10111111.11), but the next 10 bits are different, which means they cannot belong to the same network.
Option D: 128.8.129.43 and 128.8.161.55
- First IP address: 10000000.00001000.10000001.00101011
- Second IP address: 10000000.00001000.10100001.00110111
- Both IP addresses have the same network portion (10000000.00001000.10), which matches the network portion of the given subnet mask. Therefore, these IP addresses could belong to the same network as the subnet mask.
Thus, option D is the correct answer.
Assume that each character code consists of 8 bits. The number of characters that can be transmitted per second through anasynchronous serial line at 2400 baud rate, and with two stop bits is- a)109
- b)216
- c)218
- d)219
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that each character code consists of 8 bits. The number of characters that can be transmitted per second through anasynchronous serial line at 2400 baud rate, and with two stop bits is
a)
109
b)
216
c)
218
d)
219
|
|
Kavya Mukherjee answered |
Total bit per character = 8 bit data + 2 stop bit +1 start bit (#) = 11 bits
no of characters = 2400/11 = 218.18
Since it is asked for transmitted characters we take floor and answer is 218.
no of characters = 2400/11 = 218.18
Since it is asked for transmitted characters we take floor and answer is 218.
The Hamming distance between 001111 and 010011 is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Hamming distance between 001111 and 010011 is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
The hamming distance is the minimum number of positions where any two legal code words differ by bit.
Hamming distance between 001111 and 010011 is 3.
Hamming distance between 001111 and 010011 is 3.
Who can send ICMP error-reporting messages?
- a)Routers
- b)Destination hosts
- c)Source host
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who can send ICMP error-reporting messages?
a)
Routers
b)
Destination hosts
c)
Source host
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Krithika Kaur answered |
Both router and destination host can send ICMP error-reporting message to inform the source host about any failure or error occurred in packet.
In an IPv4 datagram, the M bit is 0, the value of HLEN is 10, the value of total length is 400 and the fragment offset value is300. The position of the datagram, the sequence numbers of the first and the last bytes of the payload, respectively are- a)Last fragment, 2400 and 2789
- b)First fragment, 2400 and 2759
- c)Last fragment, 2400 and 2759
- d)Middle fragment, 300 and 689
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an IPv4 datagram, the M bit is 0, the value of HLEN is 10, the value of total length is 400 and the fragment offset value is300. The position of the datagram, the sequence numbers of the first and the last bytes of the payload, respectively are
a)
Last fragment, 2400 and 2789
b)
First fragment, 2400 and 2759
c)
Last fragment, 2400 and 2759
d)
Middle fragment, 300 and 689
|
|
Arnab Desai answered |
M = 0 meaning no more fragments after this. Hence, its the last fragment.
IHL = internet header length = 10 x 8 = 2400 B coz 4 is the scaling factor for this field.
Total Length = 2400 B
Payload size = Total length - Header length = 400-40 = 360B
fragment offset = = represents how many Bytes are before this. 8 is the scaling factor here.
the first byte # = 2400
Last byte # = 300 x 8 = 2400 B first byte # + total bytes in payload - 1 = 2400+360-1=2759
option C is correct
IHL = internet header length = 10 x 8 = 2400 B coz 4 is the scaling factor for this field.
Total Length = 2400 B
Payload size = Total length - Header length = 400-40 = 360B
fragment offset = = represents how many Bytes are before this. 8 is the scaling factor here.
the first byte # = 2400
Last byte # = 300 x 8 = 2400 B first byte # + total bytes in payload - 1 = 2400+360-1=2759
option C is correct
In virtual circuit network each packet contains- a)full source and destination address
- b)a short VC number
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In virtual circuit network each packet contains
a)
full source and destination address
b)
a short VC number
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Raghav Joshi answered |
Explanation:
Virtual Circuit Network is a type of network in which a dedicated path is established between the source and destination before transmitting the data. In this network, each packet contains a short VC (Virtual Circuit) number instead of a full source and destination address.
Advantages of using VC number:
- It reduces the overhead of routing and forwarding packets by eliminating the need for address lookup in each router along the path.
- It provides faster and more efficient packet switching as the network can quickly route the packets based on the VC number.
Disadvantages of using VC number:
- It requires a lot of resources to establish and maintain the virtual circuit path, which can result in higher latency and delay in transmission.
- It can also lead to network congestion as multiple virtual circuits may share the same physical link.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that each packet in a virtual circuit network contains a short VC number instead of a full source and destination address.
