All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Liquid Phase – Intermolecular Forces (GC) for MCAT Exam
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
- a)
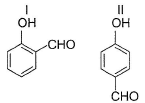
- b)
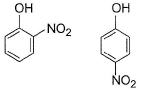
- c)

- d)
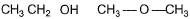
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
I. Intermolecular H-bonding makes boiling point higher than that of I. Thus, I is more volatile
II. Ortho nitrophenol is more volatile than para nitrophenol because O-Nitrophenol has intramolecular hydrogen bonding whereas para nitrophenol has inter molecular H bonding and so boils relatively at higher temperature
(c) BP of H2O > > H2S
(d) BP of CH3CH2OH (due to H-bonding) > > CH3— O — CH3
The H-bond is shortest in
- a)S— H---S
- b)N— H ... O
- c)F— H ... F
- d)F— H ... O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The H-bond is shortest in
a)
S— H---S
b)
N— H ... O
c)
F— H ... F
d)
F— H ... O
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
A hydrogen bond is a weak type of force that forms a special type of dipole-dipole attraction which occurs when a hydrogen atom bonded to a strongly electronegative atom exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons.
F is the most electronegative atom. Hence hydrogen bond is shortest in F - H ........F.
F is the most electronegative atom. Hence hydrogen bond is shortest in F - H ........F.
What is the dominant intermolecular force or bond that must be overcome in converting liquid CH3CH2OH to vapours?- a)H-bonding
- b)Dipole-dipole interactions
- c)Covalent bonds
- d)London dispersion force
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the dominant intermolecular force or bond that must be overcome in converting liquid CH3CH2OH to vapours?
a)
H-bonding
b)
Dipole-dipole interactions
c)
Covalent bonds
d)
London dispersion force

|
Swara Saha answered |
CH3CH2OH is in liquid state due to association as a result of intermolecular H-bonding.
Out of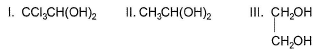 Q. unstable compound is/are
Q. unstable compound is/are - a)I and II
- b)Only I
- c)Only II
- d)Only III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of
Q. unstable compound is/are
a)
I and II
b)
Only I
c)
Only II
d)
Only III
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
I. CCI3CH (OH)2 with two — OH groups on same carbon atom is stable due to intramolecular H-bonding.
Among the following sets, highest boiling points are of the species.
I. HF, HCI, HBr, HI
II. H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te
III. NH3,PH3, AsH3,SbH3
- a)HF, H2O, NH3
- b)HCI, H2S, PH3
- c)HBr, H2Te, AsH3
- d)HI, H2S, AsH3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following sets, highest boiling points are of the species.
I. HF, HCI, HBr, HI
II. H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te
III. NH3,PH3, AsH3,SbH3
II. H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te
III. NH3,PH3, AsH3,SbH3
a)
HF, H2O, NH3
b)
HCI, H2S, PH3
c)
HBr, H2Te, AsH3
d)
HI, H2S, AsH3

|
Maheshwar Chawla answered |
F, O and N are electronegative elements. Thus, HF molecules are associated by intermolecules H-bonding giving it a liquid state and thus highest boiling point out of HF, HCl.HBr and HI.
Similarly, H2O has highest boiling point, and NH3 has highest boiling point.
Similarly, H2O has highest boiling point, and NH3 has highest boiling point.
Which of the following has maximum boiling point?- a)
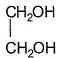
- b)CH3CH2CH2OH
- c)H2O
- d)CH3CH2CH2CH3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has maximum boiling point?
a)
b)
CH3CH2CH2OH
c)
H2O
d)
CH3CH2CH2CH3

