All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Locomotion and Movement for NEET Exam
Which one of the following pairs of chemical substances is correctly categorized? [2012M]- a)Calcitonin and thymosin - Thyroid hormones
- b)Pepsin and prolactin - Two digestive enzymes secreted in stomach
- c)Troponin and myosin - Complex proteins in striated muscles
- d)Secretin and rhodopsin - Polypeptide hormones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of chemical substances is correctly categorized? [2012M]
a)
Calcitonin and thymosin - Thyroid hormones
b)
Pepsin and prolactin - Two digestive enzymes secreted in stomach
c)
Troponin and myosin - Complex proteins in striated muscles
d)
Secretin and rhodopsin - Polypeptide hormones

|
Shounak Nair answered |
Troponin is a protein which is found on actin filament and myosin protein is found in myosin filament. Both actin and myosin are complex proteins in striated muscles.
Thymosin is a hormone secreted by the thymus that stimulates development of T cells. Prolactin is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates breast development and milk production in women. Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is not a hormone. It is a biological pigment in photoreceptor cells of the retina that is responsible for the first events in the perception of light
Thymosin is a hormone secreted by the thymus that stimulates development of T cells. Prolactin is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates breast development and milk production in women. Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is not a hormone. It is a biological pigment in photoreceptor cells of the retina that is responsible for the first events in the perception of light
The H-zone in the skeletal muscle fibre is due to : [NEET 2013]- a)The central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band.
- b)The central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
- c)Extension of myosin filaments in the central portion of the A-band.
- d)The absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The H-zone in the skeletal muscle fibre is due to : [NEET 2013]
a)
The central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band.
b)
The central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
c)
Extension of myosin filaments in the central portion of the A-band.
d)
The absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band.

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Central part of thick filament, not overlapped by thin filaments is called the ‘H’ zone. ‘H’ zone is also called Hensen’s Line.
Which ion is essential for muscle contraction? [1994]- a)Na
- b)K
- c)Ca
- d)Cl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which ion is essential for muscle contraction? [1994]
a)
Na
b)
K
c)
Ca
d)
Cl

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
Movement of Ca2+ out in sarcoplasmic reticulum controls the making and breaking of actin and myosin complex actomyosin due to which muscle contraction and relaxation takes place. Albert Szent Gyorgyi worked out biochemical events of muscle contraction.
Select the correct statement with respect to locomotion in humans : [NEET 2013]- a)Accumulation of uric acid cr ystals in joints causes their inflammation
- b)The vertebral column has 10 thoracic vertebrae.
- c)The joint between adjacent vertebrae is a fibrous joint
- d)The decreased level of progesterone causes osteoporosis in old people
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement with respect to locomotion in humans : [NEET 2013]
a)
Accumulation of uric acid cr ystals in joints causes their inflammation
b)
The vertebral column has 10 thoracic vertebrae.
c)
The joint between adjacent vertebrae is a fibrous joint
d)
The decreased level of progesterone causes osteoporosis in old people

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Vertebral column has 12th or acicvertebrate. The joints between adjacent vertebrae is cartilaginous joint which permits limited movements. Progesterone is secreted by corpus luteum which supports in pregnancy in females
Elbow joint is an example of: [2009]- a)hinge joint
- b)gliding joint
- c)ball and socket joint
- d)pivot joint
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Elbow joint is an example of: [2009]
a)
hinge joint
b)
gliding joint
c)
ball and socket joint
d)
pivot joint

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Elbow joint is an example of hinge joint. The elbow is a hinge joint; it can open and close like a door. Hinge joint is a form of diarthrosis (freely movable joint) that allows angular movement in one plane only, increasing or decreasing the angle between the bones e.g. elbow joint, knee joint etc.
Select the correct statement with respect to disorders of muscles in humans [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Rapid contractions of skeletal muscles causes muscle dystrophy
- b)Failure of neuromuscular transmission in myasthenia gravis can prevent normal swallowing
- c)Accumulation of urea and creatine in the joints cause their inflammation
- d)An over dose of vitamin D causes osteoporosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement with respect to disorders of muscles in humans [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Rapid contractions of skeletal muscles causes muscle dystrophy
b)
Failure of neuromuscular transmission in myasthenia gravis can prevent normal swallowing
c)
Accumulation of urea and creatine in the joints cause their inflammation
d)
An over dose of vitamin D causes osteoporosis

|
Shounak Nair answered |
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune muscular disease. It causes
breakdown of neuromuscular junction due to which the brain loses control over muscles. The symptoms may include drooping eyelids, difficulty in swallowing muscle fatigue, difficult breathing and inability to control facial expressions.
breakdown of neuromuscular junction due to which the brain loses control over muscles. The symptoms may include drooping eyelids, difficulty in swallowing muscle fatigue, difficult breathing and inability to control facial expressions.
Which statement is correct for muscle contraction? [2001]- a)Length of H-line decreases
- b)Length of A-band remains constant
- c)Length of I-band increases
- d)Length of two Z-lines increase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is correct for muscle contraction? [2001]
a)
Length of H-line decreases
b)
Length of A-band remains constant
c)
Length of I-band increases
d)
Length of two Z-lines increase

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
When Ca+ ions combine with troponin contraction of muscles initiates. During Contraction the Z lines come closer together and the sarcomere becomes shorter. The length of A band remains constant. I bands shortens and H-band narrows.
Sliding filament theory can be best explained as: [2015]- a)Actin and Myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
- b)Actin and Myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other
- c)When myofilaments slide pass each other, Myosin filaments shorten while Actin filaments do not shorten
- d)When myofilaments slide pass each other Actin filaments shorten while Myosin filament do not shorten
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sliding filament theory can be best explained as: [2015]
a)
Actin and Myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
b)
Actin and Myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other
c)
When myofilaments slide pass each other, Myosin filaments shorten while Actin filaments do not shorten
d)
When myofilaments slide pass each other Actin filaments shorten while Myosin filament do not shorten

|
Naman Mittal answered |
2
Select the correct matching of the type of the joint with the example in human skeletal system: [2014]Type of joint Example- a)Cartilaginous joint between frontal and pariental
- b)Pivot joint between third and fourth cervical vertebrae
- c)Hinge joint between humerus and pectoral girdle
- d)Gliding joint between carpals
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct matching of the type of the joint with the example in human skeletal system: [2014]
Type of joint Example
a)
Cartilaginous joint between frontal and pariental
b)
Pivot joint between third and fourth cervical vertebrae
c)
Hinge joint between humerus and pectoral girdle
d)
Gliding joint between carpals
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
A gliding joint is a common type of synovial joint formed between bones that meet at flat or nearly flat articular surfaces. Gliding joints allow the bones to glide past one another in any direction along the plane of the joint - up and down, left and right, and diagonally. Many gliding joints are formed in the appendicular skeleton between the carpal bones of the wrist; between the carpals and the metacarpals of the palm; between the tarsal bones of the ankle; and between the tarsals and the metatarsals of the foot.
In human body, which one of the following is anatomically correct? [2007]- a)Collar bones - 3 pairs
- b)Salivary glands - 1 pairs
- c)Cranial nerves - 10 pairs
- d)Floating ribs - 2 pairs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In human body, which one of the following is anatomically correct? [2007]
a)
Collar bones - 3 pairs
b)
Salivary glands - 1 pairs
c)
Cranial nerves - 10 pairs
d)
Floating ribs - 2 pairs

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Floating ribs are 2- pairs (11th and 12th pair) which are not attached to sternum
Name the ion responsible for unmasking of active sites for myosin for cross-bridge activity during muscle contraction. [2016]- a)Calcium
- b)Magnesium
- c)Sodium
- d)Potassium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the ion responsible for unmasking of active sites for myosin for cross-bridge activity during muscle contraction. [2016]
a)
Calcium
b)
Magnesium
c)
Sodium
d)
Potassium
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Calciumion plays an important role muscle contraction. Calcium ions bind to troponin causing a change in its shape and position. Thus in turn alters shape and position of tropomyosin to which troponin binds. This shift exposes the active sites on F-actin molecules. Myosin cross-bridge are then able to bind to these active sites.
Which is part of pectoral girdle? [1994]- a)Glenoid cavity
- b)Sternum
- c)Ilium
- d)Acetabulum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is part of pectoral girdle? [1994]
a)
Glenoid cavity
b)
Sternum
c)
Ilium
d)
Acetabulum

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Glenoid cavity is a shallow concavity on the lateral side of pectoral girdle in which the head of humerus fits making the shoulder joint.
The pivot joint between atlas and axis is a type of [2017]- a)Cartilaginous joint
- b)Synovial joint
- c)Saddle joint
- d)Fibrous joint.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pivot joint between atlas and axis is a type of [2017]
a)
Cartilaginous joint
b)
Synovial joint
c)
Saddle joint
d)
Fibrous joint.
|
|
Anirban Joshi answered |
Introduction:
The pivot joint between the atlas and axis is a crucial joint in the vertebral column that allows for rotation of the head. This joint is classified as a synovial joint.
Synovial Joints:
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body and are characterized by the presence of a synovial cavity. These joints are highly mobile and allow for various types of movements, such as flexion, extension, rotation, abduction, and adduction. Examples of synovial joints include the knee, shoulder, hip, and elbow joints.
Pivot Joint:
A pivot joint is a type of synovial joint that allows for rotation around a central axis. It consists of a rounded or pointed surface of one bone that fits into a ring or notch of another bone. The joint between the atlas (C1) and axis (C2) is a specific example of a pivot joint.
Atlas and Axis:
The atlas (C1) and axis (C2) are the first two vertebrae in the vertebral column. The atlas is responsible for supporting the weight of the head and allowing for nodding movements. The axis, on the other hand, has a unique feature called the dens or odontoid process, which acts as a pivot for rotation of the atlas and head.
Anatomical Structure:
In the pivot joint between the atlas and axis, the rounded surface of the dens fits into the ring formed by the anterior arch of the atlas. This arrangement allows for the rotation of the head, as the atlas rotates around the dens. The joint is supported by ligaments and surrounded by a synovial capsule that contains synovial fluid, which lubricates and nourishes the joint.
Function:
The pivot joint between the atlas and axis is responsible for the rotatory movements of the head. This joint allows for the shaking of the head to indicate "no" and the rotation of the head to look over the shoulder.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the pivot joint between the atlas and axis is a synovial joint that allows for rotation of the head. This joint is crucial for various movements of the head and neck and is supported by ligaments and synovial fluid.
The pivot joint between the atlas and axis is a crucial joint in the vertebral column that allows for rotation of the head. This joint is classified as a synovial joint.
Synovial Joints:
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body and are characterized by the presence of a synovial cavity. These joints are highly mobile and allow for various types of movements, such as flexion, extension, rotation, abduction, and adduction. Examples of synovial joints include the knee, shoulder, hip, and elbow joints.
Pivot Joint:
A pivot joint is a type of synovial joint that allows for rotation around a central axis. It consists of a rounded or pointed surface of one bone that fits into a ring or notch of another bone. The joint between the atlas (C1) and axis (C2) is a specific example of a pivot joint.
Atlas and Axis:
The atlas (C1) and axis (C2) are the first two vertebrae in the vertebral column. The atlas is responsible for supporting the weight of the head and allowing for nodding movements. The axis, on the other hand, has a unique feature called the dens or odontoid process, which acts as a pivot for rotation of the atlas and head.
Anatomical Structure:
In the pivot joint between the atlas and axis, the rounded surface of the dens fits into the ring formed by the anterior arch of the atlas. This arrangement allows for the rotation of the head, as the atlas rotates around the dens. The joint is supported by ligaments and surrounded by a synovial capsule that contains synovial fluid, which lubricates and nourishes the joint.
Function:
The pivot joint between the atlas and axis is responsible for the rotatory movements of the head. This joint allows for the shaking of the head to indicate "no" and the rotation of the head to look over the shoulder.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the pivot joint between the atlas and axis is a synovial joint that allows for rotation of the head. This joint is crucial for various movements of the head and neck and is supported by ligaments and synovial fluid.
The joint found between sternum and the ribs in humans is [2000]- a)angular joint
- b)fibrous joint
- c)cartilaginous joint
- d)gliding joint
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The joint found between sternum and the ribs in humans is [2000]
a)
angular joint
b)
fibrous joint
c)
cartilaginous joint
d)
gliding joint
|
|
Shivam Kapoor answered |
The joint found between the sternum and the ribs in humans is a cartilaginous joint. This type of joint is also known as a synchondrosis. It is formed by the articulation between the costal cartilages of the ribs and the sternum, specifically the first seven pairs of ribs.
Cartilaginous joints are classified into two types: synchondroses and symphyses. Synchondroses are joints where the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage, while symphyses are joints where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage.
In the case of the joint between the sternum and the ribs, it is a synchondrosis because the bones are connected by hyaline cartilage. The costal cartilages of the ribs attach to the sternum through this type of joint, allowing for some flexibility and movement.
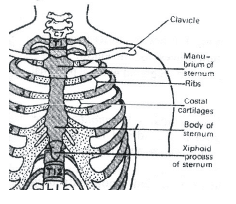
The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat bone located in the center of the chest. It consists of three parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The ribs, on the other hand, are long curved bones that form the ribcage, protecting the organs in the thoracic cavity.
The cartilaginous joint between the sternum and the ribs provides stability to the ribcage while allowing for some movement. This movement is important for activities such as breathing, as the ribcage needs to expand and contract to facilitate the inhalation and exhalation of air.
Cartilaginous joints, including the joint between the sternum and the ribs, have limited mobility compared to other types of joints such as synovial joints. This is because the cartilage connecting the bones restricts their movement to some extent. However, the flexibility provided by these joints is essential for proper functioning of the body.
In conclusion, the joint found between the sternum and the ribs in humans is a cartilaginous joint. Specifically, it is a synchondrosis formed by the articulation between the costal cartilages of the ribs and the sternum. This joint allows for some movement and flexibility, contributing to the overall function and stability of the ribcage.
Cartilaginous joints are classified into two types: synchondroses and symphyses. Synchondroses are joints where the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage, while symphyses are joints where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage.
In the case of the joint between the sternum and the ribs, it is a synchondrosis because the bones are connected by hyaline cartilage. The costal cartilages of the ribs attach to the sternum through this type of joint, allowing for some flexibility and movement.
The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat bone located in the center of the chest. It consists of three parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The ribs, on the other hand, are long curved bones that form the ribcage, protecting the organs in the thoracic cavity.
The cartilaginous joint between the sternum and the ribs provides stability to the ribcage while allowing for some movement. This movement is important for activities such as breathing, as the ribcage needs to expand and contract to facilitate the inhalation and exhalation of air.
Cartilaginous joints, including the joint between the sternum and the ribs, have limited mobility compared to other types of joints such as synovial joints. This is because the cartilage connecting the bones restricts their movement to some extent. However, the flexibility provided by these joints is essential for proper functioning of the body.
In conclusion, the joint found between the sternum and the ribs in humans is a cartilaginous joint. Specifically, it is a synchondrosis formed by the articulation between the costal cartilages of the ribs and the sternum. This joint allows for some movement and flexibility, contributing to the overall function and stability of the ribcage.
What is sarcomere? [2001]- a)Part between two H-lines
- b)Part between two A-lines
- c)Part between two I-bands
- d)Part between two Z-lines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is sarcomere? [2001]
a)
Part between two H-lines
b)
Part between two A-lines
c)
Part between two I-bands
d)
Part between two Z-lines
|
|
Shail Khanna answered |
Understanding Sarcomere
The sarcomere is the fundamental contractile unit of striated muscle tissue, playing a critical role in muscle contraction.
Structure of Sarcomere
- Z-lines: The sarcomere is defined as the segment between two Z-lines. These lines are crucial as they anchor the thin filaments (actin) and delineate the boundaries of each sarcomere.
- A-band: This region contains the thick filaments (myosin) and overlaps with the thin filaments. It appears dark under a microscope due to the density of these proteins.
- I-band: This section contains only thin filaments and is lighter in appearance. The I-band spans across two adjacent sarcomeres and extends from the Z-line to the start of the A-band.
Why Option D is Correct
- Definition: The sarcomere is specifically the area between two Z-lines. This demarcation is essential for understanding how muscle fibers contract and how they are organized.
- Functionality: During muscle contraction, the sarcomeres shorten, pulling the Z-lines closer together, which leads to the overall shortening of the muscle fiber.
- Importance in Physiology: The arrangement of sarcomeres aligns perfectly for coordinated muscle action, enabling efficient movement and strength.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' because the sarcomere is distinctly defined by the space between two Z-lines, making it the essential unit of muscle contraction. Understanding this structure is vital for students in fields related to biology and medicine, particularly in contexts like the NEET examination.
The sarcomere is the fundamental contractile unit of striated muscle tissue, playing a critical role in muscle contraction.
Structure of Sarcomere
- Z-lines: The sarcomere is defined as the segment between two Z-lines. These lines are crucial as they anchor the thin filaments (actin) and delineate the boundaries of each sarcomere.
- A-band: This region contains the thick filaments (myosin) and overlaps with the thin filaments. It appears dark under a microscope due to the density of these proteins.
- I-band: This section contains only thin filaments and is lighter in appearance. The I-band spans across two adjacent sarcomeres and extends from the Z-line to the start of the A-band.
Why Option D is Correct
- Definition: The sarcomere is specifically the area between two Z-lines. This demarcation is essential for understanding how muscle fibers contract and how they are organized.
- Functionality: During muscle contraction, the sarcomeres shorten, pulling the Z-lines closer together, which leads to the overall shortening of the muscle fiber.
- Importance in Physiology: The arrangement of sarcomeres aligns perfectly for coordinated muscle action, enabling efficient movement and strength.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' because the sarcomere is distinctly defined by the space between two Z-lines, making it the essential unit of muscle contraction. Understanding this structure is vital for students in fields related to biology and medicine, particularly in contexts like the NEET examination.
Osteoporosis, an age-related disease of skeletal system, may occur due to [2016]- a)Immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue
- b)High concentration of Ca++ and Na+
- c)Decreased level of estrogen
- d)Accumulation of uric acid leading to inflammation of joints.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Osteoporosis, an age-related disease of skeletal system, may occur due to [2016]
a)
Immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue
b)
High concentration of Ca++ and Na+
c)
Decreased level of estrogen
d)
Accumulation of uric acid leading to inflammation of joints.
|
|
Akanksha Das answered |
Understanding Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a progressive skeletal disorder characterized by decreased bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures. It is particularly common in older adults, especially postmenopausal women.
Role of Estrogen
- Estrogen is a key hormone that helps maintain bone density.
- It inhibits the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption.
- A decrease in estrogen levels, especially during menopause, leads to increased bone resorption and decreased bone formation.
Why Option C is Correct
- The correct answer is option 'C', which states that osteoporosis may occur due to decreased levels of estrogen.
- This hormonal change accelerates bone loss, making bones weaker and more susceptible to fractures.
Other Options Explained
- Option A: Immune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue does not directly relate to bone density issues.
- Option B: High concentrations of Ca++ and Na+ can affect various physiological processes but are not directly responsible for osteoporosis.
- Option D: Accumulation of uric acid leading to joint inflammation is associated with gout, not osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Understanding the hormonal influences on bone health is critical for preventing and managing osteoporosis. The decline in estrogen levels is a primary risk factor, making awareness and timely intervention essential, especially for postmenopausal women.
Osteoporosis is a progressive skeletal disorder characterized by decreased bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures. It is particularly common in older adults, especially postmenopausal women.
Role of Estrogen
- Estrogen is a key hormone that helps maintain bone density.
- It inhibits the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption.
- A decrease in estrogen levels, especially during menopause, leads to increased bone resorption and decreased bone formation.
Why Option C is Correct
- The correct answer is option 'C', which states that osteoporosis may occur due to decreased levels of estrogen.
- This hormonal change accelerates bone loss, making bones weaker and more susceptible to fractures.
Other Options Explained
- Option A: Immune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue does not directly relate to bone density issues.
- Option B: High concentrations of Ca++ and Na+ can affect various physiological processes but are not directly responsible for osteoporosis.
- Option D: Accumulation of uric acid leading to joint inflammation is associated with gout, not osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Understanding the hormonal influences on bone health is critical for preventing and managing osteoporosis. The decline in estrogen levels is a primary risk factor, making awareness and timely intervention essential, especially for postmenopausal women.
Total number of bones in the hind limb of man is[1998]- a)14
- b)30
- c)24
- d)21
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of bones in the hind limb of man is[1998]
a)
14
b)
30
c)
24
d)
21
|
|
Nishtha Dey answered |
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that the total number of bones in the hind limb of a man is 30.
The hind limb, also known as the lower limb, is the lower appendage of the human body that extends from the hip to the foot. It consists of several bones that work together to provide support, stability, and movement.
The bones in the hind limb can be divided into three main regions: the pelvic girdle, the thigh, and the leg/foot. Let's discuss each region and the bones present in them:
1. Pelvic Girdle:
- The pelvic girdle consists of two hip bones, also known as the coxal bones or innominate bones.
- Each hip bone is made up of three fused bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
- Therefore, the pelvic girdle has a total of 2 bones.
2. Thigh:
- The thigh bone is called the femur, which is the longest and strongest bone in the human body.
- Therefore, the thigh has a total of 1 bone.
3. Leg/Foot:
- The leg consists of two bones: the tibia and fibula.
- The tibia is the larger and stronger bone, located on the medial side of the leg. It bears most of the body's weight.
- The fibula is the smaller bone, located on the lateral side of the leg. It provides support and muscle attachment.
- Therefore, the leg has a total of 2 bones.
- The foot consists of several bones, including the tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
- There are 7 tarsal bones in the foot: talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid, and the three cuneiform bones.
- There are 5 metatarsal bones in the foot, which are located in the midfoot region.
- There are 14 phalanges in the foot, divided into proximal, middle, and distal phalanges.
- Therefore, the foot has a total of 26 bones (7 tarsals + 5 metatarsals + 14 phalanges).
Adding up the bones from each region:
Pelvic Girdle: 2 bones
Thigh: 1 bone
Leg: 2 bones
Foot: 26 bones
Total number of bones in the hind limb = 2 + 1 + 2 + 26 = 31
Therefore, the correct answer is not option 'B' but seems to be option 'D' which states that the total number of bones in the hind limb of a man is 21.
The hind limb, also known as the lower limb, is the lower appendage of the human body that extends from the hip to the foot. It consists of several bones that work together to provide support, stability, and movement.
The bones in the hind limb can be divided into three main regions: the pelvic girdle, the thigh, and the leg/foot. Let's discuss each region and the bones present in them:
1. Pelvic Girdle:
- The pelvic girdle consists of two hip bones, also known as the coxal bones or innominate bones.
- Each hip bone is made up of three fused bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
- Therefore, the pelvic girdle has a total of 2 bones.
2. Thigh:
- The thigh bone is called the femur, which is the longest and strongest bone in the human body.
- Therefore, the thigh has a total of 1 bone.
3. Leg/Foot:
- The leg consists of two bones: the tibia and fibula.
- The tibia is the larger and stronger bone, located on the medial side of the leg. It bears most of the body's weight.
- The fibula is the smaller bone, located on the lateral side of the leg. It provides support and muscle attachment.
- Therefore, the leg has a total of 2 bones.
- The foot consists of several bones, including the tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
- There are 7 tarsal bones in the foot: talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid, and the three cuneiform bones.
- There are 5 metatarsal bones in the foot, which are located in the midfoot region.
- There are 14 phalanges in the foot, divided into proximal, middle, and distal phalanges.
- Therefore, the foot has a total of 26 bones (7 tarsals + 5 metatarsals + 14 phalanges).
Adding up the bones from each region:
Pelvic Girdle: 2 bones
Thigh: 1 bone
Leg: 2 bones
Foot: 26 bones
Total number of bones in the hind limb = 2 + 1 + 2 + 26 = 31
Therefore, the correct answer is not option 'B' but seems to be option 'D' which states that the total number of bones in the hind limb of a man is 21.
Which of the following muscular disorders is inherited? [2019]
- a)Botulism
- b)Tetany
- c)Muscular dystrophy
- d)Myasthenia gravis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following muscular disorders is inherited? [2019]
a)
Botulism
b)
Tetany
c)
Muscular dystrophy
d)
Myasthenia gravis
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Musculardys trophy is a group of muscle diseases, marked by weakness and wasting of selected muscles, in which there is a recognizable pattern of inheritance.
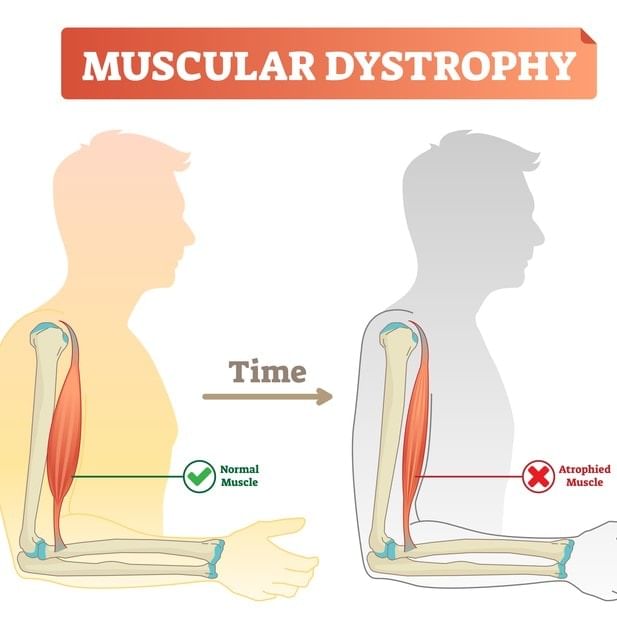
In this disorder, the mutated gene on middle of the short arm of X - chromosome is unable to produce a protein dystrophin in skeletal muscles. It is common in males, female heterozygous carriers are normal.

In this disorder, the mutated gene on middle of the short arm of X - chromosome is unable to produce a protein dystrophin in skeletal muscles. It is common in males, female heterozygous carriers are normal.
Chronic auto immune disorder affecting neuro muscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle is called as: [2021]- a)Myasthenia gravis
- b)Gout
- c)Arthritis
- d)Muscular dystrophy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chronic auto immune disorder affecting neuro muscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle is called as: [2021]
a)
Myasthenia gravis
b)
Gout
c)
Arthritis
d)
Muscular dystrophy
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Myasthenia gravis: Auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
Muscular dystrophy: Progressive degeneration of skeletal muscle mostly due to genetic disorder.
Tetany: Rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ in body fluid.
Arthritis: Inflammation of joints.
Osteoporosis: Age-related disorder characterised by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures. Decreased levels of estrogen is a common cause.
Gout: Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals.
Tetany: Rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low Ca++ in body fluid.
Arthritis: Inflammation of joints.
Osteoporosis: Age-related disorder characterised by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures. Decreased levels of estrogen is a common cause.
Gout: Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals.
Calcium is important in skeletal muscle contraction because it [2018]- a)Binds to troponin to remove the masking of active sites on aclin for myosin
- b)Activates the myosin ATPase by binding to it
- c)Detaches the myosin head from the actin filament
- d)Prevents the formation of bonds between the myosin cross bridges and the aclin filament.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calcium is important in skeletal muscle contraction because it [2018]
a)
Binds to troponin to remove the masking of active sites on aclin for myosin
b)
Activates the myosin ATPase by binding to it
c)
Detaches the myosin head from the actin filament
d)
Prevents the formation of bonds between the myosin cross bridges and the aclin filament.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Calciumion plays an important role in skeletal muscle contraction. Muscle contraction is initiated by signal sent by the central nervous system. The neural signal further spreads through the muscle fibre and causes the release of calcium ions. Increase in calcium ion levels lead to the binding of calcium with a subunit of troponin on actin filaments and thereby remove the masking of active sites for myosin.
Which one of the following is the correct matching of three items and their grouping category? [2009] 
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct matching of three items and their grouping category? [2009]

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Palak Khanna answered |
The pelvic girdle is formed by two innominate bones consists of three separate bones ilium, ischium and the pubis
Select the correct statement regarding the specific disorder of muscular or skeletal system :- [2012]- a)Muscular dystrophy - agerelated shortening or muscles.
- b)Osteoporosis - decrease in bone mass and higher chance of fractures with advancing age.
- c)Myastheniagrav is - Auto immune disorder which inhibits sliding of myosin filaments
- d)Gout - inflammation of joints due to extra deposition of calcium.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement regarding the specific disorder of muscular or skeletal system :- [2012]
a)
Muscular dystrophy - agerelated shortening or muscles.
b)
Osteoporosis - decrease in bone mass and higher chance of fractures with advancing age.
c)
Myastheniagrav is - Auto immune disorder which inhibits sliding of myosin filaments
d)
Gout - inflammation of joints due to extra deposition of calcium.

|
Yash Saha answered |
Major causative factors of osteoporosis are imbalances of hormones like calcitonin of thyroid, parathormone of parathyroids, and sex hormones and deficiencies of calcium and vitamin D.
Match the following columns and select the correct option [2020]

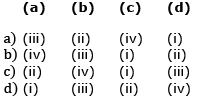
- a)(a)
- b)(b)
- c)(c)
- d)(d)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following columns and select the correct option [2020]

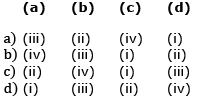

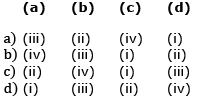
a)
(a)
b)
(b)
c)
(c)
d)
(d)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
(a) There are 12 pairs of ribs. Each rib is a thin flat bone connected dorsally to the vertebral column and ventrally to the sternum. Last 2 pairs (11th and 12th) of ribs are not connected ventrally and are therefore, called floating ribs.
(b) & (c)
Scapula is a large triangular flat bone situated in the dorsal part of the thorax between the second and the seventh ribs. The dorsal, flat, triangular body of scapula has a slightly elevated ridge called the spine which projects as a flat, expanded process called the acromion. The clavicle (collar bone) articulates with this.
(d) Below the acromion is a depression called the glenoid cavity which articulates with the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint.
(b) & (c)
Scapula is a large triangular flat bone situated in the dorsal part of the thorax between the second and the seventh ribs. The dorsal, flat, triangular body of scapula has a slightly elevated ridge called the spine which projects as a flat, expanded process called the acromion. The clavicle (collar bone) articulates with this.
(d) Below the acromion is a depression called the glenoid cavity which articulates with the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint.
Which of the following joints would allow no movement? [2014]- a)Cartilaginoius joint
- b)Synovial joint
- c)Ball and Socket joint
- d)Fibrous joint
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following joints would allow no movement? [2014]
a)
Cartilaginoius joint
b)
Synovial joint
c)
Ball and Socket joint
d)
Fibrous joint
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Fibrous joint is an attachment between bones, being held together by fibrous connective tissue. For example- suture between skull bones.
The characteristics and an example of a synovial joint in humans is : [NEET 2013]

- a)a
- b)d
- c)c
- d)b
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The characteristics and an example of a synovial joint in humans is : [NEET 2013]


a)
a
b)
d
c)
c
d)
b

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Synovial joints are distinguished by the existence of a synovial cavity filled with fluid between the surfaces of two bones that articulate with each other. These joints facilitate movement, aiding in locomotion and various other activities. Examples of synovial joints include the ball and socket joint found between the humerus and the pectoral girdle, the hinge joint present in the knee, the pivot joint located between the atlas and axis vertebrae, the gliding joint between the carpals, and the saddle joint between the carpal and metacarpal bones of the thumb.
Three of the following pairs of the human skeletal parts are correctly matched with their respective inclusive skeletal category and one pair is not matched. Identify the non-matching pair. [2011M]
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three of the following pairs of the human skeletal parts are correctly matched with their respective inclusive skeletal category and one pair is not matched. Identify the non-matching pair. [2011M]

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
Glenoid cavity is found in pectoral girdle.
Chapter doubts & questions for Locomotion and Movement - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Locomotion and Movement - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









