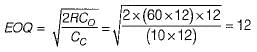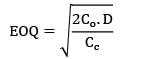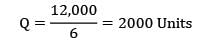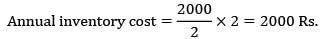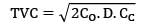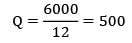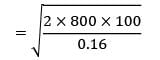All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical >
All Questions
All questions of Inventory Control for Mechanical Engineering Exam
The annual demand for an item is 4000 units, ordering cost is Rs. 200 per order and inventory holding cost is given as 8 Rs./unit/year. If 4% is offered for a lot of 1200 units then what will be economical ordering quantity. (Assume unit cost of an item is Rs. 40)- a) 1200
- b) 1200
- c) 8.5 days
- d) 9.5 days
- e) 9.5 years
Correct answer is between ' 1200, 1200'. Can you explain this answer?
The annual demand for an item is 4000 units, ordering cost is Rs. 200 per order and inventory holding cost is given as 8 Rs./unit/year. If 4% is offered for a lot of 1200 units then what will be economical ordering quantity. (Assume unit cost of an item is Rs. 40)
a)
1200
b)
1200
c)
8.5 days
d)
9.5 days
e)
9.5 years

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Frequency of production run
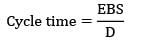
Given data,
Production rate = 24,000/day
Consumption rate = 12,000/day
CC = Rs. 0.02/unit/year
Co = Rs. 18/set‐ up
Working days = 300
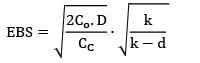
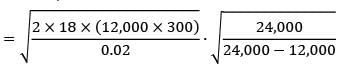
= 113841.99
Annual demand = (12,000 × 300) = 36 × 105
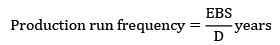
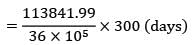
= 9.48
≃ 9.5 days
The annual demand for a product is 60,000 units, the ordering cost is Rs. 8000 per order. Considering Wilsons model, the EOQ is 12,000units. When the annual inventory cost is minimized, the annual inventory holding cost is Rs ___________- a) 40,000
- b) 40,000
Correct answer is between ' 40,000, 40,000'. Can you explain this answer?
The annual demand for a product is 60,000 units, the ordering cost is Rs. 8000 per order. Considering Wilsons model, the EOQ is 12,000
units. When the annual inventory cost is minimized, the annual inventory holding cost is Rs ___________
a)
40,000
b)
40,000
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
D = 60,000
Co = Rs. 8000/order
EOQ = 12,000
Annual inventory holding cost
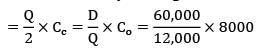
= Rs. 40,000
The annual demand for an item is 5200 units. The ordering cost is Rs. 200/order. The inventory holding cost on average inventory is 20%. The unit cost is Rs. 5 and the storage cost based on maximum inventory is 10 paise per unit per year. EOQ will be __________ units.- a) 1373
- b) 1376
Correct answer is between ' 1373, 1376'. Can you explain this answer?
The annual demand for an item is 5200 units. The ordering cost is Rs. 200/order. The inventory holding cost on average inventory is 20%. The unit cost is Rs. 5 and the storage cost based on maximum inventory is 10 paise per unit per year. EOQ will be __________ units.
a)
1373
b)
1376
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
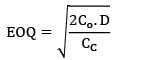
Total CC = Holding cost + Storage cost
= 0.2 × 5 + 0.1
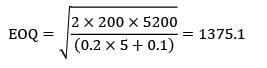
Consider the following data Annual usage = 12,000 units, carrying cost is given as 10% of the unit cost. The cost of an item is Rs. 100. The ordering cost per order is given as Rs. 60 Due to some technical reasons the supply is restricted to only 350 units. Find the total annual cost.- a) order 500 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 240 units
- b) order 500 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 100 units
- c) order 1000 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 240 units
- d) order 1000 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 100 units
- e) 1203800
Correct answer is between ' order 500 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 240 units, order 500 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 100 units'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data Annual usage = 12,000 units, carrying cost is given as 10% of the unit cost. The cost of an item is Rs. 100. The ordering cost per order is given as Rs. 60 Due to some technical reasons the supply is restricted to only 350 units. Find the total annual cost.
a)
order 500 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 240 units
b)
order 500 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 100 units
c)
order 1000 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 240 units
d)
order 1000 units of pens whenever inventory level drops to 100 units
e)
1203800
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Given,
D = 12,000 units
CC = 10% × 100 = Rs. 10/unit/year
Co = Rs. 60/order
Supply is restricted to 350 units
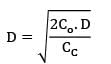
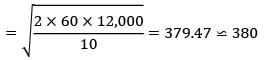
EOQ = 380 which is greater than 350 So, find total cost at 350
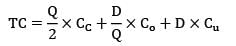
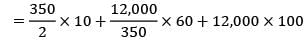
= Rs. 12,03,807
The daily demand for a commodity is given as 200 units. A fixed cost of Rs.1000 is incurred every time an order is placed. The carrying cost is given as Rs. 0.02 per unit per day. The minimum annual inventory cost is _____________- a) 32640
- b) 32650
Correct answer is between ' 32640, 32650'. Can you explain this answer?
The daily demand for a commodity is given as 200 units. A fixed cost of Rs.1000 is incurred every time an order is placed. The carrying cost is given as Rs. 0.02 per unit per day. The minimum annual inventory cost is _____________
a)
32640
b)
32650

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Given data,
Demand = 200 units/day
= 200 × 365 units/year
= 73,000 units/year
Ordering cost = Rs. 1000/order
CC = Rs. 0.02/unit/day
= 0.02 × 365/unit/year
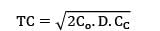
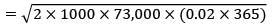
TC = Rs. 32646.59 /year
A company uses 60,000 units per annum of an item, each costing Rs. 120. The ordering cost per order is Rs. 50 and annual inventory carrying costs are 15%. If the company operates 300 days on year, the lead time is given as 10 days and safety stock is 600 units. Find out the re-order level- a) 2400
- b) 600
- c) 2600
- d) 2000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A company uses 60,000 units per annum of an item, each costing Rs. 120. The ordering cost per order is Rs. 50 and annual inventory carrying costs are 15%. If the company operates 300 days on year, the lead time is given as 10 days and safety stock is 600 units. Find out the re-order level
a)
2400
b)
600
c)
2600
d)
2000