|
Janhavi Banerjee answered |
Due to intermolecular H-bonding at two terminals boiling point of glycol is maximu
Number of water molecules directly attached to one water molecule is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of water molecules directly attached to one water molecule is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Gaurav Saini answered |
One water molecule is directly attached to four water molecules. Thus, coordination number of water is 4.
Consider the following compoundsI. HCI
II. HF
III. CH3COOH
IV. CH4
V. CH3OH
VI. CH3COO-Q.
H-bonding is not present in- a)I, III and IV
- b)I, IV and VI
- c)II, III and V
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following compounds
I. HCI
II. HF
III. CH3COOH
IV. CH4
V. CH3OH
VI. CH3COO-
II. HF
III. CH3COOH
IV. CH4
V. CH3OH
VI. CH3COO-
Q.
H-bonding is not present in
H-bonding is not present in
a)
I, III and IV
b)
I, IV and VI
c)
II, III and V
d)
None
|
|
Ameya Choudhury answered |
Explanation:
Compounds:
- I. HCI
- II. HF
- III. CH3COOH
- IV. CH4
- V. CH3OH
- VI. CH3COO-Q
H-bonding:
- Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen.
- It involves a strong dipole-dipole attraction between a hydrogen atom and a lone pair of electrons on a highly electronegative atom.
Analysis:
- Compound I (HCl) and compound IV (CH4) do not have hydrogen atoms directly bonded to highly electronegative atoms like fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen, so they do not exhibit hydrogen bonding.
- Compound VI (CH3COO-Q) is a salt and does not have hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonding.
Conclusion:
- So, the compounds where hydrogen bonding is not present are I, IV, and VI.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B (I, IV, and VI).
Compounds:
- I. HCI
- II. HF
- III. CH3COOH
- IV. CH4
- V. CH3OH
- VI. CH3COO-Q
H-bonding:
- Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen.
- It involves a strong dipole-dipole attraction between a hydrogen atom and a lone pair of electrons on a highly electronegative atom.
Analysis:
- Compound I (HCl) and compound IV (CH4) do not have hydrogen atoms directly bonded to highly electronegative atoms like fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen, so they do not exhibit hydrogen bonding.
- Compound VI (CH3COO-Q) is a salt and does not have hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonding.
Conclusion:
- So, the compounds where hydrogen bonding is not present are I, IV, and VI.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B (I, IV, and VI).
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Which of the following compounds are soluble in H2O ? - a)CH3CHO
- b)CH3COCH3
- c)CH3CH2OH
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which of the following compounds are soluble in H2O ?
a)
CH3CHO
b)
CH3COCH3
c)
CH3CH2OH
d)
All of these
|
|
Sinjini Shah answered |
All these are soluble in water due to intermolecular H-bonding.
Which of the following correctly represents H-bonding?- a)
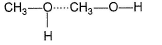
- b)
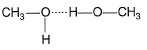
- c)
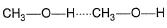
- d)
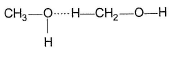
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly represents H-bonding?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Nilesh Chawla answered |
H-bonding is between polar 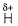 and electronegative 0, N and F C-atom or H attached to C is not polar. Thus, (a), (c), (d) are incorrect.
and electronegative 0, N and F C-atom or H attached to C is not polar. Thus, (a), (c), (d) are incorrect.
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomenon[JEE Advanced 2014]- a)ice floats in water
- b)higher Lewis basicity of primary amines than tertiary amines in aqueous solution
- c)formic acid is more acidic than acetic acid
- d)dimerisation of acetic acid (in benzene
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomenon
[JEE Advanced 2014]
a)
ice floats in water
b)
higher Lewis basicity of primary amines than tertiary amines in aqueous solution
c)
formic acid is more acidic than acetic acid
d)
dimerisation of acetic acid (in benzene
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Hydrogen bonding is responsible for the open-cage structure of ice which explains why the density of ice is less than water.
Primary amines can stabilize themselves by forming hydrogen bonds. Although tertiary amines can also participate in H-bonding the extent is much lesser.
The + I effect of the CH3 is responsible for the weakening in acidic strength.
Dimerisation here is indeed because of H-bonding:
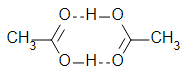
In which of the following boiling point of Column I is not higher than that of Column II?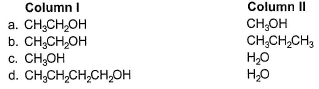
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following boiling point of Column I is not higher than that of Column II?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Bibek Desai answered |
(a) Intermolecular H-bonding, boiling point increases with molecular weight for compounds within the same family.
(b) H-bonding is absent is CH3CH2CH3.
(c) Methanol is the larger molecule but H2O has more H-bonding because of two O—H bonds.
Thus, boiling point of H2O(ll) > CH3OH(l).
(d) Molecular weight of butanol is much higher and overcomes attractive forces of butanol.
(b) H-bonding is absent is CH3CH2CH3.
(c) Methanol is the larger molecule but H2O has more H-bonding because of two O—H bonds.
Thus, boiling point of H2O(ll) > CH3OH(l).
(d) Molecular weight of butanol is much higher and overcomes attractive forces of butanol.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.Q. Match the species in Column I with rank order of their boiling point in Column II. (Species with lowest boifing points is at SN1).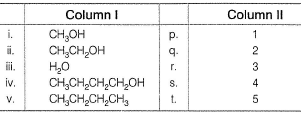

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the species in Column I with rank order of their boiling point in Column II. (Species with lowest boifing points is at SN1).
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Jatin Sharma answered |
n-butane lacks H-bonding. Hence, its boiling point is least.
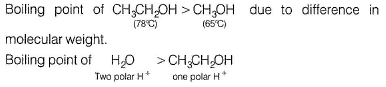
due to difference in polar H+ for H-bonding.
Boiling point of CH3CH2CH2CH2OH > H2O due to much larger size of alcohol.
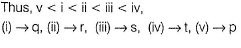
due to difference in polar H+ for H-bonding.
Boiling point of CH3CH2CH2CH2OH > H2O due to much larger size of alcohol.
In the following alcohol, which — OH group is involved to the maximum extent in H-bonding?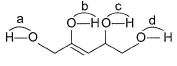
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following alcohol, which — OH group is involved to the maximum extent in H-bonding?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Raghav Chakraborty answered |
O — H group is attached to (ene) is m ost a cidic and thus, has maximum intermolecular H-bonding.
In the following compounds, select the points of interm olecular H-bonding (linear),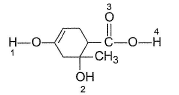
- a)1, 2, 3
- b)1, 3, 4
- c)1,2,4
- d)1,4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following compounds, select the points of interm olecular H-bonding (linear),
a)
1, 2, 3
b)
1, 3, 4
c)
1,2,4
d)
1,4

|
Arindam Unni answered |
1. Enoiic H, acidic and polar takes part in H-bonding.
2. 3° alcohol least acidic maximum basic.
3. Carbonyl oxygen is not involved.
4. Acidic and polar H, takes part in H-bonding.
Chapter doubts & questions for Liquid Phase – Intermolecular Forces (GC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Liquid Phase – Intermolecular Forces (GC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