Virtual Circuit Network is a type of network in which a dedicated path is established between the source and destination before transmitting the data. In this network, each packet contains a short VC (Virtual Circuit) number instead of a full source and destination address.
Advantages of using VC number:
- It reduces the overhead of routing and forwarding packets by eliminating the need for address lookup in each router along the path.
- It provides faster and more efficient packet switching as the network can quickly route the packets based on the VC number.
Disadvantages of using VC number:
- It requires a lot of resources to establish and maintain the virtual circuit path, which can result in higher latency and delay in transmission.
- It can also lead to network congestion as multiple virtual circuits may share the same physical link.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that each packet in a virtual circuit network contains a short VC number instead of a full source and destination address.
Identify the statement which cannot be associated with OSI model- a)A structured way to discuss and easier update syatem components
- b)One layer may duplicate lower layer functionality
- c)Functionality at one layer no way requires information from another layer
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the statement which cannot be associated with OSI model
a)
A structured way to discuss and easier update syatem components
b)
One layer may duplicate lower layer functionality
c)
Functionality at one layer no way requires information from another layer
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Megha Yadav answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: One layer may use the information from another layer Ex: time stamp value.
Explanation: One layer may use the information from another layer Ex: time stamp value.
An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 0100 0010. Which of the following is correct ?- a)The number of hops this packet can travel is 2
- b)The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
- c)The upper layer protocol is ICMP
- d)The receiver rejects the packet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 0100 0010. Which of the following is correct ?
a)
The number of hops this packet can travel is 2
b)
The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
c)
The upper layer protocol is ICMP
d)
The receiver rejects the packet
|
|
Abhiram Goyal answered |
Understanding the IP Header
An IP packet begins with a header that includes critical information. The first 8 bits of the header signify the version and the header length. In this case, the bits are "0100 0010".
Bit Analysis
- The first four bits (0100) indicate the version of the IP protocol. Here, it is IPv4 (as 0100 corresponds to version 4).
- The second four bits (0010) represent the header length. This is calculated as 2 multiplied by 4 bytes, which equals 8 bytes.
Evaluation of Options
- Option A: The number of hops this packet can travel is 2.
- Incorrect. The number of hops is determined by the Time to Live (TTL) field, not the header length.
- Option B: The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
- Incorrect. The header length is 8 bytes, which is derived from the second four bits of the first byte.
- Option C: The upper layer protocol is ICMP.
- Incorrect. The upper layer protocol is identified in the Protocol field, but this information isn’t provided in the first 8 bits.
- Option D: The receiver rejects the packet.
- Correct. If the header length is misinterpreted or if there are issues in the header, the receiver may reject the packet. Given that the header length indicates 8 bytes, if the actual packet length does not match this, it would result in rejection.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option D, as various factors can lead to packet rejection based on header information.
An IP packet begins with a header that includes critical information. The first 8 bits of the header signify the version and the header length. In this case, the bits are "0100 0010".
Bit Analysis
- The first four bits (0100) indicate the version of the IP protocol. Here, it is IPv4 (as 0100 corresponds to version 4).
- The second four bits (0010) represent the header length. This is calculated as 2 multiplied by 4 bytes, which equals 8 bytes.
Evaluation of Options
- Option A: The number of hops this packet can travel is 2.
- Incorrect. The number of hops is determined by the Time to Live (TTL) field, not the header length.
- Option B: The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
- Incorrect. The header length is 8 bytes, which is derived from the second four bits of the first byte.
- Option C: The upper layer protocol is ICMP.
- Incorrect. The upper layer protocol is identified in the Protocol field, but this information isn’t provided in the first 8 bits.
- Option D: The receiver rejects the packet.
- Correct. If the header length is misinterpreted or if there are issues in the header, the receiver may reject the packet. Given that the header length indicates 8 bytes, if the actual packet length does not match this, it would result in rejection.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option D, as various factors can lead to packet rejection based on header information.
A computer on a 10 Mbps network is regulated by a token bucket. The token bucket is filled at a rate of 2 Mbps. It is initially filled to capacity with 16 Megabits. What is the maximum duration for which the computer can transmit at the full 10 Mbps?- a)1.6 seconds
- b)2 seconds
- c)5 seconds
- d)8 seconds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A computer on a 10 Mbps network is regulated by a token bucket. The token bucket is filled at a rate of 2 Mbps. It is initially filled to capacity with 16 Megabits. What is the maximum duration for which the computer can transmit at the full 10 Mbps?
a)
1.6 seconds
b)
2 seconds
c)
5 seconds
d)
8 seconds
|
|
Kunal Choudhary answered |
New tokens are added at the rate of r bits/sec which is
2Mbps in the given question.
Capacity of the token bucket (b) = 16 Mbits
Maximum possible transmission rate (M) = 10Mbps
So the maximum burst time = b/(M-r) = 16/(10-2) = 2 seconds
here is the animation for token bucket hope this will help us to understand the concept.
2Mbps in the given question.
Capacity of the token bucket (b) = 16 Mbits
Maximum possible transmission rate (M) = 10Mbps
So the maximum burst time = b/(M-r) = 16/(10-2) = 2 seconds
here is the animation for token bucket hope this will help us to understand the concept.
In the waveform (a) given below, a bit stream is encoded by Manchester encoding scheme. The same bit stream is encoded in a different coding scheme in wave form (b). The bit stream and the coding scheme are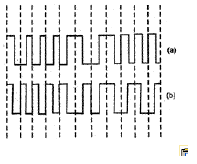
- a)1000010111 and Differential Manchester respectively
- b)0111101000 and Differential Manchester respectively
- c)1000010111 and Integral Manchester respectively
- d)0111101000 and Integral Manchester respectively
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the waveform (a) given below, a bit stream is encoded by Manchester encoding scheme. The same bit stream is encoded in a different coding scheme in wave form (b). The bit stream and the coding scheme are
a)
1000010111 and Differential Manchester respectively
b)
0111101000 and Differential Manchester respectively
c)
1000010111 and Integral Manchester respectively
d)
0111101000 and Integral Manchester respectively
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
In simple language, Manchester encoding has +A to -A transition for the clock cycle for which bit is ‘1’ and transition from -A to +A for the cycle when bit is ‘0’ (A is the amplitude).
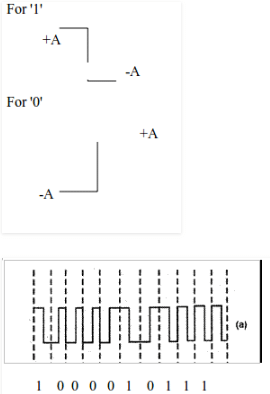
The amplitudes are bipolar in Differential manchester encoding same as manchester encoding just that it toggles at ‘1’. When bit is ‘1’ we get transition from +A to -A and it remains the same until next ‘1’ arrives. The output changes to opposite transition (-A to +A) when next ‘1’ arrives.
The second encoding resembles the differential manchester code for the given number.
The OSI model has _______ layers.- a)4
- b)5
- c)6
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The OSI model has _______ layers.
a)
4
b)
5
c)
6
d)
7
|
|
Vandana Desai answered |
Understanding the OSI Model
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework used to understand and implement networking protocols in seven distinct layers. Each layer serves a specific function in the process of data communication.
Seven Layers of the OSI Model
The OSI model consists of the following seven layers:
Importance of the OSI Model
Understanding the OSI model is crucial for several reasons:
In conclusion, the OSI model comprises seven layers, each serving a vital role in the communication process, making it a fundamental concept in computer networking.
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework used to understand and implement networking protocols in seven distinct layers. Each layer serves a specific function in the process of data communication.
Seven Layers of the OSI Model
The OSI model consists of the following seven layers:
- Layer 1: Physical Layer - Deals with the physical connection between devices, including cables, switches, and other hardware.
- Layer 2: Data Link Layer - Responsible for node-to-node data transfer and error detection/correction in frames.
- Layer 3: Network Layer - Handles routing and forwarding of data packets across the network.
- Layer 4: Transport Layer - Ensures reliable data transfer with error recovery and flow control through segments.
- Layer 5: Session Layer - Manages sessions between applications, providing control over the dialogues.
- Layer 6: Presentation Layer - Translates data formats, handles encryption, and ensures that data is in a readable format.
- Layer 7: Application Layer - Interfaces directly with end-user applications, facilitating communication between software and the network.
Importance of the OSI Model
Understanding the OSI model is crucial for several reasons:
- It standardizes networking protocols to ensure interoperability.
- It helps in troubleshooting network issues by isolating problems to specific layers.
- It provides a framework for developing and understanding new networking technologies.
In conclusion, the OSI model comprises seven layers, each serving a vital role in the communication process, making it a fundamental concept in computer networking.
Traceroute reports a possible route that is taken by packets moving from some host A to some other host B. Which of the following options represents the technique used by traceroute to identify these hosts- a)By progressively querying routers about the next router on the path to B using ICMP packets, starting with the first router
- b)By requiring each router to append the address to the ICMP packet as it is forwarded to B. The list of all routers en - route to B is returned by B in an ICMP reply packet
- c)By ensuring that an ICMP reply packet is returned to A by each router en-route to B, in the ascending order of their hop
distance from A - d)By locally computing the shortest path from A to B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Traceroute reports a possible route that is taken by packets moving from some host A to some other host B. Which of the following options represents the technique used by traceroute to identify these hosts
a)
By progressively querying routers about the next router on the path to B using ICMP packets, starting with the first router
b)
By requiring each router to append the address to the ICMP packet as it is forwarded to B. The list of all routers en - route to B is returned by B in an ICMP reply packet
c)
By ensuring that an ICMP reply packet is returned to A by each router en-route to B, in the ascending order of their hop
distance from A
distance from A
d)
By locally computing the shortest path from A to B

|
Pathways Academy answered |
A) Traceroute works by sending packets with gradually increasing TTL value, starting with TTL value of 1. The first router receives the packet, decrements the TTL value and drops the packet because it then
has TTL value zero. The router sends an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source. The next set of packets are given a TTL value of 2, so the first router forwards the packets, but the second router
drops them and replies with ICMP Time Exceeded. Proceeding in this way, traceroute uses the returned ICMP Time Exceeded messages to build a list of routers that packets traverse, until the destination is
reached and returns an ICMP Echo Reply message
has TTL value zero. The router sends an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source. The next set of packets are given a TTL value of 2, so the first router forwards the packets, but the second router
drops them and replies with ICMP Time Exceeded. Proceeding in this way, traceroute uses the returned ICMP Time Exceeded messages to build a list of routers that packets traverse, until the destination is
reached and returns an ICMP Echo Reply message
Which protocol use distance vector routing?- a)OSPF
- b)BGP
- c)RIP
- d)PPP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which protocol use distance vector routing?
a)
OSPF
b)
BGP
c)
RIP
d)
PPP
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Routing information protocol uses a distance vector protocol.
If an ethernet destination address is 07-01 -12 - 03 - 04 - 05, then that is a _____ address,- a)Unicast
- b)Multicast
- c)Broadcast
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an ethernet destination address is 07-01 -12 - 03 - 04 - 05, then that is a _____ address,
a)
Unicast
b)
Multicast
c)
Broadcast
d)
All of these
|
|
Rishabh Sharma answered |
07-01 - 12 - 03 - 04 - 05. The ethernet has more than one destinations but not all. So it is a multicast address not a broadcast address.
A packet-switching network- a)Is free
- b)Can reduce the cost of using an information utility
- c)Allows communications channels to be shared among more than one user
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A packet-switching network
a)
Is free
b)
Can reduce the cost of using an information utility
c)
Allows communications channels to be shared among more than one user
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Prateek Khanna answered |
Packet-switching network reduce cost using an inform ation utility and allow communication channels to be shared among more than one user.
A 3000 km long trunk operates at 1.536 mbps and is used to transmit 64 bytes frames and uses sliding window protocol. The propagation speed is 6 μ sec/km.
The minimum number of bits required in the sequence number field of the packet is- a)6 bits
- b)7 bits
- c)5 bits
- d)4 bits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 3000 km long trunk operates at 1.536 mbps and is used to transmit 64 bytes frames and uses sliding window protocol. The propagation speed is 6 μ sec/km.
The minimum number of bits required in the sequence number field of the packet is
The minimum number of bits required in the sequence number field of the packet is
a)
6 bits
b)
7 bits
c)
5 bits
d)
4 bits
|
|
Shanaya Chopra answered |
The first part of the question seems to be cut off. Could you please provide the complete question?
During normal IP packet forwarding by routers which of the following packet fields are updated?- a)IP header source address
- b)IP header destination address
- c)IP header TTL
- d)IP header check sum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During normal IP packet forwarding by routers which of the following packet fields are updated?
a)
IP header source address
b)
IP header destination address
c)
IP header TTL
d)
IP header check sum
|
|
Nilesh Mukherjee answered |
During forwarding of an IP packet by routers, the packet fields namely IP header source address and IP header destination address remains same whereas check own and TTL are updated.
How many bits internet address is assigned to each host on a TCP/IP internet which is used in all communication with the host?- a)16 bits
- b)32 bits
- c)48 bits
- d)64 bits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many bits internet address is assigned to each host on a TCP/IP internet which is used in all communication with the host?
a)
16 bits
b)
32 bits
c)
48 bits
d)
64 bits
|
|
Krish Datta answered |
Internet address has 32 bits, which is assigned to each host for communication on network.
