All Exams >
Electrical Engineering (EE) >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Electrical >
All Questions
All questions of DC Circuit for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam
Find the value of the currents I1 and I2 flowing clockwise in the first and second mesh respectively.
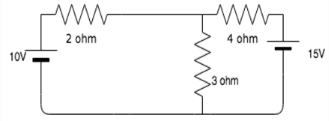
- a)5A, 0A
- b)-5A, 0A
- c)0A, 5A
- d)0A, -5A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of the currents I1 and I2 flowing clockwise in the first and second mesh respectively.

a)
5A, 0A
b)
-5A, 0A
c)
0A, 5A
d)
0A, -5A

|
Gate Gurus answered |
The two mesh equations are:
5I1-3I2=10
-3I1+7I2=-15
Solving the equations simultaneously, we get I1=0.96A and I2=-1.73A.
5I1-3I2=10
-3I1+7I2=-15
Solving the equations simultaneously, we get I1=0.96A and I2=-1.73A.
Find the value of I1, I2 and I3.
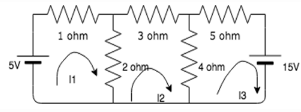
- a) -0.188A, 1.5A, -1.19A
- b)-1.5A, -0.188A, 1.19A
- c)1.5A, -0.188A, -1.19A
- d)1.19A, 0.188A, 1.5A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of I1, I2 and I3.

a)
-0.188A, 1.5A, -1.19A
b)
-1.5A, -0.188A, 1.19A
c)
1.5A, -0.188A, -1.19A
d)
1.19A, 0.188A, 1.5A
|
|
Palak Verma answered |
Using the matrix method:
Matrix(3,-2,0) (I1)=(5)
(-2,9,-4) (I2)=(0)
(0,-4,9) (I3)=(-10)
Solving this matrix equation, we get I1=1.5A, I2=-0.188A and I3=-1.19A.
Matrix(3,-2,0) (I1)=(5)
(-2,9,-4) (I2)=(0)
(0,-4,9) (I3)=(-10)
Solving this matrix equation, we get I1=1.5A, I2=-0.188A and I3=-1.19A.
The value of the 3 resistances when connected in star connection is_________
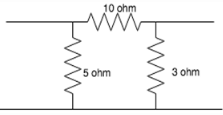
- a)2.32ohm,1.22ohm, 4.54ohm
- b)3.55ohm, 4.33ohm, 5.67ohm
- c)2.78ohm, 1.67ohm, 0.83ohm
- d)4.53ohm, 6.66ohm, 1.23ohm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of the 3 resistances when connected in star connection is_________

a)
2.32ohm,1.22ohm, 4.54ohm
b)
3.55ohm, 4.33ohm, 5.67ohm
c)
2.78ohm, 1.67ohm, 0.83ohm
d)
4.53ohm, 6.66ohm, 1.23ohm
|
|
Gargi Basak answered |
Following the delta to star conversion:
R1=10*5/(10+5+3)
R2=10*3/(10+5+3)
R3=5*3/(10+5+3).
R1=10*5/(10+5+3)
R2=10*3/(10+5+3)
R3=5*3/(10+5+3).
KCL is associated with_________- a)Mesh analysis
- b)Nodal analysis
- c)Both mesh and nodal
- d)Neither mesh nor nodal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
KCL is associated with_________
a)
Mesh analysis
b)
Nodal analysis
c)
Both mesh and nodal
d)
Neither mesh nor nodal

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
Potassium chloride (KCl) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water and its solutions have a salt-like taste.
Delta connection is also known as____________- a)Y-connection
- b)Mesh connection
- c)Either Y-connection or mesh connection
- d)Neither Y-connection nor mesh connection
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Delta connection is also known as____________
a)
Y-connection
b)
Mesh connection
c)
Either Y-connection or mesh connection
d)
Neither Y-connection nor mesh connection
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Delta connection is also known as mean connection because its structure is like a mesh, that is, a closed loop.
In source transformation________- a)Voltage source remain the same
- b)Current sources remain the same
- c)Both voltage and current source remain the same
- d)Resistances remain the same
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In source transformation________
a)
Voltage source remain the same
b)
Current sources remain the same
c)
Both voltage and current source remain the same
d)
Resistances remain the same
|
|
Sanchita Sharma answered |
In source transformation, the value of the voltage and current sources change when changed from voltage to current source and current to voltage source but the value of the resistances remains the same.
Calculate the total current in the circuit.

