All Exams >
Computer Science Engineering (CSE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE >
All Questions
All questions of Database Management System (DBMS) for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
In airline reservation system, the entities are date, flight number, place of departure, destination, type of plane and seats available. The primary key is:
- a)Flight number + date
- b)Flight number + place of departure
- c)Flight number
- d)Flight number + destination
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In airline reservation system, the entities are date, flight number, place of departure, destination, type of plane and seats available. The primary key is:
a)
Flight number + date
b)
Flight number + place of departure
c)
Flight number
d)
Flight number + destination
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Correct answer is C. Flight number because it is the unique key and it cannot be null. Using the flight number, the user can get all the information related to the reservation.
What is the min and max number of tables required to convert an ER diagram with 2 entities and 1 relationship between them with partial participation constraints of both entities?- a)Min 1 and max 2
- b)Min 1 and max 3
- c)Min 2 and max 3
- d)Min 2 and max 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the min and max number of tables required to convert an ER diagram with 2 entities and 1 relationship between them with partial participation constraints of both entities?
a)
Min 1 and max 2
b)
Min 1 and max 3
c)
Min 2 and max 3
d)
Min 2 and max 2

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Maximum number of tables required is 3 in case of many to many relationships between entities. Minimum number of tables is 1 in case of unary relationship and total participation of atleast one entity. But in case of partial participation of both entities, minimum number of tables required is 2.
In an entity relationship, y is the dominant entity and x is a subordinate entity. Which of the following is/are incorrect?- a)Operationally , if y is deleted, so is x
- b)x is existence dependent on y
- c)Operationally x is deleted, so is y
- d)Operationally, x is deleted, y remains the same
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an entity relationship, y is the dominant entity and x is a subordinate entity. Which of the following is/are incorrect?
a)
Operationally , if y is deleted, so is x
b)
x is existence dependent on y
c)
Operationally x is deleted, so is y
d)
Operationally, x is deleted, y remains the same
|
|
Abhiram Goyal answered |
1. y is dominant entity.
2. x is subordinate entity..
Since, y is dominant entity. So does not depend on any other and x is subordinate. So x is existence dependent on y and deletion of x does not effect y, So, x is detected, so y is incorrect.
Since, y is dominant entity. So does not depend on any other and x is subordinate. So x is existence dependent on y and deletion of x does not effect y, So, x is detected, so y is incorrect.
Which of the following command is used to delete a table in SQL?- a)delete
- b)truncate
- c)remove
- d)drop
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following command is used to delete a table in SQL?
a)
delete
b)
truncate
c)
remove
d)
drop
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
drop is used to delete a table completely
Consider a schema R(A,B,C,D) and functional dependencies A->B and C->D. Then the decomposition of R into R1(AB) and R2(CD) is- a)dependency preserving and lossless join
- b)lossless join but not dependency preserving
- c)dependency preserving but not lossless join
- d)not dependency preserving and not lossless join
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a schema R(A,B,C,D) and functional dependencies A->B and C->D. Then the decomposition of R into R1(AB) and R2(CD) is
a)
dependency preserving and lossless join
b)
lossless join but not dependency preserving
c)
dependency preserving but not lossless join
d)
not dependency preserving and not lossless join
|
|
Nisha Das answered |
Dependency Preserving Decomposition:
Decomposition of R into R1 and R2 is a dependency preserving decomposition if closure of functional dependencies after decomposition is same as closure of of FDs before decomposition.
A simple way is to just check whether we can derive all the original FDs from the FDs present after decomposition.
Decomposition of R into R1 and R2 is a dependency preserving decomposition if closure of functional dependencies after decomposition is same as closure of of FDs before decomposition.
A simple way is to just check whether we can derive all the original FDs from the FDs present after decomposition.
In the above question R(A, B, C, D) is decomposed into R1 (A, B) and R2(C, D) and there are only two FDs A -> B and C -> D. So, the decomposition is dependency preserving
Lossless-Join Decomposition:
Decomposition of R into R1 and R2 is a lossless-join decomposition if at least one of the following functional dependencies are in F+ (Closure of functional dependencies)
Decomposition of R into R1 and R2 is a lossless-join decomposition if at least one of the following functional dependencies are in F+ (Closure of functional dependencies)
R1 ∩ R2 → R1
OR
R1 ∩ R2 → R2
OR
R1 ∩ R2 → R2
In the above question R(A, B, C, D) is decomposed into R1 (A, B) and R2(C, D), and R1 ∩ R2 is empty. So, the decomposition is not lossless.
Consider the following database schedule with two transactions, T1 and T2.S = r2(X); r1(X); r2(Y); w1(X); r1(Y); w2(X); a1; a2;where ri(Z) denotes a read operation by transaction Ti on a variable Z, wi(Z) denotes a write operation by Ti on a variable Z and ai denotes an abort by transaction Ti . Which one of the following statements about the above schedule is TRUE?- a)S is non-recoverable
- b)S is recoverable, but has a cascading abort
- c)S does not have a cascading abort
- d)S is strict
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following database schedule with two transactions, T1 and T2.
S = r2(X); r1(X); r2(Y); w1(X); r1(Y); w2(X); a1; a2;
where ri(Z) denotes a read operation by transaction Ti on a variable Z, wi(Z) denotes a write operation by Ti on a variable Z and ai denotes an abort by transaction Ti . Which one of the following statements about the above schedule is TRUE?
a)
S is non-recoverable
b)
S is recoverable, but has a cascading abort
c)
S does not have a cascading abort
d)
S is strict
|
|
Tanishq Yadav answered |
As we can see in figure,
- T2 overwrites a value that T1 writes
- T1 aborts: its “remembered” values are restored.
- Cascading Abort could have arised if - > Abort of T1 required abort of T2 but as T2 is already aborted , its not a cascade abort. Therefore, Option C
Option A - is not true because the given schedule is recoverable Option B - is not true as it is recoverable and avoid cascading aborts; Option D - is not true because T2 is also doing abort operation after T1 does, so NOT strict.
The column of a table is referred to as the- a)Tuple
- b)Attribute
- c)Entity
- d)Degree
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The column of a table is referred to as the
a)
Tuple
b)
Attribute
c)
Entity
d)
Degree
|
|
Ameya Basak answered |
Every column of the table is referred to as attribute. Row of the table are called as tuples. Number of columns in the table defines the degree of the table.
R(A,B,C,D) is a relation. Which of the following does not have a lossless join, dependency preserving BCNF decomposition?- a)A->B, B->CD
- b)A->B, B->C, C->D
- c)AB->C, C->AD
- d)A ->BCD
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
R(A,B,C,D) is a relation. Which of the following does not have a lossless join, dependency preserving BCNF decomposition?
a)
A->B, B->CD
b)
A->B, B->C, C->D
c)
AB->C, C->AD
d)
A ->BCD
|
|
Uday Saha answered |
Background :
- Lossless-Join Decomposition:
Decomposition of R into R1 and R2 is a lossless-join decomposition if at least one of the following functional dependencies are in F+ (Closure of functional dependencies)
R1 ∩ R2 → R1
OR
R1 ∩ R2 → R2
OR
R1 ∩ R2 → R2
- dependency preserving :
Decomposition of R into R1 and R2 is a dependency preserving decomposition if closure of functional dependencies after decomposition is same as closure of of FDs before decomposition.
A simple way is to just check whether we can derive all the original FDs from the FDs present after decomposition.
Question : We know that for lossless decomposition common attribute should be candidate key in one of the relation. A) A->B, B->CD R1(AB) and R2(BCD) B is the key of second and hence decomposition is lossless. B) A->B, B->C, C->D R1(AB) , R2(BC), R3(CD) B is the key of second and C is the key of third, hence lossless. C) AB->C, C->AD R1(ABC), R2(CD) C is key of second, but C->A violates BCNF condition in ABC as C is not a key. We cannot decompose ABC further as AB->C dependency would be lost.D) A ->BCD Already in BCNF. Therefore, Option C AB->C, C->AD is the answer.
Which of the following is NOT a superkey in a relational schema with attributes V, W, X, Y, Z and primary key V Y ?- a)V X Y Z
- b)V W X Z
- c)V W X Y
- d)V W X Y Z
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a superkey in a relational schema with attributes V, W, X, Y, Z and primary key V Y ?
a)
V X Y Z
b)
V W X Z
c)
V W X Y
d)
V W X Y Z
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Super key = Candidate Key + other attributes. But option B does not include Y which is a part of PK or candidate key.
Suppose a database schedule S involves transactions T1, ....Tn. Construct the precedence graph of S with vertices representing the transactions and edges representing the conflicts. If S is serializable, which one of the following orderings of the vertices of the precedence graph is guaranteed to yield a serial schedule?- a)Topological order
- b)Depth-first order
- c)Breadth-first order
- d)Ascending order of transaction indices
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose a database schedule S involves transactions T1, ....Tn. Construct the precedence graph of S with vertices representing the transactions and edges representing the conflicts. If S is serializable, which one of the following orderings of the vertices of the precedence graph is guaranteed to yield a serial schedule?
a)
Topological order
b)
Depth-first order
c)
Breadth-first order
d)
Ascending order of transaction indices
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
Cycle in precedence graph tells that schedule is not conflict serializable. DFS and BFS traversal of graph are possible even if graph contains cycle. And hence DFS and BFS are also possible for non serializable graphs. But Topological sort of any cyclic graph is not possible. Thus topological sort guarantees graph to be serializable. Option D is not valid because in a transaction with more indices might have to come before lower one. Also two non- conflicting schedule can occur simultaneously.
Third normal form is inadequate in situations where the relation- a)Has multiple candidate keys
- b)Has candidate keys that are composite
- c)Has overlapped candidate keys
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Third normal form is inadequate in situations where the relation
a)
Has multiple candidate keys
b)
Has candidate keys that are composite
c)
Has overlapped candidate keys
d)
All of the above
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Third normal form is considered adequate for relational database design, it is inadequate in all situations with the relation having multiple, composes or overlapped candidate keys.
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to entity integrity?- a)Entity integrity constraints specify that primary key values can be composite. .
- b)Entity, integrity constraints are specified on individual relations.
- c)Entity integrity constraints are specified between weak entities.
- d)When entity integrity rules are enforced, a tuple in one relation that refers to another relation must refer to an existing tuple.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to entity integrity?
a)
Entity integrity constraints specify that primary key values can be composite. .
b)
Entity, integrity constraints are specified on individual relations.
c)
Entity integrity constraints are specified between weak entities.
d)
When entity integrity rules are enforced, a tuple in one relation that refers to another relation must refer to an existing tuple.
|
|
Ashutosh Mukherjee answered |
According to entity integrity primary key of relation should not contain null values.
Relation R has eight attributes ABCDEFGH. Fields of R contain only atomic values. F = {CH -> G, A -> BC, B -> CFH, E -> A, F -> EG} is a set of functional dependencies (FDs) so that F+ is exactly the set of FDs that hold for R. How many candidate keys does the relation R have?- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Relation R has eight attributes ABCDEFGH. Fields of R contain only atomic values. F = {CH -> G, A -> BC, B -> CFH, E -> A, F -> EG} is a set of functional dependencies (FDs) so that F+ is exactly the set of FDs that hold for R. How many candidate keys does the relation R have?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
Here we can see that D is not part of any FD's , hence D must be part of the candidate key.
Now D+ ={ D}.
Hence we have to add A,B,C,E,F,G,H to D and check which of them are Candidate keys of size 2.
We can proceed as
AD+= {A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H}
Similarly we see BD+ , ED+ and FD+ also gives us all the attributes.Hence AD,BD,ED,FD are definitely the candidate keys.
But CD+ , GD+ and HD+ doesnt give all the attributes hence CD,GD and HD are not candidate keys.
Now we need to check the candidate keys of size 3 . Since AD , BD, ED, FD are all candidate keys hence we can't find candidate keys by adding elements to them as they will give us superkeys as they are already minimal. Hence we have to proceed with CD,GD and HD.
Also we can't add any of {A,B,E,F} to CD, GD, HD as they will again give us superset of {AD,BD,ED,FD} .
Hence we can only add among {C,G,H} to CD, GD, HD.
Adding C to GD and HD we get GCD , HCD. Taking closure and we will see they are not candidate keys.
Adding H to GD we get GHD which is also not a candidate key.(no more options with 3 attributes possible)
Now we need to check for candidate keys with 4 attributes . Since only remaining options are CGH and we have to add D only possible key of size 4 is CGHD whose closure also doesn't give us all of the attributes in the relation(All possible options covered)
Hence no of candidate keys are 4 : AD,BD,ED,FD.
A functional dependency of the form X → Y is trivial if
- a)
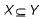
- b)
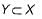
- c)
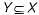
- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A functional dependency of the form X → Y is trivial if
a)
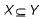
b)
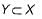
c)
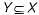
d)

|
|
Aaditya Ghosh answered |
A trivial functional dependency is a database dependency that occurs when describing a functional dependency of an attribute or of a collection of attributes that includes the original attribute.
So, Option c is correct answer.
E-R modeling technique is a- a)Top-down approach
- b)Bottom-up approach
- c)Left-right approach
- d)Both top-down and bottom-up
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
E-R modeling technique is a
a)
Top-down approach
b)
Bottom-up approach
c)
Left-right approach
d)
Both top-down and bottom-up
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
It is a top-down method.
An entity–relationship model (ER model) describes inter-related things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. An ER model is composed of entity types (which classify the things of interest) and specifies relationships that can exist between instances of those entity types.
In software engineering an ER model is commonly formed to represent things that a business needs to remember in order to perform business processes. Consequently, the ER model becomes an abstract data model that defines a data or information structure that can be implemented in a database, typically a relational database.
Some ER modelers show super and subtype entities connected by generalization-specialization relationships, and an ER model can be used also in the specification of domain-specific ontologies.
An entity–relationship model (ER model) describes inter-related things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. An ER model is composed of entity types (which classify the things of interest) and specifies relationships that can exist between instances of those entity types.
In software engineering an ER model is commonly formed to represent things that a business needs to remember in order to perform business processes. Consequently, the ER model becomes an abstract data model that defines a data or information structure that can be implemented in a database, typically a relational database.
Some ER modelers show super and subtype entities connected by generalization-specialization relationships, and an ER model can be used also in the specification of domain-specific ontologies.
Which allocation scheme would work best for a file system implemented on a device that can only be accessed sequentially, a tape drive, for instance?- a)Contiguous allocation
- b)Non Contiguous allocation
- c)Indexed allocation
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which allocation scheme would work best for a file system implemented on a device that can only be accessed sequentially, a tape drive, for instance?
a)
Contiguous allocation
b)
Non Contiguous allocation
c)
Indexed allocation
d)
None of the above
|
|
Nishanth Roy answered |
Contiguous allocation
Contiguous allocation is the allocation scheme that works best for a file system implemented on a device that can only be accessed sequentially, such as a tape drive. In this allocation scheme, files are stored on the storage medium in contiguous blocks or sections.
Advantages of Contiguous Allocation:
1. Sequential Access: Since the device can only be accessed sequentially, contiguous allocation allows for efficient sequential access of files. When a file is accessed, the next block of the file is located in the adjacent physical location on the tape, which reduces the seek time and improves performance.
2. Simplified Addressing: With contiguous allocation, the starting address of a file and its size are sufficient to locate and access the entire file. This simplifies the addressing mechanism, as the file can be located by knowing only its starting address.
3. Reduced Fragmentation: Contiguous allocation minimizes external fragmentation, as files are stored in contiguous blocks. There is no need to search for free blocks or maintain a free space list, which reduces the overhead of file allocation.
4. Efficient Disk Utilization: Since files are stored contiguously, the storage space can be utilized more efficiently. There is no wasted space between files, resulting in higher overall disk utilization.
5. Simplicity: Contiguous allocation is a simple and straightforward allocation scheme, making it easier to implement and manage. It requires less complex data structures and algorithms compared to other allocation schemes.
Disadvantages of Contiguous Allocation:
1. Fragmentation: Contiguous allocation can lead to internal fragmentation when the allocated blocks are larger than the size of the file. This can result in wasted space within the allocated blocks.
2. Limited Flexibility: Contiguous allocation does not provide much flexibility in dynamically allocating and deallocating files. It may require large contiguous free space to allocate a file, which can be a challenge in situations where the available free space is scattered.
Overall, contiguous allocation is the most suitable allocation scheme for a file system implemented on a device that can only be accessed sequentially, such as a tape drive. It provides efficient sequential access, simplified addressing, reduced fragmentation, efficient disk utilization, and simplicity in implementation.
Contiguous allocation is the allocation scheme that works best for a file system implemented on a device that can only be accessed sequentially, such as a tape drive. In this allocation scheme, files are stored on the storage medium in contiguous blocks or sections.
Advantages of Contiguous Allocation:
1. Sequential Access: Since the device can only be accessed sequentially, contiguous allocation allows for efficient sequential access of files. When a file is accessed, the next block of the file is located in the adjacent physical location on the tape, which reduces the seek time and improves performance.
2. Simplified Addressing: With contiguous allocation, the starting address of a file and its size are sufficient to locate and access the entire file. This simplifies the addressing mechanism, as the file can be located by knowing only its starting address.
3. Reduced Fragmentation: Contiguous allocation minimizes external fragmentation, as files are stored in contiguous blocks. There is no need to search for free blocks or maintain a free space list, which reduces the overhead of file allocation.
4. Efficient Disk Utilization: Since files are stored contiguously, the storage space can be utilized more efficiently. There is no wasted space between files, resulting in higher overall disk utilization.
5. Simplicity: Contiguous allocation is a simple and straightforward allocation scheme, making it easier to implement and manage. It requires less complex data structures and algorithms compared to other allocation schemes.
Disadvantages of Contiguous Allocation:
1. Fragmentation: Contiguous allocation can lead to internal fragmentation when the allocated blocks are larger than the size of the file. This can result in wasted space within the allocated blocks.
2. Limited Flexibility: Contiguous allocation does not provide much flexibility in dynamically allocating and deallocating files. It may require large contiguous free space to allocate a file, which can be a challenge in situations where the available free space is scattered.
Overall, contiguous allocation is the most suitable allocation scheme for a file system implemented on a device that can only be accessed sequentially, such as a tape drive. It provides efficient sequential access, simplified addressing, reduced fragmentation, efficient disk utilization, and simplicity in implementation.
Which of the following is correct?- a)B-trees are for storing data on disk and B+ trees are for main memory.
- b)Range queries are faster on B+ trees.
- c)B-trees are for primary indexes and B+ trees are for secondary indexes.
- d)The height of a B+ tree is independent of the number of records,
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct?
a)
B-trees are for storing data on disk and B+ trees are for main memory.
b)
Range queries are faster on B+ trees.
c)
B-trees are for primary indexes and B+ trees are for secondary indexes.
d)
The height of a B+ tree is independent of the number of records,
|
|
Navya Iyer answered |
Most database systems use indexes built on some form of a B+ tree due to its many advantages, in particular its support for range queries. Leaf nodes are linked together in B+ trees hence range queries are faster.
Which of the following statement is/are incorrect?
A: A schedule following strict two phase locking protocol is conflict serializable as well as recoverable.
B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.- a)Only 1
- b)Only 2
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is/are incorrect?
A: A schedule following strict two phase locking protocol is conflict serializable as well as recoverable.
B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.
A: A schedule following strict two phase locking protocol is conflict serializable as well as recoverable.
B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.
a)
Only 1
b)
Only 2
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
None
|
|
Niharika Ahuja answered |
< b="" />Incorrect Statement:< />
The incorrect statement is:
B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.
< b="" />Explanation:< />
1. A schedule following strict two-phase locking protocol is conflict serializable as well as recoverable:
- This statement is correct. The strict two-phase locking (2PL) protocol ensures conflict serializability by requiring that a transaction acquire and hold all its exclusive locks until it is ready to release them, and by forcing a transaction to release all its locks before acquiring any new locks. The 2PL protocol also ensures recoverability by ensuring that a transaction's updates are not visible to other transactions until it commits, and by allowing for the undoing of a transaction's updates if it aborts.
2. Checkpoints in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability:
- This statement is incorrect. Checkpoints in schedules are not inserted to ensure recoverability. Rather, checkpoints are used to improve the efficiency of recovery processes. A checkpoint is a point in a schedule where the system records the state of the database and the progress of transactions. When a failure occurs, the system can use the information recorded at the last checkpoint to reduce the amount of work required for recovery. By starting the recovery process from the last checkpoint, the system can avoid processing transactions that were already committed or aborted before the failure.
< b="" />Conclusion:< />
Based on the above explanation, the incorrect statement is B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.
The incorrect statement is:
B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.
< b="" />Explanation:< />
1. A schedule following strict two-phase locking protocol is conflict serializable as well as recoverable:
- This statement is correct. The strict two-phase locking (2PL) protocol ensures conflict serializability by requiring that a transaction acquire and hold all its exclusive locks until it is ready to release them, and by forcing a transaction to release all its locks before acquiring any new locks. The 2PL protocol also ensures recoverability by ensuring that a transaction's updates are not visible to other transactions until it commits, and by allowing for the undoing of a transaction's updates if it aborts.
2. Checkpoints in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability:
- This statement is incorrect. Checkpoints in schedules are not inserted to ensure recoverability. Rather, checkpoints are used to improve the efficiency of recovery processes. A checkpoint is a point in a schedule where the system records the state of the database and the progress of transactions. When a failure occurs, the system can use the information recorded at the last checkpoint to reduce the amount of work required for recovery. By starting the recovery process from the last checkpoint, the system can avoid processing transactions that were already committed or aborted before the failure.
< b="" />Conclusion:< />
Based on the above explanation, the incorrect statement is B: Checkpoint in schedules are inserted to ensure recoverability.
Consider an Entity-Relationship (ER) model in which entity sets E1 and E2 are connected by an m : n relationship R12, E1 and E3 are connected by a 1 : n (1 on the side of E1 and n on the side of E3) relationship R13. E1 has two single-valued attributes a11 and a12 of which a11 is the key attribute. E2 has two single-valued attributes a21 and a22 is the key attribute. E3 has two single-valued attributes a31 and a32 of which a31 is the key attribute. The relationships do not have any attributes. If a relational model is derived from the above ER model, then the minimum number of relations that would be generated if all the relations are in 3NF is ___________.- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider an Entity-Relationship (ER) model in which entity sets E1 and E2 are connected by an m : n relationship R12, E1 and E3 are connected by a 1 : n (1 on the side of E1 and n on the side of E3) relationship R13. E1 has two single-valued attributes a11 and a12 of which a11 is the key attribute. E2 has two single-valued attributes a21 and a22 is the key attribute. E3 has two single-valued attributes a31 and a32 of which a31 is the key attribute. The relationships do not have any attributes. If a relational model is derived from the above ER model, then the minimum number of relations that would be generated if all the relations are in 3NF is ___________.
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5
|
|
Nishanth Roy answered |
A data model is a collection of conceptual tools for describing- a)Data and data relationships.
- b)Data semantics and consistency constraints.
- c)Data, data relationship, data semantics and consistency constraints.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A data model is a collection of conceptual tools for describing
a)
Data and data relationships.
b)
Data semantics and consistency constraints.
c)
Data, data relationship, data semantics and consistency constraints.
d)
None of the above
|
|
Gitanjali Mishra answered |
Data models are the basic entities through which abstraction in a DBMS in introduced, It actually defines how data is connected to each other and how they are processed and stored inside the system.
Let R1 (A, B, C) and R2 (D, E) be two relation schema, where the primary keys are shown underlined, and let C be a foreign key in R1 referring to R2. Suppose there is no violation of the above referential integrity constraint in the corresponding relation instances r1 and r2. Which one of the following relational algebra expressions would necessarily produce an empty relation ?- a)
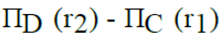
- b)
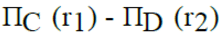
- c)
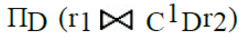
- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Let R1 (A, B, C) and R2 (D, E) be two relation schema, where the primary keys are shown underlined, and let C be a foreign key in R1 referring to R2. Suppose there is no violation of the above referential integrity constraint in the corresponding relation instances r1 and r2. Which one of the following relational algebra expressions would necessarily produce an empty relation ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Since C is a foreign key in R1 and there is no violation of the above referential integrity constraint, the set of values in C must be a subset of values in R2.
Given the functional dependencies:
X→W; X→Y; Y→Z and Z→PQ
Which of the following does not hold good?- a)X→Z
- b)W→Z
- c)X→WY
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given the functional dependencies:
X→W; X→Y; Y→Z and Z→PQ
Which of the following does not hold good?
X→W; X→Y; Y→Z and Z→PQ
Which of the following does not hold good?
a)
X→Z
b)
W→Z
c)
X→WY
d)
None of these
|
|
Saanvi Bajaj answered |
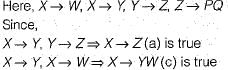
Since there is no FD’s for which W functionally depends on other attributes.
In SQL, relations can contain null values, and comparisons with null values are treated as unknown. Suppose all comparisons with a null value are treated as false. Which of the following pairs is not equivalent?- a)x = 5 AND not(not(x = 5))
- b)x = 5 AND x> 4 and x < 6, where x is an integer
- c)x < 5 AND not (x = 5)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In SQL, relations can contain null values, and comparisons with null values are treated as unknown. Suppose all comparisons with a null value are treated as false. Which of the following pairs is not equivalent?
a)
x = 5 AND not(not(x = 5))
b)
x = 5 AND x> 4 and x < 6, where x is an integer
c)
x < 5 AND not (x = 5)
d)
None of the above
|
|
Parth Sen answered |
For all values smaller than 5, x < 5 will always be true but x = 5 will be false.
Choose the correct statements:- a)Relational algebra and relational calculus are both procedural query languages.
- b)Relational algebra and relational calculus are both non-procedural query languages.
- c)Relational algebra is a procedural query language and relational calculus is a nonprocedural query language.
- d)Relational algebra is a non-procedural query language and relational calculus is a procedural query language.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statements:
a)
Relational algebra and relational calculus are both procedural query languages.
b)
Relational algebra and relational calculus are both non-procedural query languages.
c)
Relational algebra is a procedural query language and relational calculus is a nonprocedural query language.
d)
Relational algebra is a non-procedural query language and relational calculus is a procedural query language.
|
|
Avantika Menon answered |
Relation algebra is procedural query language while relational calculus is non-procedural query language.
Which of the following relational query languages have the same expressive power? - Relational algebra
- Tuple relational calculus restricted to safe expressions
- Domain relational calculus restricted to safe expressions
- a)II and III only
- b)I and II only
- c)I and III only
- d)I, II and III
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following relational query languages have the same expressive power?
- Relational algebra
- Tuple relational calculus restricted to safe expressions
- Domain relational calculus restricted to safe expressions
a)
II and III only
b)
I and II only
c)
I and III only
d)
I, II and III
|
|
Navya Iyer answered |
Relational algebra is a procedural query language where we input - relations and it yields relations as output. It provides method to get the result. It is performed recursively on a relation and the in between results are relations(output). Basic set of operations for the relational model. Relational calculus is a non - procedural query language. It provides the query to get result. Higher level declarative language for specifying relational queries. Tupple Relational Calculus operates on each tupple. Domain Relational Calculus operates on each column or attribute. Safe expression means fixed no. of tupple or column or attribute as a result But all of them has same expressive power. Just different ways to do so.
B+ trees are preferred to binary trees in databases because- a)Disk capacities are greater than memory capacities
- b)Disk access is much slower than memory access
- c)Disk data transfer rates are much less than memory data transfer rates
- d)Disks are more reliable than memory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
B+ trees are preferred to binary trees in databases because
a)
Disk capacities are greater than memory capacities
b)
Disk access is much slower than memory access
c)
Disk data transfer rates are much less than memory data transfer rates
d)
Disks are more reliable than memory
|
|
Amrutha Sharma answered |
Disk access is slow and B+ tree provide search in less number of disk hits. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+trees have very high fanout (typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduce the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree.
Entity set TRANSACTION has the attributes transaction number, date, amount. Entity set ACCOUNT has the attributes account number, customer name, balance.
Q. Which is the primary key of the weak entity?- a)Account number
- b){Account number, transaction number}
- c){Account number, date}
- d){Transaction number, date}
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Entity set TRANSACTION has the attributes transaction number, date, amount. Entity set ACCOUNT has the attributes account number, customer name, balance.
Q. Which is the primary key of the weak entity?
Q. Which is the primary key of the weak entity?
a)
Account number
b)
{Account number, transaction number}
c)
{Account number, date}
d)
{Transaction number, date}
|
|
Krithika Gupta answered |
In order to identify each transaction of any account the key of strong entity with the addition of the discriminator of weak entity can be taken. Here [Account number, transaction number] act as the primary key of weak entity. This is because weak entity has no existence without strong entity.
A relation (from the relational database model) consists of a set of tuples, which implies that- a)Relational model supports multi-valued attributes whose values can be represented in sets.
- b)For any two tuples, the values associated with all of their attributes may be the same.
- c)For any two tuples, the value associated with one or more of their attributes must differ.
- d)All tuples in a particular relation may have different attributes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A relation (from the relational database model) consists of a set of tuples, which implies that
a)
Relational model supports multi-valued attributes whose values can be represented in sets.
b)
For any two tuples, the values associated with all of their attributes may be the same.
c)
For any two tuples, the value associated with one or more of their attributes must differ.
d)
All tuples in a particular relation may have different attributes.
|
|
Baishali Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
Relational database model is based on the concept of relations or tables. A relation consists of a set of tuples, where each tuple represents a single entity or object in the real world. Each tuple has a set of attributes or fields, which represent the properties or characteristics of that entity. The values of these attributes are stored in the corresponding columns of the table.
Let us now understand the given options one by one:
a) Relational model supports multi-valued attributes whose values can be represented in sets.
This statement is incorrect. Relational model does not support multi-valued attributes. Each attribute in a relation can have only a single value. However, we can represent multiple values of an attribute by creating a separate table and establishing a relationship between the two tables.
b) For any two tuples, the values associated with all of their attributes may be the same.
This statement is also incorrect. In a relation, each tuple represents a unique entity, and therefore, the values associated with all of their attributes cannot be the same. There must be at least one attribute whose value differs between the two tuples.
c) For any two tuples, the value associated with one or more of their attributes must differ.
This statement is correct. As explained above, each tuple in a relation represents a unique entity, and therefore, the values associated with all of their attributes cannot be the same. There must be at least one attribute whose value differs between the two tuples.
d) All tuples in a particular relation may have different attributes.
This statement is also incorrect. In a relation, all tuples must have the same set of attributes, although some attributes may have null values in some tuples.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that for any two tuples, the value associated with one or more of their attributes must differ.
Relational database model is based on the concept of relations or tables. A relation consists of a set of tuples, where each tuple represents a single entity or object in the real world. Each tuple has a set of attributes or fields, which represent the properties or characteristics of that entity. The values of these attributes are stored in the corresponding columns of the table.
Let us now understand the given options one by one:
a) Relational model supports multi-valued attributes whose values can be represented in sets.
This statement is incorrect. Relational model does not support multi-valued attributes. Each attribute in a relation can have only a single value. However, we can represent multiple values of an attribute by creating a separate table and establishing a relationship between the two tables.
b) For any two tuples, the values associated with all of their attributes may be the same.
This statement is also incorrect. In a relation, each tuple represents a unique entity, and therefore, the values associated with all of their attributes cannot be the same. There must be at least one attribute whose value differs between the two tuples.
c) For any two tuples, the value associated with one or more of their attributes must differ.
This statement is correct. As explained above, each tuple in a relation represents a unique entity, and therefore, the values associated with all of their attributes cannot be the same. There must be at least one attribute whose value differs between the two tuples.
d) All tuples in a particular relation may have different attributes.
This statement is also incorrect. In a relation, all tuples must have the same set of attributes, although some attributes may have null values in some tuples.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that for any two tuples, the value associated with one or more of their attributes must differ.
AB+ tree index is to be built on the Name attribute of the relation STUDENT. Assume that all student names are of length 8 bytes, disk blocks are of size 512 bytes, and index pointers are of size 4 bytes. Given this scenario, what would be the best choice of the degree (i.e. the number of pointers per node) of the B+ tree?- a)16
- b)42
- c)43
- d)44
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
AB+ tree index is to be built on the Name attribute of the relation STUDENT. Assume that all student names are of length 8 bytes, disk blocks are of size 512 bytes, and index pointers are of size 4 bytes. Given this scenario, what would be the best choice of the degree (i.e. the number of pointers per node) of the B+ tree?
a)
16
b)
42
c)
43
d)
44
|
|
Soumya Pillai answered |
Let n be the degree
Given, k, key size (length of the name = 8 byte attribute of student)
Disk block size, B = 512 bytes
Index pointer size, b = 4 bytes
Degree of B+ tree can be calculated if we know the maximum number of key a internal node can have the formula for that is
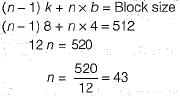
Given, k, key size (length of the name = 8 byte attribute of student)
Disk block size, B = 512 bytes
Index pointer size, b = 4 bytes
Degree of B+ tree can be calculated if we know the maximum number of key a internal node can have the formula for that is
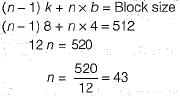
Which of the following statement is false?- a)Any relation can be decomposed into a number of relations that are in third normal form, such decomposition is lossless and preserves the dependencies.
- b)Any relation can be decomposed losslessly into relations in BCNF and decomposition into BCNF always preserve dependency.
- c)The decomposition approach using the BCNF may produce inter-relational join constraints.
- d)A decomposition of relation, into BCNF is not unique.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is false?
a)
Any relation can be decomposed into a number of relations that are in third normal form, such decomposition is lossless and preserves the dependencies.
b)
Any relation can be decomposed losslessly into relations in BCNF and decomposition into BCNF always preserve dependency.
c)
The decomposition approach using the BCNF may produce inter-relational join constraints.
d)
A decomposition of relation, into BCNF is not unique.
|
|
Divya Kaur answered |
BCNF relation may or may not preserve dependency also any relation cannot be necessarily decomposed into BCNF relation,
Let R (A, B, C, D, E, P, G) be a relational schema in which the following functional dependencies are known to hold: AB → CD, DE → P, C → E, P → C and B → G. The relational schema R is- a)in BCNF
- b)in 3NF, but not in BCNF
- c)in 2NF, but not in 3NF
- d)not in 2NF
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Let R (A, B, C, D, E, P, G) be a relational schema in which the following functional dependencies are known to hold: AB → CD, DE → P, C → E, P → C and B → G. The relational schema R is
a)
in BCNF
b)
in 3NF, but not in BCNF
c)
in 2NF, but not in 3NF
d)
not in 2NF
|
|
Garima Dasgupta answered |
Candidate key = AB
B->G is partial dependency
So, not in 2NF
B->G is partial dependency
So, not in 2NF
Consider the relation scheme R = {E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, M} and the set of functional dependencies {{E, F} -> {G}, {F} -> {I, J}, {E, H} -> {K, L}, K -> {M}, L -> {N} on R. What is the key for R?- a){E, F}
- b){E, F, H}
- c){E, F, H, K, L}
- d){E}
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the relation scheme R = {E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, M} and the set of functional dependencies {{E, F} -> {G}, {F} -> {I, J}, {E, H} -> {K, L}, K -> {M}, L -> {N} on R. What is the key for R?
a)
{E, F}
b)
{E, F, H}
c)
{E, F, H, K, L}
d)
{E}
|
|
Hiral Nair answered |
All attributes can be derived from {E, F, H} To solve these kind of questions that are frequently asked in GATE paper, try to solve it by using shortcuts so that enough amount of time can be saved.
Fist Method: Using the given options try to obtain closure of each options. The solution is the one that contains R and also minimal Super Key, i.e Candidate Key.
Fist Method: Using the given options try to obtain closure of each options. The solution is the one that contains R and also minimal Super Key, i.e Candidate Key.
A) {EF}+ = {EFGIJ} ≠ R(The given relation)
B) {EFH}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} = R (Correct since each member of the given relation is determined)
C) {EFHKL}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} = R (Not correct although each member of the given relation can be determined but it is not minimal, since by the definition of Candidate key it should be minimal Super Key)
D) {E}+ = {E} ≠ R
B) {EFH}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} = R (Correct since each member of the given relation is determined)
C) {EFHKL}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} = R (Not correct although each member of the given relation can be determined but it is not minimal, since by the definition of Candidate key it should be minimal Super Key)
D) {E}+ = {E} ≠ R
Second Method:
Since, {EFGHIJKLMN}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN}
{EFGHIJKLM}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since L -> {N}, hence can replace N by L)
In a similar way K -> {M} hence replace M by K
{EFGHIJKL}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN}
Again {EFGHIJ}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since {E, H} -> {K, L}, hence replace KL by EH)
{EFGH}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since {F} -> {I, J})
{EFH}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since {E, F} -> {G})
{EFGHIJKLM}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since L -> {N}, hence can replace N by L)
In a similar way K -> {M} hence replace M by K
{EFGHIJKL}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN}
Again {EFGHIJ}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since {E, H} -> {K, L}, hence replace KL by EH)
{EFGH}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since {F} -> {I, J})
{EFH}+ = {EFGHIJKLMN} (Since {E, F} -> {G})
A database table T1 has 2000 records and occupies 80 disk blocks. Another table T2 has 400 records and occupies 20 disk blocks. These two tables have to be joined as per a specified join condition that needs-to be evaluated for every pair of records from these two tables. The memory buffer space available can hold exactly one block of records for T1 and one block of records for T2 simultaneously at any point in time. No index is available on either table.
Q. If Nested-loop join algorithm is employed to perform the join, with the most appropriate choice of table to be used in outer loop, the number of block accesses required for reading the data are - a)800000
- b)40080
- c)32020
- d)100
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A database table T1 has 2000 records and occupies 80 disk blocks. Another table T2 has 400 records and occupies 20 disk blocks. These two tables have to be joined as per a specified join condition that needs-to be evaluated for every pair of records from these two tables. The memory buffer space available can hold exactly one block of records for T1 and one block of records for T2 simultaneously at any point in time. No index is available on either table.
Q. If Nested-loop join algorithm is employed to perform the join, with the most appropriate choice of table to be used in outer loop, the number of block accesses required for reading the data are
Q. If Nested-loop join algorithm is employed to perform the join, with the most appropriate choice of table to be used in outer loop, the number of block accesses required for reading the data are
a)
800000
b)
40080
c)
32020
d)
100
|
|
Harshitha Sarkar answered |
Here condition given only 1 block of T1 and 1 block of T2 can present simultaneously inside the memory buffer space.
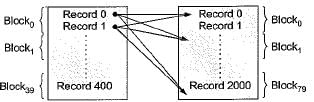
In Nested loop join every record of one table every block of second table is loaded.
So, If T1 is outer = 2000 x 20 + 80 = 40080
If T2 is outer = 400 x 80 + 20 = 32020
So we go with T2 as outer table = 32020

In Nested loop join every record of one table every block of second table is loaded.
So, If T1 is outer = 2000 x 20 + 80 = 40080
If T2 is outer = 400 x 80 + 20 = 32020
So we go with T2 as outer table = 32020
Consider the following statements:
S1 : Anchor block contains first records of chain.
S2: Anchor record is first record of a block.Which of the above statements is/are true?- a)S1 only
- b)S2 only
- c)Both S1 and S2 are true
- d)Both S1 and S2 are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
S1 : Anchor block contains first records of chain.
S2: Anchor record is first record of a block.
S1 : Anchor block contains first records of chain.
S2: Anchor record is first record of a block.
Which of the above statements is/are true?
a)
S1 only
b)
S2 only
c)
Both S1 and S2 are true
d)
Both S1 and S2 are false
|
|
Ankit Mehta answered |
Explanation:
The given statements are:
S1: Anchor block contains the first records of the chain.
S2: Anchor record is the first record of a block.
Let's analyze each statement individually:
S1: Anchor block contains the first records of the chain.
An anchor block is a special block in a blockchain that is used to reference the previous block in the chain. It serves as a starting point for the chain. The anchor block contains the first record of the chain, which is also known as the genesis block. This block typically contains information about the creation of the blockchain and sets the initial parameters for the system.
S2: Anchor record is the first record of a block.
An anchor record is a record within a block that is used to link the block to the previous block in the chain. It contains a reference to the previous block's anchor record. However, it is not necessarily the first record in the block. The anchor record is used to maintain the integrity and continuity of the blockchain by linking each block to its previous block.
Conclusion:
Based on the definitions and explanations above, we can conclude that both statements are true.
- Statement S1 is true because the anchor block does contain the first records of the chain, specifically the genesis block.
- Statement S2 is true because the anchor record is a record within a block, and it helps in linking the block to the previous block in the chain.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C: Both S1 and S2 are true.
The given statements are:
S1: Anchor block contains the first records of the chain.
S2: Anchor record is the first record of a block.
Let's analyze each statement individually:
S1: Anchor block contains the first records of the chain.
An anchor block is a special block in a blockchain that is used to reference the previous block in the chain. It serves as a starting point for the chain. The anchor block contains the first record of the chain, which is also known as the genesis block. This block typically contains information about the creation of the blockchain and sets the initial parameters for the system.
S2: Anchor record is the first record of a block.
An anchor record is a record within a block that is used to link the block to the previous block in the chain. It contains a reference to the previous block's anchor record. However, it is not necessarily the first record in the block. The anchor record is used to maintain the integrity and continuity of the blockchain by linking each block to its previous block.
Conclusion:
Based on the definitions and explanations above, we can conclude that both statements are true.
- Statement S1 is true because the anchor block does contain the first records of the chain, specifically the genesis block.
- Statement S2 is true because the anchor record is a record within a block, and it helps in linking the block to the previous block in the chain.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C: Both S1 and S2 are true.
Which indices search key defines the sequential order of file and which indices search key specifies an order different from sequential order of file?- a)Primary, Secondary
- b)Clustering, Primary
- c)Non-clustering, Secondary
- d)Clustering, Secondary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which indices search key defines the sequential order of file and which indices search key specifies an order different from sequential order of file?
a)
Primary, Secondary
b)
Clustering, Primary
c)
Non-clustering, Secondary
d)
Clustering, Secondary
|
|
Rishika Pillai answered |
Primary indices search key defines the sequential order of fill while secondary indices search key defines an order different from sequential order of fills.
A database table T1 has 2000 records and occupies 80 disk blocks. Another table T2 has 400 records and occupies 20 disk blocks. These two tables have to be joined as per a specified join condition that needs-to be evaluated for every pair of records from these two tables. The memory buffer space available can hold exactly one block of records for T1 and one block of records for T2 simultaneously at any point in time. No index is available on either table.
Q. If, instead of Nested-loop join, Block nested-loop join is used, again with the most appropriate choice of table in the outer loop, the reduction in number of block accesses required for reading the data will be- a)0
- b)30400
- c)38400
- d)798400
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A database table T1 has 2000 records and occupies 80 disk blocks. Another table T2 has 400 records and occupies 20 disk blocks. These two tables have to be joined as per a specified join condition that needs-to be evaluated for every pair of records from these two tables. The memory buffer space available can hold exactly one block of records for T1 and one block of records for T2 simultaneously at any point in time. No index is available on either table.
Q. If, instead of Nested-loop join, Block nested-loop join is used, again with the most appropriate choice of table in the outer loop, the reduction in number of block accesses required for reading the data will be
Q. If, instead of Nested-loop join, Block nested-loop join is used, again with the most appropriate choice of table in the outer loop, the reduction in number of block accesses required for reading the data will be
a)
0
b)
30400
c)
38400
d)
798400
|
|
Ipsita Dasgupta answered |
In Nested block loop join, in place of for every record of table 1, fetch every block of table 2, we go for every block of table 1, fetch every block of table 2.
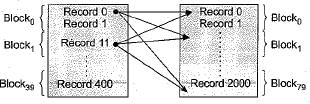
So, If T1 is outer = 80 x 20 + 80 = 1680
If T2 is outer = 80 x 20 + 20 = 1620
So we go with T2 as outer table = 1620
Reduction in number of block access
= 32020-1620 = 30400

So, If T1 is outer = 80 x 20 + 80 = 1680
If T2 is outer = 80 x 20 + 20 = 1620
So we go with T2 as outer table = 1620
Reduction in number of block access
= 32020-1620 = 30400
Consider the following three schedules of transactions T1, T2 and T3. [Notation: In the following NYO represents the action Y (R for read, W for write) performed by transaction N on object O.]
(S1) 2RA 2WA 3RC 2WB 3WA 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
(S2) 3RC 2RA 2WA 2WB 3WA 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB 3WC
(S3) 2RA 3RC 3WA 2WA 2WB 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
Q. Which of the following statements is TRUE?- a)S1, S2 and S3 are all conflict equivalent to each other
- b)No two of S1, S2 and S3 are conflict equivalent to each other
- c)S2 is conflict equivalent to S3, but not to S1
- d)S1 is conflict equivalent to S2, but not to S3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following three schedules of transactions T1, T2 and T3. [Notation: In the following NYO represents the action Y (R for read, W for write) performed by transaction N on object O.]
(S1) 2RA 2WA 3RC 2WB 3WA 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
(S2) 3RC 2RA 2WA 2WB 3WA 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB 3WC
(S3) 2RA 3RC 3WA 2WA 2WB 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
Q. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
(S1) 2RA 2WA 3RC 2WB 3WA 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
(S2) 3RC 2RA 2WA 2WB 3WA 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB 3WC
(S3) 2RA 3RC 3WA 2WA 2WB 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
Q. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a)
S1, S2 and S3 are all conflict equivalent to each other
b)
No two of S1, S2 and S3 are conflict equivalent to each other
c)
S2 is conflict equivalent to S3, but not to S1
d)
S1 is conflict equivalent to S2, but not to S3
|
|
Pritam Goyal answered |
All the conflicting pairs like (3WA, 1WA) are in the same order in both S1 and S2.
Consider the following set of functional dependencies on the scheme (A, B, C).
A —> BC, B —> C, A —> B ,A B —> C
The canonical cover for this set is
- a)A → B and B → C
- b)A → BC and AB → C
- c)A → BC and A → B
- d)A → BC and B → C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following set of functional dependencies on the scheme (A, B, C).
A —> BC, B —> C, A —> B ,A B —> C
The canonical cover for this set is
A —> BC, B —> C, A —> B ,A B —> C
The canonical cover for this set is
a)
A → B and B → C
b)
A → BC and AB → C
c)
A → BC and A → B
d)
A → BC and B → C
|
|
Anand Chatterjee answered |
In the given FDs,
1) Convert elements on LHS as singleton
Thus, A -> BC can be written as A-> B and A->C
2) Remove composite attributes from LHS
Here, AB -> C can be written as A -> C, because we have an FD {A -> B}.
3) Remove redundant attributes
We have FD = {A -> B, A -> C , B -> C}
this is a transitive depenency A -> B -> C. After remove redundancy, we get A->B, B->C.
Option A is the required answer
1) Convert elements on LHS as singleton
Thus, A -> BC can be written as A-> B and A->C
2) Remove composite attributes from LHS
Here, AB -> C can be written as A -> C, because we have an FD {A -> B}.
3) Remove redundant attributes
We have FD = {A -> B, A -> C , B -> C}
this is a transitive depenency A -> B -> C. After remove redundancy, we get A->B, B->C.
Option A is the required answer
Which of the following concurrency control protocols ensure both conflict serialzability and freedom from deadlock?
I. 2-phase locking
II. Time-stamp ordering- a)I only
- b)II only
- c)Both I and II
- d)Neither I nor II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following concurrency control protocols ensure both conflict serialzability and freedom from deadlock?
I. 2-phase locking
II. Time-stamp ordering
I. 2-phase locking
II. Time-stamp ordering
a)
I only
b)
II only
c)
Both I and II
d)
Neither I nor II
|
|
Prerna Joshi answered |
2 Phase Locking (2PL) is a concurrency control method that guarantees serializability. The protocol utilizes locks, applied by a transaction to data, which may block (interpreted as signals to stop) other transactions from accessing the same data during the transaction’s life. 2PL may be lead to deadlocks that result from the mutual blocking of two or more transactions. See the following situation, neither T3 nor T4 can make progress.
Timestamp-based concurrency control algorithm is a non-lock concurrency control method. In Timestamp based method, deadlock cannot occur as no transaction ever waits.
Timestamp-based concurrency control algorithm is a non-lock concurrency control method. In Timestamp based method, deadlock cannot occur as no transaction ever waits.
A given relation is known to be in third normal form. Select the statement which can be inferred from this- a)All attributes contribute to the primary key.
- b)Each non-key attribute determine the primary key.
- c)Each non-key attribute is determine by the primary key.
- d)Every determinant is a candidate key.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A given relation is known to be in third normal form. Select the statement which can be inferred from this
a)
All attributes contribute to the primary key.
b)
Each non-key attribute determine the primary key.
c)
Each non-key attribute is determine by the primary key.
d)
Every determinant is a candidate key.
|
|
Pranab Sharma answered |
A relation is in 3NF if for X →A
(i) X is a super key or candidate key
(ii) A is a prime attribute.
Hence, for A to be non-key attribute (non-prime attribute)
X must be satisfying (i)
(i) X is a super key or candidate key
(ii) A is a prime attribute.
Hence, for A to be non-key attribute (non-prime attribute)
X must be satisfying (i)
A Relation R with FD set {A->BC, B->A, A->C, A->D, D->A}. How many candidate keys will be there in R?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A Relation R with FD set {A->BC, B->A, A->C, A->D, D->A}. How many candidate keys will be there in R?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Pritam Goyal answered |
Simple candidate key means single attributed key. As (A)+ = {A, B, C, D}, (B)+ = {B,A, C, D}, (C)+ = {C} and (D)+ = {D, A, B, C}. So, A, B and D are candidate keys which are simple as well. So, correct option is 3.
The SQL expression :
SELECT distinct 7.branch_name
FROM branch T, branch S
WHERE T.assets >S.assets and S.branch_city = "PONDICHERRY”
Finds the names of- a)All branches that have greater assets than any branch located in PONDICHERRY.
- b)All branches that have greater assets than all branches located in PONDICHERRY.
- c)The branch that have greater assetin PONDICHERRY.
- d)Any branches that have greater asset than any branch located in PONDICHERRY.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The SQL expression :
SELECT distinct 7.branch_name
FROM branch T, branch S
WHERE T.assets >S.assets and S.branch_city = "PONDICHERRY”
Finds the names of
SELECT distinct 7.branch_name
FROM branch T, branch S
WHERE T.assets >S.assets and S.branch_city = "PONDICHERRY”
Finds the names of
a)
All branches that have greater assets than any branch located in PONDICHERRY.
b)
All branches that have greater assets than all branches located in PONDICHERRY.
c)
The branch that have greater assetin PONDICHERRY.
d)
Any branches that have greater asset than any branch located in PONDICHERRY.
|
|
Aravind Sengupta answered |
The condition T. assets > S. assets and S. branch_city = “PONDICHERRY” checks for the all those branch-name who have greater assets than any branch located in Pondicherry. The keyword distinct removes the duplicacy of branch_name satisfy the given condition.
Which level of locking provides the highest degree of concurrency in a relational data base?- a)Page
- b)Table
- c)Row
- d)Page, table and row level locking allow the same degree of concurrency
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which level of locking provides the highest degree of concurrency in a relational data base?
a)
Page
b)
Table
c)
Row
d)
Page, table and row level locking allow the same degree of concurrency
|
|
Anshu Mehta answered |
- ● Page level locking locks whole page i.e all rows therefore highly restrictive● Table locking is mainly used for concurrency control with DDL operations
- ●A row share table lock is the least restrictive, and has the highest degree of concurrency for a table.It indicates the transaction has locked rows in the table and intends to update them.
Therefore Row level provides highest level of concurrency.Hence Answer is C
In a schema with attributes A, B, C, D and E following set of functional dependencies are givenA → B A → C CD → E B → D E → AQ. Which of the following functional dependencies is NOT implied by the above set?- a)CD → AC
- b)BD → CD
- c)BC → CD
- d)AC → BC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a schema with attributes A, B, C, D and E following set of functional dependencies are given
A → B A → C CD → E B → D E → A
Q. Which of the following functional dependencies is NOT implied by the above set?
a)
CD → AC
b)
BD → CD
c)
BC → CD
d)
AC → BC
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
option (b)
For every options given, find the closure set of left side of each FD. If the closure set of left side contains the right side of the FD, then the particular FD is implied by the given set.
Option (a): Closure set of CD = CDEAB. Therefore CD->AC can be derived from the given set of FDs.
Option (c): Closure set of BC = BCDEA. Therefore BC->CD can be derived from the given set of FDs.
Option (d): Closure set of AC = ACBDE. Therefore AC->BC can be derived from the given set of FDs.
Option (b): Closure set of BD = BD. Therefore BD->CD cannot be derived from the given set of FDs.
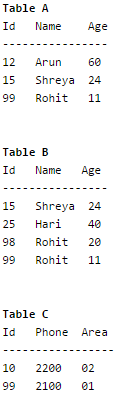
Consider the following relations A, B, C. How many tuples does the result of the following relational algebra expression contain? Assume that the schema of A U B is the same as that of A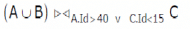
- a)7
- b)4
- c)5
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following relations A, B, C. How many tuples does the result of the following relational algebra expression contain? Assume that the schema of A U B is the same as that of A
a)
7
b)
4
c)
5
d)
9
|
|
Pallavi Saha answered |
Result of AUB will be following table
Id Name Age
----------------
12 Arun 60
15 Shreya 24
99 Rohit 11
25 Hari 40
98 Rohit 20
The result of given relational algebra expression will be
Id Name Age Id Phone Area
---------------------------------
12 Arun 60 10 2200 02
15 Shreya 24 10 2200 02
99 Rohit 11 10 2200 02
25 Hari 40 10 2200 02
98 Rohit 20 10 2200 02
99 Rohit 11 99 2100 01
98 Rohit 20 99 2100 01
---------------------------------
12 Arun 60 10 2200 02
15 Shreya 24 10 2200 02
99 Rohit 11 10 2200 02
25 Hari 40 10 2200 02
98 Rohit 20 10 2200 02
99 Rohit 11 99 2100 01
98 Rohit 20 99 2100 01
Consider the following functional dependencies in a database:Data_of_Birth → Age
Age → Eligibility
Name → Roll_number
Roll_number → Name
Course_number → Course_name
Course_number → Instructor
(Roll_number, Course_number) → Grade
Q. The relation (Roll_number, Name, Date_of_birth, Age) is:- a)In second normal form but not in third normal form
- b)In third normal form but not in BCNF
- c)In BCNF
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following functional dependencies in a database:
Data_of_Birth → Age
Age → Eligibility
Name → Roll_number
Roll_number → Name
Course_number → Course_name
Course_number → Instructor
(Roll_number, Course_number) → Grade
Age → Eligibility
Name → Roll_number
Roll_number → Name
Course_number → Course_name
Course_number → Instructor
(Roll_number, Course_number) → Grade
Q. The relation (Roll_number, Name, Date_of_birth, Age) is:
a)
In second normal form but not in third normal form
b)
In third normal form but not in BCNF
c)
In BCNF
d)
None of the above
|
|
Garima Bose answered |
The given table is not in 2NF as age is dependent on date of birth.
Relation R with an associated set of functional dependencies, F is decomposed into BCNF. The redundancy (arising out of functional dependencies) in the resulting set relations is.- a)Zero
- b)More than zero but less than that of an equivalent 3NF decomposition
- c)Proportional to the size of F+
- d)Indeterminate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Relation R with an associated set of functional dependencies, F is decomposed into BCNF. The redundancy (arising out of functional dependencies) in the resulting set relations is.
a)
Zero
b)
More than zero but less than that of an equivalent 3NF decomposition
c)
Proportional to the size of F+
d)
Indeterminate
|
|
Mahi Yadav answered |
If a relational schema is in BCNF then all redundancy based on functional dependency has been removed, although other types of redundancy may still exist.
Which of the following desired features are beyond the capability of relational algebra?- a)Aggregate computation
- b)Multiplication
- c)Finding transitive closure
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following desired features are beyond the capability of relational algebra?
a)
Aggregate computation
b)
Multiplication
c)
Finding transitive closure
d)
All of the above
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Relational algebra can not preform the following:
(a) Aggregate computation (avg, sum, etc. must be used).
(b) Multiplication
(c) Finding transitive closure
These operations are beyond the capability of relational algebra.
(a) Aggregate computation (avg, sum, etc. must be used).
(b) Multiplication
(c) Finding transitive closure
These operations are beyond the capability of relational algebra.
A relation Empdtl is defined with attribute empcode (unique), name, street, city, state and pincode. For any pincode, there is only one city and state. Also, for any given street, city and state, there is just one pincode. in normalization terms, Empdtl is a relation in
- a)2 NF and hence also in 1NF
- b)1 NF Only
- c)3 NF and hence also in 2 NF and 1NF
- d)BCNF and hence also in 3 NF, 2 NF an 1 NF
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A relation Empdtl is defined with attribute empcode (unique), name, street, city, state and pincode. For any pincode, there is only one city and state. Also, for any given street, city and state, there is just one pincode. in normalization terms, Empdtl is a relation in
a)
2 NF and hence also in 1NF
b)
1 NF Only
c)
3 NF and hence also in 2 NF and 1NF
d)
BCNF and hence also in 3 NF, 2 NF an 1 NF
|
|
Partho Joshi answered |
1) Pin code → city, state
2) Street, city, state → pin code
The candidate keys of relation is empcode as it uniquely identifies the relation.
Hence, it is in 2NF and therefore, also in 1NF.
Let R ( a, b, c) and S (d, e, f) be two relations in which d is the foreign key of S that refers to the primary key of R. Consider the following four operations.
1. Insert into R
2. Insert into S
3. Delete from R
4. Delete from SWhich of the following is true about the referential integrity constraint about?- a)None of them can cause any violation
- b)All of them can cause violation
- c)Operations (1) and (4) can cause violation
- d)Operations (2) and (3) can cause violation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Let R ( a, b, c) and S (d, e, f) be two relations in which d is the foreign key of S that refers to the primary key of R. Consider the following four operations.
1. Insert into R
2. Insert into S
3. Delete from R
4. Delete from S
1. Insert into R
2. Insert into S
3. Delete from R
4. Delete from S
Which of the following is true about the referential integrity constraint about?
a)
None of them can cause any violation
b)
All of them can cause violation
c)
Operations (1) and (4) can cause violation
d)
Operations (2) and (3) can cause violation
|
|
Rounak Chavan answered |
R (a, b, d, c) and S (e,f)
1. Insertion into R does not create any violation,
2. Insertion into S create violation.
3. Deletion in S does not create any violation.
4. Deletion in R can create violation.
1. Insertion into R does not create any violation,
2. Insertion into S create violation.
3. Deletion in S does not create any violation.
4. Deletion in R can create violation.
Chapter doubts & questions for Database Management System (DBMS) - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Database Management System (DBMS) - 6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE CSE
459 videos|1398 docs|786 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