The frame relay committed information rate represents- a)Maximum data rate on the network
- b)Steady state data rate on the network
- c)Minimum data rate on the network
- d)Interface data rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The frame relay committed information rate represents
a)
Maximum data rate on the network
b)
Steady state data rate on the network
c)
Minimum data rate on the network
d)
Interface data rate
|
|
Mainak Kulkarni answered |
Frame relay committed information rate represents minimum data rate on the network.
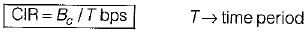
Here cumulative number of bits sent during the predefined period should not exceed Bc.
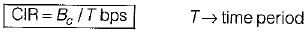
Here cumulative number of bits sent during the predefined period should not exceed Bc.
An example of a network layer is- a)Internet Protocol (IP)-ARPANET
- b)X.25 Packet Level Protocol (PLP)-ISO
- c)Source routing and domain naming-USENET
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of a network layer is
a)
Internet Protocol (IP)-ARPANET
b)
X.25 Packet Level Protocol (PLP)-ISO
c)
Source routing and domain naming-USENET
d)
All of these
|
|
Mira Rane answered |
Internet protocol (IP-ARPA NET, X.25 packet level protocoi-ISO and source routing and domain naming-USENET are example of network layer.
Multidestination routing- a)is same as broadcast routing
- b)contains the list of all destinations
- c)data is not sent by packets
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Multidestination routing
a)
is same as broadcast routing
b)
contains the list of all destinations
c)
data is not sent by packets
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Algorithms for effectively routing messages from a source to multiple destination nodes in a store-and-forward computer network are studied. The focus is on minimizing the network cost (NC), which is the sum of weights of the links in the routing path.
In the TCP/IP protocol suite, which one of the following is NOT part of the IP header?- a)Fragment Offset
- b)Source IP address
- c)Destination IP address
- d)Destination port number
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the TCP/IP protocol suite, which one of the following is NOT part of the IP header?
a)
Fragment Offset
b)
Source IP address
c)
Destination IP address
d)
Destination port number
|
|
Rounak Chavan answered |
D.) Destination Port number.
Why? Because the IP header has nothing to do with the port number.
Port numbers are used by the transport layer to ensure process to process delivery.
Why? Because the IP header has nothing to do with the port number.
Port numbers are used by the transport layer to ensure process to process delivery.
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) has been designed to compensate _________- a)Error-reporting
- b)Error-correction
- c)Host and management queries
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) has been designed to compensate _________
a)
Error-reporting
b)
Error-correction
c)
Host and management queries
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
Introduction:
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is an integral part of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is used to report errors, perform diagnostics, and exchange control messages between network devices. ICMP has been designed to compensate for various functionalities, including error reporting, error correction, and host and management queries.
Error Reporting:
ICMP provides error reporting capabilities to network devices. Whenever an error occurs during the transmission or processing of IP packets, ICMP messages are generated and sent to the source IP address. These error messages help to identify and diagnose network issues, allowing for timely resolution.
Error Correction:
ICMP also facilitates error correction mechanisms. For example, when a packet encounters an error during transmission, such as a time-to-live (TTL) exceeded or destination host unreachable, ICMP messages are sent back to the source IP address to inform the sender about the error. This allows the sender to take corrective actions, such as retransmitting the packet or choosing an alternative route.
Host and Management Queries:
In addition to error reporting and correction, ICMP supports host and management queries. ICMP messages can be used to query network devices for information or perform diagnostic tasks. For instance, the Internet Control Message Protocol Echo Request (ICMP Echo Request) is commonly known as a "ping" request. It is used to check the reachability and response time of a network host. ICMP also provides other query messages, such as Address Mask Request, Timestamp Request, and Router Solicitation, which serve various network management and troubleshooting purposes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) has been designed to compensate for error reporting, error correction, and host and management queries. It plays a crucial role in maintaining network stability, diagnosing issues, and facilitating communication between network devices. The various ICMP messages ensure that errors are reported, corrected, and that network devices can query each other for information or perform diagnostic tasks.
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is an integral part of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is used to report errors, perform diagnostics, and exchange control messages between network devices. ICMP has been designed to compensate for various functionalities, including error reporting, error correction, and host and management queries.
Error Reporting:
ICMP provides error reporting capabilities to network devices. Whenever an error occurs during the transmission or processing of IP packets, ICMP messages are generated and sent to the source IP address. These error messages help to identify and diagnose network issues, allowing for timely resolution.
Error Correction:
ICMP also facilitates error correction mechanisms. For example, when a packet encounters an error during transmission, such as a time-to-live (TTL) exceeded or destination host unreachable, ICMP messages are sent back to the source IP address to inform the sender about the error. This allows the sender to take corrective actions, such as retransmitting the packet or choosing an alternative route.
Host and Management Queries:
In addition to error reporting and correction, ICMP supports host and management queries. ICMP messages can be used to query network devices for information or perform diagnostic tasks. For instance, the Internet Control Message Protocol Echo Request (ICMP Echo Request) is commonly known as a "ping" request. It is used to check the reachability and response time of a network host. ICMP also provides other query messages, such as Address Mask Request, Timestamp Request, and Router Solicitation, which serve various network management and troubleshooting purposes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) has been designed to compensate for error reporting, error correction, and host and management queries. It plays a crucial role in maintaining network stability, diagnosing issues, and facilitating communication between network devices. The various ICMP messages ensure that errors are reported, corrected, and that network devices can query each other for information or perform diagnostic tasks.
The DHCP server can provide the _______ of the IP addresses.- a)dynamic allocation
- b)automatic allocation
- c)static allocation
- d)all of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The DHCP server can provide the _______ of the IP addresses.
a)
dynamic allocation
b)
automatic allocation
c)
static allocation
d)
all of the mentioned
|
|
Raghav Joshi answered |
Dynamic allocation, automatic allocation, and static allocation are the three ways in which the DHCP server can provide IP addresses. Let us discuss each of these in detail.
Dynamic Allocation:
When a DHCP server is configured to use dynamic allocation, it assigns an IP address to a device for a limited period of time. Once the lease time expires, the device must request a new IP address from the DHCP server. This method is useful in situations where there are more devices than available IP addresses, as it allows for the efficient use of IP addresses. Dynamic allocation also allows for easier IP address management, as the DHCP server can track which addresses are in use and which are available.
Automatic Allocation:
In automatic allocation, the DHCP server assigns a permanent IP address to a device based on its MAC address. This method is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address, such as servers or printers. Automatic allocation eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration and ensures that the device always has the same IP address.
Static Allocation:
Static allocation is when the network administrator manually assigns a fixed IP address to a device. This method is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address, such as servers or printers. However, static allocation can be time-consuming and error-prone, especially in large networks.
Conclusion:
In summary, the DHCP server can provide IP addresses through dynamic allocation, automatic allocation, and static allocation. Dynamic allocation is useful for situations where there are more devices than available IP addresses, automatic allocation is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address, and static allocation is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address and can be manually assigned by the network administrator.
Dynamic Allocation:
When a DHCP server is configured to use dynamic allocation, it assigns an IP address to a device for a limited period of time. Once the lease time expires, the device must request a new IP address from the DHCP server. This method is useful in situations where there are more devices than available IP addresses, as it allows for the efficient use of IP addresses. Dynamic allocation also allows for easier IP address management, as the DHCP server can track which addresses are in use and which are available.
Automatic Allocation:
In automatic allocation, the DHCP server assigns a permanent IP address to a device based on its MAC address. This method is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address, such as servers or printers. Automatic allocation eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration and ensures that the device always has the same IP address.
Static Allocation:
Static allocation is when the network administrator manually assigns a fixed IP address to a device. This method is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address, such as servers or printers. However, static allocation can be time-consuming and error-prone, especially in large networks.
Conclusion:
In summary, the DHCP server can provide IP addresses through dynamic allocation, automatic allocation, and static allocation. Dynamic allocation is useful for situations where there are more devices than available IP addresses, automatic allocation is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address, and static allocation is useful for devices that require a fixed IP address and can be manually assigned by the network administrator.
Transmission control protocol ___________- a)is a connection-oriented protocol
- b)uses a three way handshake to establish a connection
- c)receives data from application as a single stream
- d)all of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Transmission control protocol ___________
a)
is a connection-oriented protocol
b)
uses a three way handshake to establish a connection
c)
receives data from application as a single stream
d)
all of the mentioned
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
TCP provides reliable and ordered delivery of a stream of bytes between hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications like www, email, file transfer etc rely on TCP. TCP is connection oriented and it is optimized for accurate delivery rather than timely delivery.
Header size of the ICMP message is _________- a)8-bytes
- b)8-bits
- c)16-bytes
- d)16-bits
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Header size of the ICMP message is _________
a)
8-bytes
b)
8-bits
c)
16-bytes
d)
16-bits
|
|
Dhruba Goyal answered |
Header size of the ICMP message is 8-bytes
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network protocol used for error reporting, diagnostic, and informational purposes in IP networks. It is primarily used by network devices to communicate error messages, such as unreachable hosts or network congestion, back to the source IP address.
The ICMP message consists of two parts: the ICMP header and the ICMP data. The ICMP header contains essential information about the message, while the ICMP data carries additional details or payload.
Let's explore the header size of the ICMP message:
1. ICMP Header
The ICMP header has a fixed size of 8 bytes (64 bits). It includes the following fields:
- Type (8 bits): Specifies the type of ICMP message, such as echo request (ping), echo reply, destination unreachable, time exceeded, etc.
- Code (8 bits): Further categorizes the ICMP message type. For example, for the destination unreachable type, the code field specifies the reason for the unreachable destination.
- Checksum (16 bits): A checksum is used to detect errors in the ICMP message header and data.
- Rest of Header (32 bits): Reserved for future use and should be set to zero.
2. ICMP Data
The ICMP data field varies in size depending on the ICMP message type. It carries additional information related to the specific ICMP message. For example, in an echo request (ping) message, the data may include a payload that is sent to the destination and returned in the echo reply message.
Summary
In summary, the header size of the ICMP message is 8 bytes (64 bits). The ICMP header contains the type, code, checksum, and reserved fields, while the ICMP data carries additional information specific to the ICMP message type.
Note: It's important to note that the total size of the ICMP message, including both the header and data, may vary depending on the specific ICMP message type and the payload it carries.
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network protocol used for error reporting, diagnostic, and informational purposes in IP networks. It is primarily used by network devices to communicate error messages, such as unreachable hosts or network congestion, back to the source IP address.
The ICMP message consists of two parts: the ICMP header and the ICMP data. The ICMP header contains essential information about the message, while the ICMP data carries additional details or payload.
Let's explore the header size of the ICMP message:
1. ICMP Header
The ICMP header has a fixed size of 8 bytes (64 bits). It includes the following fields:
- Type (8 bits): Specifies the type of ICMP message, such as echo request (ping), echo reply, destination unreachable, time exceeded, etc.
- Code (8 bits): Further categorizes the ICMP message type. For example, for the destination unreachable type, the code field specifies the reason for the unreachable destination.
- Checksum (16 bits): A checksum is used to detect errors in the ICMP message header and data.
- Rest of Header (32 bits): Reserved for future use and should be set to zero.
2. ICMP Data
The ICMP data field varies in size depending on the ICMP message type. It carries additional information related to the specific ICMP message. For example, in an echo request (ping) message, the data may include a payload that is sent to the destination and returned in the echo reply message.
Summary
In summary, the header size of the ICMP message is 8 bytes (64 bits). The ICMP header contains the type, code, checksum, and reserved fields, while the ICMP data carries additional information specific to the ICMP message type.
Note: It's important to note that the total size of the ICMP message, including both the header and data, may vary depending on the specific ICMP message type and the payload it carries.
User datagram protocol is called connectionless because _____________- a)all UDP packets are treated independently by transport layer
- b)it sends data as a stream of related packets
- c)it is received in the same order as sent order
- d)it sends data very quickly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
User datagram protocol is called connectionless because _____________
a)
all UDP packets are treated independently by transport layer
b)
it sends data as a stream of related packets
c)
it is received in the same order as sent order
d)
it sends data very quickly
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
UDP is an alternative for TCP and it is used for those purposes where speed matters most whereas loss of data is not a problem. UDP is connectionless whereas TCP is connection oriented.
A link of capacity 100 Mbps is carrying traffic from a number of sources. Each source generates an on-off traffic stream;
when the source is on, the rate of traffic is 10 Mbps, and when the source is off, the rate of traffic is zero. The duty cycle,
which is the ratio of on-time to off-time, is 1 : 2. When there is no buffer at the link, the minimum number of sources that can be multiplexed on the link so that link capacity is not wasted and no data loss occurs is S1. Assuming that all sources are synchronized and that the link is provided with a large buffer, the maximum number of sources that can be multiplexed so that no data loss occurs is S2. The values of S1 and S2 are, respectively,- a)10 and 30
- b)12 and 25
- c)5 and 33
- d)15 and 22
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A link of capacity 100 Mbps is carrying traffic from a number of sources. Each source generates an on-off traffic stream;
when the source is on, the rate of traffic is 10 Mbps, and when the source is off, the rate of traffic is zero. The duty cycle,
which is the ratio of on-time to off-time, is 1 : 2. When there is no buffer at the link, the minimum number of sources that can be multiplexed on the link so that link capacity is not wasted and no data loss occurs is S1. Assuming that all sources are synchronized and that the link is provided with a large buffer, the maximum number of sources that can be multiplexed so that no data loss occurs is S2. The values of S1 and S2 are, respectively,
when the source is on, the rate of traffic is 10 Mbps, and when the source is off, the rate of traffic is zero. The duty cycle,
which is the ratio of on-time to off-time, is 1 : 2. When there is no buffer at the link, the minimum number of sources that can be multiplexed on the link so that link capacity is not wasted and no data loss occurs is S1. Assuming that all sources are synchronized and that the link is provided with a large buffer, the maximum number of sources that can be multiplexed so that no data loss occurs is S2. The values of S1 and S2 are, respectively,
a)
10 and 30
b)
12 and 25
c)
5 and 33
d)
15 and 22
|
|
Mahi Yadav answered |
Since there is no buffer.. and constraint given is there should not be any data lost, and no wastage of capacity as well..
Since data should not be lost, we calculate for the extreme case when all sources are on-time (that is transmitting)..
10 Mbps * n-station 100 Mbps
n-station = 10..
In the next part of the question it is given that the link is provided with large buffer and we are asked to find out large no. of stations..
for that we'll calculate expected value of bandwidth usage (if more data comes we store in buffer and due to expectation,
the buffer will be emptied soon):
E = 1/3 * 10 + 1/3 * 10 +...n-station times 100 Mbps [ total time is (1+2) = 3 then on time is 1 so 1/3 of BW]
=> 1/3 * 10 * n-station 100 Mbps
=> n-station = 30
so, option (A)
Since data should not be lost, we calculate for the extreme case when all sources are on-time (that is transmitting)..
10 Mbps * n-station 100 Mbps
n-station = 10..
In the next part of the question it is given that the link is provided with large buffer and we are asked to find out large no. of stations..
for that we'll calculate expected value of bandwidth usage (if more data comes we store in buffer and due to expectation,
the buffer will be emptied soon):
E = 1/3 * 10 + 1/3 * 10 +...n-station times 100 Mbps [ total time is (1+2) = 3 then on time is 1 so 1/3 of BW]
=> 1/3 * 10 * n-station 100 Mbps
=> n-station = 30
so, option (A)
A 1 Mbps satellite link connects two ground stations. The altitude of the satellite is 36,504 km and speed of the signal is 3 ×108 m/s. What should be the packet size for a channel utilization of 25% for a satellite link using go-back-127 sliding window protocol? Assume that the acknowledgment packets are negligible in size and that there are no errors during communication.- a)120 bytes
- b)60 bytes
- c)240 bytes
- d)90 bytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A 1 Mbps satellite link connects two ground stations. The altitude of the satellite is 36,504 km and speed of the signal is 3 ×108 m/s. What should be the packet size for a channel utilization of 25% for a satellite link using go-back-127 sliding window protocol? Assume that the acknowledgment packets are negligible in size and that there are no errors during communication.
a)
120 bytes
b)
60 bytes
c)
240 bytes
d)
90 bytes
|
|
Rounak Chavan answered |
Distance from Station A to Satellite = 36504 x 103 m
Time to reach satellite =
Efficiency is the ratio of the amount of data sent to the maximum amount of data that could be sent. Let X be the packet size.
In Go-Back-N, within RTT we can sent n packets. So, useful data is nxX, where X is the packet size. Now, before we can sent another packet ACK must reach back. Time for this is transmission time for a packet (other packets are pipelined and we care only for first ACK), and RTT for a bit (propagation times for the packet + propagation time for ACK +
transmission time for ACK - neglected as per question)
In Go-Back-N, within RTT we can sent n packets. So, useful data is nxX, where X is the packet size. Now, before we can sent another packet ACK must reach back. Time for this is transmission time for a packet (other packets are pipelined and we care only for first ACK), and RTT for a bit (propagation times for the packet + propagation time for ACK +
transmission time for ACK - neglected as per question)
Packet Size = 960 bits = 120 Bytes
so option (A)
so option (A)
Chapter doubts & questions for Computer Networks - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Computer Networks - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE
453 videos|1305 docs|700 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily












