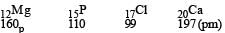All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties for NEET Exam
Which electronic configuration of an element has abnormally high difference between second and third ionization energy ? [1993]
- a)1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1
- b)1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1 3p1
- c)1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 3p2
- d)1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which electronic configuration of an element has abnormally high difference between second and third ionization energy ? [1993]
a)
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1
b)
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1 3p1
c)
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 3p2
d)
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
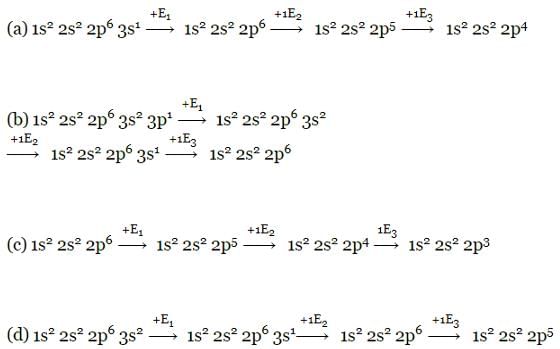
In option D, after removal of second valence electron from 3s orbital, the ion formed achieves noble gas configuration. Therefore, to remove the third electron from 2p orbital, a lot of energy is required. Thus, there is an abnormally high difference between second and third ionization enthalpies.
If the atomic number of an element is 33, it will be placed in the periodic table in the- a)First group
- b)Third group
- c)Fifteenth group
- d)Seventh group.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the atomic number of an element is 33, it will be placed in the periodic table in the
a)
First group
b)
Third group
c)
Fifteenth group
d)
Seventh group.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The electronic configuration of element with atomic number 33 is 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p3
As, its last shell have five electrons
and hence, its group is 10 + 5 = 15th or V A.
Hence,it lies in the 15th group.
As, its last shell have five electrons
and hence, its group is 10 + 5 = 15th or V A.
Hence,it lies in the 15th group.
One would expect proton to have very large- a)Charge
- b)Ionization potential
- c)Hydration energy
- d)Radius. [1993]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One would expect proton to have very large
a)
Charge
b)
Ionization potential
c)
Hydration energy
d)
Radius. [1993]

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Proton (H+) being very small in size would have very large hydration energy.
Na+, Mg2+, Al3+ and Si4+ are isoelectronic. The order of their ionic size is [1993]- a)Na+ > Mg2+ < Al3 + < Si4+
- b)Na+ < Mg2+ > Al3+ > Si4+
- c)Na+ > Mg2+ > Al3+ > Si4+
- d)Na+ < Mg2+ > Al3+ < Si4+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Na+, Mg2+, Al3+ and Si4+ are isoelectronic. The order of their ionic size is [1993]
a)
Na+ > Mg2+ < Al3 + < Si4+
b)
Na+ < Mg2+ > Al3+ > Si4+
c)
Na+ > Mg2+ > Al3+ > Si4+
d)
Na+ < Mg2+ > Al3+ < Si4+
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Amongst isoelectronic ions, the size of the cation decreases as the magnitude of the charge increases.
Which one of the following oxides is expected to exhibit paramagn etic beh aviour? [2 00 5]- a)CO2
- b)SiO2
- c)SO2
- d)ClO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following oxides is expected to exhibit paramagn etic beh aviour? [2 00 5]
a)
CO2
b)
SiO2
c)
SO2
d)
ClO2
|
|
Nidhi Tamak answered |
Paramagnetic behavior is seen by those who has unpaired electrons that's why option d is correct because it has unpaired electron.
Which one of the following ions will be the smallest in size? [1996]- a)Na+
- b)Mg2+
- c)F–
- d)O2–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following ions will be the smallest in size? [1996]
a)
Na+
b)
Mg2+
c)
F–
d)
O2–

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Greater is the positive charge on atom, large is effective nuclear charge. Hence smaller is the size
Elements of which of the following groups will form anions most readily ? [1992]- a)Oxygen family
- b)Nitrogen family
- c)Halogens
- d)Alkali metals
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Elements of which of the following groups will form anions most readily ? [1992]
a)
Oxygen family
b)
Nitrogen family
c)
Halogens
d)
Alkali metals
|
|
Chirag Mehta answered |
**Explanation:**
**Anion Formation:**
- Anions are formed when atoms gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- A stable electron configuration is typically achieved by filling the valence shell with eight electrons, known as the octet rule.
**Oxygen Family:**
- The oxygen family consists of elements such as oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), and tellurium (Te).
- These elements have six valence electrons.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to gain two electrons to complete their octet.
- Therefore, they readily form anions with a -2 charge, such as O^2-, S^2-, Se^2-, and Te^2-.
**Nitrogen Family:**
- The nitrogen family includes elements such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi).
- These elements have five valence electrons.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to gain three electrons to complete their octet.
- However, gaining three electrons is energetically unfavorable for these elements.
- Therefore, they typically form anions with a -3 charge, such as N^3-, P^3-, As^3-, Sb^3-, and Bi^3-, but not as readily as the elements in the oxygen family.
**Halogens:**
- The halogens include elements such as fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At).
- These elements have seven valence electrons.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to gain one electron to complete their octet.
- Therefore, they readily form anions with a -1 charge, such as F^-, Cl^-, Br^-, I^-, and At^-.
**Alkali Metals:**
- The alkali metals include elements such as lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), and cesium (Cs).
- These elements have one valence electron.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to lose this valence electron and form cations with a +1 charge.
- Therefore, they do not readily form anions.
**Conclusion:**
- Among the given options, the halogens (option C) will form anions most readily.
- This is because they have seven valence electrons and only need to gain one electron to complete their octet.
- The other elements in the oxygen family and nitrogen family also form anions, but not as readily as the halogens.
- The alkali metals do not readily form anions; instead, they tend to form cations by losing their valence electron.
**Anion Formation:**
- Anions are formed when atoms gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- A stable electron configuration is typically achieved by filling the valence shell with eight electrons, known as the octet rule.
**Oxygen Family:**
- The oxygen family consists of elements such as oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), and tellurium (Te).
- These elements have six valence electrons.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to gain two electrons to complete their octet.
- Therefore, they readily form anions with a -2 charge, such as O^2-, S^2-, Se^2-, and Te^2-.
**Nitrogen Family:**
- The nitrogen family includes elements such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi).
- These elements have five valence electrons.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to gain three electrons to complete their octet.
- However, gaining three electrons is energetically unfavorable for these elements.
- Therefore, they typically form anions with a -3 charge, such as N^3-, P^3-, As^3-, Sb^3-, and Bi^3-, but not as readily as the elements in the oxygen family.
**Halogens:**
- The halogens include elements such as fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At).
- These elements have seven valence electrons.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to gain one electron to complete their octet.
- Therefore, they readily form anions with a -1 charge, such as F^-, Cl^-, Br^-, I^-, and At^-.
**Alkali Metals:**
- The alkali metals include elements such as lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), and cesium (Cs).
- These elements have one valence electron.
- To achieve a stable electron configuration, they tend to lose this valence electron and form cations with a +1 charge.
- Therefore, they do not readily form anions.
**Conclusion:**
- Among the given options, the halogens (option C) will form anions most readily.
- This is because they have seven valence electrons and only need to gain one electron to complete their octet.
- The other elements in the oxygen family and nitrogen family also form anions, but not as readily as the halogens.
- The alkali metals do not readily form anions; instead, they tend to form cations by losing their valence electron.
An atom has electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2, you will place it in which group?- a)Fifth
- b)Fifteenth [2002]
- c)Secon d
- d)Third
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An atom has electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2, you will place it in which group?
a)
Fifth
b)
Fifteenth [2002]
c)
Secon d
d)
Third

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
The electronic configuration clearly suggest that it is a d-block element (having contiguration (n – 1) d1– 10 ns0 – 2) which starts from III B and goes till II B. Hence with d3 configuration it would be classified in the group.
Which one of the following ionic species has the greatest proton affinity to form stable compound?- a)NH 2-
- b)F– [2007]
- c)I–
- d)HS–
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following ionic species has the greatest proton affinity to form stable compound?
a)
NH 2-
b)
F– [2007]
c)
I–
d)
HS–

|
Smrity answered |
Correct option is a bcoz the conjugate base NH2- is weak and it is also known as strong base .
The stability of + 1 oxidation state increases in the sequence: [2009]
- a)Tl < In < Ga < Al
- b)In < Tl < Ga < Al
- c)Ga < In < Al < Tl
- d)Al < Ga < In < Tl
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The stability of + 1 oxidation state increases in the sequence: [2009]
a)
Tl < In < Ga < Al
b)
In < Tl < Ga < Al
c)
Ga < In < Al < Tl
d)
Al < Ga < In < Tl

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
The stability of +1 oxidation state increases from aluminium to thallium i.e.
Al < Ga < In < Tl
Al < Ga < In < Tl
In the periodic table from left to right in a period, the atomic volume [1993]- a)Decr eases
- b)In creases
- c)Remains same
- d)First decrease then increases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the periodic table from left to right in a period, the atomic volume [1993]
a)
Decr eases
b)
In creases
c)
Remains same
d)
First decrease then increases

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
Atomic volume is the volume occupied by one gram of an element. Within a period from left to right, atomic volume first decreases and then increases due to increases of nuclear charge and increase in the number of electrons in the valence shell.
Which of the following electronic configuration an atom has the lowest ionisation enthalpy? [2007]- a)1s2 2s2 sp3
- b)1s2 2s2 2p5 3s1
- c)1s2 2s2 2p6
- d)1s2 2s2 2p5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following electronic configuration an atom has the lowest ionisation enthalpy? [2007]
a)
1s2 2s2 sp3
b)
1s2 2s2 2p5 3s1
c)
1s2 2s2 2p6
d)
1s2 2s2 2p5

|
Devansh Mehra answered |
The electronic configuration 1s2 2s22p5 3s1 shows lowest ionisation energy because this configuration is unstable due to the presence of one electron is s- orbital. Hence, less energy is required to remove the electron.
Which of the following statements is true? [2002]- a)Silicon exhibits 4 coordination number in its compound
- b)Bond energy of F2 is less than Cl2
- c)Mn(III) oxidation state is more stable than Mn(II) in aqueous state
- d)Elements of 15th group shows only +3 and +5 oxidation states
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true? [2002]
a)
Silicon exhibits 4 coordination number in its compound
b)
Bond energy of F2 is less than Cl2
c)
Mn(III) oxidation state is more stable than Mn(II) in aqueous state
d)
Elements of 15th group shows only +3 and +5 oxidation states

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Due to small size and high electronegativity of fluorine, there exists repulsion between the nucleus of two fluorine atoms which ultimately results in the weakening of the F-F bond. Hence, the bond dissociation enthalpy of F
2
is less than that of Cl
2
Correct order of first IP among following elements Be, B, C, N, O is [2001]- a)B < Be < C < O < N
- b)B < Be < C < N < O
- c)Be < B < C < N < O
- d)Be < B < C < O < N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct order of first IP among following elements Be, B, C, N, O is [2001]
a)
B < Be < C < O < N
b)
B < Be < C < N < O
c)
Be < B < C < N < O
d)
Be < B < C < O < N

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
Be – 1s22s2; B – 1s22s22p1; C – 1s22s22p2; N – 1s22s22p3; O – 1s22s22p4. IP increases along the period. But IP of Be > B. Further IP of O < N because atoms with fully or partly filled orbitals are most stable and hence have high ionisation energy.
The element, with atomic number 118, will be- a)alkali
- b)noble gas
- c)lanthanide
- d)transition element
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The element, with atomic number 118, will be
a)
alkali
b)
noble gas
c)
lanthanide
d)
transition element

|
Krish Patel answered |
Electron ic con figuration of element with atomic number 118 will be [Rn]5f146d10 7s27p6. Since its elctronic configuration in the outer most orbit (ns2np6) resemble with that of inert or noble gases, therefore it will be noble gas element.
Which one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of least negative to most negative electron gain enthalpy for C, Ca, Al, F and O? [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Ca < Al < C < O < F
- b)Al < Ca < O < C < F
- c)Al < O < C < Ca < F
- d)C < F < O < Al < Ca
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of least negative to most negative electron gain enthalpy for C, Ca, Al, F and O? [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Ca < Al < C < O < F
b)
Al < Ca < O < C < F
c)
Al < O < C < Ca < F
d)
C < F < O < Al < Ca

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
As the nuclear charge increases, the force of attraction between the nucleus and the incoming electron increses and hence the elecron gain enthalpy becomes more negative, hence the correct order is Ca < Al < C < O < F
Amongst the elements with following electronic configurations, which one of them may have the highest ionization energy? [2009]- a)Ne [3s23p2]
- b)Ar [3d104s24p3 ]
- c)Ne [3s23p1]
- d)Ne [3s23p3]
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Amongst the elements with following electronic configurations, which one of them may have the highest ionization energy? [2009]
a)
Ne [3s23p2]
b)
Ar [3d104s24p3 ]
c)
Ne [3s23p1]
d)
Ne [3s23p3]

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
The smaller the atomic size, larger is the value of ionisation potential. Further the atoms having half filled or fully filled orbitals are comparitively more stable, hence more energy is required to remove the electron from such atoms.
Which of the following order is wrong? [2002]- a)NH3 < PH3 < AsH3 – Acidic
- b)Li < Be < B < C – First IP
- c)Al2O3 < MgO < Na2O < K2O – Basic
- d)Li+ < Na+ < K+ < Cs+ – Ionic radius
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following order is wrong? [2002]
a)
NH3 < PH3 < AsH3 – Acidic
b)
Li < Be < B < C – First IP
c)
Al2O3 < MgO < Na2O < K2O – Basic
d)
Li+ < Na+ < K+ < Cs+ – Ionic radius

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Along the period, I.P. generally increases but not regularly. Be and B are exceptions. First I.P. increases in moving from left to right in a period, but I.P. of B is lower than Be.
The electronic configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 . What is the atomic number of the element, which is just below the above element in the periodic table? [1995]- a)33
- b)34
- c)36
- d)49
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The electronic configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 . What is the atomic number of the element, which is just below the above element in the periodic table? [1995]
a)
33
b)
34
c)
36
d)
49

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
Atomic n umber of the given element is 15 and it belongs to 5th group. Therefore atomic number of the element below the above element = 15 + 18 = 33.
Which of the following does not represent the correct order of the properties indicated [1997]- a)Ni2+ > Cr2+ > Fe2+ > Mn2+ (size)
- b)Sc > Ti > Cr > Mn (size)
- c)Mn2+ > Ni2+ < Co2+ <Fe2+ (unpaired electron)
- d)Fe2+ > Co2+ > Ni2+ > Cu2+ (unpaired electron)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not represent the correct order of the properties indicated [1997]
a)
Ni2+ > Cr2+ > Fe2+ > Mn2+ (size)
b)
Sc > Ti > Cr > Mn (size)
c)
Mn2+ > Ni2+ < Co2+ <Fe2+ (unpaired electron)
d)
Fe2+ > Co2+ > Ni2+ > Cu2+ (unpaired electron)

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
In a period on moving from left to right ionic radii decreases.
(a) So order of cationic radii is Cr2+ > Mn2+ > Fe2+ > Ni2+ and
(b) Sc > Ti > Cr > Mn (correct order of atomic radii)
(c) For unpaired electrons Mn2+ (Five) Ni2+ (Two) < Co2+ (Three)<Fe2+ (Four )
(d) For unpaired electrons Fe2+(Four) < Co2+ (Three) <Ni2+ (Two)<Cu2+(One)
Of the given electronic configurations for the elements, which electronic configuration indicates that there will be abnormally high difference in the second and third ionization energy for the element? [1999]- a)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
- b)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
- c)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
- d)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the given electronic configurations for the elements, which electronic configuration indicates that there will be abnormally high difference in the second and third ionization energy for the element? [1999]
a)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
b)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
c)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
d)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
Mg = 1s2 22 2p6 3s2 After removing of 2 electron, the magnesium acquired noble gas configuration hence removing of 3rd electron will require large amount of energy.
In the periodic table, with the increase in atomic number, the metallic character of an element [1989]- a)Decreases in a period and increases in a group
- b)In creases in a period an d decr eases in a group
- c)Increases both in a period and the group
- d)Decreases in a period and the group.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the periodic table, with the increase in atomic number, the metallic character of an element [1989]
a)
Decreases in a period and increases in a group
b)
In creases in a period an d decr eases in a group
c)
Increases both in a period and the group
d)
Decreases in a period and the group.

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Metallic character decreases in a period and increases in a group.
Among K, Ca, Fe and Zn the element which can form more than one binary compound with chlorine is [2004]- a)Fe
- b)Zn
- c)K
- d)Ca
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among K, Ca, Fe and Zn the element which can form more than one binary compound with chlorine is [2004]
a)
Fe
b)
Zn
c)
K
d)
Ca

|
Maheshwar Saini answered |
Among the given options, only Fe shows variable oxidation states so it can form two chlorides, viz. FeCl2 and FeCl3.
The electronic configuration of four elements are given below. Which elements does not belong to the same family as others ? [1989]- a)[Xe]4f14 5d10 6s2
- b)[Kr ]4d10 5s2
- c)[Ne]3s23p5
- d)[Ar] 3d10 4s2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The electronic configuration of four elements are given below. Which elements does not belong to the same family as others ? [1989]
a)
[Xe]4f14 5d10 6s2
b)
[Kr ]4d10 5s2
c)
[Ne]3s23p5
d)
[Ar] 3d10 4s2
|
|
Anushka Banerjee answered |
A. B. D are the configuration of Zn, Cd and Hg respectively which belongs to the same family. But c is the configuration of nitrogen which has a different family.
Identify the correct order of the size of the following: [2007]- a)Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < Cl– < S2–
- b)Ar < Ca2+ < K+ < Cl– < S2–
- c)Ca2+ < Ar < K+ < Cl– < S2–
- d)Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < S2– < Cl–
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct order of the size of the following: [2007]
a)
Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < Cl– < S2–
b)
Ar < Ca2+ < K+ < Cl– < S2–
c)
Ca2+ < Ar < K+ < Cl– < S2–
d)
Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < S2– < Cl–
|
|
Priya Deshpande answered |
The correct order of the size of the following is:
a) Ca2
a) Ca2
Identify the wrong statement in the following: [2012]- a)Amongst isoelectronic species, smaller the positive charge on the cation, smaller is the ionic radius.
- b)Amongst isoelectronic species, greater the negative charge on the anion, larger is the ionic radius.
- c)Atomic radius of the elements increases as one moves down the first group of the periodic table.
- d)Atomic radius of the elements decreases as one moves across from left to right in the 2nd period of the periodic table.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the wrong statement in the following: [2012]
a)
Amongst isoelectronic species, smaller the positive charge on the cation, smaller is the ionic radius.
b)
Amongst isoelectronic species, greater the negative charge on the anion, larger is the ionic radius.
c)
Atomic radius of the elements increases as one moves down the first group of the periodic table.
d)
Atomic radius of the elements decreases as one moves across from left to right in the 2nd period of the periodic table.

|
Surbhi Das answered |
As the positive charge increases on metal cation, radius decreases. This is due to the fact that nuclear charge in the case of a cation is acting on lesser number of electrons and pulls them closer.
Pauling’s electronegativity values for elements are useful in predicting [1989]- a)Polarity of the molecules
- b)Position in the E.M.F. series
- c)Coordination numbers
- d)Dipole moments.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pauling’s electronegativity values for elements are useful in predicting [1989]
a)
Polarity of the molecules
b)
Position in the E.M.F. series
c)
Coordination numbers
d)
Dipole moments.

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Pauling scale of electronegativity was helpful in predicting (i) Nature of bond between two atoms (ii) Stability of bond by calculating the difference in electronegativities polarity of bond can be calculated.
Which one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy (with negative sign) of the given atomi c species? [2 00 5]- a)S < O < Cl < F
- b)Cl < F < S < O
- c)F < Cl < O < S
- d)O < S < F < Cl
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy (with negative sign) of the given atomi c species? [2 00 5]
a)
S < O < Cl < F
b)
Cl < F < S < O
c)
F < Cl < O < S
d)
O < S < F < Cl

|
Mahi Shah answered |
The amount of energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom to produce a monovalent anion is called electron gain enthalpy.
Electron affinity value generally increase on moving from left to right in a period however there are exceptions of this rule in the case of those atoms which have stable configuration. These atoms resist the addition of extra electron, therefore the low value of electron affinity
Electron affinity value generally increase on moving from left to right in a period however there are exceptions of this rule in the case of those atoms which have stable configuration. These atoms resist the addition of extra electron, therefore the low value of electron affinity
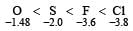
On the other hand Cl because of its compariti very bigger size than F, allow the addition of an extra electron more easily.
The correct order of the decreasing ionic radii among the following isoelectronic species are :- a)Ca2+ > K + > S2– > Cl–1 [2010]
- b)Cl – > S2+> Ca2+> K+
- c)S2– > Cl – > K + > Ca2+
- d)K + > Ca 2+ > Cl– > S2–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of the decreasing ionic radii among the following isoelectronic species are :
a)
Ca2+ > K + > S2– > Cl–1 [2010]
b)
Cl – > S2+> Ca2+> K+
c)
S2– > Cl – > K + > Ca2+
d)
K + > Ca 2+ > Cl– > S2–

|
Mahi Shah answered |
Among the isoelectronic species, size increases with the increase in negative charge. Thus S2– has the highest negative charge and hence largest in size followed by Cl–, K+ and Ca.
Ionic radii are [2004]- a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge
- b)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge
- c)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charge
- d)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear charge
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ionic radii are [2004]
a)
inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge
b)
inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge
c)
directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charge
d)
directly proportional to square of effective nuclear charge

|
Krish Saha answered |
Ion ic r adii are in ver sely pr opor tional to effective nuclear charge.
Ionic radii in the nth orbit is given as
Ionic radii in the nth orbit is given as
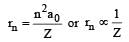
when n = principal quantum number Z-effective nuclear change.
Which of the following sets has strongest tendency to form anions ? [1993]- a)Ga, In, Tl
- b)Na, Mg, Al
- c)N, O, F
- d)V, Cr, Mn
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sets has strongest tendency to form anions ? [1993]
a)
Ga, In, Tl
b)
Na, Mg, Al
c)
N, O, F
d)
V, Cr, Mn

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
N, O and F (p-block elements) are highly electronegative non metals and will have the strongest tendency to form anions by gaining electrons from metal atoms.
The first ionization potentials (eV) of Be and B respectively are [1998]- a)8.29, 9.32
- b)9.32, 9.32
- c)8.29, 8.29
- d)9.32, 8.29
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The first ionization potentials (eV) of Be and B respectively are [1998]
a)
8.29, 9.32
b)
9.32, 9.32
c)
8.29, 8.29
d)
9.32, 8.29

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
First ionisation potential of Be is greater than boron due to following configuration 4Be=1s2,2s2 5B=1s2,2s22p1 Order of attraction of electrons towards nucleus 2s>2p, so more amount of energy is required to remove the electron with 2sorbital in comparison to 2p orbital.
One of the characteristic properties of non-metals is that they- a)have low ionization energy
- b)Form basic oxides
- c)Form cations by electron gain
- d)Are electronegative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the characteristic properties of non-metals is that they
a)
have low ionization energy
b)
Form basic oxides
c)
Form cations by electron gain
d)
Are electronegative
|
|
Sinjini Shah answered |
Non-metal like halogens are strongest oxidizing agents according to electrochemical series they form acidic oxides like SO2 they form anion by electron gain and they are highly electronegative.
(fluorine is most electronegative element of whole periodic table)
(fluorine is most electronegative element of whole periodic table)
Which of the following represents the correct order of increasing electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for the elements O, S, F and Cl ? [2010]- a)CI < F < O < S
- b)O < S < F < CI
- c)F < S < O < CI
- d)S < O < CI < F
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the correct order of increasing electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for the elements O, S, F and Cl ? [2010]
a)
CI < F < O < S
b)
O < S < F < CI
c)
F < S < O < CI
d)
S < O < CI < F

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
O < S < F < CI
Electron gain enthalpy – 141 – 200 – 333 – 349 kJ mol–1
What is the value of electron gain enthalpy of Na+ if IE1 of Na = 5.1 eV ? [2011M]- a)–5.1 eV
- b)–10.2 eV
- c)+2.55 eV
- d)+10.2 eV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the value of electron gain enthalpy of Na+ if IE1 of Na = 5.1 eV ? [2011M]
a)
–5.1 eV
b)
–10.2 eV
c)
+2.55 eV
d)
+10.2 eV

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
IE1 of Na = – Electron gain enthalpy of Na+ = – 5.1 Volt.
Chapter doubts & questions for Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily