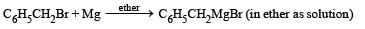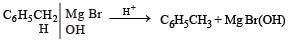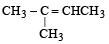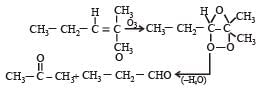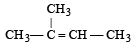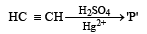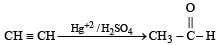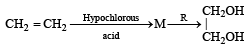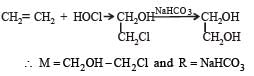All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Hydrocarbons for NEET Exam
Select the true statement about benzene amongst the following [1992]- a)Because of unsatur a tion benzene easily undergoes addition
- b)There are two types of C – C bon ds in benzene molecule
- c)There is cyclic delocalisation of pi-electrons in benzene
- d)Monosubstitution of benzene gives three isomeric products.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the true statement about benzene amongst the following [1992]
a)
Because of unsatur a tion benzene easily undergoes addition
b)
There are two types of C – C bon ds in benzene molecule
c)
There is cyclic delocalisation of pi-electrons in benzene
d)
Monosubstitution of benzene gives three isomeric products.

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
Benzene do not show addition reaction like other unsaturated hydrocarbons. However it show substitution reactions. Due to resonance all the C – C bonds have the same nature, which is possible because of the cycli c del oca lisati on of π-electr on s in benzene. Monosubstitution will give only a single product.
A hydrocarbon A on chlorination gives B which on heating with alcoholic potassium hydroxide changes into another hydrocarbon C. The latter decolourises Baeyer's reagent and on ozonolysis forms formaldehyde only. A is [1998]- a)Ethane
- b)Butane
- c)Methane
- d)Ethene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrocarbon A on chlorination gives B which on heating with alcoholic potassium hydroxide changes into another hydrocarbon C. The latter decolourises Baeyer's reagent and on ozonolysis forms formaldehyde only. A is [1998]
a)
Ethane
b)
Butane
c)
Methane
d)
Ethene

|
Prisha Singh answered |
The hydrocarbon 'a' is ethane.
Ethane on chlorination, gives 1-chloroethane, which reacts with alcoholic KOH to give a dehydro-halogenation product (Ethene). The ethene formed from this undergoes ozonolysis to break the double bond and form two molecules of formaldehyde.
'a' - Ethane
'b' - 1-chloroethane
'c' - Ethene
Ethane on chlorination, gives 1-chloroethane, which reacts with alcoholic KOH to give a dehydro-halogenation product (Ethene). The ethene formed from this undergoes ozonolysis to break the double bond and form two molecules of formaldehyde.
'a' - Ethane
'b' - 1-chloroethane
'c' - Ethene
In preparation of alkene from alcohol using Al2O3 which is effective factor? [2001]- a)Temperature
- b)Concentration
- c)Surface area of Al2O3
- d)Porosity of Al2O3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In preparation of alkene from alcohol using Al2O3 which is effective factor? [2001]
a)
Temperature
b)
Concentration
c)
Surface area of Al2O3
d)
Porosity of Al2O3

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Temperature
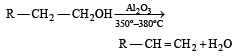
While at 220º – 250ºC it forms ether
Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point ? [1994]- a)CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
- b)CH3CH = CHCH2CH3
- c)CH3CH = CH – CH = CH2
- d)CH3CH2CH2CH3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point ? [1994]
a)
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
b)
CH3CH = CHCH2CH3
c)
CH3CH = CH – CH = CH2
d)
CH3CH2CH2CH3
|
|
Sonal Dey answered |
The compound with the lowest boiling point would be the one with the weakest intermolecular forces. In this case, it is the compound with the fewest carbon atoms and no functional groups that can form hydrogen bonds.
a) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 has 5 carbon atoms and only van der Waals forces between molecules.
b) CH3CH = CHCH2CH3 has 5 carbon atoms and can form weak London dispersion forces and weak dipole-dipole interactions.
c) CH3CH = CH has 3 carbon atoms and can only form weak London dispersion forces.
Therefore, the compound with the lowest boiling point is c) CH3CH = CH.
a) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 has 5 carbon atoms and only van der Waals forces between molecules.
b) CH3CH = CHCH2CH3 has 5 carbon atoms and can form weak London dispersion forces and weak dipole-dipole interactions.
c) CH3CH = CH has 3 carbon atoms and can only form weak London dispersion forces.
Therefore, the compound with the lowest boiling point is c) CH3CH = CH.
When hydrochloric acid gas is treated with propene in presence of benzoyl peroxide, it gives [1993]- a)2-Chloropropane
- b)Allyl chloride
- c)No reaction
- d)n-Propyl chloride.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When hydrochloric acid gas is treated with propene in presence of benzoyl peroxide, it gives [1993]
a)
2-Chloropropane
b)
Allyl chloride
c)
No reaction
d)
n-Propyl chloride.

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Peroxide effect is observed only in case of HBr. Therefore, addition of HCl to propene even in the presence of benzyoyl peroxide occurs according to Markovnikov’s rule :
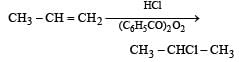
The IUPAC name of the compound CH3CH = CHC = CH is [2010]- a)Pent-l-yn-3-ene
- b)Pent-4-yn-2-ene
- c)Pent-3-en-1-yne
- d)Pent-2-en-4-yne
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the compound CH3CH = CHC = CH is [2010]
a)
Pent-l-yn-3-ene
b)
Pent-4-yn-2-ene
c)
Pent-3-en-1-yne
d)
Pent-2-en-4-yne

|
Snehal Shah answered |
When both double and triple bonds are present, then triple bond is considered as the principal group.
The reaction of C6H5CH = CHCH3 with HBr produces :- a)
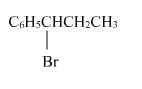
- b)
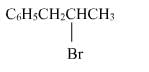
- c)
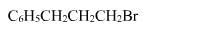
- d)
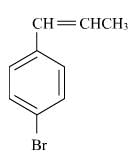
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of C6H5CH = CHCH3 with HBr produces :
a)
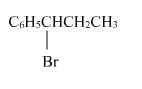
b)

c)
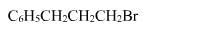
d)

|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
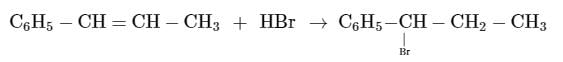
This is the electrophilic addition reaction in which addition takes place via more stable carbocation according to the Markovnikov's rule.
The radical,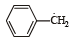 is aromatic because ithas : [NEET 2013]
is aromatic because ithas : [NEET 2013]- a)7 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons
- b)7 p-orbitals and 7 unpaired electrons
- c)6 p-orbitals and 7 unpaired electrons
- d)6 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The radical,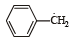 is aromatic because ithas : [NEET 2013]
is aromatic because ithas : [NEET 2013]
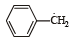 is aromatic because ithas : [NEET 2013]
is aromatic because ithas : [NEET 2013]a)
7 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons
b)
7 p-orbitals and 7 unpaired electrons
c)
6 p-orbitals and 7 unpaired electrons
d)
6 p-orbitals and 6 unpaired electrons

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Presence of 6p orbitals, each containing one unpaired electron, in a six membered cyclic structure is in accordance with Huckel rule of aromaticity.
In commercial gas olines the type of hydrocarbons which are more desirable, is- a)branched hydrocarbons [1997]
- b)straight-chain hydrocarbons
- c)aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene
- d)linear unsaturated hydrocarbons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In commercial gas olines the type of hydrocarbons which are more desirable, is
a)
branched hydrocarbons [1997]
b)
straight-chain hydrocarbons
c)
aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene
d)
linear unsaturated hydrocarbons
|
|
Ishan Ghosh answered |
Introduction:
In commercial gasoline, the type of hydrocarbons that are more desirable are branched hydrocarbons. This choice is based on several factors, including the combustion efficiency, octane rating, and volatility of the hydrocarbons.
Combustion Efficiency:
Branched hydrocarbons have a higher combustion efficiency compared to straight-chain hydrocarbons. This is because branched hydrocarbons have more surface area, which allows for better mixing with air and more efficient combustion. As a result, branched hydrocarbons produce more complete combustion, leading to better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
Octane Rating:
The octane rating is a measure of a fuel's resistance to knocking or pinging during combustion. Knocking is the undesirable phenomenon where the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely in the engine, causing a knocking sound and potentially damaging the engine. Higher octane ratings indicate better anti-knocking properties.
Branched hydrocarbons have higher octane ratings compared to straight-chain hydrocarbons. This is because the branching in the molecular structure disrupts the formation of hot spots within the fuel-air mixture, reducing the likelihood of knocking. Therefore, using branched hydrocarbons in gasoline helps to improve engine performance and prevent engine damage.
Volatility:
Volatility refers to the ability of a substance to vaporize. In the case of gasoline, the volatility of hydrocarbons is important for proper engine operation.
Branched hydrocarbons have lower volatility compared to straight-chain hydrocarbons. This is beneficial for two reasons. Firstly, lower volatility reduces the evaporation of fuel during storage and transportation, ensuring that the fuel remains stable. Secondly, lower volatility helps to prevent vapor lock, which is the phenomenon where fuel vaporizes too quickly in the fuel lines, causing the engine to stall.
Conclusion:
In summary, branched hydrocarbons are more desirable in commercial gasoline due to their higher combustion efficiency, higher octane rating, and lower volatility. These characteristics contribute to better fuel efficiency, improved engine performance, and reduced emissions.
In commercial gasoline, the type of hydrocarbons that are more desirable are branched hydrocarbons. This choice is based on several factors, including the combustion efficiency, octane rating, and volatility of the hydrocarbons.
Combustion Efficiency:
Branched hydrocarbons have a higher combustion efficiency compared to straight-chain hydrocarbons. This is because branched hydrocarbons have more surface area, which allows for better mixing with air and more efficient combustion. As a result, branched hydrocarbons produce more complete combustion, leading to better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
Octane Rating:
The octane rating is a measure of a fuel's resistance to knocking or pinging during combustion. Knocking is the undesirable phenomenon where the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely in the engine, causing a knocking sound and potentially damaging the engine. Higher octane ratings indicate better anti-knocking properties.
Branched hydrocarbons have higher octane ratings compared to straight-chain hydrocarbons. This is because the branching in the molecular structure disrupts the formation of hot spots within the fuel-air mixture, reducing the likelihood of knocking. Therefore, using branched hydrocarbons in gasoline helps to improve engine performance and prevent engine damage.
Volatility:
Volatility refers to the ability of a substance to vaporize. In the case of gasoline, the volatility of hydrocarbons is important for proper engine operation.
Branched hydrocarbons have lower volatility compared to straight-chain hydrocarbons. This is beneficial for two reasons. Firstly, lower volatility reduces the evaporation of fuel during storage and transportation, ensuring that the fuel remains stable. Secondly, lower volatility helps to prevent vapor lock, which is the phenomenon where fuel vaporizes too quickly in the fuel lines, causing the engine to stall.
Conclusion:
In summary, branched hydrocarbons are more desirable in commercial gasoline due to their higher combustion efficiency, higher octane rating, and lower volatility. These characteristics contribute to better fuel efficiency, improved engine performance, and reduced emissions.
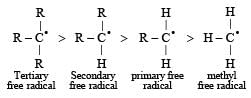
Reactivity of hydrogen atoms attached to different carbon atoms in alkanes has the order [1993]- a)Tertiary > Primary > Secondary
- b)Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)Tertiary > Secondary > Primary.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Reactivity of hydrogen atoms attached to different carbon atoms in alkanes has the order [1993]
a)
Tertiary > Primary > Secondary
b)
Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary.

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
The reactivity of H-atoms depends upon the stability of free radicals follows the order : Tertiary > secondary > primary, therefore, reactivity of H-atoms follows the same order, i.e., tertiary > secondary > primary.
Reduction of 2-butyne with sodium in liquid ammonia gives predominantly : [1993]- a)cis - 2 - Butene
- b)No reaction
- c)trans - 2 - Butene
- d)n-Butane.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reduction of 2-butyne with sodium in liquid ammonia gives predominantly : [1993]
a)
cis - 2 - Butene
b)
No reaction
c)
trans - 2 - Butene
d)
n-Butane.

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
Reduction of alkynes with Na/liq. NH3 gives trans-alkenes. This reaction is called Birch reduction
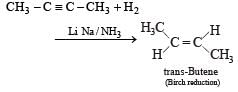
A compound is treated with NaNH2 to give sodium salt. Identify the compound [1993]- a)C2H2
- b)C6H6
- c)C2H6
- d)C2H4.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A compound is treated with NaNH2 to give sodium salt. Identify the compound [1993]
a)
C2H2
b)
C6H6
c)
C2H6
d)
C2H4.

|
Pranavi Chavan answered |
The compound that is treated with NaNH2 to give a sodium salt is option A, C2H2.
Explanation:
When a compound is treated with NaNH2, it undergoes a process called deprotonation, where a proton (H+) is removed from the compound and replaced by a sodium ion (Na+). This results in the formation of a sodium salt.
Let's analyze each option to determine which compound is likely to undergo deprotonation with NaNH2:
a) C2H2 (Acetylene): Acetylene is an alkyne compound with the molecular formula C2H2. It contains two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms. Alkynes are known to undergo deprotonation with NaNH2 to form sodium alkynides. Therefore, option A, C2H2, is a valid choice.
b) C6H6 (Benzene): Benzene is an aromatic compound with the molecular formula C6H6. It contains six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Aromatic compounds, like benzene, do not undergo deprotonation with NaNH2. Therefore, option B, C6H6, is not a valid choice.
c) C2H6 (Ethane): Ethane is an alkane compound with the molecular formula C2H6. It contains two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Alkanes do not undergo deprotonation with NaNH2. Therefore, option C, C2H6, is not a valid choice.
d) C2H4 (Ethylene): Ethylene is an alkene compound with the molecular formula C2H4. It contains two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms. Alkenes do not undergo deprotonation with NaNH2. Therefore, option D, C2H4, is not a valid choice.
In conclusion, the compound that is treated with NaNH2 to give a sodium salt is option A, C2H2.
Explanation:
When a compound is treated with NaNH2, it undergoes a process called deprotonation, where a proton (H+) is removed from the compound and replaced by a sodium ion (Na+). This results in the formation of a sodium salt.
Let's analyze each option to determine which compound is likely to undergo deprotonation with NaNH2:
a) C2H2 (Acetylene): Acetylene is an alkyne compound with the molecular formula C2H2. It contains two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms. Alkynes are known to undergo deprotonation with NaNH2 to form sodium alkynides. Therefore, option A, C2H2, is a valid choice.
b) C6H6 (Benzene): Benzene is an aromatic compound with the molecular formula C6H6. It contains six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Aromatic compounds, like benzene, do not undergo deprotonation with NaNH2. Therefore, option B, C6H6, is not a valid choice.
c) C2H6 (Ethane): Ethane is an alkane compound with the molecular formula C2H6. It contains two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Alkanes do not undergo deprotonation with NaNH2. Therefore, option C, C2H6, is not a valid choice.
d) C2H4 (Ethylene): Ethylene is an alkene compound with the molecular formula C2H4. It contains two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms. Alkenes do not undergo deprotonation with NaNH2. Therefore, option D, C2H4, is not a valid choice.
In conclusion, the compound that is treated with NaNH2 to give a sodium salt is option A, C2H2.
Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989]
- a)Sigma electron density of C – H bond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s-character
- b)Acetylene has only open hydrogen in each carbon
- c)A c etylen e co n ta in s le ast nu mb e r o f hydrogens among the possible hydrocarbons having two carbons
- d)Acetylene belongs to the class of alkynes with molecular formula, CnH2n – 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989]
a)
Sigma electron density of C – H bond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s-character
b)
Acetylene has only open hydrogen in each carbon
c)
A c etylen e co n ta in s le ast nu mb e r o f hydrogens among the possible hydrocarbons having two carbons
d)
Acetylene belongs to the class of alkynes with molecular formula, CnH2n – 2
|
|
Swara Bose answered |
Bonds is low
b)Sigma electron density of C bonds is high
c)The carbon atom is sp2 hybridized
d)The carbon atom is sp hybridized
b)Sigma electron density of C bonds is high
c)The carbon atom is sp2 hybridized
d)The carbon atom is sp hybridized
Liquid hydrocarbons can be converted to a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons by : [2010]- a)Oxidation
- b)Cracking
- c)Distillation under reduced pressure
- d)Hydrolysis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Liquid hydrocarbons can be converted to a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons by : [2010]
a)
Oxidation
b)
Cracking
c)
Distillation under reduced pressure
d)
Hydrolysis

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
During cracking higher hydrocarbons (liquid) are converted to lower gaseous hydrocarbons.
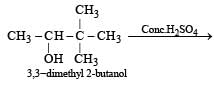
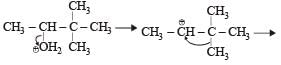
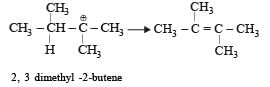
When 3, 3-dimethyl 2-butanol is heated with H2SO4, the major product obtained is [1995]- a)2,3-dimethyl 2-butene
- b)3, 3-dimethyl 1- butene
- c)2, 3-dimethyl 1- butene
- d)cis & trans isomers of 2, 3-dimethyl 2-butene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When 3, 3-dimethyl 2-butanol is heated with H2SO4, the major product obtained is [1995]
a)
2,3-dimethyl 2-butene
b)
3, 3-dimethyl 1- butene
c)
2, 3-dimethyl 1- butene
d)
cis & trans isomers of 2, 3-dimethyl 2-butene

|
Shivani Rane answered |
When 3, 3 dimethyl 2-butanol is heated with H2SO4 the major product obtained is 2, 3 dimethyl 2-butene.
Which is the most suitable reagent among the following to distinguish compound (3) from rest of the compounds ? [1989]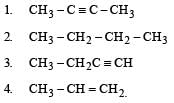
- a)Bromine in carbon tetrachloride
- b)Bromine in acetic acid
- c)Alk KMnO4
- d)Ammonical silver nitrate.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most suitable reagent among the following to distinguish compound (3) from rest of the compounds ? [1989]
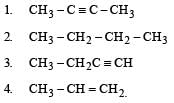
a)
Bromine in carbon tetrachloride
b)
Bromine in acetic acid
c)
Alk KMnO4
d)
Ammonical silver nitrate.

|
Arya Nair answered |
Br2 in CCl4 (a), Br2 in CH3 COOH (b) and alk.
KMnO4 (c) will react with all unsaturated compounds, i.e., 1, 3 and 4 while ammonical AgNO3 (d) reacts only with terminal alkynes, i.e., 3 and hence compund 3 can be distinguished from 1, 2 and 4 by. ammonical AgNO3 (d).
KMnO4 (c) will react with all unsaturated compounds, i.e., 1, 3 and 4 while ammonical AgNO3 (d) reacts only with terminal alkynes, i.e., 3 and hence compund 3 can be distinguished from 1, 2 and 4 by. ammonical AgNO3 (d).
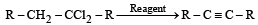 The reagent is [1993]
The reagent is [1993]- a)Na
- b)HCl in H2O
- c)KOH in C2H5OH
- d)Zn in alcohol.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
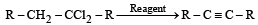
The reagent is [1993]
a)
Na
b)
HCl in H2O
c)
KOH in C2H5OH
d)
Zn in alcohol.

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
On heating ethylene chloride (1, 1 dichloro ethane) with alcoholic potash followed by sodamide alkyne is obtained
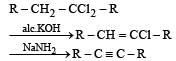
In the presence of platinum catalyst, hydrocarbon A adds hydrogen to form n-hexane. When hydrogen bromide is added to A instead of hydrogen, only a single bromo compound is formed. Which of the following is A? [1996]- a)
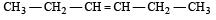
- b)
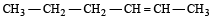
- c)
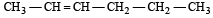
- d)
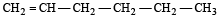
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the presence of platinum catalyst, hydrocarbon A adds hydrogen to form n-hexane. When hydrogen bromide is added to A instead of hydrogen, only a single bromo compound is formed. Which of the following is A? [1996]
a)
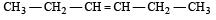
b)
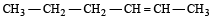
c)
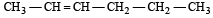
d)
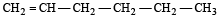

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
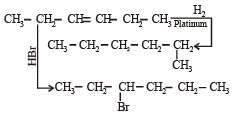
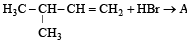 A(predominantly) is : [2008]
A(predominantly) is : [2008]- a)
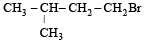
- b)
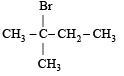
- c)
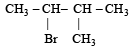
- d)
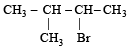
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
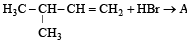 A(predominantly) is : [2008]
A(predominantly) is : [2008]a)
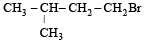
b)
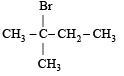
c)
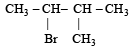
d)
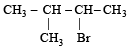

|
Aastha Kulshreshtha answered |
Through Markonikoff rule carbonium will be formed at 2-C position but, as tertiary carbonium is more stable than secondary carbonium so hydrogen shift takes place from 3-C position to 2-C position in order to form tertiary carbonium while the negative charge retains the original position. Thus after the addition reaction the major product is B.
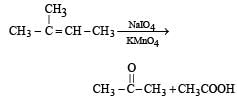
Products of the following reaction : [2005]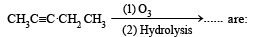
- a)CH3COOH + CO2
- b)CH3COOH + HOOC .CH2CH3
- c)CH3CHO + CH3CH2CHO
- d)CH3COOH + CH3COCH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Products of the following reaction : [2005]
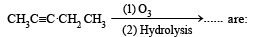
a)
CH3COOH + CO2
b)
CH3COOH + HOOC .CH2CH3
c)
CH3CHO + CH3CH2CHO
d)
CH3COOH + CH3COCH3

|
Smruti Mishra answered |
When the ozonalysis occurs then here
cH3COOH And cH2CH3COOH formed
Which of the following chemical system is non aromatic?[NEET Kar. 2013]- a)
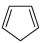
- b)

- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following chemical system is non aromatic?
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Huckel rule is not obeyed. It has only four electrons. Further it does not have continous conjugation.
The IUPAC name of the compound having the formula CH ≡ C – CH = CH2 is : [2009]- a)1-butyn-3-ene
- b)but-1-yne-3-ene
- c)1-butene-3-yne
- d)3-butene-1-yne
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the compound having the formula CH ≡ C – CH = CH2 is : [2009]
a)
1-butyn-3-ene
b)
but-1-yne-3-ene
c)
1-butene-3-yne
d)
3-butene-1-yne

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
If both the double and triple bonds are present the compound is regarded as derivative of alkyne.
Further if double and triple bonds are at equidistance from either side, the preference is given to double bond.
Further if double and triple bonds are at equidistance from either side, the preference is given to double bond.
Which one of the following alkenes will react faster with H2 under catalytic hydrogenation conditions? [2005] (R = Alkyl Substituent)- a)
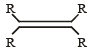
- b)
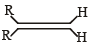
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following alkenes will react faster with H2 under catalytic hydrogenation conditions? [2005] (R = Alkyl Substituent)
a)

b)
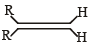
c)

d)

|
|
Malavika Roy answered |
The least stable alkene will react will reacts fastest. So in option d, we have 2 pair of alkyl groups in cis position. SO it will react fastest.
Reaction of HBr with propene in the presence of peroxide gives [2004]- a)isopropyl bromide
- b)3-bromo propane
- c)allyl bromide
- d)n-propyl bromide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Reaction of HBr with propene in the presence of peroxide gives [2004]
a)
isopropyl bromide
b)
3-bromo propane
c)
allyl bromide
d)
n-propyl bromide

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
In presence of peroxide, HBr adds on alkenes in anti–markovnikov’s way, thus
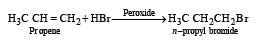
Kharasch observed that the addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkene in the presence of organic peroxides follows an opposite course to that suggested by Markownikoff . This is termed anti-Markownikoff or peroxide effect.
Which of the following reagents will be able to distinguish between 1-butyne and 2-butyne? [2012 M]- a)NaNH2
- b)HCl
- c)O2
- d)Br2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reagents will be able to distinguish between 1-butyne and 2-butyne? [2012 M]
a)
NaNH2
b)
HCl
c)
O2
d)
Br2

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
1-Butyne and 2-butyne are distinguish by NaNH2 because 1-Butyne react with NaNH2 due to presence of terminal hydrogen.
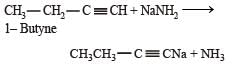
Which one of the following reactions is expected to readily give a hydrocarbon product in good yields ? [1997]- a)
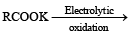
- b)
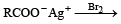
- c)
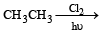
- d)
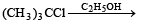
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following reactions is expected to readily give a hydrocarbon product in good yields ? [1997]
a)
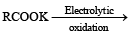
b)
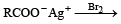
c)
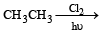
d)
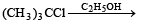

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Electrolysis of a concentrated a queous solution of either sodium or potassium salts of saturated mon-carboxylic acids yields higher alkane at anode.
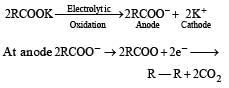
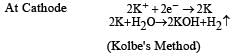
Predict the product C obtained in the following reaction of butyne-1. [2007]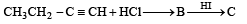
- a)
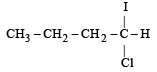
- b)
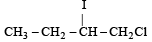
- c)
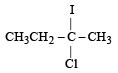
- d)
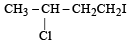
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Predict the product C obtained in the following reaction of butyne-1. [2007]
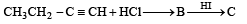
a)
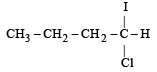
b)
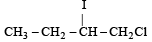
c)
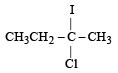
d)
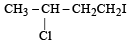
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
Both the addition reactions will take place as per the Markownikoff's rule (i.e. both on the 2nd carbon atom) so C is the ans.
The alkene R – CH = CH2 reacts readily with B2H6 and formed the product B which on oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxides produces [1995] - a)R – CH2 – CHO
- b)R – CH2 – CH2 – OH
- c)
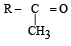
- d)
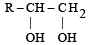
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The alkene R – CH = CH2 reacts readily with B2H6 and formed the product B which on oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxides produces [1995]
a)
R – CH2 – CHO
b)
R – CH2 – CH2 – OH
c)
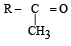
d)
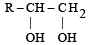

|
Aastha Kulshreshtha answered |
Its Hydroboration oxidation reaction.
In the following reactions, [2011]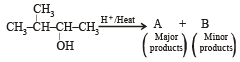
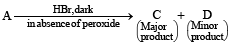 the major products (A) and (C) are respectively :
the major products (A) and (C) are respectively :- a)
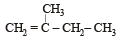
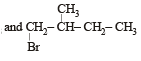
- b)
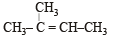
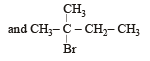
- c)
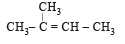
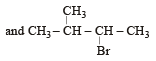
- d)
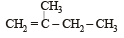
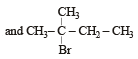
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reactions, [2011]
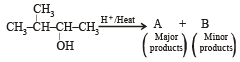
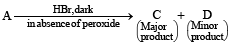
the major products (A) and (C) are respectively :
a)
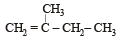
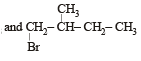
b)
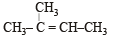
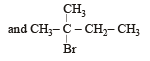
c)
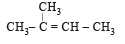
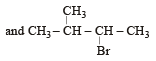
d)
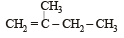
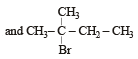

|
Shivani Tiwari answered |
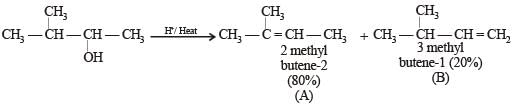
In this case dehydration is governed by Saytezeff’s rule according to which hydrogen is preferentially eliminated from the carbon atom with fewer number of hydrogen atoms i.e., poor becomes poorer. Thus, 2 methyl butene-2 is the major product.
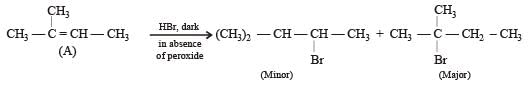
This reaction is governed by Markownikoff’s rule according to which when an unsymmetrical reagent e.g.
HBr adds to an unsymmetrical alkene, then the negative part of the reagent is added to that carbon atom of the double bond which bears the least number of hydrogen atom. Thus, in above case. 2-methyl 2-bromo butane will be the major product.
HBr adds to an unsymmetrical alkene, then the negative part of the reagent is added to that carbon atom of the double bond which bears the least number of hydrogen atom. Thus, in above case. 2-methyl 2-bromo butane will be the major product.
Chapter doubts & questions for Hydrocarbons - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Hydrocarbons - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily




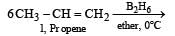
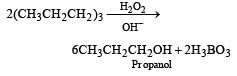

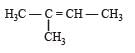
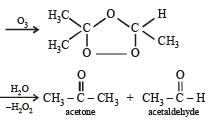


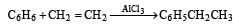

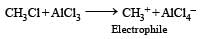

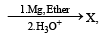 In the following reaction, C6H5CH2Br
In the following reaction, C6H5CH2Br