- a) 2.3mA
- b)4.3mA
- c)3.3mA
- d)1.3mA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the total current in the circuit.

a)
2.3mA
b)
4.3mA
c)
3.3mA
d)
1.3mA

|
Gate Funda answered |
The 9mA source connected in parallel to the 5 kohm resistor can be converted to a 45V source in series with a 5 kohm resistor. Applying mesh analysis, we get:
I=(45-3)/(5+4.7+3)= 3.3mA.
I=(45-3)/(5+4.7+3)= 3.3mA.
If there are 10 nodes in a circuit, how many equations do we get?- a)10
- b)9
- c)8
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If there are 10 nodes in a circuit, how many equations do we get?
a)
10
b)
9
c)
8
d)
7
|
|
Prateek Mehra answered |
Explanation:
In a circuit with 10 nodes, the number of equations we get depends on the type of circuit and the number of independent variables. The number of equations can be determined using Kirchhoff's laws and Ohm's law.
Kirchhoff's Laws:
1. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL): The sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node.
2. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): The sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Number of Equations:
To determine the number of equations, we need to consider the number of independent variables in the circuit.
1. For a simple resistive circuit without any independent voltage or current sources, the number of equations is equal to the number of nodes minus one. This is because the voltage at one node can be taken as a reference and all other voltages can be expressed relative to this reference node.
2. For a circuit with independent voltage sources, the number of equations is equal to the number of nodes minus the number of independent voltage sources. This is because the voltage at each node can be determined by Kirchhoff's laws, except for the nodes connected to independent voltage sources.
3. For a circuit with independent current sources, the number of equations is equal to the number of nodes minus the number of independent current sources plus one. This is because the current at each node can be determined by Kirchhoff's laws, except for the nodes connected to independent current sources. However, one additional equation is required to satisfy KCL at a reference node.
In this case, we are not given the type of circuit or the presence of any independent sources. Therefore, we assume a simple resistive circuit without any independent sources.
Using the formula for a simple resistive circuit, the number of equations we get is equal to the number of nodes minus one. Since there are 10 nodes, the number of equations is 10 - 1 = 9.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B) 9.
In a circuit with 10 nodes, the number of equations we get depends on the type of circuit and the number of independent variables. The number of equations can be determined using Kirchhoff's laws and Ohm's law.
Kirchhoff's Laws:
1. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL): The sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node.
2. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): The sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
Number of Equations:
To determine the number of equations, we need to consider the number of independent variables in the circuit.
1. For a simple resistive circuit without any independent voltage or current sources, the number of equations is equal to the number of nodes minus one. This is because the voltage at one node can be taken as a reference and all other voltages can be expressed relative to this reference node.
2. For a circuit with independent voltage sources, the number of equations is equal to the number of nodes minus the number of independent voltage sources. This is because the voltage at each node can be determined by Kirchhoff's laws, except for the nodes connected to independent voltage sources.
3. For a circuit with independent current sources, the number of equations is equal to the number of nodes minus the number of independent current sources plus one. This is because the current at each node can be determined by Kirchhoff's laws, except for the nodes connected to independent current sources. However, one additional equation is required to satisfy KCL at a reference node.
In this case, we are not given the type of circuit or the presence of any independent sources. Therefore, we assume a simple resistive circuit without any independent sources.
Using the formula for a simple resistive circuit, the number of equations we get is equal to the number of nodes minus one. Since there are 10 nodes, the number of equations is 10 - 1 = 9.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B) 9.
A current source connected in parallel with a resistor can be converted to a?- a)Current source in series with a resistor
- b)Voltage source in series with a resistor
- c)Voltage source in parallel with a resistor
- d)Cannot be modified
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A current source connected in parallel with a resistor can be converted to a?
a)
Current source in series with a resistor
b)
Voltage source in series with a resistor
c)
Voltage source in parallel with a resistor
d)
Cannot be modified
|
|
Ritika Sarkar answered |
A current source connected in parallel can be converted to a voltage source connected in series using the relation obtained from ohm’s law, that is V=IR. This equation shows that a current source connected in parallel has the same impact as a voltage source connected in series.
Calculate the value of RL across A and B.
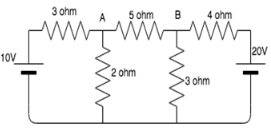
- a)3.45ohm
- b)2.91ohm
- c)6.34ohm
- d)1.54ohm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the value of RL across A and B.

a)
3.45ohm
b)
2.91ohm
c)
6.34ohm
d)
1.54ohm
|
|
Sakshi Tiwari answered |
On shorting the voltage sources:
RL=3||2+4||5.
RL=3||2+4||5.
Find the value of R if the power in the circuit is 1000W.

- a)10 ohm
- b) 9 ohm
- c) 8 ohm
- d)7 ohm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of R if the power in the circuit is 1000W.

a)
10 ohm
b)
9 ohm
c)
8 ohm
d)
7 ohm
|
|
Pallavi Nair answered |
To find the value of I:
VI=P =>100I=1000 => I=10A.
Voltage across the 2 ohm resistor= 20V.
Voltage across the R resistor= 100-20= 80V.
R=V/I => R=80/10= 8A.
VI=P =>100I=1000 => I=10A.
Voltage across the 2 ohm resistor= 20V.
Voltage across the R resistor= 100-20= 80V.
R=V/I => R=80/10= 8A.
Find the value of the node voltage V.
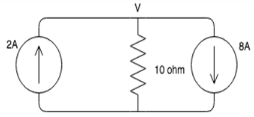
- a)60V
- b)50V
- c)40V
- d)30V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of the node voltage V.

a)
60V
b)
50V
c)
40V
d)
30V
|
|
Ashwin Kapoor answered |
The node equation is:
-2+8+V/10=0 => 6 + v/10 = 0 => v = 10*6=>60v
Solving this equation, we get V=60V.
-2+8+V/10=0 => 6 + v/10 = 0 => v = 10*6=>60v
Solving this equation, we get V=60V.
Star connection is also known as__________- a)Y-connection
- b)Mesh connection
- c)Either Y-connection or mesh connection
- d)Neither Y-connection nor mesh connection
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Star connection is also known as__________
a)
Y-connection
b)
Mesh connection
c)
Either Y-connection or mesh connection
d)
Neither Y-connection nor mesh connection
|
|
Dipika Basak answered |
The star connection is also known as the Y-connection because its formation is like the letter Y.
Hence Option (A) is correct
For detailed chapter notes on Three Phase Circuits click on the link given below::
Vth is found across the ____________ terminals of the network.- a)Input
- b)Output
- c)Neither input nor output
- d)Either input or output
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vth is found across the ____________ terminals of the network.
a)
Input
b)
Output
c)
Neither input nor output
d)
Either input or output
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
According to Thevenin’s theorem, Vth is found across the output terminals of a network and not the input terminals.
Mesh analysis is generally used to determine_________- a)Voltage
- b)Current
- c)Resistance
- d)Power
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mesh analysis is generally used to determine_________
a)
Voltage
b)
Current
c)
Resistance
d)
Power
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Mesh analysis uses Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law to find all the mesh currents. Hence it is a method used to determine current.
Isc is found across the ____________ terminals of the network.- a)Input
- b)Output
- c)Neither input nor output
- d)Either input or output
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Isc is found across the ____________ terminals of the network.
a)
Input
b)
Output
c)
Neither input nor output
d)
Either input or output
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
According to Norton’s theorem, Isc is found through the output terminals of a network and not the input terminals.
If a 6 ohm, 2ohm, and 4ohm resistor is connected in... more delta, find the equivalent star connection.
a)1ohm, 2ohm, 3ohm
b)2ohm, 4ohm, 7ohm
c)5ohm, 4ohm, 2ohm
d)1ohm, 2ohm, 2/3ohm
The correct answer is option 'D'.
Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shivam Das answered |
Using the delta to star conversion formula:
R1=2*6/(2+6+4)= 1 ohm
R2=2*4/(2+6+4)= 2/3 ohm
R3=4*6/(2+6+4)= 2 ohm
Hence, The Correct Answer is Option D
You can learn more about Delta to Star Conversion by ging through the doc:
R1=2*6/(2+6+4)= 1 ohm
R2=2*4/(2+6+4)= 2/3 ohm
R3=4*6/(2+6+4)= 2 ohm
Hence, The Correct Answer is Option D
You can learn more about Delta to Star Conversion by ging through the doc:
Mesh analysis is generally used to determine _________- a)Voltage
- b)Current
- c)Resistance
- d)Power
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mesh analysis is generally used to determine _________
a)
Voltage
b)
Current
c)
Resistance
d)
Power
|
|
Shivam Ghosh answered |
Mesh analysis uses Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law to find all the mesh currents. Hence it is a method used to determine current.
Nodal analysis is generally used to determine______- a)Voltage
- b)Current
- c)Resistance
- d)Power
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nodal analysis is generally used to determine______
a)
Voltage
b)
Current
c)
Resistance
d)
Power

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
In electric circuits analysis, nodal analysis, node-voltage analysis, or the branch current method is a method of determining the voltage (potential difference) between "nodes" (points where elements or branches connect) in an electrical circuit in terms of the branch currents.
Find the value of V if the current in the 3 ohm resistor=0.
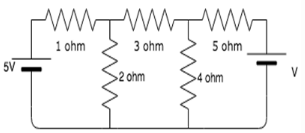
- a)3.5V
- b)6.5V
- c)7.5V
- d)8.5V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of V if the current in the 3 ohm resistor=0.

a)
3.5V
b)
6.5V
c)
7.5V
d)
8.5V
|
|
Vaishnavi Nair answered |
Taking the mesh currents in the three meshes as I1, I2 and I3, the mesh equations are:
3I1+0I2+0V=5
-2I1-4I2+0V=0
0I1+9I2+V=0
Solving these equations simultaneously and taking the value of I2=0, we get V=7.5V.
3I1+0I2+0V=5
-2I1-4I2+0V=0
0I1+9I2+V=0
Solving these equations simultaneously and taking the value of I2=0, we get V=7.5V.
Find the current in the 4 ohm resistor.
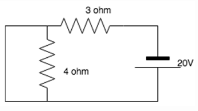
- a)4 ohm
- b)0A
- c)2.2A
- d)20A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the current in the 4 ohm resistor.

a)
4 ohm
b)
0A
c)
2.2A
d)
20A
|
|
Gaurav Chauhan answered |
The 4 ohm resistor gets shorted since current always prefers the low resistance path. All the current flows to the branch which is connected in parallel to the 4 ohm branch, hence no current flows in the 4 ohm resistance.
In Thevenin’s theorem Vth is__________- a)Sum of two voltage sources
- b)A single voltage source
- c)Infinite voltage sources
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Thevenin’s theorem Vth is__________
a)
Sum of two voltage sources
b)
A single voltage source
c)
Infinite voltage sources
d)
0
|
|
Sneha Bose answered |
Thevenin’s theorem states that a combination of voltage sources, current sources and resistors is equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R.
Calculate the current across the 4 ohm resistor.
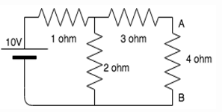
- a)0.86A
- b)1.23A
- c)2.22A
- d)0.67A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the current across the 4 ohm resistor.

a)
0.86A
b)
1.23A
c)
2.22A
d)
0.67A
|
|
Anirban Gupta answered |
Thevenin resistance is found by opening the circuit between the specified terminal and shorting all voltage sources.
When the 10V source is shorted, we get:
Rth=(1||2)+3=3.67 ohm.
Vth is calculated by opening the specified terminal.
Using voltage divider, Vth= 2*10/(2+1)=6.67V.
On drawing the Thevenin equivalent circuit, we get Rth, 4 ohm and Vth in series.
Applying ohm’s law, I=Vth/(4+Rth)= 0.86A.
When the 10V source is shorted, we get:
Rth=(1||2)+3=3.67 ohm.
Vth is calculated by opening the specified terminal.
Using voltage divider, Vth= 2*10/(2+1)=6.67V.
On drawing the Thevenin equivalent circuit, we get Rth, 4 ohm and Vth in series.
Applying ohm’s law, I=Vth/(4+Rth)= 0.86A.
What will the value of the current be once source transformation is applied to the circuit?
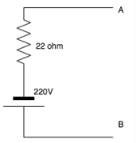
- a)10A
- b)20A
- c)30A
- d)40A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will the value of the current be once source transformation is applied to the circuit?

a)
10A
b)
20A
c)
30A
d)
40A
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Using ohm’s law, we can use the relation: V=IR.
Thus I=V/R.
I=220/22=10A.
Thus I=V/R.
I=220/22=10A.
A voltage source connected in series with a resistor can be converted to a?- a)Current source in series with a resistor
- b)Current source in parallel with a resistor
- c)Voltage source in parallel with a resistor
- d)Cannot be modified
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A voltage source connected in series with a resistor can be converted to a?
a)
Current source in series with a resistor
b)
Current source in parallel with a resistor
c)
Voltage source in parallel with a resistor
d)
Cannot be modified
|
|
Arpita Banerjee answered |
A voltage source connected in series can be converted to a current source connected in parallel using the relation obtained from ohm’s law, that is V=IR. This equation shows that a voltage source connected in series has the same impact as a current source connected in parallel.
In superposition theorem, when we consider the effect of one current source, all the other voltage sources are____________- a)Shorted
- b)Opened
- c)Removed
- d)Undisturbed
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In superposition theorem, when we consider the effect of one current source, all the other voltage sources are____________
a)
Shorted
b)
Opened
c)
Removed
d)
Undisturbed
|
|
Palak Verma answered |
In superposition theorem, whether we consider the effect of a voltage or current source, voltage sources are always shorted and current sources are always opened.
Name some devices where maximum power has to be transferred to the load rather than maximum efficiency.- a)Amplifiers
- b)Communication circuits
- c)Both amplifiers and communication circuits
- d)Neither amplifiers nor communication circuits
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Name some devices where maximum power has to be transferred to the load rather than maximum efficiency.
a)
Amplifiers
b)
Communication circuits
c)
Both amplifiers and communication circuits
d)
Neither amplifiers nor communication circuits
|
|
Upasana Joshi answered |
Maximum power transfer to the load is preferred over maximum efficiency in both amplifiers and communication circuits since in both these cases the output voltage is more than the input.
Nodal analysis is generally used to determine_______- a)Voltage
- b)Current
- c)Resistance
- d)Power
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nodal analysis is generally used to determine_______
a)
Voltage
b)
Current
c)
Resistance
d)
Power
|
|
Sravya Khanna answered |
Nodal analysis uses Kirchhoff’s Current Law to find all the node voltages. Hence it is a method used to determine voltage.
Nodal analysis can be applied for________- a)Planar networks
- b)Non-planar networks
- c)Both planar and non-planar networks
- d)Neither planar nor non-planar networks
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nodal analysis can be applied for________
a)
Planar networks
b)
Non-planar networks
c)
Both planar and non-planar networks
d)
Neither planar nor non-planar networks
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Nodal analysis can be applied for both planar and non-planar networks since each node, whether it is planar or non-planar, can be assigned a voltage.
Find the node voltage V.
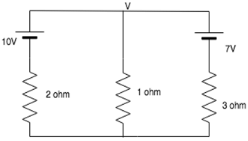
- a)1V
- b)2V
- c)3V
- d)4V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the node voltage V.

a)
1V
b)
2V
c)
3V
d)
4V
|
|
Nitin Chawla answered |
The nodal equation is:
(V-10)/2+(V-7)/3+V/1=0
Solving for V, we get V=4V.
(V-10)/2+(V-7)/3+V/1=0
Solving for V, we get V=4V.
Thevenin’s theorem is true for __________- a)Linear networks
- b)Non-Linear networks
- c)Both linear networks and nonlinear networks
- d)Neither linear networks nor non-linear networks
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Thevenin’s theorem is true for __________
a)
Linear networks
b)
Non-Linear networks
c)
Both linear networks and nonlinear networks
d)
Neither linear networks nor non-linear networks
|
|
Prisha Sengupta answered |
Thevenin’s theorem works for only linear circuit elements and not non-linear ones such as BJT, semiconductors etc.
KVL is associated with____________- a)Mesh analysis
- b)Nodal analysis
- c)Both mesh and nodal
- d)Neither mesh nor nodal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
KVL is associated with____________
a)
Mesh analysis
b)
Nodal analysis
c)
Both mesh and nodal
d)
Neither mesh nor nodal
|
|
Anshika Nambiar answered |
KVL employs mesh analysis to find the different mesh currents by finding the IR products in each mesh.
The algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop circuit is equal to:- a)One
- b)Zero
- c)Infinity
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop circuit is equal to:
a)
One
b)
Zero
c)
Infinity
d)
None of these
|
|
Anirban Gupta answered |
Explanation:
- The algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop circuit is known as Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL).
- According to KVL, the sum of all voltage drops around a closed loop circuit is equal to the sum of all voltage rises around that loop.
- The direction of voltage drop and rise should be taken into account while calculating the algebraic sum of voltages.
- Since voltage drop is negative and voltage rise is positive, the algebraic sum of voltages around a closed loop circuit is zero.
- This is because the voltage that is dropped across a component is equal to the voltage that is gained by another component in the same loop.
- Therefore, the algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop circuit is equal to zero.
If a 4ohm, 3ohm and 2ohm resistor is connected in delta, find the equivalent star connection.- a)8/9ohm, 4/3ohm, 2/3ohm
- b)8/9ohm, 4/3ohm, 7/3ohm
- c)7/9ohm, 4/3ohm, 2/3ohm
- d)8/9ohm, 5/3ohm, 2/3ohm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a 4ohm, 3ohm and 2ohm resistor is connected in delta, find the equivalent star connection.
a)
8/9ohm, 4/3ohm, 2/3ohm
b)
8/9ohm, 4/3ohm, 7/3ohm
c)
7/9ohm, 4/3ohm, 2/3ohm
d)
8/9ohm, 5/3ohm, 2/3ohm
|
|
Prasad Verma answered |
Using the delta-star conversion formula:
R1=4*3/(2+3+4)
R2=2*3/(2+3+4)
R3=2*4/(2+3+4).
R1=4*3/(2+3+4)
R2=2*3/(2+3+4)
R3=2*4/(2+3+4).
Can we use Thevinin’s theorem on a circuit containing a BJT?- a)Yes
- b)No
- c)Depends on the BJT
- d)Insufficient data provided
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Can we use Thevinin’s theorem on a circuit containing a BJT?
a)
Yes
b)
No
c)
Depends on the BJT
d)
Insufficient data provided
|
|
Sandeep Saha answered |
We can use Thevenin’s theorem only for linear networks. BJT is a non-linear network hence we cannot apply Thevenin’s theorem for it.
Which, among the following is the right expression for converting from delta to star?- a)R1=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Rc*Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
- b)R1=Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), Rc=/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
- c) R1=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
- d) R1=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which, among the following is the right expression for converting from delta to star?
a)
R1=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Rc*Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
b)
R1=Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), Rc=/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
c)
R1=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
d)
R1=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Ra*Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
|
|
Rounak Rane answered |
After converting to star, each star connected resistance is equal to the product of the resistances it is connected to and the total sum of the resistances. Hence R1=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Rc*Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc).
Rab is the resistance between the terminals A and B, Rbc between B and C and Rca between C and A. These 3 resistors are connected in star connection. After transforming to delta, the resistance at A will be?- a)Rc+Rb+Rc*Rb/Ra
- b)Rc+Rb+Ra*Rb/Rc
- c)Ra+Rb+Ra*Rc/Rb
- d)Rc+Rb+Rc*Ra/Rb
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rab is the resistance between the terminals A and B, Rbc between B and C and Rca between C and A. These 3 resistors are connected in star connection. After transforming to delta, the resistance at A will be?
a)
Rc+Rb+Rc*Rb/Ra
b)
Rc+Rb+Ra*Rb/Rc
c)
Ra+Rb+Ra*Rc/Rb
d)
Rc+Rb+Rc*Ra/Rb
|
|
Vaibhav Joshi answered |
After converting to delta, each delta connected resistance is equal to the sum of the two resistances it is connected to+product of the two resistances divided by the remaining resistance. Hence, resistance at A= Ra+Rb+Ra*Rb/Rc.
Find the value of V1 if the current through the 1 ohm resistor=0A.
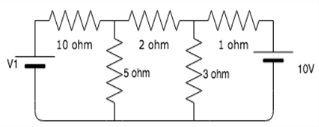
- a)83.33V
- b)78.89V
- c)87.87V
- d)33.33V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of V1 if the current through the 1 ohm resistor=0A.

a)
83.33V
b)
78.89V
c)
87.87V
d)
33.33V
|
|
Mira Mukherjee answered |
Taking I1, I2 and I3 as the currents in the three meshes and taking I3=0 since it is the current across the 1 ohm resistor, the three mesh equations are:
15I1-5I2=V1
-5I1+10I2+0V1=0
0I1-3I2+0V1=10
Solving these equations simultaneously we get V1= 83.33V.
15I1-5I2=V1
-5I1+10I2+0V1=0
0I1-3I2+0V1=10
Solving these equations simultaneously we get V1= 83.33V.
Which of the following expression correctly represents Kirchhop's Voltage Law (KVL) for the given circuit diagram?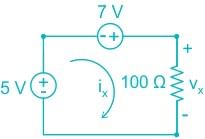
- a)- 5 - 7 + Vx = 0
- b)- 5 - 7 - Vx = 0
- c)+ 5 - 7 + Vx = 0
- d)- 5 + 7 + Vx = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expression correctly represents Kirchhop's Voltage Law (KVL) for the given circuit diagram?

a)
- 5 - 7 + Vx = 0
b)
- 5 - 7 - Vx = 0
c)
+ 5 - 7 + Vx = 0
d)
- 5 + 7 + Vx = 0
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Kirchhoffs Voltage Law (KVL):
- Kirchhoffs Voltage Law or KVL, states that “in any closed loop network, the total voltage around the loop is equal to the sum of all the voltage drops within the same loop” which is also equal to zero.
- In other words, the algebraic sum of all voltages within the loop must be equal to zero i.e. ∑V = 0
- KVL is based on the law of conservation of energy.
Consider the figure shown below:
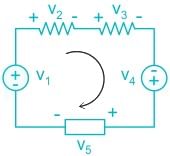
∴ According to KVL,
V1 + V2 + V3 + V4 + V5 = 0
Calculation:
The circuit diagram given in the question can be modified as:
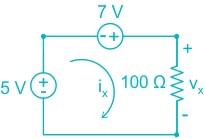
Now by applying KVL in the above circuit, we get
5 + 7 - Vx = 0
∴ - 5 - 7 + Vx = 0
If there are 3 10V sources connected in parallel then on source transformation__________- a)The effect of all the sources is considered
- b)The effect of only one source is considered
- c)The effect of none of the sources is considered
- d)The effect of only 2 sources is considered.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If there are 3 10V sources connected in parallel then on source transformation__________
a)
The effect of all the sources is considered
b)
The effect of only one source is considered
c)
The effect of none of the sources is considered
d)
The effect of only 2 sources is considered.
|
|
Kritika Gupta answered |
When voltages are connected in parallel, the effect of only one source is considered because the effect of the voltage remains the same when connected in parallel.
If a 8/9ohm, 4/3ohm and 2/3ohm resistor is connected in star, find its delta equivalent.- a)4ohm, 3ohm, 2ohm
- b)1ohm, 3ohm, 2ohm
- c)4ohm, 1ohm, 2ohm
- d)4ohm, 3ohm, 1ohm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a 8/9ohm, 4/3ohm and 2/3ohm resistor is connected in star, find its delta equivalent.
a)
4ohm, 3ohm, 2ohm
b)
1ohm, 3ohm, 2ohm
c)
4ohm, 1ohm, 2ohm
d)
4ohm, 3ohm, 1ohm
|
|
Saumya Basak answered |
Using the formula for star to delta conversion:
R1=8/9+4/3+(8/9)*(4/3)/(2/3)
R2=8/9+2/3+(8/9)*(2/3)/(4/3)
R3=2/3+4/3+(2/3)*(4/3)/(8/9).
R1=8/9+4/3+(8/9)*(4/3)/(2/3)
R2=8/9+2/3+(8/9)*(2/3)/(4/3)
R3=2/3+4/3+(2/3)*(4/3)/(8/9).
Find the voltage due to the 15A source.- a)0V
- b)2V
- c)4V
- d)6V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the voltage due to the 15A source.
a)
0V
b)
2V
c)
4V
d)
6V
|
|
Gargi Basak answered |
Due to the 15V source, the 10V and 16V sources get shorted and the 3A source acts as an open circuit. Since the 10V source is shorted, it acts as a low resistance path and current flows only within that loop and do not flow to the 20 ohm resistor. Hence the voltage is 0V.
How many nodes are taken as reference nodes in nodal analysis?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many nodes are taken as reference nodes in nodal analysis?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Siddharth Khanna answered |
In nodal analysis one node is treated as the reference node and the voltage at that point is taken as 0.
Which, among the following is the correct expression for star-delta conversion?- a)R1=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Rc*Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc)b)
- b)R1=Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), Rc=/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
- c)R1=Ra+Rb+Ra*Rb/Rc, R2=Rc+Rb+Rc*Rb/Ra, R3=Ra+Rc+Ra*Rc/Rb
- d)R1=Ra*Rb/Rc, R2=Rc*Rb/Ra, R3=Ra*Rc/Rb
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which, among the following is the correct expression for star-delta conversion?
a)
R1=Ra*Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb*Rc/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R3=Rc*Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc)b)
b)
R1=Ra/(Ra+Rb+Rc), R2=Rb/(Ra+Rb+Rc), Rc=/(Ra+Rb+Rc)
c)
R1=Ra+Rb+Ra*Rb/Rc, R2=Rc+Rb+Rc*Rb/Ra, R3=Ra+Rc+Ra*Rc/Rb
d)
R1=Ra*Rb/Rc, R2=Rc*Rb/Ra, R3=Ra*Rc/Rb
|
|
Niti Tiwari answered |
After converting to delta, each delta connected resistance is equal to the sum of the two resistance it is connected to+product of the two resistances divided by the remaining resistance. Hence R1=Ra+Rb+Ra*Rb/Rc, R2=Rc+Rb+Rc*Rb/Ra, R3=Ra+Rc+Ra*Rc/Rb.
The Norton current is the_______- a)Short circuit current
- b)Open circuit current
- c)Both open circuit and short circuit current
- d)Neither open circuit nor short circuit current
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Norton current is the_______
a)
Short circuit current
b)
Open circuit current
c)
Both open circuit and short circuit current
d)
Neither open circuit nor short circuit current
|
|
Raj Choudhary answered |
The Norton current is the short circuit current. This means that it is the current that flows through a short circuit when a load or device is connected across the terminals of a circuit. It is named after Edward Lawry Norton, an American electrical engineer who developed the Norton equivalent circuit theorem.
- Explanation of the Norton equivalent circuit theorem:
The Norton equivalent circuit theorem states that any linear electrical network with multiple sources and resistors can be represented by a single current source and a single resistor connected in parallel. This is useful for simplifying complex circuits and analyzing their behavior.
- Understanding the Norton current:
In the Norton equivalent circuit, the Norton current is the current source that represents the short circuit current of the original circuit. It is placed in parallel with the equivalent resistor, which represents the internal resistance of the original circuit.
- Significance of the Norton current:
The Norton current is an important parameter in circuit analysis because it helps in determining the maximum current that can flow through a circuit when it is shorted. This information is useful for designing circuit protection mechanisms and ensuring the safe operation of electrical systems.
- Difference between open circuit and short circuit current:
An open circuit current is the current that flows in a circuit when there is no load or device connected across the terminals. It represents the maximum current that can flow in the circuit under normal operating conditions. On the other hand, a short circuit current is the current that flows when a circuit is shorted, i.e., when the terminals are directly connected without any resistance in between.
- Conclusion:
In summary, the Norton current is the short circuit current of a circuit. It is an important parameter in circuit analysis and helps in determining the maximum current that can flow through a circuit when it is shorted. Understanding the Norton equivalent circuit theorem and its application can aid in simplifying complex circuits and analyzing their behavior.
- Explanation of the Norton equivalent circuit theorem:
The Norton equivalent circuit theorem states that any linear electrical network with multiple sources and resistors can be represented by a single current source and a single resistor connected in parallel. This is useful for simplifying complex circuits and analyzing their behavior.
- Understanding the Norton current:
In the Norton equivalent circuit, the Norton current is the current source that represents the short circuit current of the original circuit. It is placed in parallel with the equivalent resistor, which represents the internal resistance of the original circuit.
- Significance of the Norton current:
The Norton current is an important parameter in circuit analysis because it helps in determining the maximum current that can flow through a circuit when it is shorted. This information is useful for designing circuit protection mechanisms and ensuring the safe operation of electrical systems.
- Difference between open circuit and short circuit current:
An open circuit current is the current that flows in a circuit when there is no load or device connected across the terminals. It represents the maximum current that can flow in the circuit under normal operating conditions. On the other hand, a short circuit current is the current that flows when a circuit is shorted, i.e., when the terminals are directly connected without any resistance in between.
- Conclusion:
In summary, the Norton current is the short circuit current of a circuit. It is an important parameter in circuit analysis and helps in determining the maximum current that can flow through a circuit when it is shorted. Understanding the Norton equivalent circuit theorem and its application can aid in simplifying complex circuits and analyzing their behavior.
Norton’s theorem is true for __________- a)Linear networks
- b)Non-Linear networks
- c)Both linear networks and nonlinear networks
- d)Neither linear networks nor non-linear networks
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Norton’s theorem is true for __________
a)
Linear networks
b)
Non-Linear networks
c)
Both linear networks and nonlinear networks
d)
Neither linear networks nor non-linear networks
|
|
Avantika Kaur answered |
Norton’s theorem works for only linear circuit elements and not non-linear ones such as BJT, semiconductors etc.
The Thevenin voltage is the__________- a)Open circuit voltage
- b)Short circuit voltage
- c)Both open circuit and short circuit voltage
- d)Neither open circuit nor short circuit voltage
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Thevenin voltage is the__________
a)
Open circuit voltage
b)
Short circuit voltage
c)
Both open circuit and short circuit voltage
d)
Neither open circuit nor short circuit voltage
|
|
Arshiya Basu answered |
Thevenin voltage is the open circuit voltage. It is the voltage across the specified terminals. It is not the short circuit voltage because short circuit voltage is equal to zero.
Mesh analysis can be used for __________- a)Planar circuits
- b)Non-planar circuits
- c)Both planar and non-planar circuits
- d)Neither planar nor non-planar circuits
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mesh analysis can be used for __________
a)
Planar circuits
b)
Non-planar circuits
c)
Both planar and non-planar circuits
d)
Neither planar nor non-planar circuits
|
|
Harshad Singh answered |
If the circuit is not planar, the meshes are not clearly defined. In planar circuits, it is easy to draw the meshes hence the meshes are clearly defined.
Mesh analysis employs the method of ___________- a)KVL
- b)KCL
- c)Both KVL and KCL
- d)Neither KVL nor KCL
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mesh analysis employs the method of ___________
a)
KVL
b)
KCL
c)
Both KVL and KCL
d)
Neither KVL nor KCL
|
|
Juhi Joshi answered |
KVL employs mesh analysis to find the different mesh currents by finding the IR products in each mesh.
Calculate the mesh currents I1 and I2 flowing in the first and second meshes respectively.
- a)1.75A, 1.2A
- b)0.5A, 2.5A
- c)2.3A, 0.3A
- d)3.2A, 6.5A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the mesh currents I1 and I2 flowing in the first and second meshes respectively.

a)
1.75A, 1.2A
b)
0.5A, 2.5A
c)
2.3A, 0.3A
d)
3.2A, 6.5A
|
|
Tanishq Chauhan answered |
In this circuit, we have a super mesh present. The two mesh equations are:
I2-I1=3
-5I1-3I2=5
Solving these equations simultaneously, we get I1=1.75A and I2= 1.2A.
I2-I1=3
-5I1-3I2=5
Solving these equations simultaneously, we get I1=1.75A and I2= 1.2A.
Chapter doubts & questions for DC Circuit - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Electrical 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of DC Circuit - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Electrical in English & Hindi are available as part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Electrical
675 videos|1297 docs|786 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










