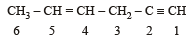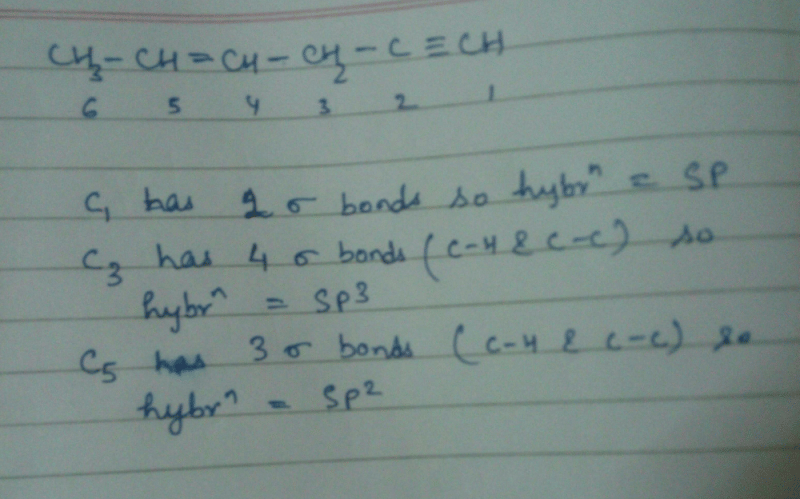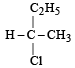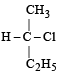All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques for NEET Exam
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating? [NEET 2013]- a)–SO3H
- b)–COOH
- c)–NO2
- d)–C ≡ N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating? [NEET 2013]
a)
–SO3H
b)
–COOH
c)
–NO2
d)
–C ≡ N

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
Decreasing order of deactivating effect of the given m-directing group is > NO2 > – CN > – SO3H > – COOH
—NO2 group is most deactivating group due to strong – E, – I and – M effects.
—NO2 group is most deactivating group due to strong – E, – I and – M effects.
For (i) I–, (ii) Cl–, (iii) Br–, the increasing order of nucleophilicity would be [2007]- a)Cl– < Br– < I–
- b)I– < Cl– < Br–
- c)Br– < Cl–< I–
- d)I– < Br– < Cl–
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For (i) I–, (ii) Cl–, (iii) Br–, the increasing order of nucleophilicity would be [2007]
a)
Cl– < Br– < I–
b)
I– < Cl– < Br–
c)
Br– < Cl–< I–
d)
I– < Br– < Cl–

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Nucleophilicity increases down the periodic table. I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Among the given compounds , the most susceptible to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group is: [2010]- a)CH3COOCH3
- b)CH3CONH2
- c)CH3COOCOCH3
- d)CH3COCI
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the given compounds , the most susceptible to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group is: [2010]
a)
CH3COOCH3
b)
CH3CONH2
c)
CH3COOCOCH3
d)
CH3COCI
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
CH3COCl
Lesser the electron density of acyl carbon atom, more will be the susceptibility of a nucleophile to attack it.
The Cl atom has strong - I effect and weakest +R effect because of the weak π-bond between the small sized C- atom and large sized Cl atom. Thus, in CH3COCl, acyl carbon has least electron density and hence, more susceptible for nucleophilic attack.
The correct order of increasing bond length of C – H, C – O, C – C and C = C is : [2011]- a)C – H < C = C < C – O < C – C
- b)C – C < C = C < C – O < C – H
- c)C – O < C – H < C – C < C = C
- d)C – H < C – O < C – C < C = C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing bond length of C – H, C – O, C – C and C = C is : [2011]
a)
C – H < C = C < C – O < C – C
b)
C – C < C = C < C – O < C – H
c)
C – O < C – H < C – C < C = C
d)
C – H < C – O < C – C < C = C

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
Bond length order is
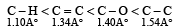
Which nomenclature is not according to IUPAC system? [2012]
- a)
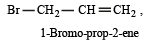
- b)
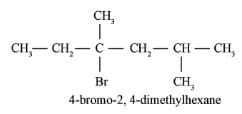
- c)
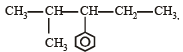 2-Methyl-3-phenylpentane
2-Methyl-3-phenylpentane
- d)
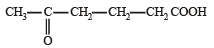 5-oxohexanoic acid
5-oxohexanoic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which nomenclature is not according to IUPAC system? [2012]
a)
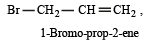
b)

c)

2-Methyl-3-phenylpentane
d)
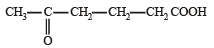
5-oxohexanoic acid

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
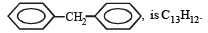
In IUPAC system of nomenclature, preference is given to multiple bond than halogen substituent, so the correct name of
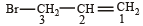 is 3-Bromoprop-1-ene.
is 3-Bromoprop-1-ene.Number of chiral carbons in β - D - (+) - glucose is [2004]- a)five
- b)six
- c)three
- d)four
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of chiral carbons in β - D - (+) - glucose is [2004]
a)
five
b)
six
c)
three
d)
four

|
Krish Patel answered |
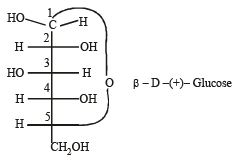
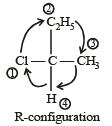
Carbon atoms from C1 to C5 are chiral
Which of the following is not chiral ? [2006]- a)2, 3- Dibromopentane
- b)3-Bromopentane
- c)2-Hydroxypropanoic acid
- d)2-Butanol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not chiral ? [2006]
a)
2, 3- Dibromopentane
b)
3-Bromopentane
c)
2-Hydroxypropanoic acid
d)
2-Butanol
|
|
Suhana Agrawal answered |
3-Bromopentane is a symmetric compound hence,achiral.
If there is no rotation of plane polarised light by a compound in a specific solvent, though to be chiral, it may mean that [2007]- a)the compound is certainly meso
- b)there is no compound in the solvent
- c)the compound may be a racemic mixture
- d)the compound is certainly a chiral.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If there is no rotation of plane polarised light by a compound in a specific solvent, though to be chiral, it may mean that [2007]
a)
the compound is certainly meso
b)
there is no compound in the solvent
c)
the compound may be a racemic mixture
d)
the compound is certainly a chiral.
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
Meso compound does not rotate plane polarised light. Compound which contains tetrahedral atoms with four different groups but the whole molecule is a chiral, is known as meso compound. It possesses a plane of symmetry and is optically inactive.
•One of the asymmetric carbon atoms turns the plane of polarised light to the right and other to the left and to the same extent so that the rotation due to upper half is compensated by the lower half, i.e., internally compensated, and finally there is no rotation of plane polarised light.
•One of the asymmetric carbon atoms turns the plane of polarised light to the right and other to the left and to the same extent so that the rotation due to upper half is compensated by the lower half, i.e., internally compensated, and finally there is no rotation of plane polarised light.
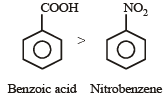
Given are cycloh exanol (I) a cetic acid (II), 2, 4, 6 – trinitrophenol (III) and phenol (IV). In these the order of decreasing acidic character will be :[2010]- a)III > II > IV > I
- b)II > III > I > IV
- c)II > III > IV > I
- d)III > IV > II > I
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given are cycloh exanol (I) a cetic acid (II), 2, 4, 6 – trinitrophenol (III) and phenol (IV). In these the order of decreasing acidic character will be :[2010]
a)
III > II > IV > I
b)
II > III > I > IV
c)
II > III > IV > I
d)
III > IV > II > I

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
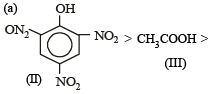
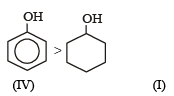
Explanation : Presence of three — NO2 groups in o–, p– positions to phenolic groups (in III) makes phenol strongly acidic because its corresponding phenate ion (conjugate base) is highly stabilised due to resonance.
Conjugate base of CH3COOH, II (i.e.
CH3COO-) is resonan ce hybr id of two equivalent structures. The conjugate base of phenol, IV is stabilized due to resonance note that here all resonating structures are not equivalent). The conjugate base of cyclohexanol, I does not exhibit resonance, hence not formed.
Conjugate base of CH3COOH, II (i.e.
CH3COO-) is resonan ce hybr id of two equivalent structures. The conjugate base of phenol, IV is stabilized due to resonance note that here all resonating structures are not equivalent). The conjugate base of cyclohexanol, I does not exhibit resonance, hence not formed.
Which one is most reactive towards electrophilic reagent? [2010]- a)
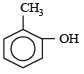
- b)
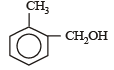
- c)
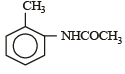
- d)
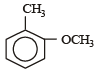
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is most reactive towards electrophilic reagent? [2010]
a)

b)
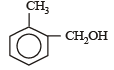
c)

d)


|
Arya Khanna answered |
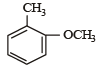
Among –OH, –CH2OH, –NHCOCH3 and – OCH3, methoxy group has the highest +M effect.
The correct order of reactivity towards the electrophilic substitution of the compounds aniline (I), benzene (II) and nitrobenzene (III) is- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I [2003]
- c)II > III > I
- d)I < II > III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of reactivity towards the electrophilic substitution of the compounds aniline (I), benzene (II) and nitrobenzene (III) is
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I [2003]
c)
II > III > I
d)
I < II > III
|
|
Dev Kumar answered |
Aniline activates benzene ring by delocalisation of electrons and increasing electron density in ortho and para positions thus making the site favourable for the attack by an electrophile.thus it is ortho and para directing group
and in Nitro benzene Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group showing -M effect and deactivates the benzene ring. so electron density on nitrobenzene increases at meta position.. so it is meta directing group.. in benzene there is no groups attached so it is normal and the correct order is 1>2>3
Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic attack ? [2008]- a)
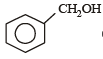
- b)
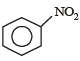
- c)
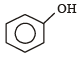
- d)
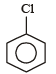
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic attack ? [2008]
a)
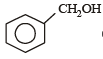
b)

c)

d)


|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
Out of the given compounds the most reactive towards nucleophilic attack
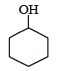
Phenoxide ion is stable due to resonance. i.e. the correct answer is option (c).
The correct IUPAC name of the compound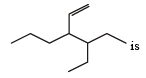
- a)4-Ethyl-3-propyl hex-1-ene [2011]
- b)3-Ethyl-4-ethenyl heptane
- c)3-Ethyl-4-propyl hex-1-ene
- d)3-(1-ethylpropyl) hex-1-ene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of the compound

a)
4-Ethyl-3-propyl hex-1-ene [2011]
b)
3-Ethyl-4-ethenyl heptane
c)
3-Ethyl-4-propyl hex-1-ene
d)
3-(1-ethylpropyl) hex-1-ene

|
Arya Nair answered |
The given compound is
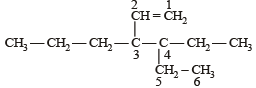
4 ethyl, 3 propyl hex – 1 – ene
The order of decreasing reactivity towards an electrophilic reagent, for the following:
i) Benzene
ii) Toluene
iii) Chlorobenzene
iv) Phenol- a)(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
- b)(ii) > (iv) > (i) > (iii)
- c)(iv) > (iii) > (ii) >(i)
- d)(iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The order of decreasing reactivity towards an electrophilic reagent, for the following:
i) Benzene
ii) Toluene
iii) Chlorobenzene
iv) Phenol
i) Benzene
ii) Toluene
iii) Chlorobenzene
iv) Phenol
a)
(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
b)
(ii) > (iv) > (i) > (iii)
c)
(iv) > (iii) > (ii) >(i)
d)
(iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Benzene having any activating group i.e, OH, R etc., undergoes electrophilic substitution very easily as compared to benzene itself. Thus toluene (C6H5CH3), phenol (C6H5OH) undergo electrophilic substitution very readily than benzene.Chlorine with +E and +M effect deactivating the ring due to strong -I effect. So, it is difficult to carry out the substitution in chlorobenzene than in benzene, so correct order is
Phenol > Toluene > Benzene > Chlorobenzene
Phenol > Toluene > Benzene > Chlorobenzene
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]- a)Ethyl chloride
- b)Isopropyl chlor ide
- c)Chlorobenzene
- d)Benzyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]
a)
Ethyl chloride
b)
Isopropyl chlor ide
c)
Chlorobenzene
d)
Benzyl chloride

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
SN1 reaction is favour ed by heavy gr oups on the carbon atom attached to halogen i.e Benzyl > allyl > tertiary > primary > secondary > primary > alkyl halides
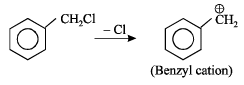
Obtained from SN1 path.
This molecule is resonance stabilised.
This molecule is resonance stabilised.
The correct order regarding the electronegativity of hybrid orbitals of carbon is [2006]- a)sp > sp2 > sp3
- b)sp < sp2 > sp3
- c)sp < sp2 < sp3
- d)sp > sp2 < sp3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order regarding the electronegativity of hybrid orbitals of carbon is [2006]
a)
sp > sp2 > sp3
b)
sp < sp2 > sp3
c)
sp < sp2 < sp3
d)
sp > sp2 < sp3

|
Smruti Mishra answered |
Electronegetivity proportional to percent of s character
so sp>sp2>sp3
so sp>sp2>sp3
Which one of the following compounds is most acidic? [2005]- a) Cl–CH2–CH2–OH
- b)
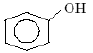
- c)
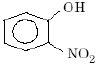
- d)
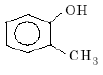
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following compounds is most acidic? [2005]
a)
Cl–CH2–CH2–OH
b)

c)

d)

|
|
Dev Kumar answered |
In (c) Due to -M effect of NO2 group at ortho position will stabilise the ortho- Nitro phenoxide ion and also NO2 shows -I effect which stabilises the conjugate base. And we know more stable the corresponding conjugate base of the acid,more acidic the acid is.
and in (d) methyl group shows +I effect and destabilises the corresponding conjugate base of the acid so the acid least acidity
in (a) there is one halide Cl which shows -I effect and stabilises the conjugate base of the acid but it's effect is not very much pronounced than that in (c) so it is less acidic than (c).
Which of the following compounds will not undergo Friedal-Craft’s reaction easily : [NEET 2013]- a)Xylene
- b)Nitrobenzene
- c)Toluene
- d)Cumene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds will not undergo Friedal-Craft’s reaction easily : [NEET 2013]
a)
Xylene
b)
Nitrobenzene
c)
Toluene
d)
Cumene

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
–NO2 is a powerful electron withdrawing group. Its presence on ring makes the ring less active
Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic reagent ? [2011]- a)
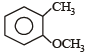
- b)
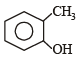
- c)
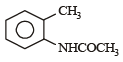
- d)
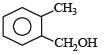
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic reagent ? [2011]
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Due to +M effect of –OH group and hyperconjugation of –CH3 group.
The IUPAC name of the following compound is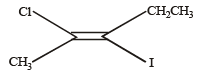
- a)trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene [2011 M]
- b)cis-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
- c)trans-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
- d)cis-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the following compound is

a)
trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene [2011 M]
b)
cis-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
c)
trans-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
d)
cis-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
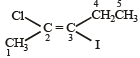
Correct IUPAC name of above compound is trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene
Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily ?- a)
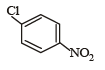
- b)
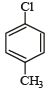
- c)
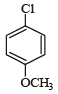
- d)
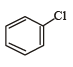
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily ?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Abhishek Desai answered |
In SNAr reactions, a carbanion is formed as an intermediate, so any substituent that increases the stability of carbanion and hence the transition state leading to its formation will enhance the SNAr reactions. To compare the rates of substitution in chlorobenzene, chlorobenzene having electron-withdrawing group, and chlorobenzene having electronreleasing group, we compare the structures carbanion I (from chlorobenzene), II (from chlorobenzene containing electron-withdrawing group) and III (from chlorobenzene containing electron-releasing group).
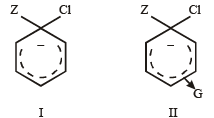
G withdraws electrons, neutralises (disperses) –ve charge of the ring, stabilises carbanion, facilitates SN reaction (activation effect)
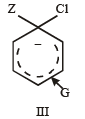
G releases electrons, intensifies –ve charge, destabilizes carbanion, retards SN reaction (deactivation) NO2 is activating group and CH3 and OCH3 are deactiving group.
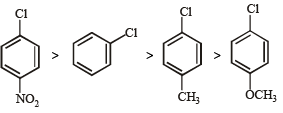
Hence, the correct order of nucleophilic substitution reactions
Hence, the correct order of nucleophilic substitution reactions
The Lassaigne’s extract is boiled with conc.HNO3 while testing for halogens. By doing so it [2011]- a)decomposes Na2S and NaCN, if formed.
- b)helps in the precipitation of AgCl.
- c)increases the solubility product of AgCl.
- d)increases the concentration of NO3– ions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Lassaigne’s extract is boiled with conc.HNO3 while testing for halogens. By doing so it [2011]
a)
decomposes Na2S and NaCN, if formed.
b)
helps in the precipitation of AgCl.
c)
increases the solubility product of AgCl.
d)
increases the concentration of NO3– ions

|
Simran Mishra answered |
The Lassaigne test, also known as the Lassaigne's test or the sodium fusion test, is a chemical test used to detect the presence of nitrogen, sulfur, or halogens in an organic compound. It was developed by French chemist Jean-Baptiste André Lassaigne in the 19th century.
The test involves the fusion of a small amount of the organic compound with sodium metal in a tube. The resulting mixture is then dissolved in water and subjected to a series of chemical reactions to detect the presence of the desired elements.
For nitrogen detection, the Lassaigne test involves the conversion of nitrogen compounds into sodium cyanide. This is achieved by treating the fused mixture with sodium hydroxide and then adding iron(II) sulfate. The presence of nitrogen is indicated by the formation of a Prussian blue precipitate.
For sulfur detection, the Lassaigne test involves the conversion of sulfur compounds into sodium sulfide. This is achieved by treating the fused mixture with sodium hydroxide and then adding lead(II) acetate. The presence of sulfur is indicated by the formation of a black precipitate of lead sulfide.
For halogen detection, the Lassaigne test involves the conversion of halogen compounds into sodium halides. This is achieved by treating the fused mixture with sodium hydroxide and then adding silver nitrate. The presence of halogens is indicated by the formation of a colored precipitate, such as silver chloride (white), silver bromide (cream), or silver iodide (yellow).
The Lassaigne test is useful in identifying the presence of these elements in organic compounds, which can be important for determining the structure, properties, and potential reactions of the compound. However, it should be noted that the test is not specific to individual compounds and can only provide a general indication of the presence of these elements.
The test involves the fusion of a small amount of the organic compound with sodium metal in a tube. The resulting mixture is then dissolved in water and subjected to a series of chemical reactions to detect the presence of the desired elements.
For nitrogen detection, the Lassaigne test involves the conversion of nitrogen compounds into sodium cyanide. This is achieved by treating the fused mixture with sodium hydroxide and then adding iron(II) sulfate. The presence of nitrogen is indicated by the formation of a Prussian blue precipitate.
For sulfur detection, the Lassaigne test involves the conversion of sulfur compounds into sodium sulfide. This is achieved by treating the fused mixture with sodium hydroxide and then adding lead(II) acetate. The presence of sulfur is indicated by the formation of a black precipitate of lead sulfide.
For halogen detection, the Lassaigne test involves the conversion of halogen compounds into sodium halides. This is achieved by treating the fused mixture with sodium hydroxide and then adding silver nitrate. The presence of halogens is indicated by the formation of a colored precipitate, such as silver chloride (white), silver bromide (cream), or silver iodide (yellow).
The Lassaigne test is useful in identifying the presence of these elements in organic compounds, which can be important for determining the structure, properties, and potential reactions of the compound. However, it should be noted that the test is not specific to individual compounds and can only provide a general indication of the presence of these elements.
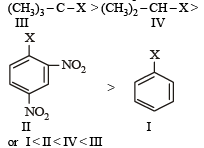
The correct order of increasing reactivity of C – X bond towards nucleophile in the following compounds is: [2010]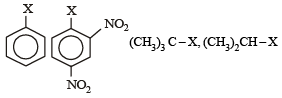 (I) (II) (III) (IV)
(I) (II) (III) (IV)- a)I < II < IV < III
- b)II < III < I < IV
- c)IV < III < I < II
- d)III < II < I < IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing reactivity of C – X bond towards nucleophile in the following compounds is: [2010]
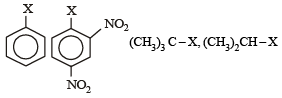
(I) (II) (III) (IV)
a)
I < II < IV < III
b)
II < III < I < IV
c)
IV < III < I < II
d)
III < II < I < IV

|
Shalini Saha answered |
Tertiary alkyl halide is most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution because the corresponding carbocation (3°) is most stable. Aryl halide is least reactive due to partial double bond character of the C – Cl bond.
Presence of — NO2 groups in ortho and para positions increases the reactivity of the – Cl towards nucleophiles.
Nitrogen detection in an organic compound is carried out by Lassaigne’s test. The blue colour formed corresponds to which of the following formulae? [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Fe3[Fe(CN)6]3
- b)Fe3[Fe(CN)6]2
- c)Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
- d)Fe4[Fe(CN)6]2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitrogen detection in an organic compound is carried out by Lassaigne’s test. The blue colour formed corresponds to which of the following formulae? [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Fe3[Fe(CN)6]3
b)
Fe3[Fe(CN)6]2
c)
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
d)
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]2

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
The blue colour is of Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
In Duma's method of estimation of nitrogen 0.35 g of an organic compound gave 55 mL of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 715 mm pressure. The percentage composition of nitrogen in the compound would be : (Aqueous tension at 300 K = 15 mm) [2011]- a)15.45
- b)16.45
- c)17.45
- d)14.45
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Duma's method of estimation of nitrogen 0.35 g of an organic compound gave 55 mL of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 715 mm pressure. The percentage composition of nitrogen in the compound would be : (Aqueous tension at 300 K = 15 mm) [2011]
a)
15.45
b)
16.45
c)
17.45
d)
14.45

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
Given wt of compound taken (w) = 0.35 g
Volume of nitrogen collected (V) = 55 ml
Room temperature (t K) = 300 K
Atmospheric pressure (P) = 715 mm Aq. tension (ρ) = 15 mm
Calculation -Volume of N2 at NTP
Volume of nitrogen collected (V) = 55 ml
Room temperature (t K) = 300 K
Atmospheric pressure (P) = 715 mm Aq. tension (ρ) = 15 mm
Calculation -Volume of N2 at NTP
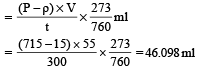
% of nitrogen
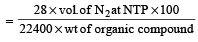
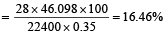
Which one is a nucleophilic substitution reaction among the following ? [2011]- a)
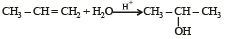
- b)
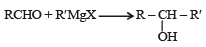
- c)
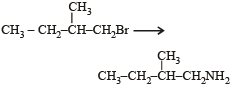
- d)
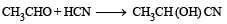
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is a nucleophilic substitution reaction among the following ? [2011]
a)
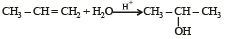
b)
c)
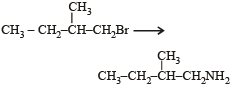
d)
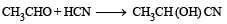

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Because of high electronegativities of the halogen atom, the carbon halogen (C – X) is highly polarised covalent bond. Thus, the carbon atom of the C – X bond becomes a good site for attack by nucleophiles (electron rich species). Nucleophilic substitution reactions are the most common reactions of alkyl halides.
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]- a)(CH3)3 C - Cl
- b)CH2 = CHCl
- c)CH3CH2Cl
- d) CH2 = CHCH2 Cl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]
a)
(CH3)3 C - Cl
b)
CH2 = CHCl
c)
CH3CH2Cl
d)
CH2 = CHCH2 Cl

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
H2C = CHCl is capable of showing resonance which develops a partial double bond, character to C–Cl bond, thereby making it less reactive toward nucleophilic substitution. ..
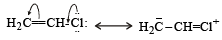
Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans (geometrical) isomerism? [2009]- a)Butanol
- b)2-Butyne
- c)2-Butenol
- d)2-Butene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans (geometrical) isomerism? [2009]
a)
Butanol
b)
2-Butyne
c)
2-Butenol
d)
2-Butene

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Alkenes with double bonds cannot undergo free rotation and can have different geometrical shapes with two different groups on each end of the double bond.
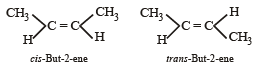
The best method for the separation of naphthalene and benzoic acid from their mixture is: [2 00 5]- a)distillation
- b)sublimation
- c)chromatography
- d)crystallisation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The best method for the separation of naphthalene and benzoic acid from their mixture is: [2 00 5]
a)
distillation
b)
sublimation
c)
chromatography
d)
crystallisation

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
Among the given compounds naph thelene is volatile but benzoic acid is non-volatile (it forms a dimer). So, the best method for their separation is sublimation, which is applicable to compounds which can be converted directly into the vapour phase from its solid state on heating and back to the solid state on cooling. Hence it is the most appropriate method.
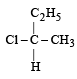
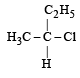
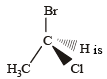
Which of the following pairs of compounds are enantiomers? [2003]- a)
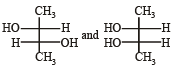
- b)

- c)
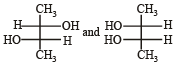
- d)
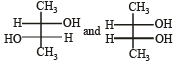
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs of compounds are enantiomers? [2003]
a)
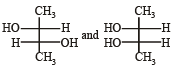
b)

c)
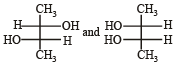
d)
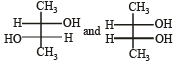

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Compound which are mirror image of each other and are not superimposable are termed as enantiomers.
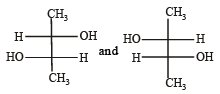
are enantiomers
A strong base can abstr act an α-hydrogen from :[2008]- a)alkene
- b)amine
- c)ketone
- d)alkane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A strong base can abstr act an α-hydrogen from :[2008]
a)
alkene
b)
amine
c)
ketone
d)
alkane

|
Shivani Rane answered |
A strong base can abstract an α-hydrogen from a ketone.
Which of the following acids does not exhibit optical isomerism ? [2012]- a)Maleic acid
- b) -amino acids
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Tartaric acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following acids does not exhibit optical isomerism ? [2012]
a)
Maleic acid
b)
-amino acids
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Tartaric acid

|
Krish Chakraborty answered |
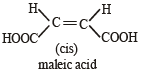
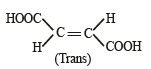
It shows geometrical isomerism but does not show optical isomerism.
Arr ange the following in increasing order of stability [NEET Kar. 2013]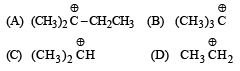
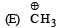
- a)E < D < C < B < A
- b)E < D < C < A < B
- c)D < E < C < A < B
- d)A < E < D < C < B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arr ange the following in increasing order of stability [NEET Kar. 2013]
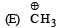
a)
E < D < C < B < A
b)
E < D < C < A < B
c)
D < E < C < A < B
d)
A < E < D < C < B

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Stability depends on number of hyperconjugative structures.
Consider the following compounds. [2007]C6H5COCl
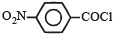
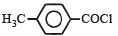
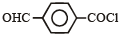 The correct decreasing order of their reactivitytowards hydrolysis is
The correct decreasing order of their reactivitytowards hydrolysis is- a)(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
- b)(iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
- c)(ii) > (iv) > (i) > (iii)
- d)(ii) > (iv) > (iii) > (i)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following compounds. [2007]
C6H5COCl






The correct decreasing order of their reactivitytowards hydrolysis is
a)
(i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
b)
(iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii)
c)
(ii) > (iv) > (i) > (iii)
d)
(ii) > (iv) > (iii) > (i)
|
|
Akash Raj answered |
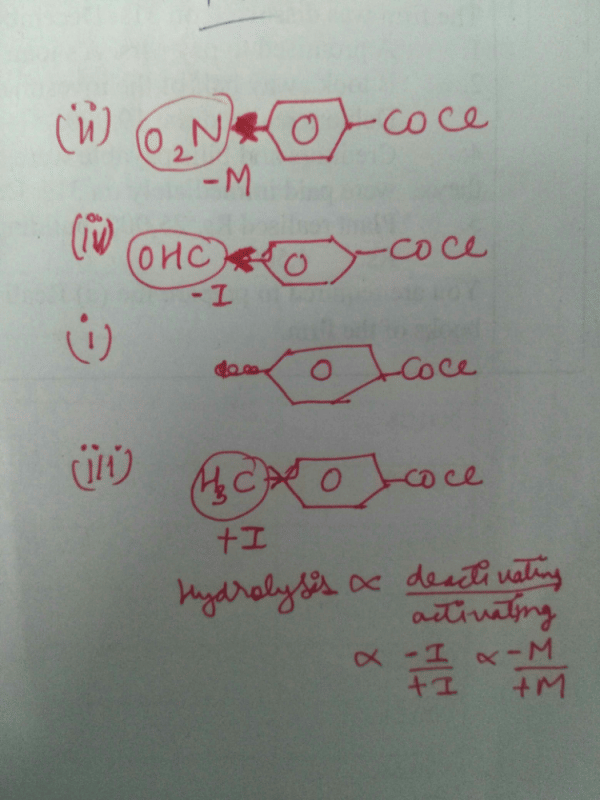
The stability of carbanions in the following :

 is in the order of : [2008]
is in the order of : [2008]
- a)(a) > (c) > (b) > (d)
- b) (b) > (c) > (d) > (a)
- c)(d) > (b) > (c) > (a)
- d) (a) > (b) > (c) > (d)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The stability of carbanions in the following :


is in the order of : [2008]
a)
(a) > (c) > (b) > (d)
b)
(b) > (c) > (d) > (a)
c)
(d) > (b) > (c) > (a)
d)
(a) > (b) > (c) > (d)
|
|
Sinjini Pillai answered |
Higher the no. of electron releasing group lower will be stability of carbanion, and vice-versa. So the order of stability of carbanions is
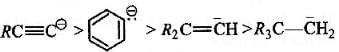
Among the following compounds the one that is most reactive towards electrophilic nitration is: [2012]- a)Benzoic acid
- b)Nitrobenzene
- c)Toluene
- d)Benzene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds the one that is most reactive towards electrophilic nitration is: [2012]
a)
Benzoic acid
b)
Nitrobenzene
c)
Toluene
d)
Benzene

|
Krish Khanna answered |
Electrophilic rate order
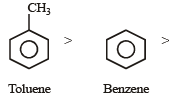
Since nitration is an electrophilic substitution hence presence of electron releasing group like CH3 in the nucleus facilitates nitration.
Which amongst the following is the most stable carbocation? [2005]- a)
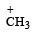
- b)
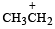
- c)
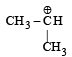
- d)
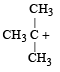
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which amongst the following is the most stable carbocation? [2005]
a)
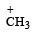
b)
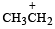
c)
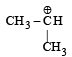
d)
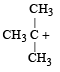
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
Teritiary carbocation is the most stable carbocation..
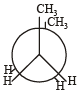
In the following the most stable conformation of n-butane is: [2010]- a)
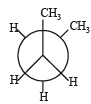
- b)
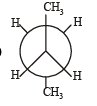
- c)
- d)
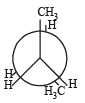
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following the most stable conformation of n-butane is: [2010]
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Sarthak Saini answered |
The bulky methyl groups are maximum away from each other.
Given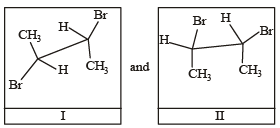 I and II are [NEET Kar. 2013]
I and II are [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)A pair of optical isomers
- b)Identical
- c)A pair of conformers
- d)A pair of geometrical isomers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given

I and II are [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
A pair of optical isomers
b)
Identical
c)
A pair of conformers
d)
A pair of geometrical isomers

|
Mahi Shah answered |
Conformers are form of stereoisomers in which isomers can be interconverted by rotations about single bonds. I and II are staggered and eclipsed conformers respectively.
Names of some compounds are given. Which one is not correct in IUPAC system? [2005]- a)
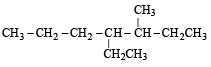 3-Methyl-4-ethyl heptane
3-Methyl-4-ethyl heptane - b)
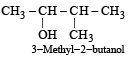
- c)
- d)
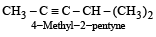
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Names of some compounds are given. Which one is not correct in IUPAC system? [2005]
a)
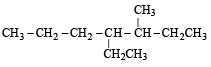
3-Methyl-4-ethyl heptane
b)
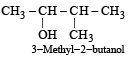
c)
d)
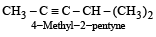

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
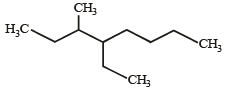
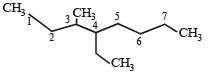
Correct IUPAC name of
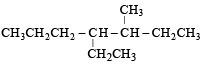
is 4-Ethyl-3–methyl heptane
Which one of the following pairs represen ts stereoisomerism? [2005]- a)Structural isomerism and Geometrical isomerism
- b)Optical isomerism and Geometrical isomerism
- c)Chain isomerism and Rotational isomerism.
- d)Linkage isomerism and Geometrical isomerism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs represen ts stereoisomerism? [2005]
a)
Structural isomerism and Geometrical isomerism
b)
Optical isomerism and Geometrical isomerism
c)
Chain isomerism and Rotational isomerism.
d)
Linkage isomerism and Geometrical isomerism

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Optical and geometrical isomerism pair up to exhibit stereoisomerism. This is because the isomers differ only in their orientation in space.
Chapter doubts & questions for Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup




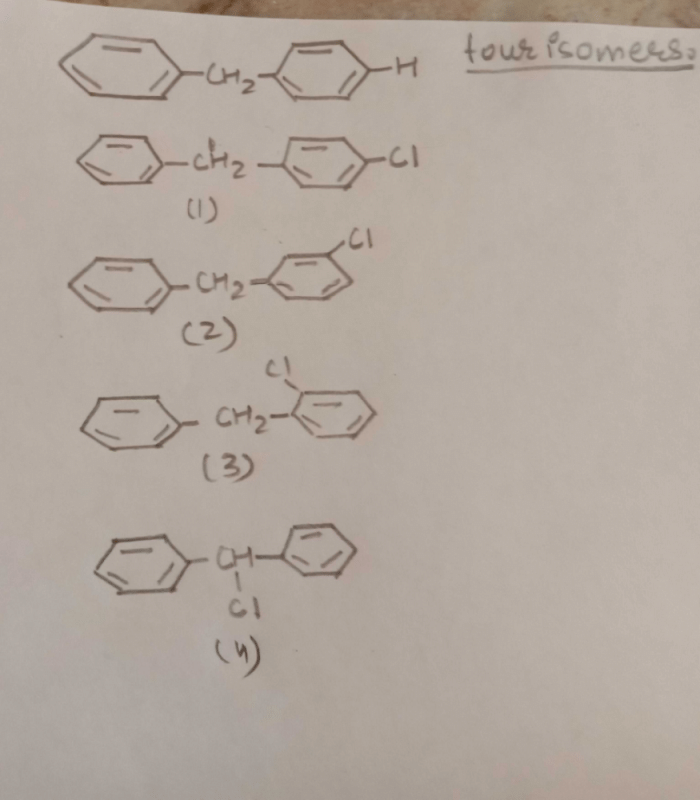
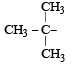
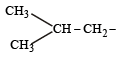

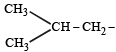 (iso-butyl group)
(iso-butyl group)