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Annual demand = 60,000 units
Unit cost = Rs120/unit
Ordering cost = Rs. 50/order
Carrying costs = 15% × unit cost = Rs. 18/unit‐year
Working days = 300
LT = 10 days
SS = 600 units
ROL = SS + LT × consumption rate
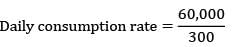 = 200 units /day
= 200 units /dayROL = 600 + 10 × 200 = 2600 units
There are two products A and B with the following characteristics product demand (in units), order cost (in Rs./order), holding cost (in Rs./unit/years)A 100 100 4B 400 100 1The economic order quantities (EOQ) of product A and B will be in the ratio of- a) 1:1
- b) 1:2
- c) 1:4
- d) 1:8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two products A and B with the following characteristics product demand (in units), order cost (in Rs./order), holding cost (in Rs./unit/years)
A 100 100 4
B 400 100 1
The economic order quantities (EOQ) of product A and B will be in the ratio of
a)
1:1
b)
1:2
c)
1:4
d)
1:8

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
EOQ of A and B is in ratio of 1:4 being

A company has an annual demand of 2000 units, ordering cost of Rs. 100/order and a carrying cost of Rs. 200/unit/year. If the shortage costs are estimated to be nearly Rs. 400/unit/year each time the company runs out of stock, then the stock justified by shortage cost is ______________- a) 22
- b) 18
- c) 40
- d) 38
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A company has an annual demand of 2000 units, ordering cost of Rs. 100/order and a carrying cost of Rs. 200/unit/year. If the shortage costs are estimated to be nearly Rs. 400/unit/year each time the company runs out of stock, then the stock justified by shortage cost is ______________
a)
22
b)
18
c)
40
d)
38

|
Pathways Academy answered |
Given data,
D = 2000 units/year
Co = Rs. 100/order
CC = Rs. 200/unit/year
CS = Rs. 400/unit/year
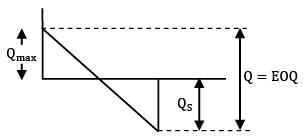
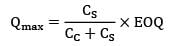
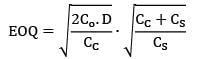
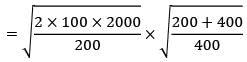
= 54.77 units
≃ 55
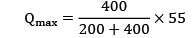
Qmax = 36.67 ≈ 37
Qmax + QS = EOQ
QS = 55 − 37
QS = 18 units
Stock justified by shortage cost
= QS = 18 units
∗ Stock justified by the shortage cost = QS
If the annual demand of an item becomes half, ordering cost double, holding cost one-fourth and the unit cost twice, then what is the ratio of the new EOQ and the earlier EOQ? [Assume that carrying cost depends on unit cost]- a)
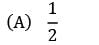
- b)
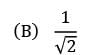
- c)
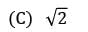
- d) 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the annual demand of an item becomes half, ordering cost double, holding cost one-fourth and the unit cost twice, then what is the ratio of the new EOQ and the earlier EOQ? [Assume that carrying cost depends on unit cost]
a)
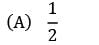
b)
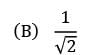
c)
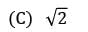
d)
2

|
Gate Funda answered |
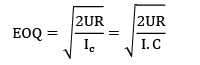
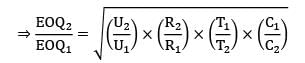
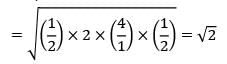
The following data is given for an inventory control system. The annual demand is given as 24,000 units and the safety stock is 200 units. The economic order quantity is 3000 units. If the lead time is 12 days and the number of working days is 300, then the reorder level is __________ units.- a) 1160
- b) 1160
Correct answer is between ' 1160, 1160'. Can you explain this answer?
The following data is given for an inventory control system. The annual demand is given as 24,000 units and the safety stock is 200 units. The economic order quantity is 3000 units. If the lead time is 12 days and the number of working days is 300, then the reorder level is __________ units.
a)
1160
b)
1160

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
Given data,
Annual demand = 24,000 units
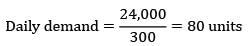
safety stock = 200 units
EOQ = 3000 units
LT = 12 days
Working days = 300
ROL = SS + Demand during LT
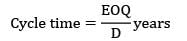
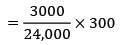
cycle time = 37.5
Lead time < cycle="" />
ROL = 200 + 80 × 12
ROL = 1160
The total cost is represented with the following equation, TC = 10,500 +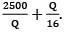 Then TC)min is __________
Then TC)min is __________- a) 10525
- b) 10525
Correct answer is option ''. Can you explain this answer?
The total cost is represented with the following equation, TC = 10,500 +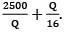 Then TC)min is __________
Then TC)min is __________
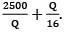 Then TC)min is __________
Then TC)min is __________a)
10525
b)
10525

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
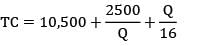
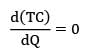
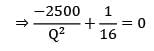
Q = 2500 × 16
Q = 200 units
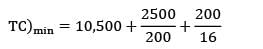
TC)min = 10,500 + 12.5 + 12.5 = 10525
Consider the following functions of inventory:
1. to decouple or separate parts of the production process.
2. to provide a stock of goods that will provide a selection for customers.
3. to take advantage of quantity discounts.
4. to hedge against inflation.Which of the above functions are valid?- a)1,2 and 3
- b)1,3 and 4
- c)2, 3 and 4
- d)1,2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following functions of inventory:
1. to decouple or separate parts of the production process.
2. to provide a stock of goods that will provide a selection for customers.
3. to take advantage of quantity discounts.
4. to hedge against inflation.
1. to decouple or separate parts of the production process.
2. to provide a stock of goods that will provide a selection for customers.
3. to take advantage of quantity discounts.
4. to hedge against inflation.
Which of the above functions are valid?
a)
1,2 and 3
b)
1,3 and 4
c)
2, 3 and 4
d)
1,2, 3 and 4

|
Kstxbrvr 100 answered |
Inventory is stored because to fulfill customers demand on time not decouple production system
In a Wilsons model, annual demand is 10,000 units, the cost of placing an order is Rs. 500. If EOQ is 2000 units then minimum inventory cost per annum is- a) Rs. 500
- b) Rs. 2500
- c) Rs. 5000
- d) Rs. 10000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a Wilsons model, annual demand is 10,000 units, the cost of placing an order is Rs. 500. If EOQ is 2000 units then minimum inventory cost per annum is
a)
Rs. 500
b)
Rs. 2500
c)
Rs. 5000
d)
Rs. 10000
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
D = 10,000 units
CO = Rs. 500/order
EOQ = 2000 units
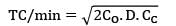
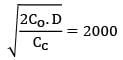
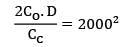
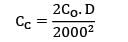
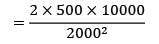
CC = Rs. 25/unit/yr
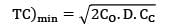
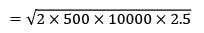
= Rs. 5000
Inventory classification based on criticality of usage is done in which of the following techniques- a) VED
- b) SOS
- c) XYZ
- d) ABC
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Inventory classification based on criticality of usage is done in which of the following techniques
a)
VED
b)
SOS
c)
XYZ
d)
ABC
|
|
Mrinalini Sharma answered |
Inventory Classification Techniques
Inventory classification is crucial in managing materials effectively, especially in a manufacturing or mechanical engineering context. Various techniques exist to categorize inventory based on different criteria.
VED Analysis
- Definition: VED stands for Vital, Essential, and Desirable. This technique classifies inventory based on the criticality of usage.
- Categories:
- Vital: Items that are essential for the operation and cannot be substituted. Their absence can halt production.
- Essential: Items necessary for functioning but can be temporarily substituted with alternatives.
- Desirable: Items that enhance efficiency but are not critical for operations.
Importance of VED
- Operational Continuity: By identifying vital items, organizations can ensure that critical components are always available, minimizing downtime.
- Resource Allocation: It helps prioritize procurement and stock management based on the importance of items, ensuring efficient use of resources.
Other Techniques
- SOS (Seasonal, Obsolescence, and Slow-moving): Focuses on the seasonality and life cycle of items rather than their criticality.
- XYZ Analysis: Primarily categorizes items based on their usage variability and demand predictability.
- ABC Analysis: Classifies inventory based on the value of items, grouping them into high, medium, and low-value categories.
Conclusion
Among these techniques, VED is the most effective for classifying inventory based on criticality of usage. It emphasizes the importance of items in operational processes, making it a valuable tool for inventory management in mechanical engineering and beyond.
Inventory classification is crucial in managing materials effectively, especially in a manufacturing or mechanical engineering context. Various techniques exist to categorize inventory based on different criteria.
VED Analysis
- Definition: VED stands for Vital, Essential, and Desirable. This technique classifies inventory based on the criticality of usage.
- Categories:
- Vital: Items that are essential for the operation and cannot be substituted. Their absence can halt production.
- Essential: Items necessary for functioning but can be temporarily substituted with alternatives.
- Desirable: Items that enhance efficiency but are not critical for operations.
Importance of VED
- Operational Continuity: By identifying vital items, organizations can ensure that critical components are always available, minimizing downtime.
- Resource Allocation: It helps prioritize procurement and stock management based on the importance of items, ensuring efficient use of resources.
Other Techniques
- SOS (Seasonal, Obsolescence, and Slow-moving): Focuses on the seasonality and life cycle of items rather than their criticality.
- XYZ Analysis: Primarily categorizes items based on their usage variability and demand predictability.
- ABC Analysis: Classifies inventory based on the value of items, grouping them into high, medium, and low-value categories.
Conclusion
Among these techniques, VED is the most effective for classifying inventory based on criticality of usage. It emphasizes the importance of items in operational processes, making it a valuable tool for inventory management in mechanical engineering and beyond.
A company has to manufacture 2,00,000 brackets in a year. It orders raw materials for the brackets in lots of 50,000 units from a vendor. It costs Rs. 40 to place an order, inventory carrying costs are 20% of the item cost/yr which is Rs. 0.2/unit. Calculate the variation of cost (in %) in their order quantity from optimal?Ans. C- a) 0.78
- b) 0.68
- c) 0.88
- d) 0.65
Correct answer is option ''. Can you explain this answer?
A company has to manufacture 2,00,000 brackets in a year. It orders raw materials for the brackets in lots of 50,000 units from a vendor. It costs Rs. 40 to place an order, inventory carrying costs are 20% of the item cost/yr which is Rs. 0.2/unit. Calculate the variation of cost (in %) in their order quantity from optimal?
Ans. C
a)
0.78
b)
0.68
c)
0.88
d)
0.65
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Annual demand = 2, 00,000 units
Ordering cost = Rs. 40/order
Carrying cost = 20% of unit cost
Unit cost = Rs. 0.2/unit-year
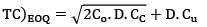
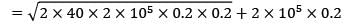
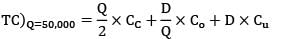
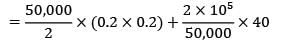
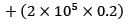
= Rs. 41160
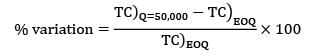
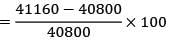
= 0.88%
A moulding firm produces and uses 39,000 units annually. The set-up cost is Rs. 20 and production rate per week is 1000 units. If inventory carrying cost is Rs. 15 per unit per annum, the maximum inventory in units is ____________- a) 162
- b) 2580
- c) 322
- d) 170
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A moulding firm produces and uses 39,000 units annually. The set-up cost is Rs. 20 and production rate per week is 1000 units. If inventory carrying cost is Rs. 15 per unit per annum, the maximum inventory in units is ____________
a)
162
b)
2580
c)
322
d)
170
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Annual production = 39,000 units
Co = Rs. 20/set‐ up
production rate = Rs. 1000/week
CC = Rs. 15/unit/annum
Qmax =?
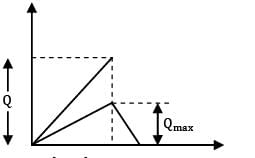
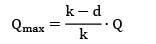
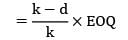
k = production rate
= 1000 units/week
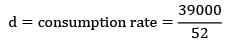 = 750 units/week
= 750 units/week
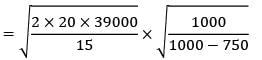
= 644.98
≃ 645
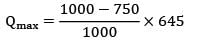
Qmax= 161.25 units ≈ 162 units
Televisions are produced in batches. The production rate is 80 units/day. The demand during production period is 50 units/day. The set-up cost of manufacturing process is 3000 per set-up and holding cost is Rs. 15/unit/year. What is the economic batch size?- a) 5578
- b) 5582
Correct answer is between ' 5578, 5582'. Can you explain this answer?
Televisions are produced in batches. The production rate is 80 units/day. The demand during production period is 50 units/day. The set-up cost of manufacturing process is 3000 per set-up and holding cost is Rs. 15/unit/year. What is the economic batch size?
a)
5578
b)
5582

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
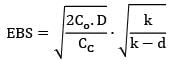
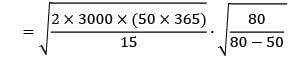
= Rs. 4412
For lead time and consumption the probabilities are given in the table below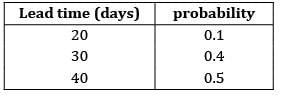
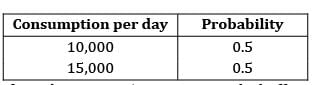 If reorder point is 5,00,000 units. The buffer stock is ______________
If reorder point is 5,00,000 units. The buffer stock is ______________- a) 50,000
- b) 75,000
- c) 25,000
- d) 1,00,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For lead time and consumption the probabilities are given in the table below


If reorder point is 5,00,000 units. The buffer stock is ______________
a)
50,000
b)
75,000
c)
25,000
d)
1,00,000
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Average lead time
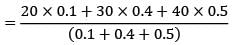
= 34 days
Average consumption
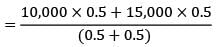
= 12500 units ROP or ROL = Buffer stock or safety stock + Avg. LT × avg. consumption
5, 00,000 = SS + 34 × 12500 SS = 75,000 units
Consider an item with the following characteristics.Annual demand = 400 /yrUnit cost = Rs. 25Inventory carrying cost = 20 % of unit costCost of one procurement = Rs. 10Shortage cost = Rs. 1.5/Unit-yearBased on the above data the time duration between two consecutive orders will be __________ months.- a) 2.28
- b) 2.34
Correct answer is between ' 2.28, 2.34'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider an item with the following characteristics.
Annual demand = 400 /yr
Unit cost = Rs. 25
Inventory carrying cost = 20 % of unit cost
Cost of one procurement = Rs. 10
Shortage cost = Rs. 1.5/Unit-year
Based on the above data the time duration between two consecutive orders will be __________ months.
a)
2.28
b)
2.34
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Given data,
D = 400 units/year
Cu = Rs. 25
Cc = Rs. 0.2 × 25 = Rs. 125/unit-year
Cs = Rs. 1.5/unit-year
Co = Rs. 10/order
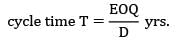
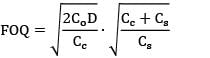
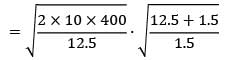
= 77.28
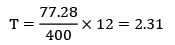
The monthly consumption of an item is 500 units. The price per unit is Rs. 25. The inventory carrying cost is 16% of item cost and ordering cost is Rs. 50 per order. For an economic order quantity model, determine the Re-order quantity- a)380 units
- b)370 units
- c)378 units
- d)388 units
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The monthly consumption of an item is 500 units. The price per unit is Rs. 25. The inventory carrying cost is 16% of item cost and ordering cost is Rs. 50 per order. For an economic order quantity model, determine the Re-order quantity
a)
380 units
b)
370 units
c)
378 units
d)
388 units

|
Constructing Careers answered |

A company follows an EOQ system with the following dataAnnual demand = 15,000 unitsunit cost = Rs. 50ordering cost = Rs. 240/ordercarrying cost = 12% × unit costlead time = 15 dayssafety stock = 150 unitsThe re-order level is __________ days.(A)760(B)770
Correct answer is between ','. Can you explain this answer?
A company follows an EOQ system with the following data
Annual demand = 15,000 units
unit cost = Rs. 50
ordering cost = Rs. 240/order
carrying cost = 12% × unit cost
lead time = 15 days
safety stock = 150 units
The re-order level is __________ days.
(A)760
(B)770
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
ROL = safety stock + Demand during lead time
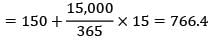
In ABC analysis of inventory control ‘A’ items have- a)very high cost
- b)intermediate cost
- c)low cost
- d)very low cost
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In ABC analysis of inventory control ‘A’ items have
a)
very high cost
b)
intermediate cost
c)
low cost
d)
very low cost

|
Anmol Choudhary answered |
In ABC analyses, item ‘A’ are high usage, valued item and extra care is required for these items.
If the ratio of total incremental cost for a quantity Q to total incremental cost for EOQ quantity is 2, then the ratio of quantity Q to EOQ is _________- a) 2.26
- b) 1.26
- c) 3.73
- d) 2.73
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the ratio of total incremental cost for a quantity Q to total incremental cost for EOQ quantity is 2, then the ratio of quantity Q to EOQ is _________
a)
2.26
b)
1.26
c)
3.73
d)
2.73
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
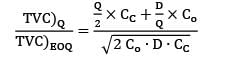
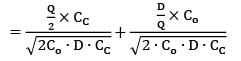
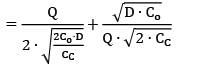
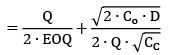
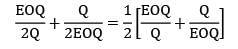
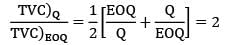
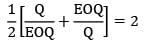
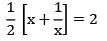
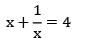
x2 + 1 = 4x
x2 − 4x + 1 = 0
x = 3.73 or 0.26
The demand during lead time is 250 units. The annual consumption is 4000 units. The company has a policy of EOQ ordering and maintains a buffer stock of 200 units. The reorder level is _____________ units.(A)450(B)450
Correct answer is between ','. Can you explain this answer?
The demand during lead time is 250 units. The annual consumption is 4000 units. The company has a policy of EOQ ordering and maintains a buffer stock of 200 units. The reorder level is _____________ units.
(A)450
(B)450
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
ROL = safety stock + lead time demand
= 200 + 250
= 450
The demand for a commodity is 100 units per day. The ordering cost is Rs. 200/order and the carrying cost is Rs. 20/unit/year. If the lead time is 13 days, the re-order point is ____________- a) 1200
- b) 1120
- c) 1300
- d) 1280
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The demand for a commodity is 100 units per day. The ordering cost is Rs. 200/order and the carrying cost is Rs. 20/unit/year. If the lead time is 13 days, the re-order point is ____________
a)
1200
b)
1120
c)
1300
d)
1280
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Daily demand = 100 units
LT = 13 days
ROP/ROL = daily demand × LT
= 100 × 13 = 1300 units
In an industry, two bin system is used to control inventory for a particular component. The first bin hold 1200 units and the second bin holds 800 units. When first bin gets empty second bin is consumed during the lead time. The annual usage of the component is 40,000 units. The cost to place an order is around Rs. 50, the annual holding cost per unit is Rs. 4. The total variable cost for the two-bin approach is __________- a) 4065
- b) 4068
Correct answer is between ' 4065, 4068'. Can you explain this answer?
In an industry, two bin system is used to control inventory for a particular component. The first bin hold 1200 units and the second bin holds 800 units. When first bin gets empty second bin is consumed during the lead time. The annual usage of the component is 40,000 units. The cost to place an order is around Rs. 50, the annual holding cost per unit is Rs. 4. The total variable cost for the two-bin approach is __________
a)
4065
b)
4068
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
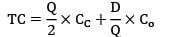
In two bin system order is placed after consuming 1st bin So, ordering quantity will be 1200 units
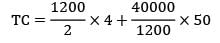
= Rs. 4066.67
A company has an annual demand of 3000 units, the ordering cost per order is Rs. 50 and the carrying cost is Rs. 5 per unit-year. The backorder costs are estimated as Rs. 20 per unit-year. The maximum inventory is (approximately)- a) 200
- b) 220
- c) 240
- d) 280
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A company has an annual demand of 3000 units, the ordering cost per order is Rs. 50 and the carrying cost is Rs. 5 per unit-year. The backorder costs are estimated as Rs. 20 per unit-year. The maximum inventory is (approximately)
a)
200
b)
220
c)
240
d)
280
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
D = 3000 units
Co = Rs. 50/order
Cc = Rs. 5/unit/year
Cs = Rs. 20/unit/year
Qs =?
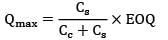
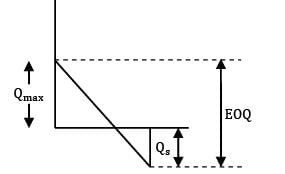
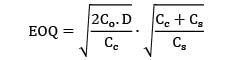
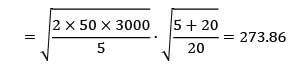
≃ 274
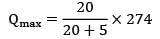
Qmax = 219.2 ≈ 220
The annual demand for an item is 12000 units and the ordering cost is Rs. 25/order. If the holding cost is 12% of the unit cost, then the number of orders per annum is __________ (Assume unit cost as Rs. 20)- a) 24
- b) 24
Correct answer is between ' 24, 24'. Can you explain this answer?
The annual demand for an item is 12000 units and the ordering cost is Rs. 25/order. If the holding cost is 12% of the unit cost, then the number of orders per annum is __________ (Assume unit cost as Rs. 20)
a)
24
b)
24
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
D = 12,000 units/year
Co = Rs. 25/order
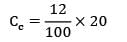

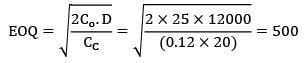
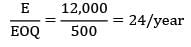
A particular item has a carrying cost of Rs. 2.4/unit/year. The total variable cost of inventory at EOQ is given as 2160. The annual demand is 9000 units. If the replacement is instantaneous then find-out the optimal number of order/year.- a) 9.8
- b) 10.2
Correct answer is between ' 9.8, 10.2'. Can you explain this answer?
A particular item has a carrying cost of Rs. 2.4/unit/year. The total variable cost of inventory at EOQ is given as 2160. The annual demand is 9000 units. If the replacement is instantaneous then find-out the optimal number of order/year.
a)
9.8
b)
10.2

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Given data,
CC = Rs. 2.4/unit/year
TVC = 2160
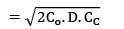
Annual demand = 9000 units

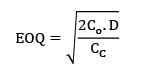
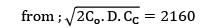
2Co. D. CC = 21602
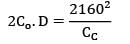
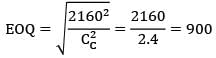
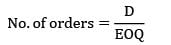
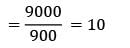
In an ideal inventory control system, the economic lot size for a part is 200 units. If the annual demand for the part is increased by 4 times and carrying cost is decreased by ½, the new EOQ is __________- a) 200/√8
- b) 200√8
- c) 100√4
- d) 100/√4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In an ideal inventory control system, the economic lot size for a part is 200 units. If the annual demand for the part is increased by 4 times and carrying cost is decreased by ½, the new EOQ is __________
a)
200/√8
b)
200√8
c)
100√4
d)
100/√4
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
EOQ 1 = 200
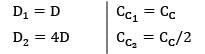

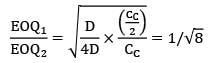
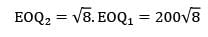
Consider the following data:Annual demand = 3000 unitsOrdering cost = Rs. 100/orderCarrying cost = 25% of unit price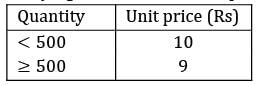 Optimal order quantity is
Optimal order quantity is- a) 447
- b) 516
- c) 500
- d) 489
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data:
Annual demand = 3000 units
Ordering cost = Rs. 100/order
Carrying cost = 25% of unit price

Optimal order quantity is
a)
447
b)
516
c)
500
d)
489
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
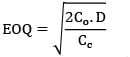

EOQ = 516.39
(Satisfying the Range) Optimal order quantity = 516
Find the economic order quantity for a product of which the price breaks are as follows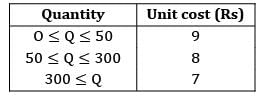 The monthly demand for the product is 200 units. The cost of holding is 25% of the unit cost and the ordering cost is Rs. 20/order.
The monthly demand for the product is 200 units. The cost of holding is 25% of the unit cost and the ordering cost is Rs. 20/order.- a) 300
- b) 300
Correct answer is between ' 300, 300'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the economic order quantity for a product of which the price breaks are as follows

The monthly demand for the product is 200 units. The cost of holding is 25% of the unit cost and the ordering cost is Rs. 20/order.
a)
300
b)
300

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
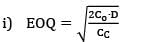
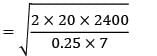
[Annual demand = 12 × 200 = 2400] EOQ = 234.2
(Not falling in the range)
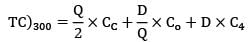
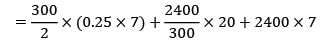
= Rs. 17222.5
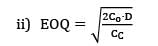
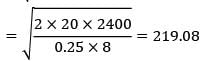
(Falling under range)
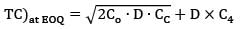
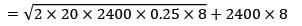
= Rs. 19,638.17
Minimum cost is at 300 Quantity
ABC analysis divides on-hand inventory into three classes, generally based on- a)item quality
- b)unit price
- c)annual rupee volume
- d)the number of units on hand
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ABC analysis divides on-hand inventory into three classes, generally based on
a)
item quality
b)
unit price
c)
annual rupee volume
d)
the number of units on hand

|
Sravya Tiwari answered |
ABC analysis is a technique used in inventory management to categorize items based on their annual rupee volume. The three classes are:
1. Class A: These are high-value items that account for a significant portion of the annual rupee volume, typically around 80%. These items are critical to the business and require careful management to ensure that they are always available.
2. Class B: These are medium-value items that account for around 15% of the annual rupee volume. They are important but not critical to the business, and require less management than Class A items.
3. Class C: These are low-value items that account for the remaining 5% of the annual rupee volume. They are typically low-cost items that are readily available and require minimal management.
The purpose of ABC analysis is to help businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts. By focusing on the most important items, businesses can ensure that they always have the inventory they need to meet customer demand, while minimizing the cost of carrying excess inventory.
In practice, ABC analysis involves calculating the annual rupee volume for each item in inventory and then ranking them from highest to lowest. The items are then divided into the three classes based on their cumulative percentage of the annual rupee volume.
Overall, ABC analysis is a valuable tool for inventory management that can help businesses optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs.
1. Class A: These are high-value items that account for a significant portion of the annual rupee volume, typically around 80%. These items are critical to the business and require careful management to ensure that they are always available.
2. Class B: These are medium-value items that account for around 15% of the annual rupee volume. They are important but not critical to the business, and require less management than Class A items.
3. Class C: These are low-value items that account for the remaining 5% of the annual rupee volume. They are typically low-cost items that are readily available and require minimal management.
The purpose of ABC analysis is to help businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts. By focusing on the most important items, businesses can ensure that they always have the inventory they need to meet customer demand, while minimizing the cost of carrying excess inventory.
In practice, ABC analysis involves calculating the annual rupee volume for each item in inventory and then ranking them from highest to lowest. The items are then divided into the three classes based on their cumulative percentage of the annual rupee volume.
Overall, ABC analysis is a valuable tool for inventory management that can help businesses optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs.
A manufacturing company has a contract to supply 5000 components to an automobile company per day. The manufacturing capacity of the company is 7000 components per day. The carrying cost of 1000 components is 20 paise per day. The set-up cost is Rs. 20. The total inventory cost per annum on optimum basis is __________- a) 230
- b) 1236
Correct answer is between ' 230, 1236'. Can you explain this answer?
A manufacturing company has a contract to supply 5000 components to an automobile company per day. The manufacturing capacity of the company is 7000 components per day. The carrying cost of 1000 components is 20 paise per day. The set-up cost is Rs. 20. The total inventory cost per annum on optimum basis is __________
a)
230
b)
1236

|
Arjun Unni answered |
To find the total inventory cost per annum on the optimum basis, we need to consider the carrying cost, set-up cost, and the production capacity of the manufacturing company.
Carrying Cost Calculation:
The carrying cost is the cost associated with holding inventory. In this case, the carrying cost of 1000 components is given as 20 paise per day. To calculate the carrying cost per annum, we need to multiply this cost by the number of days in a year (365).
Carrying cost per annum = Carrying cost per day * Number of days in a year
= 20 paise * 1000 * 365
= Rs. 7300
Set-up Cost Calculation:
The set-up cost is the cost incurred each time the manufacturing company starts a new production run. In this case, the set-up cost is given as Rs. 20 per set-up.
Total set-up cost per annum = Set-up cost per set-up * Number of set-ups per annum
Now, we need to determine the number of set-ups per annum. Since the manufacturing capacity is 7000 components per day and the automobile company requires 5000 components per day, the manufacturing company needs to produce 5000 components each day to meet the demand. Therefore, the number of set-ups per day is given by:
Number of set-ups per day = Manufacturing capacity / Components required per day
= 7000 / 5000
= 1.4
However, since the number of set-ups cannot be a fraction, we round it up to the nearest whole number. Therefore, the number of set-ups per day is 2.
Number of set-ups per annum = Number of set-ups per day * Number of working days per annum
= 2 * 365
= 730
Total set-up cost per annum = Rs. 20 * 730
= Rs. 14,600
Total Inventory Cost Calculation:
The total inventory cost per annum can be calculated by summing up the carrying cost and the set-up cost.
Total inventory cost per annum = Carrying cost per annum + Total set-up cost per annum
= Rs. 7300 + Rs. 14,600
= Rs. 21,900
Therefore, the total inventory cost per annum on the optimum basis is Rs. 21,900 (option b).
Carrying Cost Calculation:
The carrying cost is the cost associated with holding inventory. In this case, the carrying cost of 1000 components is given as 20 paise per day. To calculate the carrying cost per annum, we need to multiply this cost by the number of days in a year (365).
Carrying cost per annum = Carrying cost per day * Number of days in a year
= 20 paise * 1000 * 365
= Rs. 7300
Set-up Cost Calculation:
The set-up cost is the cost incurred each time the manufacturing company starts a new production run. In this case, the set-up cost is given as Rs. 20 per set-up.
Total set-up cost per annum = Set-up cost per set-up * Number of set-ups per annum
Now, we need to determine the number of set-ups per annum. Since the manufacturing capacity is 7000 components per day and the automobile company requires 5000 components per day, the manufacturing company needs to produce 5000 components each day to meet the demand. Therefore, the number of set-ups per day is given by:
Number of set-ups per day = Manufacturing capacity / Components required per day
= 7000 / 5000
= 1.4
However, since the number of set-ups cannot be a fraction, we round it up to the nearest whole number. Therefore, the number of set-ups per day is 2.
Number of set-ups per annum = Number of set-ups per day * Number of working days per annum
= 2 * 365
= 730
Total set-up cost per annum = Rs. 20 * 730
= Rs. 14,600
Total Inventory Cost Calculation:
The total inventory cost per annum can be calculated by summing up the carrying cost and the set-up cost.
Total inventory cost per annum = Carrying cost per annum + Total set-up cost per annum
= Rs. 7300 + Rs. 14,600
= Rs. 21,900
Therefore, the total inventory cost per annum on the optimum basis is Rs. 21,900 (option b).
A washer manufacturing company has a contract to supply 5000 washers to an automobile industry per day. The company has a capacity to manufacture 10,000 washers/day and holding cost of one washer is Rs. 0.2 per year. Set up cost is Rs. 20. The length of the production cycle is approximately (in days) __________.- a) 5.2
- b) 5.6
Correct answer is between ' 5.2, 5.6'. Can you explain this answer?
A washer manufacturing company has a contract to supply 5000 washers to an automobile industry per day. The company has a capacity to manufacture 10,000 washers/day and holding cost of one washer is Rs. 0.2 per year. Set up cost is Rs. 20. The length of the production cycle is approximately (in days) __________.
a)
5.2
b)
5.6
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Consumption rate = d = 5000/day
production rate = k = 10000/day
Cc = Rs. 0.2/unit/year
Co = Rs. 20/order
Length of production cycle = cycle time
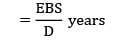
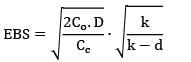
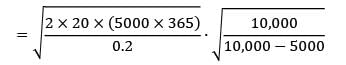
= 27018.5
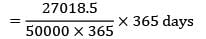
= 5.4 days
The demand during lead time varies uniformly between 8000 units and 12,000 units. The unit price is given as Rs. 4 and the selling price is Rs. 6. The unsold item has a salvage value of Rs. 2. Determine the optimal level of inventory to stock.- a) 10,000
- b) 10,000
Correct answer is between ' 10,000, 10,000'. Can you explain this answer?
The demand during lead time varies uniformly between 8000 units and 12,000 units. The unit price is given as Rs. 4 and the selling price is Rs. 6. The unsold item has a salvage value of Rs. 2. Determine the optimal level of inventory to stock.
a)
10,000
b)
10,000
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Selling price per unit = Rs. 6
Cost price per unit = Rs. 4
Salvage value = Rs. 2
Gain = S. P − C. P = 6 − 4 = 2
Loss = C. P − Salvage value = 4 − 2 = 2
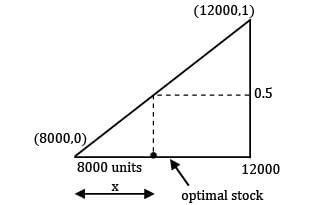
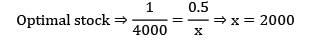
∴ Optimal stock = 8000 + 2000 = 10,000
In fixed order quantity system i.e., Q-system, orders are placed whenever- a) stock equal’s to buffer stock
- b) stock equals to ROP
- c) stock equals to EOQ
- d) None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In fixed order quantity system i.e., Q-system, orders are placed whenever
a)
stock equal’s to buffer stock
b)
stock equals to ROP
c)
stock equals to EOQ
d)
None
|
|
Meera Bose answered |
Understanding the Fixed Order Quantity System (Q-System)
The fixed order quantity system, commonly referred to as the Q-system, is a widely used inventory management approach. This system is designed to maintain optimal inventory levels by determining when to reorder stock based on specific criteria.
Key Concept: Reorder Point (ROP)
- The primary trigger for placing an order in a Q-system is when stock levels reach the Reorder Point (ROP).
- ROP is the inventory level at which a new order should be initiated to replenish stock before it runs out.
- This ensures that the inventory does not fall below a critical level, preventing stockouts.
Why ROP is the Correct Answer
- Buffer Stock: This refers to the extra inventory held to safeguard against fluctuations in demand or supply. It is not the trigger for ordering but rather a safety measure.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): While this is a method used to determine the optimal order size that minimizes total inventory costs, it does not dictate when to place an order.
- Stock Equals Buffer Stock: This condition does not trigger a reorder in the Q-System. Buffer stock is maintained to absorb variability, rather than serve as a reorder signal.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' because the Q-system relies on the Reorder Point (ROP) to dictate when orders should be placed. By monitoring stock levels and utilizing ROP effectively, organizations can ensure a seamless supply chain and avoid interruptions in operations.
The fixed order quantity system, commonly referred to as the Q-system, is a widely used inventory management approach. This system is designed to maintain optimal inventory levels by determining when to reorder stock based on specific criteria.
Key Concept: Reorder Point (ROP)
- The primary trigger for placing an order in a Q-system is when stock levels reach the Reorder Point (ROP).
- ROP is the inventory level at which a new order should be initiated to replenish stock before it runs out.
- This ensures that the inventory does not fall below a critical level, preventing stockouts.
Why ROP is the Correct Answer
- Buffer Stock: This refers to the extra inventory held to safeguard against fluctuations in demand or supply. It is not the trigger for ordering but rather a safety measure.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): While this is a method used to determine the optimal order size that minimizes total inventory costs, it does not dictate when to place an order.
- Stock Equals Buffer Stock: This condition does not trigger a reorder in the Q-System. Buffer stock is maintained to absorb variability, rather than serve as a reorder signal.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' because the Q-system relies on the Reorder Point (ROP) to dictate when orders should be placed. By monitoring stock levels and utilizing ROP effectively, organizations can ensure a seamless supply chain and avoid interruptions in operations.
Two groups of costs in inventory control are- a)carrying costs and ordering costs
- b)relevant costs and ordering costs
- c)carrying costs and total costs '
- d)relevant costs and total costs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two groups of costs in inventory control are
a)
carrying costs and ordering costs
b)
relevant costs and ordering costs
c)
carrying costs and total costs '
d)
relevant costs and total costs

|
Raghavendra Goyal answered |
Two costs are involved in inventory control viz. carrying cost and ordering cost.
The lead time and consumption pattern of a component is as follows: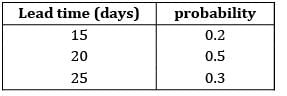
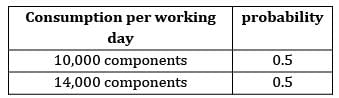 If safety stock = 54,000 units. The ROL is
If safety stock = 54,000 units. The ROL is- a) 2,50,000
- b) 3,00,000
- c) 2,46,000
- d) 2,40,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The lead time and consumption pattern of a component is as follows:


If safety stock = 54,000 units. The ROL is
a)
2,50,000
b)
3,00,000
c)
2,46,000
d)
2,40,000
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Average lead time
= 0.2 × 15 + 0.5 × 20 + 0.3 × 25
= 20.5
Average consumption
= 0.5 × 10,000 + 0.5 × 14,000
= 12,000 units
ROL = SS + Avg. lead time × Avg. consumption
= 54,000 + 20.5 × 12,000
= 3,00,000
Economic Order Quantity is the quantity at which the cost of carrying is- a) minimum
- b) equal to the cost of ordering
- c) less than the cost of ordering
- d) cost of over-stocking
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Economic Order Quantity is the quantity at which the cost of carrying is
a)
minimum
b)
equal to the cost of ordering
c)
less than the cost of ordering
d)
cost of over-stocking
|
|
Priyanka Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a method used in inventory management to determine the optimal quantity of goods to order at one time in order to minimize the total costs associated with ordering and carrying inventory. The EOQ formula takes into account the cost of ordering, the cost of carrying inventory, and the demand for the product.
The formula for EOQ is:
EOQ = √((2DS)/H)
Where:
D = Annual demand
S = Cost of placing an order
H = Holding cost per unit per year
Minimum Cost:
The objective of EOQ is to find the quantity that minimizes the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory. The total cost includes the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory. When the quantity ordered is too small, the cost of ordering will be high, as the order will need to be placed frequently. On the other hand, if the quantity is too large, the cost of carrying inventory will be high, as the inventory will need to be stored for a longer period of time. Therefore, the optimal quantity is the one that minimizes the total cost.
Equal Cost:
The EOQ model is based on the assumption that the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory are the only costs associated with inventory. The optimal quantity is the one that balances the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory. When the quantity ordered is equal to the EOQ, the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory is minimized.
Less than the Cost of Ordering:
If the quantity ordered is less than the EOQ, the cost of ordering will be high, as the order will need to be placed frequently. This will increase the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory.
Cost of Over-stocking:
If the quantity ordered is more than the EOQ, the cost of carrying inventory will be high, as the inventory will need to be stored for a longer period of time. This will increase the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory, and may lead to over-stocking, which can result in additional costs such as obsolescence and storage costs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is the quantity at which the cost of carrying is equal to the cost of ordering. The EOQ model is based on the assumption that the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory are the only costs associated with inventory. When the quantity ordered is equal to the EOQ, the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory is minimized.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a method used in inventory management to determine the optimal quantity of goods to order at one time in order to minimize the total costs associated with ordering and carrying inventory. The EOQ formula takes into account the cost of ordering, the cost of carrying inventory, and the demand for the product.
The formula for EOQ is:
EOQ = √((2DS)/H)
Where:
D = Annual demand
S = Cost of placing an order
H = Holding cost per unit per year
Minimum Cost:
The objective of EOQ is to find the quantity that minimizes the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory. The total cost includes the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory. When the quantity ordered is too small, the cost of ordering will be high, as the order will need to be placed frequently. On the other hand, if the quantity is too large, the cost of carrying inventory will be high, as the inventory will need to be stored for a longer period of time. Therefore, the optimal quantity is the one that minimizes the total cost.
Equal Cost:
The EOQ model is based on the assumption that the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory are the only costs associated with inventory. The optimal quantity is the one that balances the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory. When the quantity ordered is equal to the EOQ, the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory is minimized.
Less than the Cost of Ordering:
If the quantity ordered is less than the EOQ, the cost of ordering will be high, as the order will need to be placed frequently. This will increase the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory.
Cost of Over-stocking:
If the quantity ordered is more than the EOQ, the cost of carrying inventory will be high, as the inventory will need to be stored for a longer period of time. This will increase the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory, and may lead to over-stocking, which can result in additional costs such as obsolescence and storage costs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is the quantity at which the cost of carrying is equal to the cost of ordering. The EOQ model is based on the assumption that the cost of ordering and the cost of carrying inventory are the only costs associated with inventory. When the quantity ordered is equal to the EOQ, the total cost of ordering and carrying inventory is minimized.
In the ABC method of inventory control, Group A constitutes costly items. What is the usual percentage of such items of the total items?- a) 10 to 20%
- b) 20 to 30%
- c) 30 to 40 %
- d) 40 to 50 %
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the ABC method of inventory control, Group A constitutes costly items. What is the usual percentage of such items of the total items?
a)
10 to 20%
b)
20 to 30%
c)
30 to 40 %
d)
40 to 50 %
|
|
Sagarika Mukherjee answered |
Understanding the ABC Method
The ABC method of inventory control categorizes inventory into three classes: A, B, and C, based on their value and importance to the business.
Category A: Costly Items
- Group A items are the most valuable in terms of cost.
- These items represent a small percentage of the total inventory but account for a significant portion of the overall inventory value.
- Typically, Group A comprises about 10 to 20% of the total items.
Importance of Group A Items
- Monitoring and managing Group A items is crucial because they have a higher impact on the company’s finances.
- Effective control of these items can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency improvements.
Distribution of Inventory Value
- The distribution often follows the Pareto principle, where 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
- In inventory terms, 10 to 20% of items (Group A) can account for up to 70-80% of the total inventory costs.
Conclusion
- The classification helps businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts.
- By focusing on the costly items in Group A, companies can optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and improve cash flow.
This strategic approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively, maximizing profitability while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
The ABC method of inventory control categorizes inventory into three classes: A, B, and C, based on their value and importance to the business.
Category A: Costly Items
- Group A items are the most valuable in terms of cost.
- These items represent a small percentage of the total inventory but account for a significant portion of the overall inventory value.
- Typically, Group A comprises about 10 to 20% of the total items.
Importance of Group A Items
- Monitoring and managing Group A items is crucial because they have a higher impact on the company’s finances.
- Effective control of these items can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency improvements.
Distribution of Inventory Value
- The distribution often follows the Pareto principle, where 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
- In inventory terms, 10 to 20% of items (Group A) can account for up to 70-80% of the total inventory costs.
Conclusion
- The classification helps businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts.
- By focusing on the costly items in Group A, companies can optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and improve cash flow.
This strategic approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively, maximizing profitability while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Which of the following statement is correct regarding EOQ?- a) Carrying cost is minimum
- b) Ordering cost is minimum
- c) Total inventory cost is minimum
- d) Ordering quantity is minimum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is correct regarding EOQ?
a)
Carrying cost is minimum
b)
Ordering cost is minimum
c)
Total inventory cost is minimum
d)
Ordering quantity is minimum

|
Mahesh Yadav answered |
Understanding EOQ (Economic Order Quantity)
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model is a crucial concept in inventory management that helps businesses determine the optimal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs.
What is Total Inventory Cost?
Total inventory cost comprises three main components:
- Carrying Costs: These are costs associated with holding inventory, such as storage, insurance, and depreciation.
- Ordering Costs: These costs are incurred each time an order is placed, including shipping and handling costs.
- Stockout Costs: Costs arising when inventory runs out and includes lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Why is Option C Correct?
- Minimization of Total Inventory Costs: The EOQ model aims to find the order quantity that minimizes the total inventory costs. It balances the carrying and ordering costs effectively.
- Trade-off Between Costs: As order quantity increases, carrying costs rise due to more inventory being held. However, ordering costs decrease as fewer orders are needed. The EOQ formula identifies the point where these two costs are minimized together.
- Optimal Quantity: The EOQ leads to a specific order quantity that, when followed, results in the lowest total cost. This is critical for businesses to maintain efficiency and profitability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct statement regarding EOQ is that it minimizes total inventory costs (Option C). Understanding this helps businesses manage their inventory more effectively, balancing the costs associated with ordering and carrying inventory.
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model is a crucial concept in inventory management that helps businesses determine the optimal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs.
What is Total Inventory Cost?
Total inventory cost comprises three main components:
- Carrying Costs: These are costs associated with holding inventory, such as storage, insurance, and depreciation.
- Ordering Costs: These costs are incurred each time an order is placed, including shipping and handling costs.
- Stockout Costs: Costs arising when inventory runs out and includes lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Why is Option C Correct?
- Minimization of Total Inventory Costs: The EOQ model aims to find the order quantity that minimizes the total inventory costs. It balances the carrying and ordering costs effectively.
- Trade-off Between Costs: As order quantity increases, carrying costs rise due to more inventory being held. However, ordering costs decrease as fewer orders are needed. The EOQ formula identifies the point where these two costs are minimized together.
- Optimal Quantity: The EOQ leads to a specific order quantity that, when followed, results in the lowest total cost. This is critical for businesses to maintain efficiency and profitability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct statement regarding EOQ is that it minimizes total inventory costs (Option C). Understanding this helps businesses manage their inventory more effectively, balancing the costs associated with ordering and carrying inventory.
Chapter doubts & questions for Inventory Control - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Inventory Control - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical
499 videos|1037 docs|710 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup